Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tissues
Tissues
Uploaded by
Lara C.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views16 pagesTissues are groups of cells that work together to perform specialized functions. There are four main types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Epithelial tissues line and cover surfaces and glands. Connective tissues connect and support other tissues. Muscle tissues allow movement. Nervous tissues control and coordinate body functions through electrical signals between neurons.
Original Description:
Original Title
3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTissues are groups of cells that work together to perform specialized functions. There are four main types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Epithelial tissues line and cover surfaces and glands. Connective tissues connect and support other tissues. Muscle tissues allow movement. Nervous tissues control and coordinate body functions through electrical signals between neurons.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views16 pagesTissues
Tissues
Uploaded by
Lara C.Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform specialized functions. There are four main types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Epithelial tissues line and cover surfaces and glands. Connective tissues connect and support other tissues. Muscle tissues allow movement. Nervous tissues control and coordinate body functions through electrical signals between neurons.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Tissues https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=O0ZvbPak4ck&t=162s
A group of cells that usually have a common
origin in an embryo and function together to carry
out specialized activities.
Histology – is the study of tissues.
Pathologist - a physician that specializes in
laboratory studies of cells and tissues to help
other doctors make accurate diagnoses
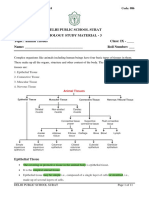
Types of Tissues
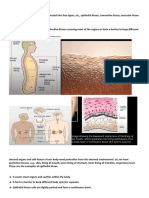
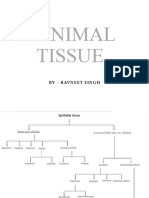
1. Epithelial Tissues
Perform functions
like protection,
secretion,
absorption, excretion
, filtration, diffusion,
and sensory
reception.
Type Location Functions
Air sacs of the lungs and Allows materials to pass
the lining of the heart, through diffusion or
blood vessels and filtration and secrete
lymphatic vessels. lubricating substance.
In ducts and secretory Secretes and absorbs
portions of the small
glands and in kidney
tubules.
Ciliated tissues are in the Secretes mucus; ciliated
bronchi, uterine tubes and tissue moves mucus
uterus; Non ciliated or
smooth are in the digestive
tract and bladder.
Type Location Functions
Lines the esophagus, Protects against
mouth and vagina. abrasions.
Sweat glands, salivary Protective tissue
glands and mammary
glands
The male urethra and the Secretes and protects.
ducts of some glands.
Type Location Functions
Lines the bladder, urethra Allows the urinary organs
and uterus. to expand and stretch.
2. Connective Tissues (“Connects everything”
meaning it provides support and hold body’s
tissue together)
They range from avascular to highly vascular &
composed extracellular matrix that separates
the cells of the tissue.
Types of Connective Tissue Fibers
A. Collagen fibers. Make up 25% of protein in
the body and are tough, resistant to pull,
yet flexible.
B. Elastin fibers. Like in the lungs, blood
vessels, ear cartilages. It can stretch up to
150% and return to normal size.
C. Reticular fibers. Spleen and lymph
nodes, thin, branched fibers that form
framework of the organs, formed from
protein collagen
3. Muscle Tissues (“Moves everything).
4. Nervous Tissues. is found in the brain, spinal
cord, and nerves.
It stimulates muscle contraction, creates an
awareness of the environment, and plays a
major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning.
Types of Nervous Tissue
1. Neurons, the largest tissue and responsible
for the transmission of impulses.
2. Neuroglial tissue, smaller but more abundant
and supports neurons
They are a group of supportive cells for
the neurons.
You might also like
- Introduction Maternity Pediatric Nursing 8th Leifer Test BankDocument11 pagesIntroduction Maternity Pediatric Nursing 8th Leifer Test Banksonyaaaq100% (4)
- Chapter 23 - Conditions Occurring After DeliveryDocument6 pagesChapter 23 - Conditions Occurring After DeliveryEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Desertation in Obg RguhsDocument23 pagesDesertation in Obg RguhsVantrigaru Veeresh Bangi89% (44)
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- Placenta Previa PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePlacenta Previa Pathophysiologykathy85% (20)
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- Handout Animal Tissues 2023 2024Document4 pagesHandout Animal Tissues 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument91 pagesTissuesSon Ezekiel Gabriel I. BenitezNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- Histology: Study of Body TissuesDocument17 pagesHistology: Study of Body Tissuesbella dwiNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissues: StructureDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissues: StructureKristine JamilleNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Document10 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Saurav Soni100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument6 pagesEpithelial TissueDEBASISH MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- Animal Structure and FunctionDocument9 pagesAnimal Structure and FunctionkpenalesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyShem DelolaNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- General Biology Reporting 2Document10 pagesGeneral Biology Reporting 2Cheska Faith EstudilloNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Stations 1-3Document4 pagesEpithelial Tissue Stations 1-3api-692335939No ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- HP I P2 Tissues and MembranesDocument38 pagesHP I P2 Tissues and MembranesNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- Education Notes 2Document6 pagesEducation Notes 2Rwynn MemoryNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument74 pagesTissuesMonica Sree100% (1)
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIDocument110 pagesAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- Animal TissuesDocument15 pagesAnimal TissuesLitaMeilinaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesCells and Tissues: Tissueقى قىNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueSagar GavasNo ratings yet
- 1) Epithelial TissueDocument4 pages1) Epithelial TissueElleNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Anatomy 1)Document83 pagesTissues (Anatomy 1)nanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Tissue ReportDocument10 pagesTissue ReportMukisa EliasNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument31 pagesTissuealiyyah aswinanda100% (1)
- Animal Tissues Levels of Organization: TissueDocument15 pagesAnimal Tissues Levels of Organization: TissueDiane Fontanilla100% (1)
- Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument68 pagesTissue Level of OrganizationCecil AlbaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument70 pagesTissuesayssNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisation: Cell Specialisation in Multicellular OrganismsDocument48 pagesCell Organisation: Cell Specialisation in Multicellular OrganismsMia Mygul100% (1)
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#2 MED3Document3 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#2 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - PhysicsDocument30 pagesGen Bio - PhysicsEzel MayNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesAnimal TissuesEduard LaudeNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument17 pagesAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue (Finale)Document2 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Finale)Adz Na HarNo ratings yet
- Classification of Tissue: Suman Kumar Mekap Asst. Professor (Pharmacology) CUTM, BhubaneswarDocument20 pagesClassification of Tissue: Suman Kumar Mekap Asst. Professor (Pharmacology) CUTM, BhubaneswarSaad Zafar AwanNo ratings yet
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDocument37 pagesZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in AnimalsDocument7 pagesStructural Organization in AnimalsVedant BondeNo ratings yet
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- Anatomy LectureDocument76 pagesAnatomy LectureLagnajit Behera100% (1)
- Additional Topics CHAPTER 3 4Document8 pagesAdditional Topics CHAPTER 3 4pinieraaurapaulaNo ratings yet
- LSM1301 Animal Form and FunctionDocument13 pagesLSM1301 Animal Form and FunctionantheaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Module 1 2Document12 pagesGeneral Biology Module 1 2cabellaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisation in AnimalsDocument30 pagesCell Organisation in Animalsputeri 93100% (2)
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Human Tissues - 1Document43 pagesHuman Tissues - 1Angel Diadem ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument15 pagesEpithelial Tissueravneet.singh.7500No ratings yet
- BIO 9 SM3 23-24pDocument11 pagesBIO 9 SM3 23-24pNandini Pritesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Physiology - 4th SemDocument76 pagesPhysiology - 4th SemSandeep AdapalaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Integumentary System and Bone TissueDocument12 pagesTissues, Integumentary System and Bone TissueChristine BalanzaNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Human Body OrganizationDocument6 pagesHuman Body OrganizationWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: - Are Widespread Throughout The BodyDocument9 pagesEpithelial Tissue: - Are Widespread Throughout The BodyElyka AbellaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 The Tissues MembranesDocument60 pagesWeek 2 The Tissues MembranesJeqtopher RoaNo ratings yet
- Scratch AnaphyDocument5 pagesScratch Anaphymooshee06No ratings yet
- Mucosal Membrane Health: The Key to Preventing Inflammatory Conditions, Infections, Toxicity and DegenerationFrom EverandMucosal Membrane Health: The Key to Preventing Inflammatory Conditions, Infections, Toxicity and DegenerationNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- W1-L3-Human Development - Heredity and Environment200414060604044949Document14 pagesW1-L3-Human Development - Heredity and Environment200414060604044949Sachidananda AngomNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 - Labor, Delivery, and Postpartum Issues and Care - UpToDateDocument25 pagesCOVID-19 - Labor, Delivery, and Postpartum Issues and Care - UpToDateCamilo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding in IslamDocument2 pagesBreastfeeding in IslammascomwebNo ratings yet
- Aakarshi Rawal Final NTCCDocument11 pagesAakarshi Rawal Final NTCCAakarshi RawalNo ratings yet
- Nurturing Care Components 1Document2 pagesNurturing Care Components 1Jeff WigginsNo ratings yet
- Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Clinical Features and DiagnosisDocument21 pagesCongenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Clinical Features and Diagnosisgomitas21No ratings yet
- RegistrarGuidelines VS34Document7 pagesRegistrarGuidelines VS34Don BetoNo ratings yet
- Managing Medical and Obstetric Emergencies and Trauma A Practical Approach 4Th Edition Rosamunde Burns Editor Full ChapterDocument65 pagesManaging Medical and Obstetric Emergencies and Trauma A Practical Approach 4Th Edition Rosamunde Burns Editor Full Chaptersteven.webb781100% (4)
- Black Cohosh 20020729Document10 pagesBlack Cohosh 20020729Margaret ThatcherNo ratings yet
- Antenatal AssessmentDocument9 pagesAntenatal Assessmentjyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Anaemia in Pregnancy Malaysia, APJCN2006 PDFDocument10 pagesAnaemia in Pregnancy Malaysia, APJCN2006 PDFAkhmal SidekNo ratings yet
- Dapus 15 (Conceptual Model)Document5 pagesDapus 15 (Conceptual Model)Justin IqbalNo ratings yet
- PNLE: Maternal and Child Health Nursing Exam 1: Text ModeDocument47 pagesPNLE: Maternal and Child Health Nursing Exam 1: Text ModeAngelica SorianoNo ratings yet
- Indianbank Policy WordingsDocument32 pagesIndianbank Policy WordingsRaja KatareNo ratings yet
- Focus Charting: Date Time Focus Nurse'S Remarks D She Is Is Gravid 2, paraDocument6 pagesFocus Charting: Date Time Focus Nurse'S Remarks D She Is Is Gravid 2, paraVincent SalvadorNo ratings yet
- ST Matthew 19 20Document30 pagesST Matthew 19 20Dhang Nario De TorresNo ratings yet
- 10 Effective Transfusion in Paediatric PracticeDocument11 pages10 Effective Transfusion in Paediatric PracticeArman PratomoNo ratings yet
- Pot Term pregnancy-MOMANYIDocument2 pagesPot Term pregnancy-MOMANYISally Gesembe100% (1)
- Abnormal LaborDocument21 pagesAbnormal LaborCharisse Aser Flores AquinoNo ratings yet
- OSHWA Maternity BookDocument135 pagesOSHWA Maternity BookAbo Ahmed TarekNo ratings yet
- Essential Management of Obstetric EmergenciesDocument2 pagesEssential Management of Obstetric Emergenciestiara merdeka putriNo ratings yet
- Hormones Beta HCG - SerumDocument1 pageHormones Beta HCG - SerumsaniyaNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Atosiban in Preterm Labor ManagementDocument45 pages2021 - Atosiban in Preterm Labor ManagementM Wahyu UtomoNo ratings yet
- SGD Case 2 Written Output-1Document19 pagesSGD Case 2 Written Output-1Jam PanumpangNo ratings yet
- Newborn ReflexesDocument10 pagesNewborn ReflexesJayrelle D. Safran100% (1)
- Women and Mental HealthDocument17 pagesWomen and Mental Healthmerin sunilNo ratings yet