Professional Documents
Culture Documents
U1有机
Uploaded by
malvinalaiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
U1有机
Uploaded by
malvinalaiCopyright:
Available Formats
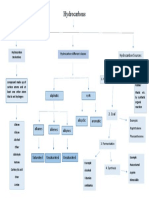
It is covalent compounds which contain only
Almost all organic compounds are hydrocarbon.
carbon and hydrogen atoms
Saturated 和 unsaturated 的hydrocarbon的概念
Def: 饱和
Alkanes
氢的个数完整
不饱和
Simple hydrocarbon Alkenes
氢的个数稀少
Alkynes
Covalent compound Contain covalent bond
Simple molecular structure Low boiling and melting point
Combustible
A cancer-causing agent (carcinogen) or
substance with respiratory, reproductive or
organ toxicity that causes damage over time (a
chronic, or long-term, health hazard).
Health hazard
Flammable materials or substances liable to
self ignite when exposed to water or air (
pyrophoric), or which emit flammable gas.
Flame
An immediate skin, eye or respiratory tract
irritant, or narcotic.
Exclamation mark
Structural characteristics and properties
Materials causing skin corrosion/burns or eye
damage on contact, or that are corrosive to
metals.
Corrosion
A chemical substance relates to the inherent
Hazard 8 types of hazard warning symbols
properties of the substance
Explosives, including organic peroxides and
highly unstable material at risk of exploding
even without exposure to air (self-reactives).
Exploding Bomb
Identifies oxidizers. Oxidizers are chemicals
that facilitate burning or make fires burn hotter
and longer.
Flame over circle
Hazard and risk
Substances, such as poisons and highly
concentrated acids, which have an immediate
and severe toxic effect (acute toxicity).
Skull and crossbones
Chemicals toxic to aquatic wildlife. (Non-
Mandatory)
Environmental Hazard
Is more to do with how you plan to use it and
Risk
the chance of it causing harm
含碳原子最多的链为主链
优先级最高的官能团的编号数字最小
对碳链进行编号
如果没有优先级高的官能团,尽可能使所有取代基的
位次最小
当两个卤原子在不同的两端,为此相同,那就按照
alphabet排列
位次 数字编号表明在碳链中的位置
1. Meth-
2. Eth-
3. Prop-
4. But-
表示主链上的碳原子数 5. Pent-
6. Hex-
7. Hept
8. Oct-
书写形式一般为位次+前缀+尾缀 前缀
9. Non-
10. Dec-
IUPAC Naming
Floro-
Chloro-
如果是Halogenalkanes就要在那之前在加上
Bromo-
Iodo-
Alkanes(烷类): -ane
Branched alkanes(支链烷烃): alkyl-/-yl
Alkenes(烯烃类): -ene
后缀 Alcohols(醇类): -ol
体现官能团
Hydrocarbon Aldehydes(醛类): -al
Ketones(酮类): -one
Cycloalkanes(环烷烃): cyclo-…-ane
Carboxylic acid(羧酸类): -oic acid
如果化合物中有多个相同基团,合并位次用逗号连
接,再使用di-,tri-,tert-,prefix-,
同源级数的化合物有相同的分子式
General formula(通式) 描述一种化合物中任意一个化合物的代数公式
Empirical formula(经验式) 化合物中每个元素的原子的最简整数比
Know hydrocarbon Molecular formula(分子式) 分子中每个元素的实际原子数
6 types of formula Structural formula(结构式) 显示碳原子的排列和附着的氢和官能团
只显示碳的骨架和任意官能团的键和官能团,不显示
Skeletal formula(键线式) 大量使用于绘制大型复杂结构的有机化合物
氢原子和碳原子
Displayed formula(结构显式) 显示所有原子的排列,以及它们之间的所有键。
先写出主链
减一个碳
把第一个碳连在主链的不同的位次上
烷烃 减碳法
减一个C2H5
减两个碳 两个碳可以在不同位次
链异构 带支链
两个碳也可以在相同位次
烯烃 和上方烷烃相同
异构体
官能团的位次不同
位置异构
烯烃的双键异构体
官能团异构
Def: 发生化学反应的片段
相同功能团 功能团
常见功能团: 双键,羟基(OH),卤原子
相似化学性质
推同系物结构
同系物 Charactor 相差CH2
Physical property逐步变化 eg. 熔沸点随着CH2的增加逐步上升
相同通式
Introduction of crude oil A bid mixture of hydrocarbon
The cude oil vaporized at about 350 degrees
先蒸发再冷凝
The largest hydrocarbons don’t vaporise at all,
The vaporised crude oil goes into a
because their boiling points are too high, so
fractionating column and rises up through the
they just run to the bottom and form a gooey
trays.
residue(粘稠的残留物).
Process of fractionation
Because the alkane molecules have different
chain lengths, they have different boiling points,
so each fraction condenses at a different
As the crude oil vapour goes up the temperature.
fractionating column, it gets cooler.
The fractions are drawn off at different levels in
the column.
The hydrocarbons with the lowest boiling points They’re drawn off as gases at the top of the
don’t condense. column.
Breaking long-chain alkanes into smaller
Def: 长直链变短链
hydrocarbons (which include alkenes)
Crude oil
Chain breaks is random, so you will get a
different mixture of products every crack a
hydrocarbon
Cracking Take place at high temperature(up to 1000
degree) and pressure(up to 70 atm)
Thermal Cracking
Produce alkenes more 用来制造聚合物eg.聚乙烯
Use zeolite catalyst(hydrated alumiosilicate)铝的
Two types of cracking: 氧化物
Take place at slight pressure and high
temperature(about 450 degree)
Catalytic Cracking
Produce aromatic hydrocarbons(芳香化合物)
and motor fuels(汽车燃油) more
cut costs Lower pressure and lower temperature
advantage:
Speed up the reaction (saving time)
A reaction convert straight-chain alkanes into
Def: 直链变支链或环状
branched chain alkanes and cyclic hydrocarbons
Reforming
需要使用催化剂
General formula CnH2n+2
结构特点 是饱和(saturated)化合物,所有只有单键
碳成4个键
Naming
一般反应式 C2H6(g)+2O2(g)->C(s)+CO(g)+3H2O(g)
Incomplete combustion:
C, CO, CO2,H2O
可能产物
CO的中毒机制 和血液中的heamoglobine结合,阻止氧气的运输
一般反应式 C3H8(g)+5O2(g) -> 3CO2(g)+4H2O(g)
Chemical properties Combustion reaction: Complete combustion:
产物 CO2, H2O
如果是液态的烷烃那么就要先蒸发,再燃烧
长链烷烃的燃烧需要更多的能量,因为他们有更多的
键需要断
Bond breaks evenly and form a free radical
Bond fission in alkanes Homolytic fission
Free radical are very reactive
反应物 烷烃+卤素
Alkanes(烷烃)
反应条件 UV light
一卤代烷
产物
多卤代烷
Free radical substitution
总反应式 Cl2+CH4->(UV light) CH3Cl+HCl
Initiation: Cl2->(UV light)2Cl· Homolytic fission
Cl· +CH4-> ·CH3+HCl
反应举例 eg. Propagation:
·CH3+Cl2->CH3Cl+Cl·
Cl· +CH3Cl-> ·CH2Cl+HCl ·CH2Cl+Cl2 -> CH2Cl2+Cl·
U1 Organic Chemistry
Further reaction: Cl· +CH2Cl2-> ·CHCl2+HCl ·CHCl2+Cl2 -> CHCl3+Cl· 由一卤代烷生成多卤代烷
Cl· +CHCl3-> ·CCl3+HCl ·CCl3+Cl2 -> CCl4+Cl·
Combustion 产物
eg. CO,unburnt hydrocarbons,carbon
particulates from incomplete combustion of
fuels, 硫氧化物,氮氧化物
Fossil fuels Will cause pollution CO toxic 因为CO比氧气更加容易carry血红蛋白
含硫的化石燃烧引起酸雨
硫氧化物&氮氧化物
高温高压使氮和氧一起反应形成氮氧化物,并且溶解
在水分中转换为硝酸,硝酸会像酸雨一样落下
it is non-renewable
unsaturated hydrocarbons,带双键
General formula CnH2n+2
所以双键的周围的原子一定是planer,比如说C2H4
它是一个平面模型。
结构特点 双键的性质 双键不可以被旋转
但是如果C2H4中的任意一个H被一个官能团取代掉
的话,那么那个支出去的官能团就不是平面的
Hydrocarbon 的种类
结构异构体 同样的分子式,不同的结构式
异构体 E-/trans异构体: 双键边上的相同官能团在不同侧
当双键上的两个原子各自有两个不同的原子或基团附
立体异构体 同样的分子式,同样的结构式,不同的空间结构排布 Z-/cis异构体: 双键边上的相同官能团在相同侧
着的时候,就会产生立体异构体
不同官能团区分E/Z异构体的方法: 按照原子序数的高低排列 左右两边原子序数同样高低的为“相同官能团”
Alkene molecules have at least one c=c double
covalent bond
燃烧反应 和烷烃类似
反应特点 一个双键被打开成两个单键
⚠
condition: 300 degrees and 60-70 atm 反应需
要磷酸(H3PO4)作为催化剂
和水蒸气反应
H2C=CH2(g)+H2O(g)->CH3CH2OH(g)
加成反应 实验现象 紫色褪色
卤素的电子偏离到一个原子上形成异裂
和卤素反应
c=c双键吸引delta+原子去打掉双键形成单键
反应机理
所以另一个c变+然后剩下的一个卤素原子带着两个点
子和c+成键
反应类型
最终卤素取代掉两个H
H2C=CH2+HX->CH2XCH3
和HX反应
根据马尔科夫尼科夫规则
产物
氢+氢多
经典反应类型
催化剂 Ni, Pd, Pt
和H2反应
产物是烷烃
反应条件 酸性高锰酸钾
Alkenes(烯烃)
烯烃形成两个羟基
氧化反应 反应机理
H2C=CH2->H2OHC-CH2OH
反应现象 紫色褪色成无色
从单体变成聚合物 将一个双键打开变成两个单键来连接两个结构单元
加成聚合反应
从聚合物变成单体 将连接两个结构单元的单键还原成双键
反应物烯烃+卤素/氢卤酸
一卤代烷
反应产物
二卤代烷
双键是负电子的功能团
亲电加成反应 分析分子的dipole
全箭头由双键指向dipole的正极
Tertiary carbocation
碳正离子的种类 Secondary carbocation
反应机理 Primary carbocation
生成carbocation 碳正离子的稳定性 3>2>1
3不连H
分级 观察碳正离子连接氢的数量 2连一个H
1连两个H
稳定产物
Addition(加成) 至少两个原子连接在一起
Polymerisation(聚合) 简单的分子结合在一起
Elimination(消除) 小原子从大分子中脱离
7 types of reaction Substitution(取代) 一个元素被另一个元素取代
Hydrolysis(水解) 和水反应将一个分子分裂成两个新分子
Oxidation(氧化) 任何失电子的反应
Reduction(还原) 任何得电子的反应
结构 其中一些氢气被替换成卤素
卤代烷烃
命名 以bromo, chloro, iodo, floro为前缀
碳氢化合物的衍生物
结构 其中一些氢气被替换成羟基
醇
命名 以-ol为尾缀
烷烃 燃料 让汽油燃烧更平缓
用途
烯烃 合成高分子聚合物 eg.塑料
Landfill(掩埋) 弊端 难以降解
降解高分子聚合物的方法 Burned(焚烧) 弊端: 产生有毒气体
能安全快速的降解
生物降解 优势:
不会对环境造成伤害
环境问题 氮氧化物 和氧气反应生成硝酸
烷烃燃烧 产物 硫氧化物 和氧气反应形成硫酸
CO 和haemoglobin结合,阻止氧气流通
解决方法
You might also like
- Coulometric and Volumetric Determination of Moisture in Plastics Using The Karl Fischer Reaction (The Reaction of Iodine With Water)Document4 pagesCoulometric and Volumetric Determination of Moisture in Plastics Using The Karl Fischer Reaction (The Reaction of Iodine With Water)Mohanad50% (2)
- Studio Arts Chemical Safety GuidelinesDocument19 pagesStudio Arts Chemical Safety GuidelinesMarius SrrNo ratings yet
- Chemical Inventory Sheet: Name of Company/Production UnitDocument4 pagesChemical Inventory Sheet: Name of Company/Production UnitNur E Alam NuruNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds NotesDocument42 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compounds NotesMahalaksshmi .DNo ratings yet
- The Using of Alkanes in The Role of FuelDocument1 pageThe Using of Alkanes in The Role of FuelCosmescu Mario FlorinNo ratings yet
- 4248 Mflex Tubing Selection GuideDocument3 pages4248 Mflex Tubing Selection GuideMARCO PaganiniNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument30 pagesDangerous Goodsdrr1117No ratings yet
- CCKR4U BoardingPassDocument2 pagesCCKR4U BoardingPassOana IftimieNo ratings yet
- Mckee 2015Document93 pagesMckee 2015Lasagna katNo ratings yet
- C7 Organic ChemistryDocument2 pagesC7 Organic ChemistryFiona Tobi LawalNo ratings yet
- CHE 422 Fall 2021 L7Document8 pagesCHE 422 Fall 2021 L7Zain GillaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Safety SignsDocument2 pagesChemical Safety SignsPaolo CabatoNo ratings yet
- 04 FuelsDocument24 pages04 FuelsAndri Parnaungan HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Ghs Adg Quick Guide Web PDFDocument2 pagesGhs Adg Quick Guide Web PDFAlejandro Gallego SernaNo ratings yet
- Chemical IncompatibilityDocument1 pageChemical Incompatibilityjuan manuel valdez von furthNo ratings yet
- Chemical Incompatibility - tcm17-6734 PDFDocument1 pageChemical Incompatibility - tcm17-6734 PDFBasha Yazn AnjakNo ratings yet
- Que Agota La Materia de Que Se Trata O, Es Muy CompletoDocument2 pagesQue Agota La Materia de Que Se Trata O, Es Muy CompletoMisael Santiago ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Hydrocarbons Experiment 7Document18 pagesClassification Tests For Hydrocarbons Experiment 7Jerome Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkenes and AlcoholsDocument4 pagesReactions of Alkenes and AlcoholsRaquel da Silva JustinoNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Mind MapDocument1 pageAmmonia Mind MapPeer MohamedNo ratings yet
- Unit02 - Hazard Comm. GHS LabelingDocument2 pagesUnit02 - Hazard Comm. GHS LabelingRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Clinical Toxicology - HydroCarbons - Pharmadost PDFDocument11 pagesClinical Toxicology - HydroCarbons - Pharmadost PDFRaju NiraulaNo ratings yet
- P Omaha Cova 2009Document5 pagesP Omaha Cova 2009Jack BravoNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Matriz Compatibilidad SQ Sugerida Por MerckDocument2 pages2.2 Matriz Compatibilidad SQ Sugerida Por MerckMonroy EAndrésNo ratings yet
- Changes On Mesoscale & Microscale: Air QualityDocument1 pageChanges On Mesoscale & Microscale: Air QualityAfiq JohariNo ratings yet
- Files 2Document1 pageFiles 2joseNo ratings yet
- Glosario CC: Inglés Español Fuente Pronunciación Comentarios/ DefiniciónDocument9 pagesGlosario CC: Inglés Español Fuente Pronunciación Comentarios/ Definiciónanalia aviazziNo ratings yet
- Blue Modern Medical BrochureDocument2 pagesBlue Modern Medical BrochureyeishaNo ratings yet
- HHSRS LeafletDocument4 pagesHHSRS LeafletBock MusNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument33 pagesOrganic ChemistryFari Sweet PumpkinNo ratings yet
- Storage of Chemicals: Hydrogen Peroxide Organic Solvents and Hydrocarbons Solid WastesDocument1 pageStorage of Chemicals: Hydrogen Peroxide Organic Solvents and Hydrocarbons Solid WastesTAN HONG SHEN MoeNo ratings yet
- SAS 8 For StudentsDocument13 pagesSAS 8 For Studentsqdt282r4n8No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument1 pageHydrocarbonsDiana BuisNo ratings yet
- Gesulga-Vuelban Pit Orgchem2Document1 pageGesulga-Vuelban Pit Orgchem2John Nicholson LanderoNo ratings yet
- Diccionario para IngenierosDocument2 pagesDiccionario para IngenieroslosmisteriosdemovilleNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document3 pagesCH 2MD100% (1)
- Safe 1986Document29 pagesSafe 1986Ryea Chayankka TwentysevendNo ratings yet
- Classification of Dangerous Goods: Class 1:explosivesDocument5 pagesClassification of Dangerous Goods: Class 1:explosivesSherwin Delfin CincoNo ratings yet
- Relative ExposureDocument11 pagesRelative ExposurenasjabNo ratings yet
- Study of CompoundsDocument17 pagesStudy of CompoundsGodhuliNo ratings yet
- How Refinery WorksDocument7 pagesHow Refinery WorksmuraliNo ratings yet
- O Level Organic Chemistry Online Class Notes 2023 PDFDocument5 pagesO Level Organic Chemistry Online Class Notes 2023 PDFAli NishanNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument5 pagesDangerous GoodsFrancis Charles AriolaNo ratings yet
- RO GHS ADG Quick Guide v99x210 v28 PDFDocument2 pagesRO GHS ADG Quick Guide v99x210 v28 PDFsemeneh haile100% (1)
- Test For Hydrocarbons: Laboratory Activity CHEM 525Document39 pagesTest For Hydrocarbons: Laboratory Activity CHEM 525Jherby TeodoroNo ratings yet
- E. Annex A: Quality Control Guidance For Analytical Test Data - Supporting ZDHC MRSL V2.0 ConformanceDocument11 pagesE. Annex A: Quality Control Guidance For Analytical Test Data - Supporting ZDHC MRSL V2.0 ConformanceVIJAYAKUMAR K ANo ratings yet
- BROCHURE Product Range - I&I and Home Care Solutions Europe-BASF-09-18Document19 pagesBROCHURE Product Range - I&I and Home Care Solutions Europe-BASF-09-18Francesco RicciNo ratings yet
- Material: Notable Hazard StatementsDocument1 pageMaterial: Notable Hazard StatementsTom HartNo ratings yet
- DOT LabelsDocument1 pageDOT LabelsCoronavilleNo ratings yet
- Human Cancer: Known Causes and Prevention by Organ SiteDocument1 pageHuman Cancer: Known Causes and Prevention by Organ SiteFlaKitaNo ratings yet
- NEXT - MRSL (Next) DDocument8 pagesNEXT - MRSL (Next) DDyeing DyeingNo ratings yet
- Training Session 2011: Training Subject: Training RoomDocument17 pagesTraining Session 2011: Training Subject: Training RoomSrikanth0% (1)
- Chemical Hazard LabelDocument2 pagesChemical Hazard LabelmohamudNo ratings yet
- COURSE OUTLINE (Materi Pembelajaran) : Organic Hydrocarbon: Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkyneDocument9 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE (Materi Pembelajaran) : Organic Hydrocarbon: Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkyneAmmar AbiNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Goods Classifications - 112Document7 pagesDangerous Goods Classifications - 112Mauro CunhaNo ratings yet
- Molecules: New Biosourced Flame Retardant Agents Based On Gallic and Ellagic Acids For Epoxy ResinsDocument22 pagesMolecules: New Biosourced Flame Retardant Agents Based On Gallic and Ellagic Acids For Epoxy ResinsAbd BaghadNo ratings yet
- Appendix 5 Hazmat Inventory SheetDocument1 pageAppendix 5 Hazmat Inventory Sheetaldrb hospitalNo ratings yet
- POPs HandsoutDocument2 pagesPOPs HandsoutMarie Kris NogaNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Goods Are Everywhere.: 1. Identify Your Shipment 2. Package Your Shipments CorrectlyDocument1 pageDangerous Goods Are Everywhere.: 1. Identify Your Shipment 2. Package Your Shipments CorrectlyDelta-007No ratings yet
- p4 NotesDocument20 pagesp4 NotesmalvinalaiNo ratings yet
- 剑桥雅思15Test4Passage2阅读原文翻译 Silbo Gomero - the whistle language of the Canary Islands-老烤鸭雅思-专注雅思备考Document1 page剑桥雅思15Test4Passage2阅读原文翻译 Silbo Gomero - the whistle language of the Canary Islands-老烤鸭雅思-专注雅思备考malvinalaiNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry Experiment KeyDocument16 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Experiment KeymalvinalaiNo ratings yet
- S1 Chapter 5 NotesDocument4 pagesS1 Chapter 5 NotesmalvinalaiNo ratings yet
- 1993 2021年历年真题 BMO Round 1Document35 pages1993 2021年历年真题 BMO Round 1malvinalaiNo ratings yet
- G10 Chemistry STB 2023 WebDocument306 pagesG10 Chemistry STB 2023 Webgetacheweyob74No ratings yet
- Estimation of Urea by DAM MethodDocument3 pagesEstimation of Urea by DAM Methodmdanasd123No ratings yet
- Alkenes Reaction Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesAlkenes Reaction Worksheet PDFLeslie HernandezNo ratings yet
- Titrations in Analytical ChemistryDocument28 pagesTitrations in Analytical ChemistryRolen Simcha Castillo SamsNo ratings yet
- MOLE NotesDocument12 pagesMOLE NotesShanzay WaqarNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondsDocument3 pagesCovalent BondselizabethNo ratings yet
- N. Tewari, Vol-2, Organic ChemistryDocument920 pagesN. Tewari, Vol-2, Organic ChemistryVijay RaghavaNo ratings yet
- Polyurethane ReviewDocument30 pagesPolyurethane Reviewivan192010No ratings yet
- RoClean L403Document1 pageRoClean L403eduardoNo ratings yet
- Pesticide Residue Analysis of Fruits and Vegetables: Full Length Research PaperDocument10 pagesPesticide Residue Analysis of Fruits and Vegetables: Full Length Research PaperSajib RezaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument25 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsRaichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry From 3D Printed ObjectsDocument10 pagesChemistry From 3D Printed ObjectsHiran ChathurangaNo ratings yet
- Action of Synthetic Detergents On TheDocument23 pagesAction of Synthetic Detergents On TheTalita ColomeuNo ratings yet
- 13 Reaction Kinetics (S)Document32 pages13 Reaction Kinetics (S)Mr TanNo ratings yet
- Outstanding Chemical Resistance Apply by Brush, - Roller or Spray Unlimited Shelf Life - 100% Solids - Simple To Use - DurableDocument2 pagesOutstanding Chemical Resistance Apply by Brush, - Roller or Spray Unlimited Shelf Life - 100% Solids - Simple To Use - DurableAlfred GomoeliaNo ratings yet
- Acronal+S+790 TDS 30718249Document2 pagesAcronal+S+790 TDS 30718249Andy Cadillo Gonzales100% (1)
- Arathy 10Document24 pagesArathy 10Naveed BNo ratings yet
- Review of LiteratureDocument33 pagesReview of LiteratureChinedu OdaliNo ratings yet
- SDS PageDocument12 pagesSDS PageShadia HeyariNo ratings yet
- Finishing-Spin FinishDocument7 pagesFinishing-Spin FinishSethupathi K PNo ratings yet
- Expt 7 LipidsDocument34 pagesExpt 7 LipidsColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondDocument12 pagesIonic Bondsacheetha giriNo ratings yet
- Materials Science & Engineering B: Mohammad Jafar MolaeiDocument14 pagesMaterials Science & Engineering B: Mohammad Jafar MolaeiNgo Thuy Hong LamNo ratings yet
- Bitter Drugs: Preparation of ExtractsDocument25 pagesBitter Drugs: Preparation of ExtractsAmmy Joana Gallegos GarcíaNo ratings yet
- In thinking HL Topic 3&13 Periodicity and transition metals (1) - 副本Document7 pagesIn thinking HL Topic 3&13 Periodicity and transition metals (1) - 副本Xueren LyuNo ratings yet
- Chap - 06 Polimer KimyasiDocument19 pagesChap - 06 Polimer Kimyasiozguncrl1No ratings yet
- Chemosphere: Xiaolei Zhang, Satinder Kaur Brar, Song Yan, Rajeshwar Dayal Tyagi, Rao Y. SurampalliDocument13 pagesChemosphere: Xiaolei Zhang, Satinder Kaur Brar, Song Yan, Rajeshwar Dayal Tyagi, Rao Y. SurampalliMaja TastanoskaNo ratings yet
- QC SkillDocument31 pagesQC SkillJagdish100% (1)
- Chemistry 1 - 11 - Q1 - M8Document14 pagesChemistry 1 - 11 - Q1 - M8Elisa PauloNo ratings yet