Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ultrasonic Course Summary
Uploaded by
NIZAR EKA SAPUTRA ICALOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasonic Course Summary
Uploaded by
NIZAR EKA SAPUTRA ICALCopyright:
Available Formats
PT.
Karsa Kencana Indonesia
Technical Testing & Inspection Services
ULTRASONIC TEST COURSE SUMMARY
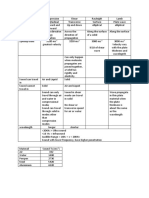
Type of Ultrasonic wave Velocity
Compression or Longitudinal wave (Normal probe) Velocity is “Speed of sound inside the material”
Particle oscillating in the direction of propagation Material Compression Shear
Can be propagated through Solid, Liquid and Gas Water 1480 m/s -
Perspex 2740 m/s 1320 m/s
Shear or Transverse wave ( Angle probe) Copper 4760 m/s 2325 m/s
Stainless Steel 5740 m/s 3130 m/s
Particle oscillating perpendicullar to the direction of Carbon steel 5960 m/s 3240 m/s
propagation
Can be propagated only at Solid
*Velocity of Surface wave = 90% of shear wave
Rayleigh or Surface wave
Depth of penetration is no more than 1 wavelength
Lamb wave
Can be flow in thin material
Good for detect Sub-surface discontinuities
Surface scale and dirt will affect the test, clean
surface is required
Wavelength Frequency
Wavelength is “distance between two successive peak” Frequency is
Expressed as lambda ( λ ) “Repetition rate or number of vibration in one
period”
Practically, a probe can detect a flaw whose diameter is ½ of
their wavelength
Expressed in cycles per second ( Hz )
The higher the Frequency = the shorter wavelength
K2i – investing on skill Ultrasonic Test course summary Page 1 of 8
- Ardian Antarja -
PT. Karsa Kencana Indonesia
Technical Testing & Inspection Services
Ultrasonic Energy Type of Crystal
Produced by crystal or transducer due to Piezo Electric. Barium Titanate
Piezo Electric = converting electrical energy to mechanical Curie point 140° C
and vice versa Heat above curie point will destroy the crystal
Lead Zirconate Titanate
Excellent sensitivity, little noise
Commonly used in NDT field
Lithium Sulphate
Dissolve in water
Mostly used in Medical field
Lead metaniobate
To produce various frequencies, crystal thickness is the main High internal damping coefficient
factor. Transmitting very narrow pulse
Probes Probes
Single crystal or Transceiver Dual Crystal
Use only 1 crystal for Transmit and Receive energy Use 2 crystal, one for Transmit & one for
Operated in “Pulse-Echo” mode Receive
Operated in “Dual “mode
Eleminate dead-zone, good for surface defect
Cork Separator used to reduce cross-talk
chatter
K2i – investing on skill Ultrasonic Test course summary Page 2 of 8
- Ardian Antarja -
PT. Karsa Kencana Indonesia
Technical Testing & Inspection Services
Ultrasonic Beam
Dead zone Near zone ( Fresnel Zone )
Ringing time of crystal The ultrasonic beams remain parallel and have
the same diameter as the crystal over a distance.
Can be minimized by using damping medium behind However, it is reduced up to the end of the near field
the crystal which is called the focus.
Shown as initial pulse at the screen time-base Within the near zone unreliable signals amplitude
occurs.
Not possible to detect defect
Dead zone increase if frequency decreased
Far zone ( Fraunhoffer Zone ) Beam Spread
The zone where beam start to diverging Beam spread is function of Frequency & crystal
diameter
Beam intensity is decreased as distance is increased
• Large reflector, amplitude is reduced by 50% (6
dB)
• Small reflector, amplitude is reduced by 25% (12
dB)
Frequency increased = Beam spread decreased
Diameter increased = Beam spread decreased
K2i – investing on skill Ultrasonic Test course summary Page 3 of 8
- Ardian Antarja -
PT. Karsa Kencana Indonesia
Technical Testing & Inspection Services
Reflection Refraction
When a beam of sound energy strikes a boundary, it is When sound wave pass from one medium to
normally reflected at the same angle as the incident angle. another, a change in wavelength takes place due to
the differing acoustic velocities of each medium.
The angle of incident equals to the angle of reflection
As a result, the angle at which the sound enters
the second medium does not equal that of the first
medium. This is known as refraction
Snell’s law Critical Angle
Snell’s law determines the angular relationship between First critical angle ( 27.4° )
the incident and refracted beam on transmission between When the incident angle reaches the first critical
two media with different velocities. angle, longitudinal wave will be internally reflected
through 90o.
Only transverse waves exist in the second medium
Second critical angle ( 57.7° )
When the incident angle reaches the second critical
angle, transverse wave is internally reflected
through 90o.
Surface wave will exist at the surface
K2i – investing on skill Ultrasonic Test course summary Page 4 of 8
- Ardian Antarja -
PT. Karsa Kencana Indonesia
Technical Testing & Inspection Services
Decibel ( dB ) Acoustic impedance
Decibel is a unit of comparison, it is the measurement of
changes in sound intensities and has a logarithmic base
At any interface between two media of differing
acoustic impedance, part of the ultrasonic energy is
reflected and the remainder is transmitted into the
second material.
Energy transmitted Energy reflected
Resolution Attenuation or Absorption
Resolution is “The ability to identify two or more reflector Attenuation or weakening of the echoes is a
that are close each other” combination of absorption and scattering, leading to
energy loss.
Absorption of the wave can refer to loss through heat
due to internal friction.
High frequency = High Attenuation = Low Penetration
High frequency = Good Resolution Surface condition, Acoustic impedance, couplant,
mode conversion and Spurious indication are
affecting Ultrasonic.
CRT Presentation
A-scan ( Amplitude Vs Time ) B-Scan ( Cross-sectional ) C-Scan ( Plan View )
K2i – investing on skill Ultrasonic Test course summary Page 5 of 8
- Ardian Antarja -
PT. Karsa Kencana Indonesia
Technical Testing & Inspection Services
Indication, Discontinuity and Defect
Indication = Response from the method or apparatus, could be the results of something in the specimen under
investigation, faulty equipment, or external factor.
Discontinuity = Interruption in the physical structure or configuration of a material or component.
Defect = Discontinuity which is unacceptable to the quality level established by the specification.
Indication type Discontinuity type
Linear (planar)
Aligned Indication Two dimensional resembling a straight line,
which length is greater than its width.
Indication that having length
greater than three times its width Crack, lack of fusion, incomplete penetration,
burn through, undercut, cold lap, misalignment.
Spherical (volumetric)
Three dimensional having the form of a sphere.
Single pores, non-elongated slag.
Rounded Indication
One of circular or elliptical Cylindrical (volumetric)
shape with a length equal or Three dimensional having the form of a cylinder.
less than three times its width
Elongated slag, wormholes, aligned pores,
hollow bead, and concave root.
Probe movement in discontinuity
The reflector is to be scanned by “Orbital”, “Swivel” and “Lateral” movement of the probe
Orbital scanning is made around the discontinuity in a circular path
with the discontinuity at the centre of the circle.
Swivel scanning involves rotation of the probe around an axis through
the centre of the probe body.
Lateral scanning is movement of the probe perpendicular to the
scanning surface.
K2i – investing on skill Ultrasonic Test course summary Page 6 of 8
- Ardian Antarja -
PT. Karsa Kencana Indonesia
Technical Testing & Inspection Services
Discontinuity signal interpretation
Spherical reflector
The signal remains basically unchanged as the probe moved around the reflector in orbital fashion
There is no respond signal to “swivel “ scan and shows no length with the “lateral “ movement
Signal normally small with narrow base, because only small area of the discontinuity actually reflects the
ultrasonic beam.
A single pore produces sharp indication and a cluster pore will produce multiple or broad based indication
with many peaks.
Cylindrical reflector
Produce weak indication signal if “orbital “ or “swivel “ scanning is performed
With “swivel “scan, the peak of indication signal will be decreased, but in the same time another peak in
the same signal will rise.
With “lateral” movement of the probe, a varying constant signal may result, continuity of the signals
indicates length of the reflector
When tested with different probe angles, will produce equivalent or significant signal at all angles of
incidence
Planar reflector
Produce no indication signal if “orbital “ or “swivel “ scanning is performed
With “lateral” movement of the probe, a varying constant signal may result, continuity of the signals
indicates length of the reflector
When tested with different probe angles, significantly greater amplitude signal from a particular angle
probe will occur, because sound is reflected at its maximum from only one angle of interception, i.e.
around 90°
Crack indications typically show multiple peaks and of wider shape because of the many discontinuity
facets usually presents. When the probe is rotated (orbited) 20° to 30° angle can be maintained before
the echo is totally reflected.
Lack of side-wall fusion produce sharp indication and usually detectable from one side. The maximum
signal remains constant for some distance of the probe movement perpendicular to the weld axis.
K2i – investing on skill Ultrasonic Test course summary Page 7 of 8
- Ardian Antarja -
PT. Karsa Kencana Indonesia
Technical Testing & Inspection Services
Common screen signal interpretation
Root
Excess
Pent.
Inclusion / Slag Excess Penetration Porosity
Lack Of Fusion Crack
K2i – investing on skill Ultrasonic Test course summary Page 8 of 8
- Ardian Antarja -
You might also like
- TWI UT Self NotesDocument12 pagesTWI UT Self NotesAnna PariniNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing (Ut)Document23 pagesUltrasonic Testing (Ut)ManoNo ratings yet
- Crystal THK / 2, Wave Length in Crystal: Piezo-Electric EffectDocument1 pageCrystal THK / 2, Wave Length in Crystal: Piezo-Electric Effectarkaprava ghoshNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing (Ut) : This Is The Method, Ultrasound (20,000Hz) Is Used To Find The Defect Up ToDocument30 pagesUltrasonic Testing (Ut) : This Is The Method, Ultrasound (20,000Hz) Is Used To Find The Defect Up ToKrishnamoorthi GovinthanNo ratings yet
- TestingDocument18 pagesTestingVivekanandan JNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing MethodsDocument67 pagesUltrasonic Testing MethodsMOHAMMAD ALINo ratings yet
- Twi Ut2Document38 pagesTwi Ut2Ahmed El GehaniNo ratings yet
- NDT UtDocument42 pagesNDT UthassanNo ratings yet
- 2 Basics of UtDocument52 pages2 Basics of Utmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestDocument116 pagesUltrasonic TestMuhamad AnwarudinNo ratings yet
- Ri Presentation Part - 1Document116 pagesRi Presentation Part - 1Hao TranNo ratings yet
- Probe ConstructionDocument13 pagesProbe ConstructionAdarsh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT) : The Engineers Edge Institute of NDTDocument83 pagesUltrasonic Testing (UT) : The Engineers Edge Institute of NDTThe Engineers EDGE, CoimbatoreNo ratings yet
- 4 Master Class - ID Creep Wave MethodDocument22 pages4 Master Class - ID Creep Wave Methodnathaniel ekaikoNo ratings yet
- UltrasoundDocument12 pagesUltrasoundAngelica Montalbo NavaNo ratings yet
- NDT-Ultrasonic TestingDocument42 pagesNDT-Ultrasonic TestingSameer Mohammad100% (4)
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument85 pagesUltrasonic TestingSathish Raams100% (2)
- Launch Cables PDFDocument17 pagesLaunch Cables PDFMehdi SHNo ratings yet
- T Annoy' S Dual Concentric by DefinitionDocument27 pagesT Annoy' S Dual Concentric by DefinitionГригорий БоржковскийNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument36 pagesLaserprince wrathNo ratings yet
- Slide UT Part 2Document46 pagesSlide UT Part 2Trung Tinh HoNo ratings yet
- Lasers in Ophthalmology Part - 1Document53 pagesLasers in Ophthalmology Part - 1bhartiNo ratings yet
- Digital RT PPT (04.04.2018)Document134 pagesDigital RT PPT (04.04.2018)AURORA NDT Services67% (3)
- ATR PrinciplesDocument21 pagesATR PrinciplesKassimNo ratings yet
- Pana USDocument52 pagesPana USflorin100% (1)
- AttenuationDocument37 pagesAttenuationvirat viratNo ratings yet
- Intec UT P3Document25 pagesIntec UT P3shajeerNo ratings yet
- 16 NDT MethodDocument1 page16 NDT MethodRambir sisodiaNo ratings yet
- NDT MethodsDocument25 pagesNDT Methodsamittwi100% (1)
- Baron Gen3 Radar: 1 MW C-Band Klystron SystemDocument2 pagesBaron Gen3 Radar: 1 MW C-Band Klystron SystemRudy ZNo ratings yet
- Slide UT Part 1Document42 pagesSlide UT Part 1Trung Tinh HoNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Part 2 PDFDocument24 pagesCH 2 Part 2 PDFRadheNo ratings yet
- Depth of Penetration & Current Density: Home - Education Resources - NDT Course Material - EC TestingDocument4 pagesDepth of Penetration & Current Density: Home - Education Resources - NDT Course Material - EC TestingBAWAg PİNDĪNo ratings yet
- Ee242 Lect1 PostDocument97 pagesEe242 Lect1 PostAhmed mohyNo ratings yet
- 1.2 M Ku Band Data SheetDocument1 page1.2 M Ku Band Data Sheetpk srinivasanNo ratings yet
- NDT Lecture 1Document36 pagesNDT Lecture 1AtifNo ratings yet
- Titanium Sapphire Lasers and Femtosecond LasersDocument25 pagesTitanium Sapphire Lasers and Femtosecond LasersaliflailasurumiNo ratings yet
- FLS1000 Data-Sheet 2023Document2 pagesFLS1000 Data-Sheet 2023robertkingsysuNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Ultrasonic TestingDocument70 pagesIntroduction of Ultrasonic TestingMAXX ENGINEERS100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing: by Geetanjali Sharma Devendra Singh Amit Kumar JhaDocument55 pagesUltrasonic Testing: by Geetanjali Sharma Devendra Singh Amit Kumar Jhajhaamit4100% (2)
- Lasers Used in Operative Dentistry and EndodonticsDocument28 pagesLasers Used in Operative Dentistry and EndodonticsNingombam Robinson Singh0% (1)
- 2402H-8 JBLDocument2 pages2402H-8 JBLAntonio Perez PerezNo ratings yet
- RT Finalpresenatation08 161118104713Document56 pagesRT Finalpresenatation08 161118104713sajay2010No ratings yet
- Laser Welding MiyachiDocument66 pagesLaser Welding Miyachijesus100% (2)
- TakamoriDocument9 pagesTakamoriRamdani SaputraNo ratings yet
- 1.2 M Ku-Band Data-SheetDocument1 page1.2 M Ku-Band Data-SheetdipayanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 M Ku-Band Data-SheetDocument1 page1.2 M Ku-Band Data-SheetdipayanNo ratings yet
- Twi Ut Notes PDFDocument158 pagesTwi Ut Notes PDFGanesh Sekar100% (1)
- Lec 09 - Ultrasonic Testing PDFDocument92 pagesLec 09 - Ultrasonic Testing PDFBenidiktus Ma'dikaNo ratings yet
- Construction of Optical FiltersDocument34 pagesConstruction of Optical FiltersAvnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Paper For Upload PDFDocument6 pagesPaper For Upload PDFAnonymous uJpBMLqHNo ratings yet
- docs/Technology/Presentations/RPG Specialty AbsorbersDocument50 pagesdocs/Technology/Presentations/RPG Specialty AbsorbersJay JayNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument57 pagesUltrasonic TestingAshraf Bottani100% (1)
- 905nm Pulsed Semiconductor Laser 4-Channel Array Preliminary DatasheetDocument7 pages905nm Pulsed Semiconductor Laser 4-Channel Array Preliminary DatasheetVandana SinghNo ratings yet
- getPDF BDocument7 pagesgetPDF BZakwan ZakariahNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current TestingDocument58 pagesEddy Current Testingjyounas93% (15)
- Pass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewFrom EverandPass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Acoustic Wave Sensors: Theory, Design and Physico-Chemical ApplicationsFrom EverandAcoustic Wave Sensors: Theory, Design and Physico-Chemical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- VibroSight Release NotesDocument50 pagesVibroSight Release NotesfazzlieNo ratings yet
- Afcona - 6220 Tds EngDocument1 pageAfcona - 6220 Tds EngHamood AbdoNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval MOPX310SDocument64 pagesAlfa Laval MOPX310SvaleriyNo ratings yet
- Top DriveDocument4 pagesTop DriveJorge FreireNo ratings yet
- IFEM - ch24 Iso P TriangularDocument21 pagesIFEM - ch24 Iso P TriangularSimon DelmasNo ratings yet
- Hotpoint-Ariston ARMXXD 129 (EU) Washer-DryerDocument60 pagesHotpoint-Ariston ARMXXD 129 (EU) Washer-DryerAdrian Iulian VladNo ratings yet
- 988H M&O ManualDocument170 pages988H M&O Manualr1p2100% (4)
- Scale Tm-Xa Series PDFDocument153 pagesScale Tm-Xa Series PDFArmen ManasyanNo ratings yet
- Melsoft FR Configurator Sw3 Vf1Document8 pagesMelsoft FR Configurator Sw3 Vf1mo_be81No ratings yet
- Welding Processes PDFDocument44 pagesWelding Processes PDFHusain AliNo ratings yet
- IEEETPCTutorial Sag TensionCalcsDocument11 pagesIEEETPCTutorial Sag TensionCalcsjoelduparNo ratings yet
- Types of DamagesDocument1 pageTypes of Damagessanchitha RNo ratings yet
- 002 Turbine Engine Fuel Metering Notes1Document116 pages002 Turbine Engine Fuel Metering Notes1Yasser Zubaidi100% (2)
- Forces Worksheet #4 - Newton's Laws Problems: FrictionDocument2 pagesForces Worksheet #4 - Newton's Laws Problems: FrictionSTEVEN ST ANGELNo ratings yet
- DJI Air 2S User ManualDocument52 pagesDJI Air 2S User ManualAlexandre Costa de LimaNo ratings yet
- ch6 AnsDocument96 pagesch6 AnsAnonymous RzU94z50% (4)
- Assessment of Two Sweet Orange Cultivars Grafted On RootstockDocument11 pagesAssessment of Two Sweet Orange Cultivars Grafted On RootstockAhmad Hassan ChNo ratings yet
- ICL8038Document14 pagesICL8038RAYLINo ratings yet
- Dka GuidelineDocument16 pagesDka GuidelineGhada HusseinNo ratings yet
- 02 Asae 101892Document1 page02 Asae 101892raviteja036No ratings yet
- WTL Developer's GuideDocument225 pagesWTL Developer's GuideIvan Martyushov100% (1)
- Earth Fault Protection in A Solidly Effectively Earthed High Voltage Power SystemsDocument13 pagesEarth Fault Protection in A Solidly Effectively Earthed High Voltage Power SystemsMarian MarianNo ratings yet
- Design Plans For The " ": Advantage 10,000 Gallon Koi PondDocument19 pagesDesign Plans For The " ": Advantage 10,000 Gallon Koi PondMamad KoiNo ratings yet
- Reverse Ömer Faruk TunçDocument3 pagesReverse Ömer Faruk TunçÖmer Faruk TUNÇNo ratings yet
- Commodore 128 Assembly Language ProgrammingDocument402 pagesCommodore 128 Assembly Language ProgrammingBobby Guerra100% (5)
- Hazira Enquiry15012021Document36 pagesHazira Enquiry15012021Rakesh MenonNo ratings yet
- Lenovo YOGA 310 User GuideDocument36 pagesLenovo YOGA 310 User GuidesilvofNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Multiple Linear Regression: Ray-Bing Chen Institute of Statistics National University of KaohsiungDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Multiple Linear Regression: Ray-Bing Chen Institute of Statistics National University of KaohsiungTrina Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- T014108e PDFDocument5 pagesT014108e PDFSilvester KolicNo ratings yet