Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth Science
Uploaded by
gwenstefanabag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesEarth Science - Science 10 notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEarth Science - Science 10 notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesEarth Science
Uploaded by
gwenstefanabagEarth Science - Science 10 notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Earth Science
Geology is the Science that examines Our planet is composed of different
the Earth’s form, composition, and the spheres/layers. Atmosphere,
changes it undergoes. Hydrosphere, Geosphere/Lithosphere.
EARTH Atmosphere: gaseous layer
Age: 4.55B years old Troposphere: oxygen, high alt low temp,
weather disturbances
Earth and meteorites were possibly Stratosphere: thinner air, high alt high
formed from the same materials — temp (bc of the ozone layer), airplanes
nebula, a huge swirling cloud of gasses Ionosphere: produce ions, where radio
that was disturbed and collapsed. waves bounce back.
Exosphere: outer portion of the
NEBULA THEORY atmosphere, gas molecules are far
– The Earth was formed at the same apart due to the lack of gravity
time as other members of the solar Hydrosphere: 70.8% of the Earth. Water
system. The nebula collapsed due to its found in oceans, seas, glaciers, vapor in
gravity, it spun faster and flattened into air.
a disk. Cryosphere: water in solid form like ice,
snow, glaciers. Indicator of climate
change.
Earth has gone through major Ave. Depth: 3.7km
biological and geological changes like Challenger Deep, Mariana Trench:
volcanic eruptions, collision of plate 10.994km. Named after Challenger the II
boundaries, etc. (British survey ship)
It also suffered from bombardment from Geosphere: interior structure, rocks,
cosmic bodies. One very large collision minerals, land forms, etc.
is believed to be the cause of the Crust: light rocks
Earth’s tilting and the formation of the Mantle: thicker, denser
moon. Outer: molten iron and nickel
Inner: solid iron and nickel
Its circumference is 43,200km and it is
an oblate spheroid (a slightly PLATE TECTONICS:
flattened/squashed sphere)
Raisin Theory: like a grape that
Rotation: spinning motion of an object contracted into a raisin due to cold
around its own axis, causes day and temperature.
night. 24hrs (also called solar day)
Tectonic plates or Lithospheric plates
Revolution: orbital motion of an object are small slabs that are on top of a
around another object, causes changes mobile material called asthenosphere.
in season. 365.25 days (solar year/star
year) specific: 365d 6hrs 9m 10s
These plates fit together and the Continental Plate: The solid ground
movement ranged from less than 1 to where we stand. Thicker but has lighter
more than 15cm per year resulting in materials like granite rocks. Formed by
the opening and closure of bodies of volcanic eruptions (magma)
water and different landforms.
Abraham Ortelius suggested that Basement Rock : oldest foundation/rock
America was originally connected to Platform Rock: younger and made of
Europe and Africa. sedimentary rocks.
Alfred Wegener: Continental Drift Cratons: platforms are connected with
Theory. Supercontinent named basement rocks
Rodinia/Pangaea.
Pangaea: Continental Margins: edges of cratons
Laurasia (Northern)
Gondwanaland(Southern) Oceanic Crust: made up of heavier
Panthalassa basalt and gabbro rocks. Younger than
continental rocks. Also formed by
It is believed that soon, these plates will magma. Has a limited lifespan. Oceanic
move towards each other, reforming Crust + Continental Crust = OC will sink
Pangaea.
RECALL:
Earth is generally composed of 58
crustal plates. 15 are major tectonic Raisin Theory (Big Bang)
plates, 7 or 8 are primary plates and the The contraction caused some parts to
others are smaller plates. move upwards (mountains) and the
other parts to buckle downwards (ocean
Primary Plates: basins)
● African Plate
● Eurasian Plate Tectonic Plates are rigid sections of the
● Indo-Australian Plate lithosphere that move as a unit.
● Pacific Plate
● South American Plate with the Movement can result in the opening of
Nazca Plate as a secondary plate oceans and formation of continents
Secondary Plates: and other mountain ranges.
● Arabian Plates
● Caribbean Plate North America smashed into
● Cocos Plate Northwestern Africa = mountain range
● Indian Plate (Applachians)
● Juan de fuca Plate
● Philippines Sea Plate Drifting = Valley = Atlantic Ocean
● Scotia Plate
India moves Northward and collided
● Nazca Plate
with SE Asia - created Himalayas
Collide - form mountain ranges Shield - broad, gently sloping landform,
Drift apart - bodies of water basaltic lava
Cinder - steep conical hill
VOLCANOES: Composite - larger than cinder, can
grow bigger due to its resistance of
A volcano is a mountain that opens erosion
downward to a reservoir of molten rock
called magma. PARTS OF A VOLCANO
Cone - most striking part of the volcano
A vent hill or mountain from which Vent - opening through which molten
molten or hot rock of gaseous materials rock escapes
are ejected. Magma Chamber - large underground
pool of liquid rock found beneath the
They differ from most mountains crust
because they have vents. Crater - basin like depression over a
vent at the summit of a cone
Magma : a kneaded mixture which Caldera - volcanic depression larger
moves out of an erupting volcano. It is a than the crater
combination of liquid, solid, and gas. Lava - magma expelled from volcanic
eruption that cools and hardens
Fumes are a sign that a volcano Magma - the molten rocks inside the
is/might erupt. These fumes have toxic volcano
gasses. Conduit - channel or pipe conveying the
magma
The pyroclastic materials are Summit - highest point of volcano
dangerous because the rock fragments
are sharp. There are more than 1.5k volcanoes on
Earth that have the potential of being
CLASSIFICATION OF VOLCANOES active
A. Duration or Frequency of Activities Volcanoes can be found in all
continents, their characteristics
Active - currently erupting or showing depends on its location
signs of unrest activities. Gas emissions
or frequent seismic waves. Ex. Taal THREE STAGES OF A VOLCANO’S LIFE
Volcano and Mayon Volcano
Invasion of magma - because of the
Dormant - has not erupted in 2k years extreme temperature, magma rises thru
and traces of volcanic heat weak spots
disappeared but might erupt in the
future. Ex. Mt. Makiling Building pressure - due to the release of
gasses and water dissolved in molten
Extinct - period of dormancy exceeded rocks
10k yrs and lava supply was cut off
B. Shape of Volcano
Eruption - when the magma can no The Philippines is prone to volcanic
longer be contained below the Earth’s eruptions because it is located on the
surface pacific ring of fire. A volcano eruption
can also trigger another volcano
About 95% of the world’s volcanoes are eruption.
located near the boundaries of tectonic
plates while the remaining 5% are
associated with the mantle plumes and
hotspots
Mantle plumes and hotspots were
discovered in the 1960’s by John Tuzo
Wilson. He found 3 linear chains of
volcanoes and submarine volcanoes
His theory states that volcanic chains
are results from the slow movement of a
tectonic plate across a fixed hotspot
Mantle Plumes are areas or columns
where magma in the mantle rises
towards Earth’s surface. Located
underneath continental/oceanic crust
or along plate boundaries
Hotspots are locations on the Earth’s
surface that have experienced active
volcanic activities.
There are about 40-50 identified
hotspots in the world.
ACTIVE SITES OF VOLCANOES
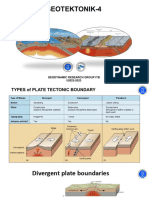
- along divergent plate boundaries
(spreading)
- along convergent plate boundaries
- in areas of continental extension
(underlying mantle is rising)
- hotspots
VOLCANISM refers to the process and
phenomena associated with the
surficial discharge of molten rock and
other materials into the surface of the
Earth
You might also like
- Geology For Kids - Pictionary | Geology Encyclopedia Of Terms | Children's Rock & Mineral BooksFrom EverandGeology For Kids - Pictionary | Geology Encyclopedia Of Terms | Children's Rock & Mineral BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument7 pagesReviewer in ScienceAndrea OsiasNo ratings yet
- Strat I Graphy InterpretationDocument6 pagesStrat I Graphy Interpretationjyoti tanwarNo ratings yet
- Observing The Earth Es 1000 Exam 2 Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesObserving The Earth Es 1000 Exam 2 Review QuestionsortijuanNo ratings yet
- Science Week 5-6Document6 pagesScience Week 5-67xnc4st2g8No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPlate TectonicsZara AhmedNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes IGCSE RevisionDocument10 pagesEarthquakes IGCSE RevisionZcNo ratings yet
- Ess106 NotesDocument34 pagesEss106 Notesapi-340040888No ratings yet
- CH5 VolcanismDocument8 pagesCH5 VolcanismNovie GraceNo ratings yet
- Notes Leaving Certificate Physical GeographyDocument39 pagesNotes Leaving Certificate Physical GeographySurbhi Singhal 0313No ratings yet
- Crust and Plate BoundariesDocument46 pagesCrust and Plate BoundariesQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes: Dr. Gaurav GargDocument14 pagesVolcanoes: Dr. Gaurav GargXabi MonteroNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument84 pagesVolcanoJM LomoljoNo ratings yet
- Volcanic LandformsDocument65 pagesVolcanic LandformsAniket KannoujiyaNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and EarthquakesDocument104 pagesVolcanoes and EarthquakesAlleli AspiliNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument8 pagesVolcanoaditya2053No ratings yet
- VolvanoDocument6 pagesVolvanoZarinaNo ratings yet
- Volcano - WikipediaDocument99 pagesVolcano - WikipediaMattyNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument17 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesChristle NgoveNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes Everything You Need To KnowDocument5 pagesVolcanoes Everything You Need To KnowDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- Geo Report 11Document8 pagesGeo Report 11Rafiqul Islam NoyonNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Volcanic ActivityDocument45 pagesVolcanoes and Volcanic ActivityatikaNo ratings yet
- Magma and Volcanism Reviewer GROUP 4Document7 pagesMagma and Volcanism Reviewer GROUP 4muhamsumandresNo ratings yet
- Science Q3 Week 1 2printDocument8 pagesScience Q3 Week 1 2printChelsea BialaNo ratings yet
- Science First Grading ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience First Grading ReviewerAngela FerrerNo ratings yet
- Elec 1 The Physical W0RLDDocument6 pagesElec 1 The Physical W0RLDAwhaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 First Monthly ReviewerDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 First Monthly ReviewerRaizza Mae NovelaNo ratings yet
- CE 203-Class Note 2 (Part 2) - SKSDocument32 pagesCE 203-Class Note 2 (Part 2) - SKSKNOWLEDGE HUBNo ratings yet
- Science 1st QuartDocument6 pagesScience 1st QuartArisa h.No ratings yet
- Lawrence Q1 ScienceDocument12 pagesLawrence Q1 ScienceJoshua ReytaNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument8 pagesVolcanoesShah KhanNo ratings yet
- Geotectonic-4Document58 pagesGeotectonic-4Arieq ClasherNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci ReviewerDocument7 pagesEarth Sci ReviewerELSYIANE RICCI D. LAONo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Physical Geography - Study GuideDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Physical Geography - Study Guidebooks_kittiesNo ratings yet
- Earth's Interior, Continental Drift & Plate TectonicsDocument32 pagesEarth's Interior, Continental Drift & Plate Tectonicssyrine mendozaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Plate BoundariesIsla VermilionNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument37 pagesLayers of The Earth Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics TheoryJunai AlontoNo ratings yet
- Qiii-Melc 1Document46 pagesQiii-Melc 1MARY JOY PIOSCANo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument12 pagesEarth ScienceJames DJmanahan AnuranNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer: Lesson 1Document2 pagesScience Reviewer: Lesson 1AMIEL MOIRA BERNARDONo ratings yet
- Sci ReviewerDocument7 pagesSci ReviewerBxbble BerriNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes - Module 1 FinalDocument69 pagesVolcanoes - Module 1 FinalAngel rose OrbeNo ratings yet
- Revision Lesson Plate TectonicsDocument19 pagesRevision Lesson Plate Tectonicsapi-336814146No ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- Revision-Notes Earthquakes - VolcanoesDocument10 pagesRevision-Notes Earthquakes - VolcanoesTomato PotatoNo ratings yet
- Formation and Classification of Volcanoes Based On BehaviorDocument32 pagesFormation and Classification of Volcanoes Based On BehaviorUserJoshNo ratings yet
- Class11 - Fundamentals of GeographyDocument25 pagesClass11 - Fundamentals of GeographyAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Een 2.1 Review PDFDocument10 pagesEen 2.1 Review PDFquandric glennNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument49 pagesVolcanoesJuan Sebastian Bohorquez RozoNo ratings yet
- Earth's Interior, Continental Drift & Plate TectonicsDocument32 pagesEarth's Interior, Continental Drift & Plate TectonicsOmar NajmNo ratings yet
- VolcanismDocument97 pagesVolcanismKristina ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Features of A VolcanoDocument46 pagesFeatures of A Volcanoジェーン サラNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About The Geological Feature. For Other Uses, See - "Volcanic" Redirects Here. For Other Uses of "Volcanic", SeeDocument13 pagesThis Article Is About The Geological Feature. For Other Uses, See - "Volcanic" Redirects Here. For Other Uses of "Volcanic", SeeEdiBerisha1No ratings yet
- Geological Processes Handouts Earth SciDocument8 pagesGeological Processes Handouts Earth SciTheo Jhullian CabasalNo ratings yet
- Sust2701 GalapexDocument24 pagesSust2701 Galapexapi-283747608No ratings yet
- Morphology of VolcanoesDocument15 pagesMorphology of VolcanoesMichaella ReliNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study Guide GEOL 1014 24534Document6 pagesExam 1 Study Guide GEOL 1014 24534Jason WolfeNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScienceRaquel JeriahNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document7 pagesScience 10Anonymous t2Y8WBZGNo ratings yet
- ES - Unit 2 Course Notes DRAFTDocument14 pagesES - Unit 2 Course Notes DRAFTEmmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ijeegsfeb20171Document14 pages1 Ijeegsfeb20171TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 01landers SnowCreek 87Document63 pages01landers SnowCreek 87Tony Hartono BagioNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil - Module 2Document40 pagesBasic Civil - Module 2SEKHAR JNo ratings yet
- 8 Probabilistic Ground Motions in Earthquake Resistant Design of BuildingsDocument34 pages8 Probabilistic Ground Motions in Earthquake Resistant Design of BuildingsF Azam Khan AyonNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Second Quarter-Reg 8Document6 pagesSummative Test Second Quarter-Reg 8Erick ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Forecast of Pressure and Working Conditions in Rock Tunnels ROCK TUNNELING WITH STEEL SUPPORT CHAPTER 5Document13 pagesForecast of Pressure and Working Conditions in Rock Tunnels ROCK TUNNELING WITH STEEL SUPPORT CHAPTER 5Johana JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q4 Week1 Module1 LocatingPlacesoftheEarth V1Document23 pagesScience7 Q4 Week1 Module1 LocatingPlacesoftheEarth V1Leslie S. AndresNo ratings yet
- CE 407 Earthquake Engineering 2019Document20 pagesCE 407 Earthquake Engineering 2019Andrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Utah Earthquake Safety GuideDocument36 pagesUtah Earthquake Safety GuideMistifireNo ratings yet
- Target Diamond Dr.S.Ravi PDFDocument154 pagesTarget Diamond Dr.S.Ravi PDFshivam tiwariNo ratings yet
- To Rubble Slabs Sprung Up Heaved Gutted Pall Razed: News Item 8: EARTHQUAKE IDocument2 pagesTo Rubble Slabs Sprung Up Heaved Gutted Pall Razed: News Item 8: EARTHQUAKE Iroxana_boraNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 3Document3 pagesSummative Test 3Noronisa Sanday MalaNo ratings yet
- Growth of Continental Crust: A Balance Between Preservation and RecyclingDocument16 pagesGrowth of Continental Crust: A Balance Between Preservation and RecyclingMilton ObandoNo ratings yet
- Map Showing The Fireline of Brgy. Small Banisilon, Kolambugan, Lanao Del NorteDocument1 pageMap Showing The Fireline of Brgy. Small Banisilon, Kolambugan, Lanao Del NorteAlga Zalli Datu-daculaNo ratings yet
- Celestial Navigation 2Document44 pagesCelestial Navigation 2Derick KatunziNo ratings yet
- Origing and Evolution of The Ocean FloorDocument22 pagesOriging and Evolution of The Ocean FloorDiego Julián Montes AlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Indian PlateDocument4 pagesIndian Platenosferatu jodNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesDocument35 pagesPlate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesHara Shelle AcompaniadoNo ratings yet
- Fossil EvidenceDocument18 pagesFossil EvidenceMomi BearFruitsNo ratings yet
- 2020-01-08-FEMA P-2078 NEHRP USGS Procedures For Developing Multi Period Response-SpectraDocument558 pages2020-01-08-FEMA P-2078 NEHRP USGS Procedures For Developing Multi Period Response-SpectraALFONSO NIEVESNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - PPT - Sarulla Geothermal EnergyDocument32 pagesGroup 7 - PPT - Sarulla Geothermal EnergyAthallah NaufalNo ratings yet
- ADM - Grade 11 - Quarter 1 (S1112ES-Id-20)Document29 pagesADM - Grade 11 - Quarter 1 (S1112ES-Id-20)josephine alcantara100% (1)
- Science 10 Module 2.2-1Document88 pagesScience 10 Module 2.2-1marisNo ratings yet
- 2023 - std10 - Landscape Analysis Through MapsDocument4 pages2023 - std10 - Landscape Analysis Through MapsHarry KELANTHODIKA MOHAMMED 10 D-9142No ratings yet
- Fill in The Blanks With The Suitable Word:: Plate TectonicsDocument3 pagesFill in The Blanks With The Suitable Word:: Plate TectonicsAriel NgNo ratings yet
- Geology & Earth's TreasureDocument34 pagesGeology & Earth's TreasureHelaina MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Bhuj Earthquake India 2001Document5 pagesBhuj Earthquake India 2001dgrsri100% (1)
- Seismic Method in The ExplorationDocument3 pagesSeismic Method in The ExplorationRahmat Fadhilah100% (2)
- TINGKATAKTIVITASSEISMIKDANKERAPUHANBATUANBuletin Balai Wilayah IIBMKGDocument14 pagesTINGKATAKTIVITASSEISMIKDANKERAPUHANBATUANBuletin Balai Wilayah IIBMKGVina Rosmauli PardedeNo ratings yet
- Glaser2000 PDFDocument16 pagesGlaser2000 PDFGOYO BERNARDINO CISNEROS GARCIANo ratings yet