Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RWS
Uploaded by
Sofia Monique Afable0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesRWS
Uploaded by
Sofia Monique AfableCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
RWS Reviewer making.
Identify reliable information
LESSON 1 and make reliable judgements.
CRITICAL THINKING Non-Critical Thinking
What do you think is the relationship of the - focused on merely accepting and
two? understanding information from a
Reading source without examining them
- provides you an extensive range of happens when you construct thoughts
written texts essential for discourse based purely on emotions jumping to
constructs necessary in the conclusions without proof or evidence.
development of language acquisition. based on intuition, emotion and/or
Reading exposes you exposes you to opinion.
other styles, other voices, other forms, Critical Thinking
and other genres of writing - based on verifiable data and facts.
- A writer who does not read is like a involves a series of complex thought
filmmaker who does not watch films. processes which allow you to make
Writing reasoned judgements. assess the way
- equips you with skills in the writing you think, and solve problems
process, text structures, paragraph or effectively.
sentence construction. Those skills are TAXONOMY OF COGNITIVE DOMAIN:
tools to improve your reading FIRST 3 LEVELS OF THINKING
comprehension. Rembering
Critical - involves retrieval, recalling of
- from the Greek word kritikos meaning information, memorization, or the
able to discern, If being critical means statement of information.
being able to discern, critical thinking Understanding
is therefore, a deeper kind of thinking - refers to construction meaning from
in which we do not take things for verbal and non verbal messages, always
granted but question, analyse and require discussion, description,
evaluate what we read, hear, say, or paraphrasing or explanation.
write. Applying
WHAT IS CRITICAL THINKING? - refers to implementation of knowledge
Critical thinking in various situations. answers require
- as defined by National Council for demonstration, solution or the use of
Excellence in Critical Thinking, "is the information.
intellectually disciplined process of HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
actively and skillfully conceptualizing, Analyzing
applying, analyzing, synthesizing, - breaking down ideas into parts and
and/or evaluating information gathered relating these parts to one another.
from, or generated by, observation, answers require comparison,
experience, reflection, reasoning, or - integration or the structuring of
communication, as a guide to belief and information.
action." leads to effective decision
Evaluating While Reading
- making judgements on the value and - getting the meaning of words through
validity of ideas and events. answers context clues, predicting, inferencing,
require judgement and testing of an monitoring comprehension, annotating
idea based on certain rules or standards. the text, and reflecting.
Creating Post Reading
- combining parts to form a well - reflecting, summarizing, paraphrasing,
designed whole. require production, drawing conclusions, making graphic
designing, or construction of new organizers, and journal writing
information or ideas. Rapid reading
- aims to locate specific information or
LESSON 2: main ideas in a very short span of time.
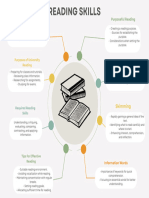
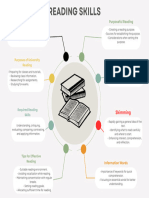
FUNDAMENTAL READING SKILLS Pre-reading skills such as skimming and
PURPOSES OF TEXT scanning are examples of rapid reading
- Inform * Skimming
- Persuade - is a type of quick reading which aims to
- Entertain get the main idea and C overview of the
COHERENCE material
- means a text must be composed of * Locating
sentences with connected ideas - the main idea is a reading skill which
GENRE involves identifying the central message
* business letter of a reading selection when it is not
* news found in either or both the first and last
* film critique sentences.
* product * Scanning
* brochure - is a reading skill in which the reader is
TEXT TYPE focused on getting a specific
* expository / procedure information from the text.
* recount Previewing
* review - is a skill in which a reader looks over a
* descriptive / comparison contrast material and focuses on the
information.
Pre Reading Previewing
- previewing, free writing, surveying, - is a skill in which a reader looks over a
questioning, making assumptions material and focuses on the
about the author, identifying the information found to be relevant. This
purpose, and selecting a reading system allows readers to set the purpose and
such as SQ3R (survey, question, read, link the content of the material to their
recite, review) background knowledge, It is also a skill
used during the pre-reading stage
Literal reading Pleasure Reading
- involves the understanding of ideas ● aims to provide enjoyment and
and facts that are directly stated in the entertainment.
material. This skill includes Functional Reading
note-taking, paraphrasing, and ● to help readers learn basic functional
summarizing. These are typically done reading, such as reading school for
in the post reading stage. forms and instructions.
* Summarizing Remedial Reading
- is a technique that involves condensing ● to help readers learn basic functional
a lengthy text into a shorter passage reading, such as reading school for
which is usually 15 to 30 percent of the forms and instructions aims to correct
source material while retaining its the effects of poor teaching and poor
essence. learning.
* Paraphrasing
- involves restating ideas from the LESSON 3
original text. Unlike the summary, the SELECTING AND ORGANIZING
length of a paraphrased text is almost INFORMATION
similar to the length of the original text Brainstorming
Inferential reading - It helps people establish patterns of
- refers to the process of deducing facts ideas, develop new ways of thinking,
and ideas not directly expressed in the activate background knowledge, and
text. Also known as "reading between overcome mental block.
the lines," this skill includes making
generalizations, inferences, and METHODS OF BRAINSTORMING
conclusions. * IDEA LIST
* IDEA MAP
This is applied during the while-reading
stage GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS
Critical reading - They are visual representation of
- refers to the close and thorough concepts that help you structure
evaluation of the claims in the text in information into organizational
terms of relevance, validity, and logic. patterns.
This skill which also happens in the - Active learning is promoted
while-reading stage, includes - Becomes easier to focus your attention
distinguishing facts from opinions and on key elements
detecting logical fallacies - information are presented into a
Purpose of Reading coherent framework
● aims to develop the readers reading - can easily integrate new knowledge into
skills. your current knowledge
TYPES OF GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS
Venn Diagram
• used to show comparison and contrast
Network Tree
• used to represent hierarchy, classification and
branching
Spider Map
• used to investigate and enumerate various
aspects of central idea, which could be a
concept, topic or theme
Problem - Solution Map
• used to display the nature of the problem and
how it can be solved
Timeline
• used to show the chronological order of events
through a long bar with dates and specific
events
Plot Diagram
• used to map events in a story, making it easier
to analyze the major parts of the plot
Series of Events Chain
• used to show the logical consequences of
events
Fishbone Map
• used to present the casual relationship of a
complex phenomenon
Cycle
• used to describe how a series of events interact
to produce a set of results repeatedly
Persuasion Map
• used to map out arguments and evidence that
prove a view point
Outline
• set as series of input, shows the logical
arrangement of ideas that you have read or ideas
that you intend to include in vour essay
REMEMBER:
FORMAT - alphanumeric, decimal
PRINCIPLES - coordination, subordination,
division, parallelism
KINDS / STRUCTURE - topic, sentence
You might also like
- A Beginner's Guide To Carl Jung's : Individuation ProcessDocument10 pagesA Beginner's Guide To Carl Jung's : Individuation Processmasterjugasan6974100% (1)
- EAProfDocument2 pagesEAProfLyrielle DagsaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Session 1-10 - DRDocument32 pagesNotes On Session 1-10 - DRDeblina SaharoyNo ratings yet
- Ross Tayler & Fraser Parker - KINGS NEVER DIEDocument149 pagesRoss Tayler & Fraser Parker - KINGS NEVER DIESpockCritical CriticalNo ratings yet
- Effortless Meditation Step by StepDocument29 pagesEffortless Meditation Step by Stepjslaughter100% (1)
- SCD Wiki ProjectDocument6 pagesSCD Wiki Projectrohehin224No ratings yet
- Time Management - Anthony RobbinsDocument55 pagesTime Management - Anthony RobbinsWind100% (24)
- Academic Reading Writing SecondSem Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesAcademic Reading Writing SecondSem Midterm ReviewerMa Irish SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument6 pagesReading and WritingjhanisekateNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing ReviewerDocument2 pagesReading and Writing ReviewerChrisna LagoNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument5 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional PurposesMary MoralesNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument7 pagesEnglishJona BugarinNo ratings yet
- EFFECTIVE READING STRATEGIES FOR ACADEMIC SUCCESSDocument12 pagesEFFECTIVE READING STRATEGIES FOR ACADEMIC SUCCESSBeefWith PorkNo ratings yet
- RWS ReviewerDocument2 pagesRWS ReviewerAiko NanaseNo ratings yet
- q3 Engacprof ReviewerDocument3 pagesq3 Engacprof ReviewerAllysa Kim DumpNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing 3rd QuarterDocument3 pagesReading and Writing 3rd QuarterSerenity MoonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Raws: Lesson 1Document4 pagesReviewer in Raws: Lesson 1jeffdelacruzNo ratings yet
- RwwsssDocument2 pagesRwwsssSeanmyca IbitNo ratings yet
- Rewri NotesDocument1 pageRewri NotesCZARINA JOVIENNE PUMANESNo ratings yet
- ENG02Q3_-_CO1-1Document8 pagesENG02Q3_-_CO1-1KC Angelica LoricaNo ratings yet
- RAW ReviewerDocument2 pagesRAW Reviewerlovelyjoyvarela0518No ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument7 pagesReading and WritinglexieNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading TechniquesDocument7 pagesAcademic Reading TechniquesAnne Marie SanchezNo ratings yet
- RAW ReviewerDocument3 pagesRAW ReviewerJoshua DayritNo ratings yet
- 5 Macro SkillsDocument3 pages5 Macro SkillsaigurlroarNo ratings yet
- Reading Skills Cheat SheetDocument1 pageReading Skills Cheat SheetRuSimbolonNo ratings yet
- Reading Writing Week 5 6 Concept NotesDocument18 pagesReading Writing Week 5 6 Concept NotesHaizel Faith Carmelo PatuboNo ratings yet
- READING AND WRITING - FUNDAMENTAL READING SKILLSDocument1 pageREADING AND WRITING - FUNDAMENTAL READING SKILLSMuneYakitoriNo ratings yet
- Colorful Calm Corporate Clean Mind Map (2)Document1 pageColorful Calm Corporate Clean Mind Map (2)Azul Vazquez MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- MAPSDocument4 pagesMAPSEdgar Empeño Jr.No ratings yet
- MODULE 4. Developmental Reading Topic 4. Reading For Specific PurposeDocument7 pagesMODULE 4. Developmental Reading Topic 4. Reading For Specific PurposeBeverly Panganiban CadacioNo ratings yet
- CRWT111 ReviewerDocument12 pagesCRWT111 ReviewerPatricia ParicoNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing and Its ProcessDocument4 pagesAcademic Writing and Its ProcessMariaceZette RapaconNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Midterm Reviewer Grade 11 - ABMDocument7 pagesReading and Writing Midterm Reviewer Grade 11 - ABMErica Lalaine Salazar100% (1)
- Critical ThinkingDocument4 pagesCritical ThinkingjennywrenwattsNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledMa. Leiah Ericka De ChavezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Reading A Critical Evaluation PaperDocument6 pagesLesson 6: Reading A Critical Evaluation PaperSophia ManubayNo ratings yet
- Eng 102 First MonthDocument2 pagesEng 102 First MonthHarhel Dawn PecundoNo ratings yet
- EAPP MediaDocument2 pagesEAPP MediaJaemsNo ratings yet
- Reading & WritingDocument9 pagesReading & WritingJahzara Daveigh BolivarNo ratings yet
- Rapid Reading: Linear ComparativeDocument2 pagesRapid Reading: Linear ComparativeEunice C. LoyolaNo ratings yet
- EAPP ReviewerDocument7 pagesEAPP Reviewerbepaca6152No ratings yet
- Critical Reading and Thinking SkillsDocument7 pagesCritical Reading and Thinking Skillsoliver justin lontocNo ratings yet
- ENG-2ND-SEM2Document5 pagesENG-2ND-SEM2kateangela2006No ratings yet
- 1st Week - Day 1 (Reading and Writing)Document40 pages1st Week - Day 1 (Reading and Writing)Catherine QuilizaNo ratings yet
- Colorful Calm Corporate Clean Mind Map (1)Document1 pageColorful Calm Corporate Clean Mind Map (1)Azul Vazquez MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Raw 4THQ ReviewerDocument7 pagesRaw 4THQ ReviewerFatima Shamira ArapNo ratings yet
- EAPPReviewerDocument3 pagesEAPPReviewerNikolai NoveroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document91 pagesLesson 1EVA MAE BONGHANOYNo ratings yet
- Enhanced FinalsDocument5 pagesEnhanced FinalsLee Ann FermilNo ratings yet
- Esen Reading ReviewerDocument2 pagesEsen Reading ReviewerJoshua ManzanoNo ratings yet
- EAPPDocument3 pagesEAPPAdrian KentNo ratings yet
- Unit II ReadingDocument24 pagesUnit II Readingkhanlala50263No ratings yet
- Developmental Reading Final LectureDocument141 pagesDevelopmental Reading Final LectureDavid-Aragorn Peredo TelmoNo ratings yet
- ENGACPROF patrickDocument4 pagesENGACPROF patrickkateangela2006No ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes ReadingDocument3 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes ReadingairajoisNo ratings yet
- GGGDocument13 pagesGGGomaoma883No ratings yet
- Reading and Writing: Critical Reading As ReasoningDocument3 pagesReading and Writing: Critical Reading As ReasoningRainee Anne DeveraNo ratings yet
- Reflections On Readings October 11 2022Document5 pagesReflections On Readings October 11 2022Lê Ngọc ÂnNo ratings yet
- RW Topic 6 - Critical Reading and ThinkingDocument21 pagesRW Topic 6 - Critical Reading and ThinkingLyka Bactong DICES MNKNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Topic 1 ReadingDocument4 pagesPart 3 - Topic 1 ReadingApenton MimiNo ratings yet
- 3rd QT NotesDocument31 pages3rd QT NotesClaire Faith TanquinoNo ratings yet
- READING AND WRITING STRATEGIES FOR COMPREHENSIONDocument6 pagesREADING AND WRITING STRATEGIES FOR COMPREHENSIONJaykuNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading: Length of Reading MaterialDocument3 pagesAcademic Reading: Length of Reading MaterialNicole EsmeraldaNo ratings yet
- S2-Q1-W7-READING AND WRITING- PPTDocument20 pagesS2-Q1-W7-READING AND WRITING- PPTAivy Bartolata officialNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument2 pagesBusiness ProposalSofia Monique AfableNo ratings yet
- Three Little Pigs StoryDocument3 pagesThree Little Pigs StorySofia Monique AfableNo ratings yet
- April May Billing Statement PDFDocument1 pageApril May Billing Statement PDFSofia Monique AfableNo ratings yet
- Contract of LeaseDocument1 pageContract of LeaseSofia Monique AfableNo ratings yet
- BJORN'S INTERIOR DESIGN PROGRESS BILLINGDocument4 pagesBJORN'S INTERIOR DESIGN PROGRESS BILLINGSofia Monique AfableNo ratings yet
- Rapid ManifestationDocument20 pagesRapid ManifestationSalai LokeshNo ratings yet
- Qusthan Abqary-Rethinking Tan Malaka's MadilogDocument12 pagesQusthan Abqary-Rethinking Tan Malaka's MadilogAhmad KamilNo ratings yet
- Healing PranaDocument19 pagesHealing Pranatambulero100% (3)
- Demoteaching DLP English q4Document6 pagesDemoteaching DLP English q4Susie CruzNo ratings yet
- Bergson and The Metaphysics of Media PDFDocument197 pagesBergson and The Metaphysics of Media PDFDrMlad100% (1)
- Cost Accounting Horngren 15th Edition Test BankDocument38 pagesCost Accounting Horngren 15th Edition Test Bankmitchellunderwooda4p4d100% (16)
- Language Art JSSDocument165 pagesLanguage Art JSSmohamedsantoskamara62100% (1)
- Opmt 620Document9 pagesOpmt 620MaraquechNo ratings yet
- Strategy Schools and Strategic Thinking FrameworksDocument3 pagesStrategy Schools and Strategic Thinking FrameworksYahya ChiguerNo ratings yet
- Embodiment and the unseen in everyday lifeDocument22 pagesEmbodiment and the unseen in everyday lifeTrf BergmanNo ratings yet
- Trasparency of Things Contemplating The Nature of Experience Rupert Spira PDFDocument271 pagesTrasparency of Things Contemplating The Nature of Experience Rupert Spira PDFRitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Importance of Planning in Management Developing Organization by L. Jeseviciute-UfartieneDocument6 pagesImportance of Planning in Management Developing Organization by L. Jeseviciute-UfartieneGrace MañaleNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Ecosystem: Towards A Transcendental EcologyDocument20 pagesPhilosophy and Ecosystem: Towards A Transcendental EcologyAnthonyPaulSmithNo ratings yet
- Upaam 1135891 202105060749199700Document18 pagesUpaam 1135891 202105060749199700Kartik KapoorNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of MusicDocument57 pagesPhilosophy of MusicSilvestreBoulez100% (1)
- Overview of Social Cognitive Theory and of Self EfficacyDocument5 pagesOverview of Social Cognitive Theory and of Self Efficacydata kuNo ratings yet
- scp6 Pulling It All TogetherDocument7 pagesscp6 Pulling It All Togetherapi-601585033No ratings yet
- Aghora Iii - The Law of KarmaDocument385 pagesAghora Iii - The Law of KarmaVinay Sagar LNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement About Benefits of InternetDocument6 pagesThesis Statement About Benefits of InternetAllison Thompson100% (2)
- 2023-24 Thinking Sociologically Module Handbook. Draft Version 260923Document7 pages2023-24 Thinking Sociologically Module Handbook. Draft Version 260923simranv491No ratings yet
- Technology As A Way of RevealingDocument4 pagesTechnology As A Way of RevealingGeemaica MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Project Renaissance, Welcome To Image-Streaming (Page 1 of 2)Document16 pagesProject Renaissance, Welcome To Image-Streaming (Page 1 of 2)iluminat8841No ratings yet
- Barry Long, Eckhart Tolle - Knowing Yourself - The True in The False-Barry Long Books (1996)Document108 pagesBarry Long, Eckhart Tolle - Knowing Yourself - The True in The False-Barry Long Books (1996)fozwalNo ratings yet
- Incessance (Incesancia)Document400 pagesIncessance (Incesancia)Ivana DislaNo ratings yet