Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kinetic Theory of Gases and Thermodynamics: DPP 01 (Of Lec-03) - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)
Uploaded by
rahulrudraa2030Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kinetic Theory of Gases and Thermodynamics: DPP 01 (Of Lec-03) - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)
Uploaded by
rahulrudraa2030Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Yakeen NEET 2.0 (Legend)
Kinetic Theory of Gases & Thermodynamics DPP-01
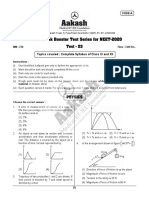
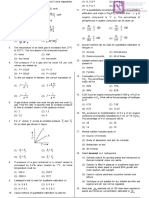
1. In a cyclic process shown on the P–V diagram, the 4. Two monoatomic ideal gas at temperature T1and T2
magnitude of the work done is : are mixed. There is no loss of energy. If the mass
of molecules of the two gases are m1 and m2 and
number of their molecules are n1 and n2 respectively,
then temperature of the mixture will be:
T T T T
(1) 1 2 (2) 1 2
n1 n2 n1 n2
n2T1 n1T2 n1T1 n2T2
(3) (4)
n1 n2 n1 n2
P P
2
(1) 2 1
2 5. For a gas Cv = 4.96 cal/mole K, the increase in
V V
2 internal energy of 2 mole gas in heating from 340
(2) 2 1 K to 342 K will be :-
2
(1) 27.80 cal (2) 19.84 cal
(3) (P2 – P1)(V2 – V1) (3) 13.90 cal (4) 9.92 cal
4
(4) (P2V2 – P1V2)
6. One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is heated at
a constant pressure of one atmosphere from 0°C to
2. The work by an ideal monoatomic gas along the
100°C. Then the change in the internal energy is
cyclic path LMNOL is
(1) 20.80 × 102 J (2) 12.48 × 102 J
2
(3) 832 × 10 J (4) 6.25 × 102 J
7. The ratio of average translational kinetic energy to
rotational kinetic energy of a diatomic molecule at
temperature T is
(1) 3 (2) 7/5
(3) 5/3 (4) 3/2
(1) PV (2) 2 PV
(3) 3 PV (4) 4 PV
8. A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of oxygen and
4 moles of argon at temperature T. Neglecting all
3. The work done by a gas taken through the closed
process ABCA is vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the
system is
(1) 4 RT (2) 15 RT
(3) 9 RT (4) 11 RT
9. Relation between the ratio of specific heats () of
gas and degree of freedom ‘f’ will be
1 1 1
(1) = f + 2 (2)
f 2
(1) 6P0V0 (2) 4P0V0
(3) P0V0 (4) zero (3) f = 2/( – 1) (4) f = 2( – 1)
2
Note: Kindly find the Video Solution of DPPs Questions in the DPPs Section.
Answer Key
1. (3) 6. (2)
2. (1) 7. (4)
3. (1) 8. (4)
4. (4) 9. (3)
5. (2)
PW Web/App - https://smart.link/7wwosivoicgd4
Library- https://smart.link/sdfez8ejd80if
You might also like
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- FT(RM)Phase-3_Test -5(A3)_(08-12-2021)Document19 pagesFT(RM)Phase-3_Test -5(A3)_(08-12-2021)Anand RockyNo ratings yet
- ktg thermodynamics_QuestionsDocument8 pagesktg thermodynamics_QuestionsbalramsharmaNo ratings yet
- WT-08 - Target Batches - Code-B - (18-12-2022)Document17 pagesWT-08 - Target Batches - Code-B - (18-12-2022)Virat ValiNo ratings yet
- Lakshya JEE (2024) : Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesLakshya JEE (2024) : Chemical KineticsDev KotechaNo ratings yet
- NEET (Pre-Medical) - Conquer Batch-1, 2 & PKL - Minor Test-08 - (19!11!2023) - PaperDocument26 pagesNEET (Pre-Medical) - Conquer Batch-1, 2 & PKL - Minor Test-08 - (19!11!2023) - Paperaakritisharma.xibNo ratings yet
- NEET 2016 Question Paper Phase 2 Code DD SS ZZDocument19 pagesNEET 2016 Question Paper Phase 2 Code DD SS ZZShobhit JainNo ratings yet
- Jee Main P+C+M - 02-04-2022 (Main Exam)Document24 pagesJee Main P+C+M - 02-04-2022 (Main Exam)SOHAIL MOHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- The Cook Book of Chemistry: Rajat Kalia - Alpha ClassesDocument299 pagesThe Cook Book of Chemistry: Rajat Kalia - Alpha ClassesRajat KaliaNo ratings yet
- CCJMG2B2016DT05 SolutionDocument5 pagesCCJMG2B2016DT05 SolutionSRIJANo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics DPP08Document3 pagesChemical Kinetics DPP08Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Jee Xi GD Goenka (04 Feb 2024)Document8 pagesJee Xi GD Goenka (04 Feb 2024)kaushiki6707No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03) - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesChemical Equilibrium - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03) - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024yahini8041No ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of Gases +thermodynamics (Xii 2022-24) (Ans) 15 06 23Document2 pagesKinetic Theory of Gases +thermodynamics (Xii 2022-24) (Ans) 15 06 23Piyush Student Acc JEENo ratings yet
- Test 17 Heat & ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesTest 17 Heat & Thermodynamicsumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Aakash Physics Study Package 4 SolutionsDocument134 pagesAakash Physics Study Package 4 SolutionsHarshit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Final Test Series For Neet-2022Document21 pagesFinal Test Series For Neet-2022sneha sahaNo ratings yet
- Optical fiber reflectionsDocument23 pagesOptical fiber reflectionsSBNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics - DPP 09 - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesChemical Kinetics - DPP 09 - Lakshya JEE 2024Hrishith SavirNo ratings yet
- NEET Booster Test Series Physics QuestionsDocument17 pagesNEET Booster Test Series Physics QuestionsAksheshNo ratings yet
- Aakash Physics Study Package 4 SolutionsDocument134 pagesAakash Physics Study Package 4 SolutionsfociweNo ratings yet
- Toppers Neet Practice Sheet-05Document6 pagesToppers Neet Practice Sheet-05RussNo ratings yet
- NEET Physics, Chemistry, Botany and Zoology TestDocument17 pagesNEET Physics, Chemistry, Botany and Zoology TestOm JethwaniNo ratings yet
- POLL 1 P+ C+B+Z 12th OYM BATCH QUE PAPER @CET - JEE - NEETDocument11 pagesPOLL 1 P+ C+B+Z 12th OYM BATCH QUE PAPER @CET - JEE - NEETKrins GopaniNo ratings yet
- Physics: AIM NEET Full Test-20Document17 pagesPhysics: AIM NEET Full Test-20Swaraj BoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PDFDocument30 pagesChapter 13 PDFRG RAJNo ratings yet
- Aakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020Document17 pagesAakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020Anish TakshakNo ratings yet
- PhySICS Paper With AnswerDocument5 pagesPhySICS Paper With Answersudhir_narang_3No ratings yet
- NEET (UG) 2017 Paper Solution PDFDocument45 pagesNEET (UG) 2017 Paper Solution PDFManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- Jee Main 2018 Chemistry Sample Question PaperDocument9 pagesJee Main 2018 Chemistry Sample Question PaperNIKHIL BHATTNo ratings yet
- States of Matter - DPP 06 - Yakeen 2.0 2023 VP StarsDocument3 pagesStates of Matter - DPP 06 - Yakeen 2.0 2023 VP Starslocohe4969No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium - DPP 04 (Of Lec 06) - Arjuna JEE 2024Document3 pagesChemical Equilibrium - DPP 04 (Of Lec 06) - Arjuna JEE 2024nrashmi743No ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 17 March Shift 1 PhysicsDocument13 pagesJEE Main 2021 17 March Shift 1 PhysicsAditya Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- KFT232 Sem2 2009 2010Document11 pagesKFT232 Sem2 2009 2010sha_amaneNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical KineticsShivani VermaNo ratings yet
- Set 16 Quiz 2 Physics Quiz Vidyapeeth Gulhan Jha Sir & MR Sir VikashDocument1 pageSet 16 Quiz 2 Physics Quiz Vidyapeeth Gulhan Jha Sir & MR Sir VikashSharvikrajNo ratings yet
- E-Caps-12 - Class Xii (SS) - Chem - FinalDocument5 pagesE-Caps-12 - Class Xii (SS) - Chem - FinalKrishnendu SahaNo ratings yet
- The Lamb Shift of Hydrogen and Low-Energy Tests of QedDocument30 pagesThe Lamb Shift of Hydrogen and Low-Energy Tests of QedTL NarasimhamNo ratings yet
- Aakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020Document15 pagesAakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020Indian VanguardsNo ratings yet
- STATES OF MATTER 20 YEARS PYQ'S WITH SOLUTION Nitesh DevnaniDocument4 pagesSTATES OF MATTER 20 YEARS PYQ'S WITH SOLUTION Nitesh Devnanisakshimodi2004No ratings yet
- 6564cd159017b30018bd620e - ## - Kinetic Theory of Gases and Gas Law Practice SheetDocument16 pages6564cd159017b30018bd620e - ## - Kinetic Theory of Gases and Gas Law Practice Sheetran69jsjsjsijbsaNo ratings yet
- NEET Test 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesNEET Test 1 SolutionsJai 5.0No ratings yet
- BHU M.Sc. CHEMISTRY ENTRANCE - 2011 practice questionsDocument15 pagesBHU M.Sc. CHEMISTRY ENTRANCE - 2011 practice questionsLORD RAVANNo ratings yet
- KTG and Thermodynamics Cheat Code NotesDocument23 pagesKTG and Thermodynamics Cheat Code NotesCranxtorNo ratings yet
- Bphe-106 (2019) emDocument30 pagesBphe-106 (2019) emRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Rank Booster TEst - II, 15.03.2024Document20 pagesRank Booster TEst - II, 15.03.2024ntype795No ratings yet
- 10-2-2020 Mock Test Paper QPDocument16 pages10-2-2020 Mock Test Paper QPVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- 2. Exercise 1 to 3 1. Theory KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument34 pages2. Exercise 1 to 3 1. Theory KTG & ThermodynamicsRakesh Singh kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 20 Years Pyq's SheetDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure 20 Years Pyq's Sheetsakshimodi2004No ratings yet
- Kcet Model Qp - Chemistry - 15-04-2024Document8 pagesKcet Model Qp - Chemistry - 15-04-2024mahadevipatil.patil04No ratings yet
- ATOMIC STRUCTURE NEET Previous Year Q Bank Till 2020Document9 pagesATOMIC STRUCTURE NEET Previous Year Q Bank Till 2020Arnav SinghalNo ratings yet
- Chem - 24.03.2020 - Full Test - Naresh Sir: ChemistryDocument7 pagesChem - 24.03.2020 - Full Test - Naresh Sir: ChemistryDrNaresh SahuNo ratings yet
- Rms speeds and gas properties from particle speedsDocument2 pagesRms speeds and gas properties from particle speedsMaya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Mock Test - 01 (03-08-2021)Document15 pagesMock Test - 01 (03-08-2021)dhruv kakadiyaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Physics QuestionsDocument14 pagesStatistical Physics QuestionsramsheydjNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument38 pagesStates of MatterJack LupinoNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : J J J JDocument5 pagesPart - A (Physics) : J J J Jsusheel_uiitshimlaNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 4 Paper Neet SolDocument16 pagesMock Test 4 Paper Neet Solspamhater566No ratings yet
- Pre NEET Mock Test PhysicsDocument18 pagesPre NEET Mock Test Physicspubg boy ASNo ratings yet
- Echotrac Mkiii: Model DFDocument2 pagesEchotrac Mkiii: Model DFjonathansolverNo ratings yet
- How you seize the space between next and nowDocument11 pagesHow you seize the space between next and nowMathan J RNo ratings yet
- Data File: Äkta Explorer Ancillary EquipmentDocument4 pagesData File: Äkta Explorer Ancillary EquipmentCarlos Alberto Ramirez GarciaNo ratings yet
- First Principle Applications in RoRo-Ship Design PDFDocument7 pagesFirst Principle Applications in RoRo-Ship Design PDFFerdy Fer DNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Theory States That The EarthDocument2 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory States That The EarthPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Photogrammetry and Remote SensingDocument14 pagesPhotogrammetry and Remote SensingJoseph Dincht83% (6)
- IEEE Guide For Batteries For Uninterruptible Power Supply SystemsDocument73 pagesIEEE Guide For Batteries For Uninterruptible Power Supply Systemsفريد قادريNo ratings yet
- Salary Statement 10 01 2018Document7 pagesSalary Statement 10 01 2018lewin neritNo ratings yet
- Tutorial HMM CIDocument14 pagesTutorial HMM CITrương Tiểu PhàmNo ratings yet
- Full Download Law and Ethics For The Health Professions 6th Edition Judson Harrison Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument20 pagesFull Download Law and Ethics For The Health Professions 6th Edition Judson Harrison Test Bank PDF Full Chapterhorriblebaculite0ly6t100% (14)
- MINI R56 N12 Valve Stem Seal ReplacementDocument9 pagesMINI R56 N12 Valve Stem Seal ReplacementJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica SpikaDocument2 pagesFicha Tecnica SpikaJosé Luis RubioNo ratings yet
- Colonial Philippines in Transition - SEA StudiesDocument197 pagesColonial Philippines in Transition - SEA StudiesYong Mosqueda100% (1)
- Reading PDFDocument6 pagesReading PDFoviNo ratings yet
- Science: Locating Places On Earth Using Coordinate SystemDocument29 pagesScience: Locating Places On Earth Using Coordinate Systemlawrence maputolNo ratings yet
- Panasonic Phone System KXT308Document6 pagesPanasonic Phone System KXT308Kellie CroftNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychological Assessment and PsychodiagnosisDocument75 pagesIntroduction To Psychological Assessment and PsychodiagnosisNishesh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Raw To Scaled Mark DatabaseDocument10 pagesRaw To Scaled Mark DatabaseKelly ChuNo ratings yet
- HD 9 Manual 5900123 Rev F 10 1 13Document60 pagesHD 9 Manual 5900123 Rev F 10 1 13Karito NicoleNo ratings yet
- PLC ProjectsDocument7 pagesPLC ProjectsshakirNo ratings yet
- Integral Mechanical Attachment A Resurgence of The Oldest Method of JoiningDocument427 pagesIntegral Mechanical Attachment A Resurgence of The Oldest Method of JoiningGabriel LópezNo ratings yet
- Natural Lighting at The Kimbell Museum: Gifford Pierce of IdahoDocument5 pagesNatural Lighting at The Kimbell Museum: Gifford Pierce of IdahoPriscilia ElisabethNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode OperationDocument8 pagesPN Junction Diode OperationAyush NinaweNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Fuel System (Diesel Supply System For Generator)Document16 pagesMethod Statement For Fuel System (Diesel Supply System For Generator)BAVA M.H100% (1)
- INGLES TECNICO IV (En Ambas Caras)Document45 pagesINGLES TECNICO IV (En Ambas Caras)ESGUAR INSTRUCTORESNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry Topic 13 Carbonates AnsDocument7 pagesIgcse Chemistry Topic 13 Carbonates AnsCClfourNo ratings yet
- Chap 008Document69 pagesChap 008jjseven22100% (1)
- Digital Signal Processing Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesDigital Signal Processing Exam QuestionsecehodaietNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Salem PossessedDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Salem PossessedCharity BurgessNo ratings yet