Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211459 - 0000
BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211459 - 0000
Uploaded by
Christine Jade TanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211459 - 0000
BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211459 - 0000
Uploaded by
Christine Jade TanCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOCHEMISTRY
BSN INTRODUCTION: BIOCHEMISTRY
COLLEGE OF HEALTH AND
SCIENCES EDUCATION
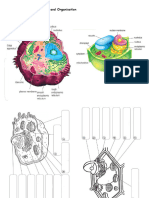
fungi, plants, and animals are multicellular lipids provide the basic structure of biological
eukaryotes (with few unicellular eukaryotes) membranes.
proteins are embedded in the membranes
the main difference between prokaryotic and and provide channels/carriers for the
eukaryotic cells is the existence of transport of ions and nutrients.
organelles, especially the nucleus, in
eukaryotes. Notes:
an organelle is a part of the cell that has a fats and carbohydrates - protein sparer
distinct function; it is surrounded by its own carbohydrates
membrane within the cell. supply energy throughout the body.
protein
10% of glucose
enzyme
information
messenger
transport, etc.
uric acid
waste product of purine metabolis
purine
from protein
monggo - mataas ang purine kaya
hindi pwede sa may arthritis.
urea
from the ammonia
NH
amine group that is a toxic substances.
ammonia is removed in the body in the
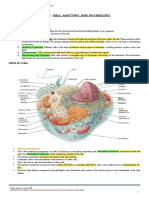
CELL MEMBRANE process of deamination and is converted
a semi-permeable membrane surrounding into urea by liver and is excreted by kidney.
the cell separating its internal environment ammonia
from the external environment; comes from protein
permits and/or enhances the absorption of energy
essential nutrients into the cell while stored in the mitochondria of animals;
preventing the diffusion of needed and is stored in the chloroplast in
metabolites plants.
a lipid bilayer that mechanically holds cell glucose
together. is the form of energy for the entire body,
component biomolecules: but ATP in cells.
lipids: phospholipids, cholesterol ribosomes
proteins site for synthesis for proteins.
carbohydrates
5.
You might also like
- Experiment 1Document9 pagesExperiment 1Froileth PulidoNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Protein MetabolismDocument9 pagesProteins and Protein MetabolismclaireNo ratings yet
- Fermentation ChemistryDocument2 pagesFermentation ChemistryDayana camargo garciaNo ratings yet
- MC 2 Notes (Midterm)Document4 pagesMC 2 Notes (Midterm)Francine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Module 5 ProteinDocument14 pagesModule 5 ProteinBroskiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids - ProteinDocument25 pagesAmino Acids - ProteinViragNo ratings yet
- Karen Natasha-ProteinDocument1 pageKaren Natasha-ProteinKAREN NATASHANo ratings yet
- CHONDocument4 pagesCHON2083385No ratings yet
- L1 & L2 NotesDocument8 pagesL1 & L2 Notes17 ERMINO, Nicole AngelaNo ratings yet
- BIO First Quarter ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO First Quarter ReviewerBb. JayNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 3Document11 pagesDigestive System 3Shubham HarishNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Prelim ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Prelim ReviewerRosette Go80% (5)
- Ruminant Protein Nutrition: Lebih Di Kenal Dengan Metabolisme Nitrogen Dalam RumenDocument24 pagesRuminant Protein Nutrition: Lebih Di Kenal Dengan Metabolisme Nitrogen Dalam RumenIsnainiwnNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - Macronutrient (PROTEIN)Document3 pagesMODULE 2 - Macronutrient (PROTEIN)Donna MarieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Protein MetabolismDocument7 pagesLesson 12 Protein Metabolismsaculala0291pamNo ratings yet
- The Contribution of The Large Intestine To Energy Supplies in Man1'2Document5 pagesThe Contribution of The Large Intestine To Energy Supplies in Man1'2gopnarayansamyakNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ReviewerDocument15 pagesEnzymes ReviewerAbby Dimalaluan OquendoNo ratings yet
- Protein - Britannica Online Encyclopedia PDFDocument46 pagesProtein - Britannica Online Encyclopedia PDFanant mishraNo ratings yet
- Human Histology 2 CytologyDocument6 pagesHuman Histology 2 CytologyBlubby BleuNo ratings yet
- MacromoleculeDocument25 pagesMacromoleculeMuhammad AjmalNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Module 4Document18 pagesBiochemistry - Module 4ricky fecaraNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport: AP BiologyDocument49 pagesCell Transport: AP BiologychangagNo ratings yet
- 2.01 - Cell Organelles and MacromoleculesDocument2 pages2.01 - Cell Organelles and MacromoleculesJuan Miguel SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Bean Proteins: ProteinDocument14 pagesIsolation of Bean Proteins: ProteinElizabeth TanguilanNo ratings yet
- Biochem PrelimDocument3 pagesBiochem PrelimErich ElloNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Proteins)Document22 pagesMind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Proteins)Gus LionsNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Nutrit IonDocument17 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Nutrit IonAdel Kristine EusebioNo ratings yet
- ZOO 103 Lecture 09 19 ProteinsDocument12 pagesZOO 103 Lecture 09 19 ProteinsKaelyn MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Protein and Amino Acids: Metabolism and AnalysisDocument35 pagesProtein and Amino Acids: Metabolism and AnalysisWindi MoseNo ratings yet
- Bio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Document6 pagesBio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Mia NavarroNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211407 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211407 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PhysiologyDocument6 pagesMicrobiology PhysiologyLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Oxidation and The Production of UreaDocument64 pagesAmino Acid Oxidation and The Production of UreaAsif JavedNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument112 pagesAnimal NutritionJessa PalbanNo ratings yet
- 2Document5 pages2Nunee AyuNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- Membran Sel Dan Matriks EkstraselularDocument78 pagesMembran Sel Dan Matriks EkstraselularneviNo ratings yet
- Art Bio To InglesDocument129 pagesArt Bio To InglesDiana MoranNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211520 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211520 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- The Structures: Protein FactsDocument3 pagesThe Structures: Protein FactsCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- Proteins PDFDocument3 pagesProteins PDFCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- F4 C2 NotesDocument15 pagesF4 C2 Notesmarisyayasmin050907No ratings yet
- Nutrition & Diet Theraphy: 2 SEMESTER, A.Y. 2023 - 2024 (PRELIMS)Document5 pagesNutrition & Diet Theraphy: 2 SEMESTER, A.Y. 2023 - 2024 (PRELIMS)x9wmymnkn6No ratings yet
- Bm01 - Structure and Function - 2020Document28 pagesBm01 - Structure and Function - 2020Kresnawati Wahyu SetionoNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 Protein Metabolism - No Voice 1Document31 pagesLec 9 Protein Metabolism - No Voice 1staenley estacioNo ratings yet
- 002 Cell Membrane PhysiologyDocument12 pages002 Cell Membrane PhysiologyAlfred BajarNo ratings yet
- The Cell Membrane: AP BiologyDocument53 pagesThe Cell Membrane: AP BiologythalesNo ratings yet
- Science Textbook Lesson-4Document6 pagesScience Textbook Lesson-4Rahul DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsDocument53 pagesAmino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsDanica RevillaNo ratings yet
- THE Function of ProteinDocument2 pagesTHE Function of ProteinGwyNo ratings yet
- CELL-STRUCTURE Cell StructureDocument5 pagesCELL-STRUCTURE Cell StructureJacqueline Rose Alipo-onNo ratings yet
- MBG312 Chp23 BDDocument47 pagesMBG312 Chp23 BDBaran KirdarNo ratings yet
- Proteins Notes and TestsDocument5 pagesProteins Notes and TestsJanicSmithNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Protein Dalam Tubuh ManusiaDocument9 pagesMetabolisme Protein Dalam Tubuh ManusiaFirly AlimansyahNo ratings yet
- Gala - BrylleJhon - Lecture Activity 3Document3 pagesGala - BrylleJhon - Lecture Activity 3ANGEL JOY RAVALONo ratings yet
- Metabolizable Protein Systems in Ruminant NutritioDocument8 pagesMetabolizable Protein Systems in Ruminant Nutritiojss_bustamanteNo ratings yet
- Biologie Celulara - Prima ParteDocument37 pagesBiologie Celulara - Prima ParteNacu AndreiNo ratings yet
- Biochem Trans Unit 1Document8 pagesBiochem Trans Unit 1David MangawilNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria in Higher Plants: Structure, Function, and BiogenesisFrom EverandMitochondria in Higher Plants: Structure, Function, and BiogenesisNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Transes - 20231111 - 202740 - 0000Document1 pageEnvironmental Science Transes - 20231111 - 202740 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument13 pagesENGLISHChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tintin's 1ST Lab Act BioDocument2 pagesTintin's 1ST Lab Act BioChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Brochure Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesBrochure Skeletal SystemChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211407 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211407 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211520 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211520 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211609 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211609 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211654 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211654 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tan - Lesson 2 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningDocument5 pagesTan - Lesson 2 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tan - Lesson 1 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningDocument3 pagesTan - Lesson 1 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- AortaDocument6 pagesAortaChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Muscular System QuizDocument2 pagesMuscular System QuizChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- CMRIDocument20 pagesCMRINauman JavedNo ratings yet
- Ghafoor SalivaryGlandsDocument6 pagesGhafoor SalivaryGlandsMamadou DIENENo ratings yet
- F Y B SC Botany (Revised) - 19.062020Document12 pagesF Y B SC Botany (Revised) - 19.062020Pooja SaryawanshiNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2007 Mark SchemeDocument64 pagesKS3 Science 2007 Mark SchemeM.Humayun WaqasNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument12 pagesRespiration in PlantsNalla Raghuram ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyDocument12 pagesThe Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyJean Rose SalahayNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - ABG INTERPRETATIONDocument2 pagesGroup 2 - ABG INTERPRETATIONJilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument32 pagesMitochondriaDayana Prasanth100% (1)
- Sergey Nikolayevich WinogradskyDocument3 pagesSergey Nikolayevich WinogradskyangelsburgermdNo ratings yet
- Preservative and Fixative Methods of Brain Biopsy-Review: Savitha Dental College and Hospital, Chennai AbstractDocument5 pagesPreservative and Fixative Methods of Brain Biopsy-Review: Savitha Dental College and Hospital, Chennai AbstractShianeleyeEnriqueDelosSantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Science Form 3)Document3 pagesChapter 2 (Science Form 3)Shatviga VisvalingamNo ratings yet
- Sedative and HypnoticsDocument37 pagesSedative and Hypnoticsprajyot khedekarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Gas Exchange Diffusionof Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Through The Respiratory MembraneDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Gas Exchange Diffusionof Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Through The Respiratory MembraneSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- Guideline Fluido 2013Document11 pagesGuideline Fluido 2013larissa0semeaoNo ratings yet
- Paul Buchner (1886-1978) and Hereditary Symbiosis in InsectsDocument7 pagesPaul Buchner (1886-1978) and Hereditary Symbiosis in InsectsDalek CaanNo ratings yet
- Epigenetic SDocument19 pagesEpigenetic SNoor SabahNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: What Is The Same About You and The Doughnut?Document16 pagesDigestive System: What Is The Same About You and The Doughnut?Shotika ChatratichartNo ratings yet
- 9700 s10 Ms 42Document10 pages9700 s10 Ms 42just-maybe202No ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form 1Document49 pagesBiology Notes Form 1Raphael DikhandaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer - BAYLONDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer - BAYLONElijah Joaquin Payumo BaylonNo ratings yet
- Metamorphica ClassicDocument156 pagesMetamorphica ClassicbobNo ratings yet
- Leaf Bubbles Lab by Kato Lwebuga: Here Is A Video From Oregon Forests If You Are A Visual LearnerDocument5 pagesLeaf Bubbles Lab by Kato Lwebuga: Here Is A Video From Oregon Forests If You Are A Visual Learnerapi-554072790No ratings yet
- Artículo 5Document9 pagesArtículo 5Zoé RodríguezNo ratings yet
- General Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas ADocument33 pagesGeneral Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas AEmilie ArvidsonNo ratings yet
- Elsc 11 20Document21 pagesElsc 11 20Mark John Paul CablingNo ratings yet
- Toads PDFDocument12 pagesToads PDFChloe AnneNo ratings yet
- Starling ForcesDocument2 pagesStarling ForcesMerlyn Chrislia RumtheNo ratings yet
- Importance of The Mitral Apparatus For Left Ventricular Function: An Experimental ApproachDocument8 pagesImportance of The Mitral Apparatus For Left Ventricular Function: An Experimental ApproachThanh BinhNo ratings yet
- Jawapan: 1.1 Organisasi Tisu Tumbuhan 1 2Document29 pagesJawapan: 1.1 Organisasi Tisu Tumbuhan 1 2ThimNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting EnzymesDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting EnzymesJohn Carlo G. NolascoNo ratings yet