Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bitumens - Metals REVIEWER
Bitumens - Metals REVIEWER
Uploaded by
lizhientmozoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bitumens - Metals REVIEWER
Bitumens - Metals REVIEWER
Uploaded by
lizhientmozoCopyright:
Available Formats
BITUMINOUS MATERIALS & FERROUS AND NONFERROUS METALS
(REVIEWER)
BITUMINOUS MATERIALS- Bituminous materials are dark brown or
black semi-solid or liquid thermoplastic hydrocarbon mixtures formed
from natural or manufactured processes in which hydrocarbon
mixtures lose their volatile components, leaving a heavier residue.
Pitch is a solid or semi-solid byproduct of tar partial evaporation or
fractional distillation.
Coal-tar pitch is the most common material of this kind of pitch.
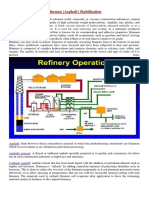
Bitumen- A thick black mixture of hydrocarbons obtained naturally or
as a byproduct of petroleum distillation. It is used in road surfacing
and roofing.
Bitumen occurs naturally in the mud at the bottom of lakes and other
water sources, can also be found from existing sources of petroleum.
It is primarily used for industrial purposes. It is used as a binder in
asphalt for roads, runways, parking lots and foot paths. Gravel and
crushed rocks are mixed with bitumen and applied to roadways.
ASPHALT
Two types of asphalt:
The natural asphalt obtains naturally.
The residual asphalt occurs by fractional distillation of crude
petroleum oil with an asphalt base.
Asphalt paving cements are employed as binders in the construction
of more expensive asphalt pavements.
Liquid Paving asphalts- Paving with liquid asphalts is a
cost-cuttingmeasure. When gasoline is employed as asolvent, it
produces a fast-curing liquid asphalt;kerosene produces a
medium-curing asphalt;and heavier fuel oils make a slow-curing
asphalt.
Cutback Bitumen- Bitumen mix with a volatile solvent is cutback
bitumen. This enables its applicationconsiderable at low temperature.
Bitumen Emulsion- Liquid product form by mixing molten bitumen
with hot water in the presence of an emulsifying agent. It consists of
soap or resinous bodies.
FERROUS & NON- FERROUS
Ferrous comes to us from the Latin word ferrum, which means “iron.”
That's also where the Atomic symbol for iron, Fe, comes from.
FERROUS METALS
Steel - a malleable alloy of iron and carbon produced by melting and
refining pig iron and/ or
scrap steel, graded according to the carbon content. Elements such
as manganese and silicon may be included to provide special
properties. Produce by three basic raw materials, iron ore, and
limestone.
Cold Rolled Steel- Has a fine surface finish, tight size tolerance, and
excellent machinability. Therefore, it is widely used in many
applications, including manufacturing, construction, home
appliances, automobiles, machinery, and so on.
Wrought Iron- Is produced when pig iron is melted in such a way as to
remove nearly all of the carbon and other impurities. It is easily
worked and is tough and ductile. It's main use
are for roofing sheets, wire and metal ornaments.Historical uses of
wrought iron were decorative: fences, gates, railings, balconies,
porches, canopies, roof cresting, lamp, grilles, hardware, nails, etc..
Manganese Steel- O ffers great resistance to abrasion and finds
important use in the cutting edges of heavy digging tools.
Because of its self hardening properties, manganese steel has been
used in the mining industry for many years – cement mixers, rock
crushers, crawler treads for tractors, elevator and shovel buckets – as
well as in the rail industry (switches and crossings) and other high
impact environments.
Weathering/Cortez Steel- A recently developed grade of steel. It forms
its own protection against atmospheric corrosion and thus requires
no painting.
Rivets- A type of fastener that is used for permanent assembly of
product or workpiece.
Copper- Has high resistance to corrosion and used for making sheets
and metal lath
Lead- used for roofing, flashing and spandrel wall panels. It is very
easy to cut and work with
You might also like
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- A752Document9 pagesA752Muhamed RafficNo ratings yet
- Aluminium CastingDocument5 pagesAluminium CastingBalaji RajaNo ratings yet
- Types of CementDocument7 pagesTypes of Cementmohamed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Cement Technology PDFDocument11 pagesBasic Cement Technology PDFYunus Ahmed80% (5)
- Cement and Cement ConcreteDocument38 pagesCement and Cement ConcreteIka Alam SariNo ratings yet
- Buildning Materials:: CementDocument20 pagesBuildning Materials:: CementNitin RaoNo ratings yet
- Cement and LimeDocument172 pagesCement and LimeMargie Lou Ardiente100% (2)
- Asphalt ConcreteDocument6 pagesAsphalt ConcretemechnsatheeshNo ratings yet
- BitumenDocument35 pagesBitumenamanbhu1991100% (5)
- Furniture Production Materials - 2Document9 pagesFurniture Production Materials - 2Pitz Shady ShinNo ratings yet
- Cement ChemistryDocument12 pagesCement ChemistryAJAY KUMAR T.MNo ratings yet
- Cement, Gypsum Product, Quartz SandDocument14 pagesCement, Gypsum Product, Quartz SandHuda FauziNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Materials Data HandbookDocument137 pagesCryogenic Materials Data HandbookhemakumarsNo ratings yet
- 7 - Concrete-1 PDFDocument73 pages7 - Concrete-1 PDFjinnaNo ratings yet
- Lime and Dolomite For The Steel IndustryDocument8 pagesLime and Dolomite For The Steel IndustrychmsarfrazNo ratings yet
- 150 Sample-Chapter PDFDocument25 pages150 Sample-Chapter PDFMochammad Waris SNo ratings yet
- Blacksmithing on the Farm - With Information on the Materials, Tools and Methods of the BlacksmithFrom EverandBlacksmithing on the Farm - With Information on the Materials, Tools and Methods of the BlacksmithNo ratings yet
- Cement: Nilanjan MitraDocument25 pagesCement: Nilanjan MitrassriramiitNo ratings yet
- Cement and ConcreteDocument81 pagesCement and Concretejeo TinioNo ratings yet
- Bituminious MaterialsDocument53 pagesBituminious MaterialsMuhammad Zulhusni Che RazaliNo ratings yet
- Steel Slag. Conversion of An Industrial Waste Material Into A Value Adding Asphalt IngredientDocument8 pagesSteel Slag. Conversion of An Industrial Waste Material Into A Value Adding Asphalt IngredientMehdi FarrokhiNo ratings yet
- Types of Cement and ReinforcementsDocument25 pagesTypes of Cement and ReinforcementsJyothishNo ratings yet
- BitumenDocument41 pagesBitumenKenneth YeoNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous MaterialsDocument67 pagesMiscellaneous MaterialsSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Materials and ConstructionDocument17 pagesUnit 2: Materials and Constructionthejitu1No ratings yet
- Bituminous MaterialsDocument6 pagesBituminous MaterialsImmanuel LangatNo ratings yet
- Intended Learning Outcomes: Portland Cements, Calcium and Compounds Magnesium - 1Document4 pagesIntended Learning Outcomes: Portland Cements, Calcium and Compounds Magnesium - 1alyssaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Opus Caementicium: Romans Masonry Concrete Lime Volcanic Ash BrickDocument10 pagesOpus Caementicium: Romans Masonry Concrete Lime Volcanic Ash BrickRachana Kandari GargNo ratings yet
- Concrete: Muhammad Arslan, Department of Civil Engineering Uet LahoreDocument73 pagesConcrete: Muhammad Arslan, Department of Civil Engineering Uet LahoreMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- Waste Material in Village Road ConsturctionDocument30 pagesWaste Material in Village Road ConsturctionLaxmi PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Cement TechuDocument11 pagesCement Techuadediran adeyemiNo ratings yet
- Metals Problem Set 1Document5 pagesMetals Problem Set 1Rufo Daskeo Jr.No ratings yet
- Friction Musical Instruments Zippers: Alloy Copper Tin ArsenicDocument7 pagesFriction Musical Instruments Zippers: Alloy Copper Tin ArsenicShawn GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials NotesDocument25 pagesEngineering Materials NotesRoobanesh ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Bitumen 1Document18 pagesBitumen 1amanbhu1991100% (1)
- TOPIC 2 DCC30103 JUN2020 - Pavement MaterialDocument65 pagesTOPIC 2 DCC30103 JUN2020 - Pavement MaterialMuhd FareezNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument25 pagesMaterialsMickaela Kassandra Padilla ParanNo ratings yet
- Business English Assignment - Session 13-Zidan fasha-20210010047-TS21EDocument2 pagesBusiness English Assignment - Session 13-Zidan fasha-20210010047-TS21EZidan FashaNo ratings yet
- Hwno.5 Bsa-1a AlcantaraDocument22 pagesHwno.5 Bsa-1a AlcantaraAngel Mine AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Cement Specification: Group 4Document9 pagesCement Specification: Group 4geeteshmalhotra1No ratings yet
- CementDocument12 pagesCementMazharYasinNo ratings yet
- MaachDocument16 pagesMaachAg AbderazakNo ratings yet
- Building Constrction MaterialsDocument43 pagesBuilding Constrction MaterialsJaki KaliNo ratings yet
- Foundry PracticeDocument11 pagesFoundry PracticeNatalie WyattNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials (CE 1206) : Bituminous MaterialDocument22 pagesConstruction Materials (CE 1206) : Bituminous Materialvarunsingh214761100% (1)
- Group 6 - AsphaltDocument15 pagesGroup 6 - AsphaltVeeNo ratings yet
- Bituminous MaterialDocument10 pagesBituminous Materialsenbonzakura101No ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Semi Noncrystalline Amorphous Materials SPJDocument6 pagesChapter-8 Semi Noncrystalline Amorphous Materials SPJAvesh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron ComposiotionDocument34 pagesCast Iron ComposiotionMubash AbdNo ratings yet
- Men /as Pha LTDocument35 pagesMen /as Pha LTndali_2No ratings yet
- Food Packaging Technology Unit 2 Part CDocument20 pagesFood Packaging Technology Unit 2 Part CAkash DuttaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Historic Age: CementDocument10 pagesPre-Historic Age: CementMary Louisse ManaloNo ratings yet
- Lecture EightDocument8 pagesLecture EightMohamed AdnanNo ratings yet
- ConcreteDocument18 pagesConcreteMiyeon KimNo ratings yet
- Cast IronDocument9 pagesCast Ironedward biwottNo ratings yet
- Lecture #5 Supplementry Cementing MaterialsDocument25 pagesLecture #5 Supplementry Cementing MaterialsMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- CementsssDocument3 pagesCementsssSujathaa NagappanNo ratings yet
- CE112 Lecture 4Document30 pagesCE112 Lecture 4Muhammad Israr KhanNo ratings yet
- EAT 258-Lecture 4 (Cement Type of Cement) 06112019Document13 pagesEAT 258-Lecture 4 (Cement Type of Cement) 06112019GEETHA A/P MURUKAIYA STUDENTNo ratings yet
- BT1 ConcreteDocument5 pagesBT1 ConcretelizhientmozoNo ratings yet
- Bu 1Document4 pagesBu 1lizhientmozoNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1lizhientmozoNo ratings yet
- Valves 1Document1 pageValves 1lizhientmozoNo ratings yet
- Project Ppt-Final 2020Document36 pagesProject Ppt-Final 2020shrivardhanNo ratings yet
- Slurry Components in Metal Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP) Process A Review PDFDocument13 pagesSlurry Components in Metal Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP) Process A Review PDFMax HaroutunianNo ratings yet
- CHM 3609 - Inorganic Chemistry: X y Z XDocument3 pagesCHM 3609 - Inorganic Chemistry: X y Z XJoshua JordanNo ratings yet
- Kimia - BuferDocument12 pagesKimia - BuferHaryo Anggoro Permadi100% (1)
- Concrete Protection Materials & TechniquesDocument34 pagesConcrete Protection Materials & TechniquesSasikumar ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Vanilla FlavourDocument11 pagesVanilla FlavourAYESHAAZHER KIDWAINo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Fuels and CombustionDocument72 pagesChapter 4 Fuels and CombustionKaran ThelakkatNo ratings yet
- Alba Milagro KatalogDocument82 pagesAlba Milagro KatalogDavid GluhićNo ratings yet
- Trinox OxDocument2 pagesTrinox OxJorge RibeiroNo ratings yet
- EPA 245.5 HGDocument4 pagesEPA 245.5 HGAarón CespedesNo ratings yet
- GC Feature-4Document11 pagesGC Feature-4Lysa GINo ratings yet
- Classifying Metals, Metalloids, and Non-MetalsDocument3 pagesClassifying Metals, Metalloids, and Non-Metalsnona wayne dela peñaNo ratings yet
- 804.doc - Bioterge804Document2 pages804.doc - Bioterge804Onesany TecnologiasNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 D Block AND F BLOCK QN BANKDocument7 pagesUnit 8 D Block AND F BLOCK QN BANKDharaneesh S.k.No ratings yet
- Avances en Soldadura de Materiales DisimilesDocument5 pagesAvances en Soldadura de Materiales DisimilesDebora ChavezNo ratings yet
- Fuel and Energy AbstractsDocument91 pagesFuel and Energy Abstractsashkanr65100% (1)
- Solid Fuels2020 2021Document37 pagesSolid Fuels2020 2021Eli EliNo ratings yet
- Applied Catalysis A, General: Research PaperDocument10 pagesApplied Catalysis A, General: Research PaperDeisy González PinillaNo ratings yet
- Target: Figure 1. Citrus Fruits Sprayed With WaterDocument7 pagesTarget: Figure 1. Citrus Fruits Sprayed With WaterGrace AmarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Processing Technology: Maciej Sienkiewicz, Kaja Borz Ędowska-Labuda, Artur Wojtkiewicz, Helena JanikDocument8 pagesFuel Processing Technology: Maciej Sienkiewicz, Kaja Borz Ędowska-Labuda, Artur Wojtkiewicz, Helena JanikMEHDI FARROKHINo ratings yet
- Tholander (Compatibility Mode)Document58 pagesTholander (Compatibility Mode)Aous Al AgaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Production by Dark Fermentation - AidicDocument6 pagesHydrogen Production by Dark Fermentation - AidicĐêmTrắngNo ratings yet
- Spirit Blue AgarDocument2 pagesSpirit Blue AgarEugenia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Poly Vinyl Alcohol and Borax SlimeDocument11 pagesPoly Vinyl Alcohol and Borax SlimeEvelyn GómezNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONSDocument17 pagesHYDROCARBONSsarahNo ratings yet
- Kids' Conditioners: INCI Name, Trade Name Weight % Weight % Function Product PropertiesDocument2 pagesKids' Conditioners: INCI Name, Trade Name Weight % Weight % Function Product Propertiesgabriel oliveira monteiroNo ratings yet
- Vam Veova Copolymer EmulsionDocument1 pageVam Veova Copolymer Emulsionاسلام ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- 8.applied Catalysis BDocument13 pages8.applied Catalysis BCristianAtanasiuNo ratings yet