Professional Documents
Culture Documents
20AE503 - CFAD Unit - II
Uploaded by
FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
20AE503 - CFAD Unit - II
Uploaded by
FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGECopyright:
Available Formats
EXCEL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Autonomous)
Aeronautical Engineering
Fourth Semester
20AE503- Compressible Flow Aerodynamics
Regulations 2020
Question Bank
UNIT – II Normal and Oblique Shocks
PART- A
Q.No Questions Marks CO BL
1 What is Normal shock? 2 CO1 R
2 Write the Hugonoit equation. 2 CO1 R
3 What is meant by detached shocks? 2 CO1 R
4 Define shock polar. 2 CO1 R
5 State the Mach angle. 2 CO1 R
6 Write the θ-β-M relation. 2 CO1 R
7 Define flow deflection angle. 2 CO1 R
8 What is hodograph plane? 2 CO1 R
9 State bow shock. 2 CO1 R
10 What is sonic circle? 2 CO1 R
11 What is Oblique shock? 2 CO1 R
12 Draw the detached shock on blunt body. 2 CO1 R
13 What is concave corner? 2 CO1 R
14 Define Mach wave. 2 CO1 R
15 Write the Mach angle–Mach number relation. 2 CO1 R
16 State the Weak Shock. 2 CO1 R
17 Write the compressible flow normal shock equation. 2 CO1 R
18 State Shock Tube. 2 CO1 R
19 What is strong shock? 2 CO1 R
20 What is convex corner? 2 CO1 R
PART- B
Q.No Questions Marks CO BL
1 Derive – Normal shock equation. 16 CO1 AP
2 Derive Rankine - Hugoniot equation. 16 CO1 AP
3 Show the expression of Prandtl equation for an oblique shock wave. 16 CO1 AP
4 A re-entry vehicle (RV) is at an altitude of 15 000 m and has a velocity of 1850 m s-1. A
bow shock wave envelops the RV. Neglecting dissociation, determine the static pressure
and temperature and the stagnation pressure and temperature just behind the shock wave 16 CO1 AP
on the RV center line where the shock wave may be treated as a normal shock. Assume
that the air behaves as perfect gas, with 𝛾 = 1.4 and R = 287 J (kg K)-1.
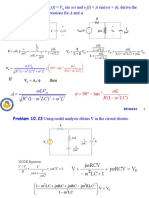
5 A normal shock moves in a constant area tube, as shown in Figure. In region 1 V1 = 100 m
s-1, T 1 = 30 ∘C, and p1 = 0.7 atm. Shock speed Cs with respect to a fixed coordinate
system is 600 m s-1. Find fluid properties in region 2.
16 CO1 AP
6 Explain the Shock Polar. 16 CO1 U
7 Consider a supersonic flow with M=2, P=1atm, T=288k. This flow is deflected at a
compression corner through 200. Calculate M, P, T, P 0, and T0 behind the resulting oblique
shock wave.
16 CO1 AP
8 Derive the oblique shock wave relation. 16 CO1 AP
9 Explain the Pitot static tube corrections for subsonic and supersonic flows. 16 CO1 AP
10 Short note on i) Detached shock wave.
ii) Concave corner and Convex corner. 16 CO1 AP
iii) Flow past over a wedges.
(Note:*Blooms Level (R – Remember, U – Understand, AP – Apply, AZ – Analyze, E – Evaluate, C – Create))
PART A- Blooms Level: Remember, Understand, Apply
PART B- Blooms Level: Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate (if possible)
(Marks: 16 Marks, 8+8 Marks, 10+6 Marks)
Subject In charge Course Coordinator HOD IQAC
(Name & Signature) (Name & Signature)
You might also like
- 20AE503 - CFAD Unit - IVDocument2 pages20AE503 - CFAD Unit - IVFIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- 20AE503 - CFAD Unit - IIIDocument3 pages20AE503 - CFAD Unit - IIIFIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Broadway Hilti Handrail Base PDFDocument4 pagesBroadway Hilti Handrail Base PDFjijinjohnNo ratings yet
- 10 A - Internal Ouestion - R 21Document1 page10 A - Internal Ouestion - R 21JaisiPrabaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6a Oscillators PDFDocument26 pagesTopic 6a Oscillators PDFAbdulrahman NasserNo ratings yet
- 22par102-Theory of Vibration Iae-1Document1 page22par102-Theory of Vibration Iae-1Christan LNo ratings yet
- 16CE SM2 R16 QB-2020 Final1Document14 pages16CE SM2 R16 QB-2020 Final1Ajeesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Te2501 Set 2Document3 pagesTe2501 Set 2r.rabinNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Question Bank 20-11-23Document3 pagesPower Electronics Question Bank 20-11-23ckissyou04No ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Chap 2 - Electrostatics (Compatibility Mode)Document182 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Chap 2 - Electrostatics (Compatibility Mode)Eugune Chow Mun WaiNo ratings yet
- Som 5Document1 pageSom 5Er Rahul BhandariNo ratings yet
- Open-Circuit Time Constant Analysis: Asas As Hs K Bsbs BsDocument24 pagesOpen-Circuit Time Constant Analysis: Asas As Hs K Bsbs BsSHAIK MUSTHAFANo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument1 pageEquation Sheethellblaster5No ratings yet
- From Unimap, Malaysia Louisiana State U HK City U Eastern Washington UDocument31 pagesFrom Unimap, Malaysia Louisiana State U HK City U Eastern Washington UKingLokeshNo ratings yet
- 09-Wien Bridge Oscillator Using OpAmp PDFDocument4 pages09-Wien Bridge Oscillator Using OpAmp PDFVishesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Year/Sem:III/V Duration: 3 Hour Max. Marks: 100: BAN 501-Aircraft Structure-IIDocument3 pagesYear/Sem:III/V Duration: 3 Hour Max. Marks: 100: BAN 501-Aircraft Structure-IIMuthukrishnan biherNo ratings yet
- Year/Sem:II/IV Duration: 3 Hour Max. Marks: 100: Ban504-Flight MechanicsDocument3 pagesYear/Sem:II/IV Duration: 3 Hour Max. Marks: 100: Ban504-Flight MechanicsMuthukrishnan biherNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2018-19 EEE1001 ETH TT305 VL2018191000890 Reference Material I Unit 2 ProblemsDocument45 pagesFALLSEM2018-19 EEE1001 ETH TT305 VL2018191000890 Reference Material I Unit 2 ProblemsAddisu Amare Zena 18BML0104No ratings yet
- Radio-Frequency Circuit4Document25 pagesRadio-Frequency Circuit4mumtazNo ratings yet
- Ch9 12Document286 pagesCh9 12Ram MurthyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Microelectronics IIDocument44 pagesFundamentals of Microelectronics IIAbrham GojjamNo ratings yet
- BM8501 QPDocument1 pageBM8501 QPMonika GNo ratings yet
- Colpitts Hartley Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument5 pagesColpitts Hartley Wein Bridge OscillatorRidwanAbrarNo ratings yet
- D0685 Phy Paper 5Document18 pagesD0685 Phy Paper 5blogeraryanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IVDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit IVMowleen ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Relaxation Oscillators Triangular Waveform Generators: Two Mark Questions One Mark QuestionsDocument3 pagesRelaxation Oscillators Triangular Waveform Generators: Two Mark Questions One Mark QuestionsAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Assignment Spectoscopy 1st Sem 2022Document7 pagesAssignment Spectoscopy 1st Sem 2022Debasish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Analog Sample Interview QuestionsDocument30 pagesAnalog Sample Interview QuestionsSampoornaGonellaNo ratings yet
- ET1006 Chapter16 RL Part 1Document20 pagesET1006 Chapter16 RL Part 1fastNo ratings yet
- Ifv (T) V Sin (T) A Sin, Derive The Expressions For A andDocument12 pagesIfv (T) V Sin (T) A Sin, Derive The Expressions For A andWESTLY JUCONo ratings yet
- School of Engineering and TechnologyDocument2 pagesSchool of Engineering and TechnologyMegha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 QBDocument2 pagesUnit 2 QBECE SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Lecturer Tutorial Sp025 20212022Document135 pagesLecturer Tutorial Sp025 20212022faris zainuddinNo ratings yet
- EEG 262: Electronics II: Experiment 2: Linear and Non-Linear Applications of Op AmpDocument5 pagesEEG 262: Electronics II: Experiment 2: Linear and Non-Linear Applications of Op Ampعلي حسنNo ratings yet
- ASC Question BankDocument4 pagesASC Question Bankanirudh pNo ratings yet
- ch3 OscDocument14 pagesch3 OscHayel ZayedNo ratings yet
- 2 ND UnitDocument3 pages2 ND UnitB.BijuNo ratings yet
- 4eceec8453 QB1Document11 pages4eceec8453 QB1Karuppaiah SNo ratings yet
- Acs - R15 Question Bit BankDocument20 pagesAcs - R15 Question Bit BankHariNagaRajaThotaNo ratings yet
- Mos II Unit 1Document9 pagesMos II Unit 1iploguNo ratings yet
- Em Cat 2Document4 pagesEm Cat 2சற்குணத்தமிழன் செNo ratings yet
- BEEEDocument2 pagesBEEEIts my VlogsNo ratings yet
- PHYS 102 - General Physics II Final Exam Solutions: Duration: 120 Minutes Wednesday, 22 May 2019Document4 pagesPHYS 102 - General Physics II Final Exam Solutions: Duration: 120 Minutes Wednesday, 22 May 2019Serkan Doruk HazinedarNo ratings yet
- Upsee Solution Paper 2 Set BaDocument15 pagesUpsee Solution Paper 2 Set BasachinNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Oscillators: X X X XDocument16 pagesSinusoidal Oscillators: X X X XRashid ShababNo ratings yet
- Interconnect and Packaging Lecture 3: Skin Effect: Chung-Kuan Cheng UC San DiegoDocument16 pagesInterconnect and Packaging Lecture 3: Skin Effect: Chung-Kuan Cheng UC San DiegoMustafa Berkan BİÇERNo ratings yet
- AIPMT Mains 2004 SolvedDocument17 pagesAIPMT Mains 2004 SolvedS A ABDUL SUKKURNo ratings yet
- 新版中興電機所100 111年歷試簡答Document31 pages新版中興電機所100 111年歷試簡答game davidNo ratings yet
- ET1006 Chapter15 RC Part 1Document21 pagesET1006 Chapter15 RC Part 1fastNo ratings yet
- A Summary of AVO and Inversion TechniquesDocument69 pagesA Summary of AVO and Inversion TechniquesriyadiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EM - MOD-1Document7 pagesQuestion Bank EM - MOD-1Zameen ShamjadNo ratings yet
- 24012017ii Btech Ece I Mid PDC Question BankDocument6 pages24012017ii Btech Ece I Mid PDC Question BankLakka Gopichandu100% (1)
- 20 Most Important Questions of Class 12Document39 pages20 Most Important Questions of Class 12Shrey ShreyNo ratings yet
- (I) (Ii) With (C) : (D) RzoDocument2 pages(I) (Ii) With (C) : (D) RzoRɩsʜʌv SɩŋʛʜNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03Document5 pagesAssignment 03Akshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31 Ee205Document14 pagesLecture 31 Ee205Muhammad hashimNo ratings yet
- Iae - I - Asm QPDocument2 pagesIae - I - Asm QPChristan LNo ratings yet
- Part-A Q. No Question(s) Skills CO: 34032 & Electrical Circuits and InstrumentationDocument2 pagesPart-A Q. No Question(s) Skills CO: 34032 & Electrical Circuits and InstrumentationDr.V.R.VelmuruganNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Advances in Quantum Electronics: Volume 3From EverandAdvances in Quantum Electronics: Volume 3D. W. GoodwinNo ratings yet
- AVI QB For Unit IDocument12 pagesAVI QB For Unit IFIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- L.N - Ra&i - Unit - 5Document13 pagesL.N - Ra&i - Unit - 5FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- ASI QB For Unit IIIDocument12 pagesASI QB For Unit IIIFIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- AVI QB For Unit IVDocument12 pagesAVI QB For Unit IVFIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- L.N - Ra&i - Unit - 1Document12 pagesL.N - Ra&i - Unit - 1FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- L.N - Ra&i - Unit - 2Document17 pagesL.N - Ra&i - Unit - 2FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- L.N - Ra&i - Unit - 4Document18 pagesL.N - Ra&i - Unit - 4FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- L.N - Ra&i - Unit - 3Document9 pagesL.N - Ra&i - Unit - 3FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Newton S Laws Ex1Document3 pagesNewton S Laws Ex1Ahmed ZakiNo ratings yet
- Citation Mustang-Air ConditioningDocument11 pagesCitation Mustang-Air Conditioningalejo.ramuzziNo ratings yet
- Scorpion's Coming of Age: Gripen E Flight Test Report L-159 ALCADocument100 pagesScorpion's Coming of Age: Gripen E Flight Test Report L-159 ALCAAnthony Van HamondNo ratings yet
- F135 StovlDocument2 pagesF135 Stovluma shankarNo ratings yet
- Rotorcraft Engine Type Certificate PDFDocument8 pagesRotorcraft Engine Type Certificate PDFsebastian becerraNo ratings yet
- Bjorns Corner Efficient Systems Part 2Document3 pagesBjorns Corner Efficient Systems Part 2upsasaNo ratings yet
- 6B Circular Motion & Gravitation 2020-2021Document46 pages6B Circular Motion & Gravitation 2020-2021RandominicNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of An Airfoil For Small Wind TurbinesDocument88 pagesDesign and Analysis of An Airfoil For Small Wind Turbinesaravindkumar030% (1)
- Air India AirlinesDocument2 pagesAir India Airlinestom jerryNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics of Ducted Re-Entry VehiclesDocument16 pagesAerodynamics of Ducted Re-Entry VehiclesDANUSH DATTHATHIREYAN KNo ratings yet
- Esarr 2 e 20 RiDocument30 pagesEsarr 2 e 20 RiΜαρία Ελευθεριαδου-ΖαντανίδουNo ratings yet
- Airframe, Vol.1 StructuresDocument707 pagesAirframe, Vol.1 Structuresronaldo fransiskusNo ratings yet
- 2011-03-16 B350 Efis 85 SopDocument53 pages2011-03-16 B350 Efis 85 SopLeonardo Santana100% (1)
- Airbus ISI 21.21.00011Document10 pagesAirbus ISI 21.21.00011Роман ДяченкоNo ratings yet
- CF6-80C2 Reliability Scorecards - Monthly - MAR2017-R1 PDFDocument68 pagesCF6-80C2 Reliability Scorecards - Monthly - MAR2017-R1 PDFFaraz Khan100% (1)
- Fighter Lead-In Training + Light Combat AircraftDocument17 pagesFighter Lead-In Training + Light Combat AircraftBryan Abad Jimenez100% (3)
- Hydrodynamic Point of View To Rudder Design PDFDocument11 pagesHydrodynamic Point of View To Rudder Design PDFRISHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Avleg - CASR Part 1Document20 pagesAvleg - CASR Part 1Fadil Arif BudimanNo ratings yet
- Start Up Space Supply Chain 2017Document40 pagesStart Up Space Supply Chain 2017Kamalanathan KasparNo ratings yet
- Ad 2016-18-01Document10 pagesAd 2016-18-01yuhusaNo ratings yet
- DCS M-2000C Flight Manual enDocument320 pagesDCS M-2000C Flight Manual enDave91No ratings yet
- F-16 Wing Structure LifecycleDocument4 pagesF-16 Wing Structure LifecyclenileshraneNo ratings yet
- Current Online CatalogDocument1 pageCurrent Online CatalogamandaNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172 DesignDocument20 pagesCessna 172 Designwillmike100% (2)
- Blackhawk - XP42 Engine Upgrade King Air 200 Series - BilingualDocument4 pagesBlackhawk - XP42 Engine Upgrade King Air 200 Series - BilingualjhNo ratings yet
- 752 Checklist V 0.6 Full PageDocument20 pages752 Checklist V 0.6 Full PageVasilis100% (1)
- Sample Private Pilot Asel Practical Test ScenarioDocument8 pagesSample Private Pilot Asel Practical Test ScenarioIbrahim MedNo ratings yet
- My Favourite Business LeaderDocument6 pagesMy Favourite Business Leadersheetal KhannaNo ratings yet
- SIE5632 SBLO-SBSP (12-Nov-2019) #1Document7 pagesSIE5632 SBLO-SBSP (12-Nov-2019) #1Luiz HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Oeb Tracking PolicyDocument7 pagesOeb Tracking PolicybarbarbiroUNo ratings yet