Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Visual Chart
Uploaded by
simiprince800 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis document summarizes sections from a chapter on polynomial arithmetic and word problems. It includes:
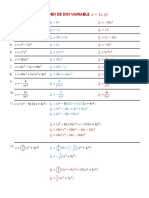
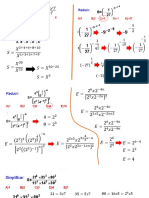
1) Definitions of polynomial parts like terms and examples of polynomials like a trinomial.
2) An example of long-hand polynomial division showing the process.
3) Examples of factoring techniques like perfect squares, sums/differences of cubes, and differences of squares.
4) An example word problem where variables are plugged in and the equation is set to equal 0 and factored to solve for the unknown value.
Original Description:
A chart for mathematics students
Original Title
Visual chart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes sections from a chapter on polynomial arithmetic and word problems. It includes:
1) Definitions of polynomial parts like terms and examples of polynomials like a trinomial.
2) An example of long-hand polynomial division showing the process.
3) Examples of factoring techniques like perfect squares, sums/differences of cubes, and differences of squares.
4) An example word problem where variables are plugged in and the equation is set to equal 0 and factored to solve for the unknown value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageVisual Chart
Uploaded by
simiprince80This document summarizes sections from a chapter on polynomial arithmetic and word problems. It includes:
1) Definitions of polynomial parts like terms and examples of polynomials like a trinomial.
2) An example of long-hand polynomial division showing the process.
3) Examples of factoring techniques like perfect squares, sums/differences of cubes, and differences of squares.
4) An example word problem where variables are plugged in and the equation is set to equal 0 and factored to solve for the unknown value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
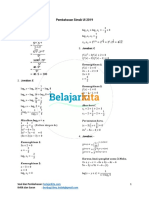
SECTION TOPIC DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES
5-1 Polynomial Polynomial Parts
Arithmetic Ex
−3𝑥 5𝑦 2 + 2𝑥 4 + 5 𝑇ℎ𝑟𝑒𝑒 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑠 = 𝑡𝑟𝑖𝑛𝑜𝑚𝑖𝑎𝑙
Leading term: −3𝑥5 5𝑦 2 • Leading coefficient: -3 • Degree: 7
5-2 Polynomial Long-hand
division (𝟖𝒙 3 − 𝟑𝟒𝒙 2 + 𝟒𝟑𝒙 − 𝟕𝟑) ÷ (𝟐𝒙 − 𝟕)
4𝑥 2 − 3𝑥 + 11
2𝑥 − 7 8𝑥 3− 34𝑥2 + 43𝑥 – 73
8𝑥 3 − 28𝑥 2
−6𝑥 2 + 43𝑥
−6𝑥 2 + 21𝑥
22𝑥 − 73
22𝑥 – 77
4
2
4𝑥 − 3𝑥 + 11 + 4/ 2𝑥 − 7
5-3 Factoring Perfect Square Sum/Diff of cubes
𝑎 2 + 2𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏2 = (𝑎 + 𝑏)2 𝑎3 ± 𝑏3 = (𝑎 ± 𝑏)(𝑎2 ∓ 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏2 )
Example: 49𝑥2 − 56𝑥 + 16= (7𝑥 − 4)2 Example
27𝑥3 − 512
Diff of Squares (3𝑥)3 – 83
𝑎2 – 𝑏2 = (𝑎 − 𝑏)(𝑎 + 𝑏) (3𝑥 − 8)(9𝑥2 + 24𝑥 + 64)
25𝑥2 − 49 =(5𝑥 − 7)(5𝑥 + 7)
5-5 Word Formulas
Problems • Plug in the given data
• Get = 0, Factor, etc. Example
The profit of a small company when they make x thingamabobs is 𝑷 = 𝟐𝒙 2 − 𝟏𝟕𝒙.
How many will they need to make to get a profit of $30?
30 = 2𝑥2 − 17𝑥
0 = 2𝑥2 − 17𝑥 – 30
0 = 2𝑥2 − 20𝑥 + 3𝑥 – 30
0 = 2𝑥(𝑥 − 10) + 3(𝑥 − 10)
0 = (2𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 − 10)
𝑥 = − 3 /2, 𝑥 = 10
𝑇ℎ𝑒𝑦 𝑚𝑢𝑠𝑡 𝑚𝑎𝑘𝑒 10 𝑡𝑜 ℎ𝑎𝑣𝑒 𝑎 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡 𝑜𝑓 $30.
Example 2
A box has a height of 3 in. Its length is two inches longer than its width. If it has a
total surface area of 𝟐𝟐𝟐 𝒊𝒏2 , what are the dimensions?
ℎ = 3 𝑙 = 𝑤 + 2 𝑆𝐴 = 2ℎ𝑙 + 2𝑙𝑤 + 2ℎw,= 222 = 2 ⋅ 3(𝑤 + 2) + 2(𝑤 + 2)𝑤 + 2 ⋅ 3w
222 = 6𝑤 + 12 + 2𝑤2 + 4𝑤 + 6w= 0 = 2𝑤2 + 16𝑤 − 210 0 = 2(𝑤2 + 8𝑤 − 105) 0 = 2(𝑤
+ 15)(𝑤 − 7)
𝑤 = −15
𝑤 = 7 𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑑𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠 𝑎𝑟𝑒 3 𝑖𝑛, 7 𝑖𝑛, 𝑎𝑛𝑑 9 𝑖𝑛.
You might also like
- Dissonant Heritage. The Management of The Past As A Resource in Conflict. J.E. Tunbridge and G.J. AshworthDocument305 pagesDissonant Heritage. The Management of The Past As A Resource in Conflict. J.E. Tunbridge and G.J. AshworthFRANCISCO ALBERTO DE LA ROSA MANJARREZ100% (1)
- Matrices 1. Escribir Explícitamente Las Siguientes MatricesDocument4 pagesMatrices 1. Escribir Explícitamente Las Siguientes MatricesJhoel Yoplac ChávezNo ratings yet
- Evaluación de LogaritmosDocument6 pagesEvaluación de LogaritmosMiguel MonasterioNo ratings yet
- Simak UI 2019 Matdas Bagian 1Document2 pagesSimak UI 2019 Matdas Bagian 1God UsouppNo ratings yet
- L PretestDocument2 pagesL PretestMartyn PereiraNo ratings yet
- XXxrolfuzxXX Algebra TRPR 2Document22 pagesXXxrolfuzxXX Algebra TRPR 2Rolando BozasNo ratings yet
- Soal CCM MTK 2017Document7 pagesSoal CCM MTK 2017MarfiNo ratings yet
- Review For Prelim in BascalDocument12 pagesReview For Prelim in Bascaljoreza.diazNo ratings yet
- 10ENG - 2023 - T2b - Grade 10 - SolutionsDocument86 pages10ENG - 2023 - T2b - Grade 10 - SolutionsAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SSC-I Solution of 2nd Set Model Question PaperDocument10 pagesMathematics SSC-I Solution of 2nd Set Model Question PaperFaisal SamiNo ratings yet
- Progress Exercises 1 - MathDocument4 pagesProgress Exercises 1 - MathStefani VeronikaNo ratings yet
- Progress Exercises 1.1: Revision On BasicsDocument4 pagesProgress Exercises 1.1: Revision On BasicsStefani VeronikaNo ratings yet
- Límites EAODocument20 pagesLímites EAOLuis Manuel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Calculo Diferencial Actividad 3. Derivación de Orden Superior e Implícita Héctor Paniagua Flores ES172011207 LT-LCDI-1902-B1-002Document6 pagesCalculo Diferencial Actividad 3. Derivación de Orden Superior e Implícita Héctor Paniagua Flores ES172011207 LT-LCDI-1902-B1-002hectorNo ratings yet
- PART P02 - SaintekDocument43 pagesPART P02 - SaintekHadi NursyamNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Solutions - Algebra, Equations and Inequalities - 2020-2Document9 pagesWorksheet Solutions - Algebra, Equations and Inequalities - 2020-2Shinyi GohNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tambahan: Modul Mas (Minimum Adequate Syllabus) SPM 2019Document37 pagesMatematik Tambahan: Modul Mas (Minimum Adequate Syllabus) SPM 2019Jinny NeutrollNo ratings yet
- MethodsDocument3 pagesMethodsbrosreaperNo ratings yet
- Adma G.C.E P1 2020 SolutionsDocument11 pagesAdma G.C.E P1 2020 SolutionsChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Linear EquationDocument1 pageSimultaneous Linear EquationAaranaNo ratings yet
- PM-Bracket Removal and Factorisation PDFDocument5 pagesPM-Bracket Removal and Factorisation PDFfifak44760No ratings yet
- Memo Maths Grade 11 Test 1 March 2024Document5 pagesMemo Maths Grade 11 Test 1 March 2024abuttieymadumaneNo ratings yet
- N2 Mathematics EX 1 MemoDocument2 pagesN2 Mathematics EX 1 MemoAnesu MasirahaNo ratings yet
- 2022 TEST 2 SOLUTION INTEGRATION (PURE MATHEMATICS) ShareDocument7 pages2022 TEST 2 SOLUTION INTEGRATION (PURE MATHEMATICS) SharenomoszengNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Solving Equations Module Review SolutionsDocument6 pagesFactoring and Solving Equations Module Review SolutionsElaine zhuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 11 Revision - Memo Term 1 - 2023Document11 pagesMathematics Grade 11 Revision - Memo Term 1 - 2023ora mashaNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio 14, 15Document16 pagesLaboratorio 14, 15Piero Sebastian ParedesNo ratings yet
- Produtos Notáveis e Fatoração PDFDocument7 pagesProdutos Notáveis e Fatoração PDFRobério BacelarNo ratings yet
- Tarea 11 PDFDocument4 pagesTarea 11 PDFJuan Daniel Ferrer ReyesNo ratings yet
- G11-GenMath FinalsExamDocument24 pagesG11-GenMath FinalsExambrgy.agdaoproper2023No ratings yet
- MATH05 PT2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesMATH05 PT2 ReviewerLum JakNo ratings yet
- Materi LesDocument23 pagesMateri LesyennyNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Ans)Document10 pagesDifferentiation (Ans)MARCUS MSLCNo ratings yet
- SOLUCIONARIODocument8 pagesSOLUCIONARIOLuz mery Juárez chinchaiNo ratings yet
- Taller 3 Octava Parte Del 1 Al 12Document1 pageTaller 3 Octava Parte Del 1 Al 12Osmal MoránNo ratings yet
- Universitaria Virtual Internacional: Hecho PorDocument6 pagesUniversitaria Virtual Internacional: Hecho PoryurleyNo ratings yet
- Gr10t1 Exponents Expontential EquationsDocument3 pagesGr10t1 Exponents Expontential EquationsFonNo ratings yet
- PM RationalExpressions PDFDocument1 pagePM RationalExpressions PDFfifak44760No ratings yet
- Unidad 8Document14 pagesUnidad 8Ernesto MaxNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 8 - Higher Order Derivatives - With SamplesDocument16 pagesLECTURE 8 - Higher Order Derivatives - With SamplesJulius CodiamatNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Haidar - 2B - MTKDocument3 pagesAhmad Haidar - 2B - MTKMass KefinnNo ratings yet
- Justificaciones CG M Geometria AnaliticaDocument20 pagesJustificaciones CG M Geometria AnaliticaKhris AndrNo ratings yet
- Derivative Handout 2021 GR 11engineeringDocument14 pagesDerivative Handout 2021 GR 11engineeringDevin Jonathan ThedyNo ratings yet
- Derivacion Implicita2Document12 pagesDerivacion Implicita2Dr. Daniel ArizmendiNo ratings yet
- U4 Problemario1 de DerivadasDocument2 pagesU4 Problemario1 de DerivadasFrida IbarraNo ratings yet
- Tugas Matematika TeknikDocument3 pagesTugas Matematika TeknikPutri AliyyahNo ratings yet
- 3Rd Quarter Performance Task Faith Catholic School Stem Grade 11Document5 pages3Rd Quarter Performance Task Faith Catholic School Stem Grade 11Mark Reynier De VeraNo ratings yet
- BTMG 511 Assignment 1 Due Date 13-5-2022Document3 pagesBTMG 511 Assignment 1 Due Date 13-5-2022TshwaneloNo ratings yet
- De Gala GuiwanDocument10 pagesDe Gala GuiwanRhofel IbañezNo ratings yet
- Mastery Notes 01 MESLDocument6 pagesMastery Notes 01 MESLMarlo SertimoNo ratings yet
- Mate 2Document4 pagesMate 2Bryhan Padillo cuevaNo ratings yet
- General Differentiation Formula 1. Derivative of A Constant ( ) 0Document10 pagesGeneral Differentiation Formula 1. Derivative of A Constant ( ) 0anon_422073337No ratings yet
- 11 Practice Test MemoDocument4 pages11 Practice Test Memoburtontris23No ratings yet
- Maths Class10 Worksheet5Document8 pagesMaths Class10 Worksheet5ssainani1965No ratings yet
- Practica Resuelve Por FactorizaciónDocument17 pagesPractica Resuelve Por FactorizaciónLee HansonNo ratings yet
- Coba Ini-DigabungkanDocument8 pagesCoba Ini-DigabungkanEvelyn Selina Belva Sable SihonoNo ratings yet
- Algebra Pre Test Solutions Cal 1 ModuleDocument8 pagesAlgebra Pre Test Solutions Cal 1 Modulekyledarbymanalo1437No ratings yet
- DerivadasDocument4 pagesDerivadasDiogo LimonesNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Action Research On Spelling AbilityDocument7 pagesAction Research On Spelling AbilityCiedelle Honey Lou Dimalig100% (1)
- The Influence of The Integrated Marketing Communication On The Consumer Buying Behaviour PDFDocument5 pagesThe Influence of The Integrated Marketing Communication On The Consumer Buying Behaviour PDFPrimaGriseldaNo ratings yet
- Space TelescopesDocument141 pagesSpace TelescopesPat StakemNo ratings yet
- Cochin University of Science & Technology: KOCHI-682022Document5 pagesCochin University of Science & Technology: KOCHI-682022navinNo ratings yet
- Cryptool Lab f05Document6 pagesCryptool Lab f05Vanesa Daza50% (2)
- Create Database Oracle DatabaseDocument18 pagesCreate Database Oracle DatabaseBackhamla MichividNo ratings yet
- 5 Reception and Hospitality: The Importance of ReceptionDocument12 pages5 Reception and Hospitality: The Importance of ReceptionBryan JamaludeenNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 3 Clouds WeatherDocument3 pagesScience Lesson 3 Clouds Weatherapi-636459501No ratings yet
- Improving Efficiency Thru ModellingDocument5 pagesImproving Efficiency Thru ModellingAli AliNo ratings yet
- Siprotec 4 Und Siprotec Compact: Service Information FirmwareupdateDocument45 pagesSiprotec 4 Und Siprotec Compact: Service Information FirmwareupdateAbhishek RajputNo ratings yet
- 3 CPCCCM2001A Student Learning GuideDocument60 pages3 CPCCCM2001A Student Learning GuideAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kirlosker Working Capital ManagementDocument81 pagesKirlosker Working Capital ManagementShamseer UmmalilNo ratings yet
- Compressed Earth Blocks PDFDocument15 pagesCompressed Earth Blocks PDFPrashanth Penta ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nilp Education Gov in Nilp About UsDocument2 pagesNilp Education Gov in Nilp About UsH1190506M2009No ratings yet
- EnglishexamDocument10 pagesEnglishexamSushant YadavNo ratings yet
- Ba40-Ba80-Ba160 Anten RFI OmniDocument1 pageBa40-Ba80-Ba160 Anten RFI OmniBao Quoc MaiNo ratings yet
- AN2799 Application Note: Measuring Mains Power Consumption With The STM32x and STPM01Document14 pagesAN2799 Application Note: Measuring Mains Power Consumption With The STM32x and STPM01am1liNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.1 Chapter 2 - Word Classes - Ballard, Kim. 2013. The Frameworks of English. - ReadDocument37 pagesUnit 2.1 Chapter 2 - Word Classes - Ballard, Kim. 2013. The Frameworks of English. - ReadJoão FreitasNo ratings yet
- Service Note Replacement of - High-Pass Filter Board - Rev001 - 2011-07-11Document3 pagesService Note Replacement of - High-Pass Filter Board - Rev001 - 2011-07-11Dinesh SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 5 Group 4Document31 pagesChapter 1 5 Group 4John Patrick TurgoNo ratings yet
- FS Data - NIC0020 - Anhydro Evaporator v002Document6 pagesFS Data - NIC0020 - Anhydro Evaporator v002john kenneth vasquez vasquezNo ratings yet
- HRACM Assignment III - Infosys Case StudyDocument4 pagesHRACM Assignment III - Infosys Case Studysupriya sonkusareNo ratings yet
- TWB in Prop BundlesDocument4 pagesTWB in Prop BundlesEleazarNo ratings yet
- Lista de Peças de Reposição: R902470249 R910992439 Desenho: Número Do MaterialDocument11 pagesLista de Peças de Reposição: R902470249 R910992439 Desenho: Número Do MaterialMarcus PereiraNo ratings yet
- LogDocument1,025 pagesLogAkmal Al AzamNo ratings yet
- Art of Solving Business Problems The Data Science Way Shweta Doshi DileepDocument75 pagesArt of Solving Business Problems The Data Science Way Shweta Doshi DileepSreekanth AkulaNo ratings yet
- Brain Controlled Car For Disabled Using AiDocument21 pagesBrain Controlled Car For Disabled Using AiS.T KAUSALYAA100% (1)
- IELTS Writing Task #2: Two-Part QuestionDocument16 pagesIELTS Writing Task #2: Two-Part QuestionMirayya AidarovaNo ratings yet
- Canvass Form BlankDocument21 pagesCanvass Form Blankjertin0% (1)