Professional Documents
Culture Documents
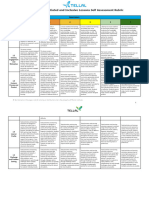
Rigour - & - Relevance - Rubric - QAT - FIS - Rigour - & - Relevance - Rubric - v4 - FINAL
Uploaded by
Horizon BeyondOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rigour - & - Relevance - Rubric - QAT - FIS - Rigour - & - Relevance - Rubric - v4 - FINAL
Uploaded by
Horizon BeyondCopyright:
Available Formats
Relevance Rubric
Support teachers in building effective instruction based on relevance of experiences to learners. The three indicators for relevance are: meaningful work, authentic resources,
and learning connections.
Meaningful Work
Lesson requires students
to complete relevant, real-
world tasks that connect 1 – Beginning 2 – Emerging 3 – Developed 4 – Well Developed
to tasks typically
completed in related
careers
Student Learning • Student work is procedural and • Students think critically about content • Students think critically about content • Students think and act critically to
structured, reflecting a basic and apply information learned to and apply information learned to curate content and apply information
understanding of information learned address a specific task. address a range of cross-disciplinary learned to address a range of cross-
during the lesson/unit. • Student work demonstrates tasks. Student work demonstrates disciplinary tasks which are both
B1S • Student work focuses on class- originality. creativity and originality. creative and original.
specific content, with an emphasis on • Student work requires application of • Student work requires real-world • Student work requires the ability to
building skills, developing knowledge learned during the predictable and/or unpredictable select, organize, and present content
comprehension, or other foundational lesson/unit. application that has a direct connection through relevant products with multiple
skills. to a career in the related field of study. solutions.
Teacher Actions • (Captivate) Teacher states some • (Captivate) Teacher models for • (Captivate) Teacher models for • (Captivate) Teacher encourages
relavant ATL Skills and makes limited students to think critically using students to think critically using students to independently think
interdisciplinary connections relavant ATL Skills and makes some relavant ATL Skills and makes range of critically using relavant ATL Skills and
• (Challenge) Teacher provides limited interdisciplinary connections interdisciplinary connections makes meaningful interdisciplinary
B1T support for students in being able to • (Challenge) Teacher supports students • (Challenge) Teacher supports students connections
make real world scenario connections to in being able to make superficial real in being able to make real world • (Challenge) Teacher encourages
content studied. world scenario connections to content scenario connections to content studied. students in being able to independently
studied. make real world scenario connections to
content studied.
Authentic Resources:
Lesson includes a range of
sources of information and
requires students to use 1 – Beginning 2 – Emerging 3 – Developed 4 – Well Developed
information from sources
with relevant, real-world
tasks.
Student Learning • Students mainly engage with one • Students engage with one primary • Students engage with multiple sources • Students engage with multiple sources
source of information for the lesson source of information for the lesson of information, both primary and of information, both primary and
and/or unit. and/or unit, and use secondary, during a lesson/unit. secondary, during a lesson/unit,
B2S • Students use one source to complete secondaryresources to support it. • Students use multiple sources of including multi-format resources.
tasks focused on making simple • Students use one or more sources to information to complete real-world • Students select and use a variety of
connections to content. complete real-world tasks focused on tasks involving comparisons, analysis, resources to solve predictable or
making simple connections tocontent. argument, and research. unpredictable real-world scenarios.
Learning Connections:
Lesson includes a variety
of opportunities for
students to make 1 – Beginning 2 – Emerging 3 – Developed 4 – Well Developed
connections between what
they are learning and real-
world applications.
Student Learning • Students seldom have the opportunity • Students occasionally engage in • Students engage in content that has • Students discover opportunities to
to engage in content that has explicit content that has explicit connection to explicit connections to real- apply content to their lives as well as
connection to real-world application. real-world application. worldapplications. real-world application.
• Some students may attempt to make • Some students begin to articulate the • Students clearly articulate the • Students independently make
B3S
connections between content learned connections between content learned connections between content learned thoughtful connections between content
and real-world application, but these and real-world application. and real-world application. learned and real-world unpredictable
connections are volunteered rather than situations.
included as part of the lesson.
Teacher Actions • (Consolidate) Teacher reviews and • (Consolidate) Teacher occasionally • (Consolidate) Teacher reviews and • (Consolidate) Teacher encourages
summarises what has been taught at reviews and summarises what has been summarises what has been taught at students to independently summarise
the end of each lesson taught at the end of each lesson, the end of each lesson, highlighting what has been taught at the end of
• (Consolidate) Teacher explains stating relationships between ideas and relationships between ideas and real each lesson, and to highlight
connections between current lessons, real world application world application relationships between ideas and real
and previous learned facts • (Consolidate) Teacher encourages • (Consolidate) Teacher explains world application
• (Captivate) Teacher provides limited some students to make connections connections between current lessons, • (Consolidate) Teacher encourages
opportunities to convey the relevance or between current lessons, and previous and previous learned facts, concepts, students to identify connections
importance of key facts and learned facts, and relationship to real skills and relationship to real world between current lessons, and previous
relationship to real world application world application application learned facts, concepts, skills and
B3T
• (Captivate) Teacher provides limited • (Captivate) Teacher sometimes • (Captivate) Teacher conveys the relationship to real world application
opportunities to highlight the ways the conveys the relevance or importance of relevance or importance of key facts • (Captivate) Teacher encourages
lessons can contribute to their lives key facts and relationship to real world ideas, concepts and skills and students tomake thouyghtful
application relationship to real world application connections to the relevance or
• (Captivate) Teacher sometimes • (Captivate) Teacher highlights the importance of key facts ideas, concepts
highlights the ways the lessons can ways trhe lessons can contribute to and skills and relationship to real world
contribute to their lives their lives application
• (Captivate) Teacher encourages
students to highlights the ways the
lessons can contribute to their lives
Learner Engagement Rubric
Support teachers in creating and implementing an effective learner environment that is engaging and aligned to learner needs. The three indicators for learner engagement
are: active participation, learning environment, and formative processes and tools.
Active Participation:
Lesson is designed to
maximize engagement of 1 – Beginning 2 – Emerging 3 – Developed 4 – Well Developed
all students throughout
the duration of the lesson.
Student Learning • Limited student engagement, with the • Most students remain focused and on- • All students remain on-task, • All students remain on-task and
exception of hand-raising. Some task during the lesson. Students answer responding to frequent opportunities for proactively engaged throughout the
students are off-task or have questions when asked, but not all active engagement throughout the lesson.
disengaged from the lesson and arenot students have the opportunity to lesson. • Students take ownership of learning
C1S
redirected. actively respond. • Lesson is led by both teacher and new content, actively seeking ways to
• Lesson is teacher led and students • Lesson is led by the teacher, and students, and students productively improve their own performance.
progress through new learning with students productively progress through progress through new learning.
some challenges with productivity. new learning.
Teacher Actions Facilitating Active Participation Facilitating Active Participation Facilitating Active Participation Facilitating Active Participation
• (Captivate) Teacher uses a limited • (Captivate) Teacher uses a variety of • (Captivate) Teacher uses a variety of • (Captivate) Teacher uses a variety of
methods for promoting interaction methods for promoting interaction methods for promoting interaction methods for promoting interaction
amongst few students as they engage amongst some students as they engage amongst most students as they engage amongst all students as they engage
with ideas and materials with ideas and materials with ideas and materials with ideas and materials
• (Captivate) Teacher uses limited • (Captivate) Teacher uses simulations • (Captivate) Teacher uses simulations • (Captivate) Teacher uses simulations
simulations or interactive online or interactive online activities to engage or interactive online activities to engage or interactive online activities to engage
activities to engage few students in some students in learning most students in learning all students in learning
learning • (Captivate) Teacher provides • (Captivate) Teacher provides • (Captivate) Teacher provides
• (Captivate) Teacher provides few opportunities for some students to use opportunities for most students to use opportunities for all students to use
opportunities for few students to use digital tools to explore, create and digital tools to explore, create and digital tools to explore, create and
digital tools to explore, create and communicate both indvidually and communicate both indvidually and communicate both indvidually and
CT1 communicate both indvidually and collaboratively collaboratively collaboratively
collaboratively • (Consolidate) Teacher asks students • (Consolidate) Teacher asks most • (Consolidate) Teacher asks students
• (Consolidate) Teacher provides limited to reflect on what they have learned students to reflect on what they have to reflect on what they have learned
opportunitis for students to reflect on and how they can improve their own learned and how they can improve their and how they can improve their own
what they have learned and how they performance own performance performance
can improve their own performance • (Confer) Teacher incorporates some • (Confer) Teacher incorporates • (Confer) Teacher incorporates
• (Confer) Teacher attempts to interactive practices like reciprocal relevant interactive practices like relevant interactive practices like
incorporates interactive practices like teaching, collaborative problem solving reciprocal teaching, collaborative reciprocal teaching, collaborative
reciprocal teaching, collaborative and peer feedback problem solving and peer feedback problem solving and peer feedback
problem solving and peer feedback
Learning Environment:
Classroom environment is
centered around a culture 1 – Beginning 2 – Emerging 3 – Developed 4 – Well Developed
of respect and
commitment to learning.
Student Learning • Students rely on peers or teacher for • Students exhibit some evidence that • Students are encouraged to take risks • Students are encouraged to take risks
answers to questions. There is a lack of they are beginning to take risks and and persevere through productive and persevere through productive
evidence of students being required to persevere in learning rigorous content. struggle. Students are praised for struggle. Students are provided with
persevere in responding to rigorous • Students demonstrate respect for the demonstrating commitment to learning. effective feedback to guide them in their
C2S
tasks or questions. learning environment, but challenges • Students demonstrate respect for learning.
• Students demonstrate a lack of exist in demonstrating respect for peers, teacher, and the learning • Students demonstrate respect for
respect for peers, teacher, and/or peers. environment. peers, teacher, and the learning
learning environment. environment.
Teacher Actions Managing Activities Managing Activities Managing Activities Managing Activities
Positive, and purposeful • (Classroom Management) Teacher • (Classroom Management) Teacher • (Classroom Management) Teacher • (Classroom Management) Teacher
atmosphere created states, routines and strategies to explains, and sometimes models and explains, models and implement consistently explains, models and
through effective use of systematise classroom processes implement routines and strategies to routines and strategies to systematise implement routines and strategies to
the 7C's of Effective • (Classroom Management) Teacher systematise classroom processes classroom processes systematise classroom processes,
Teaching: attempts to ensure that activities run • (Classroom Management) Teacher • (Classroom Management) Teacher • (Classroom Management) Teacher
Care, Confer, Captivate, smoothly, but does not manage sometimes ensures that some activities often ensures that activities run consistently ensures that activities run
Clarify, Consolidate, interrruptions and transitions run smoothly due to materials being smoothly due to materials being readily smoothly due to materials being readily
Classroom Management • (Care) Teacher attempts to foster a readily accessible and time being accessible and time being managed accessible and time being managed
culture that encourages students to managed effectively, including during effectively, including during effectively, including during
seek and accept help, and persevere interrruptions and transitions interrruptions and transitions for most interrruptions and transitions
• (Care) Teacher fosters a culture that students • (Care) Teacher fosters a culture that
Managing Behaviour encourages some students to seek and • (Care) Teacher fosters a culture that encourages all students to seek and
• (Classroom Management) Teacher accept help for some students encourages most students to seek and accept help, for all students
states routines and strategies related to accept help, for most students
eliciting positive behaviour, but these Managing Behaviour Managing Behaviour
are not followed through consistently • (Classroom Management) Teacher Managing Behaviour • (Classroom Management) Teacher
C2T
• (Classroom Management) Teacher explains, and sometimes models and • (Classroom Management) Teacher consistently explains, models and
states needs for high standards for implement routines and strategies that explains, models and implement implement routines and strategies that
student conduct, but is not consistent in elicit positive behaviour routines and strategies that elicit elicit positive behaviour
holding students to account in a fair and • (Classroom Management) Teacher positive behaviour • (Classroom Management) Teacher
consistent way states need for high standards for • (Classroom Management) Teacher establishes and consistently encourages
• (Challenge) Teacher requires few student conduct, coaches students on establishes and regularly encourages high standards for student conduct,
students to try hard, expecially those how to meet those standards. high standards for student conduct, coaches students on how to meet those
who may be disengaged • (Challenge) Teacher requires some coaches students on how to meet those standards, and holds students to
• (Challenge) Teacher attempts students to try hard, expecially those standards, and holds students to account in a fair and consistent manner
communicates that when work is who may be disengaged account in a fair and consistent manner • (Challenge) Teacher consistently
difficult, effort and persistence lead to • (Challenge) Teacher sometimes • (Challenge) Teacher requires most requires all students to try hard,
personal growth and ultimate success communicates that when work is students to try hard, expecially those expecially those who may be
difficult, effort and persistence lead to who may be disengaged disengaged
personal growth and ultimate success • (Challenge) Teacher regularly • (Challenge) Teacher consistently
communicates that when work is communicates that when work is
difficult, effort and persistence lead to difficult, effort and persistence lead to
personal growth and ultimate success personal growth and ultimate success
Formative Processes and
Tools:
Lesson is tailored to meet
the needs of all students,
including using results
1 – Beginning 2 – Emerging 3 – Developed 4 – Well Developed
from formative tools and
processes to plan for
differentiated instruction.
Student Learning • Lesson includes few instances of • Students demonstrate mastery of • Students demonstrate mastery of • Students demonstrate mastery of
formative assessment to evaluate content by engaging in formative content by completing a variety of content through opportunities to self-
students’ mastery of content. assessments that allow for reciprocal formative assessments that allow for reflect, set learning goals, and share
Assessment results indicate that student feedback. Assessment results indicate reciprocal feedback. Assessment results responsibility for their learning.
growth is minimal. that student growth is progressing. indicate that students are meeting • Assessment results indicate that
C3S • Students are partnered or grouped, • Students are partnered or grouped expectations. students are exceeding expected
but all students receive the same lesson and receive some opportunities for • Students are strategically partnered or outcomes.
content, process, and product. differentiated learning based on grouped based on data. Lesson content,
adjusting content, process, and/or process, and/or product is clearly
product. differentiated to support varying and
specific student needs.
Teacher Actions • The AfLT if present, refers only to • The lesson ends with an AfLT, like a • The AfLT effectively summary / • Building on AfLT through the lesson,
1. AfL Using evidence what has been done and does not summary / plenary; reference is made plenary the learning; examples of work the Learning Objectives are extended;
about students' provide an opportunity to reflect on the to the Learning Objectives and Success that exemplify the Learning Objectives students articulate and communicate
knowledge, understanding learning. No exit plenary is conducted Criteria. and Success Criteria are shared; their learning; wider implications and
and skills to inform their students are actively involved, including links are clarified; links made to future
teaching. Sometimes group/peer/self evaluation. learning through summary / plenary
referred to as ‘formative Checking for Understanding
assessment', it usually • (Clarify) Teacher monitors student Checking for Understanding Checking for Understanding Checking for Understanding
occurs throughout the work • (Clarify) Teacher sometimes checks • (Clarify) Teacher often checks • (Clarify) Teacher checks regularly for
teaching and learning • (Challenge) Teacher does not for understanding using techniques such regularly for understanding using understanding using techniques such as
process to clarify student differentiate instructions to provide as questioning, quizzes, exit slips and techniques such as questioning, questioning, quizzes, exit slips and
learning and appropriate levels of challenge for monitoring some studenta work quizzes, exit slips and monitoring monitoring student work
understanding. students at different skill levels • (Clarify) Teacher sometimes asks student work • (Clarify) Teacher asks all students to
2. AoL Students are their • (Challenge) Teacher attempts to some students to check their work • (Clarify) Teacher often asks students check their work against rubric or
own assessors. Students differentiate instructions to provide against peers to check their work against rubric or exemplars
monitor their own appropriate levels of challenge for • (Challenge) Teacher begins to exemplars • (Clarify) Teacher consistently
learning, ask questions students at different skill levels differentiate instructions to provide • (Clarify) Teacher often surfaces surfaces misunderstandings and
C3T and use a range of appropriate levels of challenge for misunderstandings and addresses them addresses them effectively.
strategies to decide what Providing Constructive Feedback students at different skill levels effectively. • (Challenge) Teacher consistently
they know and can do, and • (Clarify) Teacher provides feedback • (Challenge) Teacher often differentiates instructions to provide
how to use assessment for on student work, but not linked to Providing Constructive Feedback differentiates instructions to provide appropriate levels of challenge for
new learning. standards and established criteria for • (Clarify) Teacher provides somewhat appropriate levels of challenge for students at different skill levels
3. AaS Using evidence of success specific, descriptive, concise feedback students at different skill levels
student learning to assess • (Clarify) Teacher feedback on work on student work, linked to standards Providing Constructive Feedback
achievement against focuses on supporting students' and established criteria for success Providing Constructive Feedback • (Clarify) Teacher provides specific,
outcomes and standards. academic performance • (Clarify) Teacher feedback on work • (Clarify) Teacher often provides descriptive, concise feedback on student
• (Clarify) Teacher attempts to sometimes focuses on supporting specific, descriptive, concise feedback work, linked to standards and
customise feedback on students' work students' academic performance on student work, linked to standards established criteria for success
to guide their next steps • (Clarify) Teacher sometimes and established criteria for success • (Clarify) Teacher feedback on work
customises feedback on students' work • (Clarify) Teacher feedback on work always focuses on supporting students'
to guide their next steps often focuses on supporting students' thinking and self directed problem
academic performance solving
• (Clarify) Teacher is able to customise • (Clarify) Teacher consistently
feedback on students' work to guide customises feedback on students' work
their next steps to guide their next steps
You might also like
- ROJO - Teachers and Students in The Digital AgeDocument2 pagesROJO - Teachers and Students in The Digital AgeESTHER ROSE ROJONo ratings yet
- Project-Based and Problem-BasedDocument21 pagesProject-Based and Problem-BasedJocel EngcoNo ratings yet
- Element Checklist For MYP Unit Planners: Does The Unit Include The Following?Document8 pagesElement Checklist For MYP Unit Planners: Does The Unit Include The Following?Shantha KundapuraNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Teacher Names: Sean, Sebastian, JavierDocument5 pagesObjectives: Teacher Names: Sean, Sebastian, Javierapi-351842671No ratings yet
- BPS Teacher Rubrics PDFDocument50 pagesBPS Teacher Rubrics PDFFazal NiaziNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Integrating New Literacies in The Curriculum: Nicole Beatriz C. CalacalDocument51 pagesModule 4: Integrating New Literacies in The Curriculum: Nicole Beatriz C. CalacalKhristel Alcayde50% (2)
- Technology Integration Jfites PresentationsDocument2 pagesTechnology Integration Jfites Presentationsapi-349408841No ratings yet
- Instructional Competence CriteriaDocument6 pagesInstructional Competence CriteriaJoan Ong-BayaniNo ratings yet
- Continuum PracticeDocument18 pagesContinuum PracticeSaid HbadNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 MergedDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 MergedAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Curriculum AssessmentDocument30 pagesCriteria For Curriculum AssessmentMissia H. Sabtal67% (3)
- DLL APP3 Q4 Week 1Document5 pagesDLL APP3 Q4 Week 1milane pradiaNo ratings yet
- Tabing RpmsDocument1 pageTabing RpmsEric John Vegafria100% (3)
- Week 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Document22 pagesWeek 6 - Unit 5.1: Learning Processes: Curriculum and Course Design - PER 3260Alexandra Bachero BeltránNo ratings yet
- Self Reflection Rubric TeacherDocument7 pagesSelf Reflection Rubric TeacherRo MyNo ratings yet
- 20.teacher Centered Vs Learner Centered ParadigmsDocument2 pages20.teacher Centered Vs Learner Centered ParadigmsManisha Pachauri100% (1)
- 20.teacher Centered Vs Learner Centered Paradigms PDFDocument2 pages20.teacher Centered Vs Learner Centered Paradigms PDFJanine PalizaNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Assessment of InstructionDocument16 pagesCriteria For Assessment of InstructionChebel LiedrugNo ratings yet
- Field Study 2 Episode 5Document6 pagesField Study 2 Episode 5Nenen LugoNo ratings yet
- 3 Column TableDocument6 pages3 Column Tableapi-607566496No ratings yet
- Evaluating MYP Rubrics in WORDDocument11 pagesEvaluating MYP Rubrics in WORDJoseph VEGANo ratings yet
- Technology Integration-PortfolioDocument3 pagesTechnology Integration-Portfolioapi-404362749No ratings yet
- 1.0 Teaching AND Learning.: ObjectivesDocument12 pages1.0 Teaching AND Learning.: ObjectivesEric KisiluNo ratings yet
- Teaching Differentiated and Inclusive Lessons Self Assessment RubricDocument2 pagesTeaching Differentiated and Inclusive Lessons Self Assessment Rubricsoumia shineNo ratings yet
- Option 2: Insiders - Instructional Design For A Real StudentDocument4 pagesOption 2: Insiders - Instructional Design For A Real StudentsherrymiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Student-Centered Learning and Philosophies of Teaching PracticesDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Student-Centered Learning and Philosophies of Teaching PracticesFikri Arvitesar IINo ratings yet
- Technology Integration-Portfolio Tel 311Document2 pagesTechnology Integration-Portfolio Tel 311api-383729824No ratings yet
- I ObjectivesDocument2 pagesI ObjectivesBlessed Joy PeraltaNo ratings yet
- FIELD STUDY 2 LEARNING EPISODE 11 Delivering My Lesson PlanDocument13 pagesFIELD STUDY 2 LEARNING EPISODE 11 Delivering My Lesson PlanJayrel Fabrero100% (1)
- Module 2-Lyka Marasigan (2a3)Document23 pagesModule 2-Lyka Marasigan (2a3)Jane Bermoy100% (1)
- Admin - Lesson Plan GuidelinesDocument4 pagesAdmin - Lesson Plan GuidelinesDamion BrusselNo ratings yet
- PLP Powerful Literacy Instructional PracticesDocument2 pagesPLP Powerful Literacy Instructional PracticesSivakumar BakthavachalamNo ratings yet
- Year 12 HistDocument44 pagesYear 12 Histapi-319802646No ratings yet
- Domain 1 Artifacts 4 Column - TeachersDocument4 pagesDomain 1 Artifacts 4 Column - Teachersapi-384069095No ratings yet
- Differentiate Project-Based and Problem-Based Learning ApproachesDocument28 pagesDifferentiate Project-Based and Problem-Based Learning ApproachesPaul Alan LadionNo ratings yet
- Active Learning Poster (ABK Suggestions)Document1 pageActive Learning Poster (ABK Suggestions)nkoganNo ratings yet
- LP - ClineDocument9 pagesLP - ClineDeo RamosNo ratings yet
- VocaularyDocument10 pagesVocaularyapi-710409218No ratings yet
- I ObjectivesDocument3 pagesI ObjectiveszamorasvivramNo ratings yet
- Maam Jasmin Daantos PresentationDocument15 pagesMaam Jasmin Daantos PresentationVangie Lepiten100% (1)
- POT Chapter 3Document39 pagesPOT Chapter 3kibaoremalynNo ratings yet
- Greeley-Evans Abc Configuration MasterDocument9 pagesGreeley-Evans Abc Configuration Masterapi-635175552No ratings yet
- Claudia Haro Lesson Plan FormalDocument6 pagesClaudia Haro Lesson Plan Formalapi-467608657No ratings yet
- Group Instructional Design - Multiple Intelligences & Flipped ClassroomDocument9 pagesGroup Instructional Design - Multiple Intelligences & Flipped ClassroomSAVIRA MARETTANo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - HPGD1103 - E-Tutorial - Part1 - January 2023Document28 pagesLecture 1 - HPGD1103 - E-Tutorial - Part1 - January 2023Ihwanor AsrafNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation Tool COTDocument4 pagesClassroom Observation Tool COTRudy ClariñoNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 MergedDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 MergedAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Designing InstructionDocument2 pagesDesigning InstructionJarra RuddyNo ratings yet
- Teacher Preparation Collaborative (TPC) Evaluation FormDocument9 pagesTeacher Preparation Collaborative (TPC) Evaluation Formapi-396872239No ratings yet
- Chapter II The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityDocument36 pagesChapter II The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityLes SircNo ratings yet
- Manjusha SeminarDocument18 pagesManjusha SeminarMANJUSHA S SNo ratings yet
- MathDocument4 pagesMathapi-700103272No ratings yet
- L3 Constructivism and Direct InstructionDocument31 pagesL3 Constructivism and Direct Instructionasmahmahadi92_620656No ratings yet
- K To 12 Pedagogical ApproachesDocument109 pagesK To 12 Pedagogical ApproachesDianne Permejo del Prado100% (3)
- Oliver Sarah - Reading Lesson PlanDocument15 pagesOliver Sarah - Reading Lesson Planapi-607301023No ratings yet
- Group 2 TTL 1 PPT 1Document56 pagesGroup 2 TTL 1 PPT 1Kates DinongonNo ratings yet
- Edu601 Lesson 6-11Document2 pagesEdu601 Lesson 6-11Jo MomNo ratings yet
- InformalDocument4 pagesInformalapi-362351442No ratings yet
- Output 2Document9 pagesOutput 2Kathy Claire BallegaNo ratings yet
- Pedagogies for Student-Centered Learning: Online and On-GoundFrom EverandPedagogies for Student-Centered Learning: Online and On-GoundRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- WOJH Course Catalog RemediatedDocument25 pagesWOJH Course Catalog RemediatedHorizon BeyondNo ratings yet
- Texas Middle School - TEKS Science - ch112bDocument27 pagesTexas Middle School - TEKS Science - ch112bHorizon BeyondNo ratings yet
- Texas Middle School SCDocument15 pagesTexas Middle School SCHorizon BeyondNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Lesson Evaluation - V2Document2 pagesRubric For Lesson Evaluation - V2Horizon BeyondNo ratings yet
- DSKP KSSM Bahasa Inggeris Aliran Kemahiran Tingkatan 4 5Document96 pagesDSKP KSSM Bahasa Inggeris Aliran Kemahiran Tingkatan 4 5Horizon BeyondNo ratings yet
- Paul Scheele Transformational SheetDocument2 pagesPaul Scheele Transformational SheetPaul R. Scheele100% (1)
- Microsoft Student Partners ApplicationDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Student Partners ApplicationSerhat VarolgunesNo ratings yet
- SSIP Project Proposal FormatDocument9 pagesSSIP Project Proposal FormatPritNo ratings yet
- Jamia BPTDocument78 pagesJamia BPTLohit AudhkhasiNo ratings yet
- The Silent WayDocument11 pagesThe Silent WayDewi Ratnah100% (3)
- Application Form (Medicine) - 5Document2 pagesApplication Form (Medicine) - 5Kaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Dr. Md. Iftekhar Hossain, Professor and Head, Department of Psychology, Patna UniversityDocument10 pagesDr. Md. Iftekhar Hossain, Professor and Head, Department of Psychology, Patna UniversityfanNo ratings yet
- FSTFD Brochure PDFDocument4 pagesFSTFD Brochure PDFDalibor ŽivićNo ratings yet
- Year 4 SLIIT Civil Engineering - V - 1Document1 pageYear 4 SLIIT Civil Engineering - V - 1Shifrath AhamedNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness X©Document1 pageMindfulness X©funkyhonkyNo ratings yet
- TLE-IA6 q0 Mod14 Products From RecyclingDocument24 pagesTLE-IA6 q0 Mod14 Products From RecyclingPAUL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- HG-G11 Module 3 RTPDocument9 pagesHG-G11 Module 3 RTPRubenNo ratings yet
- Transition To Post-Pandemic Education in The Philippines: Unfolding InsightsDocument7 pagesTransition To Post-Pandemic Education in The Philippines: Unfolding InsightsAshley JoyceNo ratings yet
- UEO Sample Papers For Class 2Document4 pagesUEO Sample Papers For Class 2Biswabharati PandaNo ratings yet
- Networking WorksheetDocument2 pagesNetworking WorksheetChris GNo ratings yet
- Solved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Document1 pageSolved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Final 2011 CV - FuadDocument3 pagesFinal 2011 CV - FuadNil SabbirNo ratings yet
- Does The Student Trust EasilyDocument2 pagesDoes The Student Trust EasilyAthena MaderaNo ratings yet
- The Active Classroom: Supporting Students With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Through ExerciseDocument8 pagesThe Active Classroom: Supporting Students With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Through ExerciserobfoxNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch2 QI W1 Definition Characteristics and Types of Quantitative Research Ver 2 Language EditedDocument13 pagesPracticalResearch2 QI W1 Definition Characteristics and Types of Quantitative Research Ver 2 Language EditedKristine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 2011 Texas A&m Foundation College Station TX 77840Document5 pages2011 Texas A&m Foundation College Station TX 77840NotgivenNo ratings yet
- .Spiral Progression Approach in Teaching ScienceDocument9 pages.Spiral Progression Approach in Teaching ScienceYHTAK1792No ratings yet
- Cognitive Ability Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesCognitive Ability Sample QuestionsPrithi Usha Rao100% (1)
- Final Janssenville Es Esip2022 2025Document48 pagesFinal Janssenville Es Esip2022 2025Janette BolanteNo ratings yet
- Multicultural Education Issues and Perspectives Seventh Edition - Chapter 3 ReviewDocument4 pagesMulticultural Education Issues and Perspectives Seventh Edition - Chapter 3 ReviewElizabeth DentlingerNo ratings yet
- Existentialism and Man's Search For Meaning Learning IntentDocument2 pagesExistentialism and Man's Search For Meaning Learning IntentJershon’s ChannelNo ratings yet
- Action Research ProposalDocument4 pagesAction Research ProposalGrimaldo Anna MarieNo ratings yet
- Sociology Through Film - Spring10Document8 pagesSociology Through Film - Spring10JodiNo ratings yet
- Ocs Candidate Guide 2019Document18 pagesOcs Candidate Guide 2019JohnNo ratings yet
- 14.1downes. Giordano BrunoDocument38 pages14.1downes. Giordano BrunoJavier SuarezNo ratings yet