Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arithmetic Mean and Standard Deviation
Uploaded by
vishantgilhotra00010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views15 pagesThe document discusses arithmetic mean, standard deviation, and how to calculate them. It provides examples and explanations of key terms like mean, variability, normal distribution, parameters, and qualitative scales. It then gives a problem set involving calculating mean, standard deviation, and interpreting scores on a 5-point scale for 5 statements with responses from 10 respondents.
Original Description:
Original Title
6. Arithmetic Mean and Standard Deviation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses arithmetic mean, standard deviation, and how to calculate them. It provides examples and explanations of key terms like mean, variability, normal distribution, parameters, and qualitative scales. It then gives a problem set involving calculating mean, standard deviation, and interpreting scores on a 5-point scale for 5 statements with responses from 10 respondents.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views15 pagesArithmetic Mean and Standard Deviation
Uploaded by
vishantgilhotra0001The document discusses arithmetic mean, standard deviation, and how to calculate them. It provides examples and explanations of key terms like mean, variability, normal distribution, parameters, and qualitative scales. It then gives a problem set involving calculating mean, standard deviation, and interpreting scores on a 5-point scale for 5 statements with responses from 10 respondents.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Research department
ARITHMETIC MEAN AND STANDARD
DEVIATION
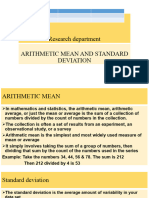
ARITHMETIC MEAN
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, arithmetic average,
or just the mean or average is the sum of a collection of numbers divided
by the count of numbers in the collection.
The collection is often a set of results from an experiment, an
observational study, or a survey
Arithmetic mean is the simplest and most widely used measure of mean
or average
It simply involves taking the sum of a group of numbers, then dividing
that sum by the count of the numbers used in the series
Example: Take the numbers 34, 44, 56 & 78. The sum is 212
Then 212 divided by 4 is 53
Standard deviation
The standard deviation is the average amount of variability in your data
set
It tells you, on average, how far each value lies from the mean
A high standard deviation means that values are generally far from the
mean, while a low standard deviation indicates that values are clustered
close to the mean
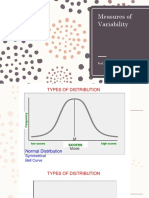
Standard deviation is a useful measure of spread for normal distributions.
Normal distribution – also known as Gaussian distribution, is a probability
distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the
mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean.
Standard deviation
In normal distributions, data is symmetrically distributed with no skew.
Skew = neither parallel nor at right angles to a specified or implied
line, change of ddirection
Askew = crooked
Most values cluster around a central region, with values tapering off as
they go further away from the center.
The standard deviation tells you how spread out from the center of the
distribution your data is on average.
In graphical form, the normal distribution appears as a “bell curve”
Normal curve with standard deviation
Calculating standard deviation
Calculating the Standard Deviation (STD) the shortest way:
1. Use excel in your laptop
2. Write the data in the first column consecutively down the column
3. On the next cell type = STD
4. Highlights the data and enter
parameters
Parameters – a numerical characteristic of a population, as distinct from a
static of a sample
An arbitrary constant whose value characterizes a member of a system (
such as family curves) also; a quantity (such as a mean or variance) that
describes a statistical
Parameter is a limit that affects how something can be done, and
perimeter is the outline of a physical area
Actual parameters – are the variables that are transferred to the function
when it is requested
The formal parameters are the values determined by the function that
accepts values when the function is declared
In actual parameters, only trhe variable is mentioned, not the data types
parameters
Upper limit – is the highest value of the class interval
Lower limit – is the smallest value of the class interval
Weighted Mean Verbal Qualitative
Scale Range Interpretation Description
5 4.51 - 5.00 Strongly agree Excellent
4 3.51 - 4.50 Agree Very good
3 2.51 - 3.50 Moderately agree Good
2 1.51 - 2.50 Slightly agree Fair
1 1.00 - 1.5 Disagree Poor
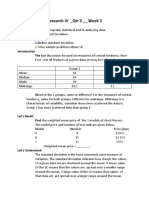
PROBLEM SET # 3
Make a table indicating the mean, Standard deviation, Verbal Interpretation
and the Qualitative description of the following data in a 5- point scale
Statement Score WM STD VI QD
Data:
Statement 1: Respondent 1 = strongly agree
Respondent 2 = agree
Respondent 3 = strongly agree
Respondent 4 = disagree
parameters
Respondent 5 – agree
Respondent 6 – disagree
Respondent 7 – agree
Respondent 8 - disagree
Respondent 9 - agree
Respondent 10 – strongly agree
Statement 2 Respondent 1 = moderately agree
Respondent 2 = agree
Respondent 3 = strongly agree
Respondent 4 = disagree
Respondent 5 – agree
Respondent 6 – disagree
Respondent 7 – agree
Respondent 8 - disagree
Respondent 9 - moderately agree
Respondent 10 – strongly agree
Statement 3 Respondent 1 - agree
Respondent 2 - moderately agree
Respondent 3 - strongly agree
Respondent 4 - disagree
Respondent 5 - Moderately agree
Respondent 6 – disagree
Respondent 7 – agree
Respondent 8 - disagree
Respondent 9 - moderately agree
Respondent 10 – agree
Statement 4 Respondent 1 = moderately agree
Respondent 2 = agree
Respondent 3 = strongly agree
Respondent 4 = disagree
Respondent 5 – disagree
Respondent 6 – disagree
Respondent 7 – moderately agree
Respondent 8 - disagree
Respondent 9 - moderately agree
Respondent 10 – strongly agree
Statement 5 Respondent 1 = agree
Respondent 2 = agree
Respondent 3 = strongly agree
Respondent 4 = disagree
Respondent 5 – moderately agree
Respondent 6 – disagree
Respondent 7 – moderately agree
Respondent 8 - disagree
Respondent 9 - moderately agree
Respondent 10 – strongly agree
You might also like
- Statistics and Standard DeviationDocument50 pagesStatistics and Standard DeviationRon April Custodio Frias100% (10)
- Sourcebook For Programmable Calculators INDICEDocument2 pagesSourcebook For Programmable Calculators INDICELeon Ziegler50% (2)
- Analysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataDocument50 pagesAnalysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataJayson EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix DesignDocument7 pagesConcrete Mix Designadil271No ratings yet
- Math Method Textbook Unit 4 RevisionDocument22 pagesMath Method Textbook Unit 4 RevisionJohn KIM0% (1)
- Change Orders Impact On Project CostDocument14 pagesChange Orders Impact On Project CostzzzNo ratings yet
- Statistical TreatmentDocument2 pagesStatistical TreatmentLynx Seth Bataan88% (16)
- Module 3 - StatisticsDocument27 pagesModule 3 - StatisticsRoussel PalmariaNo ratings yet
- Finals in Edu 533Document11 pagesFinals in Edu 533ISSUE TVNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variability: Prof. Michelle M. Mag-IsaDocument46 pagesMeasures of Variability: Prof. Michelle M. Mag-IsaMichelle MalabananNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency - FinalDocument33 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency - FinalPranav KumarNo ratings yet
- BORRADAILE 2003 - Statistics of Earth Science Data LB 6029 PDFDocument371 pagesBORRADAILE 2003 - Statistics of Earth Science Data LB 6029 PDFEduardo100% (1)
- Statistics in Assessment of LearningDocument11 pagesStatistics in Assessment of LearningMeAnn SaludoNo ratings yet
- Mean and Standard Deviation 2Document16 pagesMean and Standard Deviation 2Madhu MithaNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Assessment Results: Graphical Presentation & Quantitative AnalysisDocument33 pagesInterpretation of Assessment Results: Graphical Presentation & Quantitative AnalysisMarvinApostolNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency-IV-1Document55 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency-IV-1Abhijeet BhardwajNo ratings yet
- PPT2 Central Tendency and VariabilityDocument28 pagesPPT2 Central Tendency and Variabilityzy- SBGNo ratings yet
- 0validitas Item Ok Training (Spss Pa Ali)Document20 pages0validitas Item Ok Training (Spss Pa Ali)Aninda MenduzaNo ratings yet
- New Lesson 2Document69 pagesNew Lesson 2King charles jelord Cos-agonNo ratings yet
- Stats Psyc RV 2018 SpringDocument32 pagesStats Psyc RV 2018 Springapi-391411195No ratings yet
- Module Assessment1 C7.Document15 pagesModule Assessment1 C7.maria elaine melo colesioNo ratings yet
- Statical Data 1Document32 pagesStatical Data 1Irma Estela Marie EstebanNo ratings yet
- EDUC 75 Module 7revised Measures of Central Tendency.Document14 pagesEDUC 75 Module 7revised Measures of Central Tendency.Cielo DasalNo ratings yet
- Types of Data & Descriptive StatisticsDocument31 pagesTypes of Data & Descriptive StatisticsJie YingNo ratings yet
- Pink Green Colorful Vintage Aesthetic Minimalist Manhwa Interior Decor Illustration Work From Home Basic PresentationDocument18 pagesPink Green Colorful Vintage Aesthetic Minimalist Manhwa Interior Decor Illustration Work From Home Basic PresentationRandom PersonNo ratings yet
- Analysis, Interpretation & Use of Test Data: What Are Measures of Central Tendency?Document10 pagesAnalysis, Interpretation & Use of Test Data: What Are Measures of Central Tendency?JUDE VINCENT VISTRONo ratings yet
- Central Tendency, Measures of Dispersion, NormalDocument31 pagesCentral Tendency, Measures of Dispersion, NormalShad RahmanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis With Software Application: Module No. 4Document13 pagesStatistical Analysis With Software Application: Module No. 4Vanessa UbaNo ratings yet
- Module 16 - Analyzing Data - 2Document37 pagesModule 16 - Analyzing Data - 2voiceofmehmoodNo ratings yet
- Q3Basic Statistics Week 3Document7 pagesQ3Basic Statistics Week 3Jessa Bienel Biagtas OlescoNo ratings yet
- Assess of Learning 2Document47 pagesAssess of Learning 2Jessie DesabilleNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendecyDocument5 pagesMeasures of Central TendecyLight_of_LifeNo ratings yet
- Educ 203 Finals Jenny Rose B. RoblesDocument11 pagesEduc 203 Finals Jenny Rose B. RoblesSummer R. DominguezNo ratings yet
- Session 11Document18 pagesSession 11Nyagawa GodkNo ratings yet
- Module 8-Students'Document11 pagesModule 8-Students'calzosheniahNo ratings yet
- Math 7-Q4-Module-6Document16 pagesMath 7-Q4-Module-6Cher Anna MarieNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods: Dr. Asim KhwajaDocument37 pagesMathematical Methods: Dr. Asim KhwajahammadNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Statistics Data Analysis and Decision Modeling 5th Edition Evans Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Statistics Data Analysis and Decision Modeling 5th Edition Evans Solutions Manual PDFgiaocleopatra192y100% (11)
- Module 7 Weeks 14 15Document9 pagesModule 7 Weeks 14 15Shīrêllë Êllézè Rīvâs SmïthNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument53 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyMarwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Final Measures of Dispersion DR LotfiDocument54 pagesFinal Measures of Dispersion DR Lotfi1givemesome1No ratings yet
- Attitude ScalesDocument20 pagesAttitude ScalesaviralNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Descriptives StatisticsDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Descriptives StatisticsKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - StatisticsDocument30 pagesModule 3 - StatisticsJomil CompelNo ratings yet
- Data ManagementDocument44 pagesData ManagementStephen Sumipo BastatasNo ratings yet
- Modified Unit 5, Class Lecture On Measures of Variability, PSY102, 2020Document18 pagesModified Unit 5, Class Lecture On Measures of Variability, PSY102, 2020Rafid RahmanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document15 pagesQuiz 3diana_762131871No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 MAEMDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 MAEMJhay-ar FernandezNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument11 pagesMeasures of Central Tendencyyousuf pogiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Range, Variance, Standard DeviationDocument31 pagesModule 5 - Range, Variance, Standard DeviationKenneth tejamNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics and Inferential Statistics: Part 1Document65 pagesDescriptive Statistics and Inferential Statistics: Part 1துர்காதேவி சௌந்தரராஜன்No ratings yet
- Statistical Organization of ScoresDocument109 pagesStatistical Organization of ScorestalesfottoNo ratings yet
- Data Summary: Lesson 4 StatisticsDocument38 pagesData Summary: Lesson 4 StatisticsAndrea Cayetano100% (1)
- 2.data DescriptionDocument57 pages2.data DescriptionLong Nguyen Duc ThangNo ratings yet
- Rasco, Marinella F. - Likert Scale - Q&ADocument7 pagesRasco, Marinella F. - Likert Scale - Q&AMarlNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and ModeDocument21 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and ModeRoselyn BecherNo ratings yet
- Research IV - QTR 3 - Week 3Document7 pagesResearch IV - QTR 3 - Week 3andrei bercadezNo ratings yet
- Attitude ScalesDocument14 pagesAttitude ScalesSusmita SenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 OrganizerDocument15 pagesChapter 13 OrganizerBrettNo ratings yet
- Performance Task Title: What I Have Learned From Miss ADocument3 pagesPerformance Task Title: What I Have Learned From Miss Anickie jane gardoseNo ratings yet
- Median and Mode CalculationDocument34 pagesMedian and Mode CalculationAnu YadavNo ratings yet
- To Statistics: Semester-V Fall 2021 Ms. Fatima Salman Psychology Department Lahore Garrison UniversityDocument36 pagesTo Statistics: Semester-V Fall 2021 Ms. Fatima Salman Psychology Department Lahore Garrison UniversityZeeshan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- B, M, W, M: ConsistencyDocument3 pagesB, M, W, M: ConsistencyDavid AsandemNo ratings yet
- CEP Presentation Explained Part 2Document139 pagesCEP Presentation Explained Part 2Catty FordNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5001Document32 pagesChapter 5001jangra014100% (1)
- ECE R19 - 2nd Year Course Structure SyllabusDocument70 pagesECE R19 - 2nd Year Course Structure SyllabusSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Texture Analysis To Detect Malaria Tropica in Blood Smears Image Using Support Vector MachineDocument6 pagesTexture Analysis To Detect Malaria Tropica in Blood Smears Image Using Support Vector MachineIJIRAE- International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced EngineeringNo ratings yet
- MA2001D Tutorial Sheet 3Document5 pagesMA2001D Tutorial Sheet 3Ritesh rajNo ratings yet
- Intro To Data Science SummaryDocument17 pagesIntro To Data Science SummaryHussein ElGhoulNo ratings yet
- Confidence IntervalDocument2 pagesConfidence IntervalSaruNo ratings yet
- Stat100b Gamma Chi T FDocument18 pagesStat100b Gamma Chi T FSusan ChenNo ratings yet
- Help AnClimDocument12 pagesHelp AnClimhcsrecsNo ratings yet
- Department of Statistical and Actuarial Sciences SS 2864b Jan-Apr 2010 Instructor: D. Murdoch Final Exam, April 27, 1-4 PMDocument13 pagesDepartment of Statistical and Actuarial Sciences SS 2864b Jan-Apr 2010 Instructor: D. Murdoch Final Exam, April 27, 1-4 PMArth PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Sampling Distribution and Confidence Interval1Document54 pagesChapter 3 - Sampling Distribution and Confidence Interval1Ahmad HanifNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Standard Normal TableDocument1 pageCumulative Standard Normal TableDian Paul100% (1)
- Subjective Type TestDocument51 pagesSubjective Type TestMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Taller y No QuizDocument17 pagesTaller y No QuizFabian Ricardo VargasNo ratings yet
- Can Single-Loop Detectors Do The Work of Dual-Loop Detectors?Document35 pagesCan Single-Loop Detectors Do The Work of Dual-Loop Detectors?Alexandra Elena BalanoiuNo ratings yet
- PSHADocument22 pagesPSHA2K2O-A17-11 Vishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Main NotesDocument227 pagesMain NotesNguyễn Minh HiếuNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4.48, 5.47, 5.50, 6.75, 6.76Document12 pagesExercise 4.48, 5.47, 5.50, 6.75, 6.76adee_usonNo ratings yet
- Random Variables PDFDocument90 pagesRandom Variables PDFNJNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Statistics and Probability For Data ScienceDocument94 pagesFoundations of Statistics and Probability For Data Sciencepranav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Johansen, S. (1988) - Statistical Analysis of Cointegration VectorsDocument24 pagesJohansen, S. (1988) - Statistical Analysis of Cointegration VectorsJoshua Maverick Ecafssa Sparrow100% (2)
- Corrosion of Rebar in Concrete Part II Literature Survey and Statistical Analysis of Exsting Data On Chloride ThresholdsDocument14 pagesCorrosion of Rebar in Concrete Part II Literature Survey and Statistical Analysis of Exsting Data On Chloride ThresholdsIsrael WakumaNo ratings yet
- Statistics 12th Edition McClave Test Bank 1Document16 pagesStatistics 12th Edition McClave Test Bank 1kenneth100% (46)
- SNM 2017 18 Tutorial QuestionsDocument42 pagesSNM 2017 18 Tutorial QuestionsMuthuraman SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Elementary Statistics 3rd Edition Navidi Solutions ManualDocument31 pagesElementary Statistics 3rd Edition Navidi Solutions Manualluongsophieixvqp100% (27)