Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Uploaded by
Kath Garlet0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageHistory
Original Title
JABIR-IBN-HAYYAN
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHistory
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageJabir Ibn Hayyan
Uploaded by
Kath GarletHistory
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
JABIR IBN HAYYAN (geber)- Father of chemistry
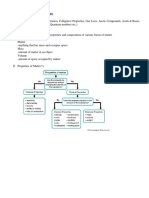
Chemistry- is the study of the properties of matter
INTER-MOLECULAR FORCES OF ATTRACTION-forces of
and the changes it undergoes.
attraction that exist between molecules or ions
Matter-is anything that occupy space and has mass
Energy- is the ability to do work 4 Common IMFA
Mixture- It is a combination of two or more *Van Der Waals or London Dispersion Forces-
substances Force that exists in ALL molecules, even nonpolar
Homogeneous- It is a combination of two or more atoms/ molecules
substances in which it is present in one (1) phase. *Dipole-Dipole Interactions- Interaction between the
Heterogeneous- a compound’s composition is not permanent dipole in polar molecules
uniform or you can see two or more phase *Hydrogen Bonding- Interaction between O-H, N-H
Pure substances- Is a form of matter that has a and F-H bonds
definite (constant) composition and distinct properties *Ion-dipole Interactions-Interaction between ION and
Compounds- It is a combination of two or more POLAR molecule
similar or different elements.
Element- is a substance that cannot be separated into SOLUTIONS-A homogeneous mixture of 2 or more
simpler substances by chemical means. substances in which the dispersed particles are
ACCURACY- Refers to the closeness of measurements molecular or ionic in size
to the true value. Solvent-Component in greatest amount
PRECISION- Refers to the closeness of measurements Solute-Component(s) in lesser amount(s)
with each other. TYPES OF SOLUTIONS Saturated
Chemistry has five (5) main branches: Solutions-A solution with the maximum amount
*BIO CHEMISTRY- The study of life at the molecular of solute dissolved
level and the processes associated with life. Unsaturated Solutions-A solution with LESS
*INORGANIC CHEMISTRY- The study of matter that THAN the maximum amount of solute dissolved
consists of all of the elements and compounds other Supersaturated Solutions-An unstable solution
than carbon or organic compound. with MORE THAN the maximum amount of
*ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Is the study of matter that is solute dissolved
composed principally of carbon. STOICHIOMETRY -the area of study that examines the
*ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY-Involves the analysis of quantities of substance consumed and produced in
matter determine its composition (qualitative analysis) chemical reactions
and the quantity (quantitative analysis) of each kind of
matter that is present. Limiting Reagent The reactant that gets completely
*PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY-It is the study of theoretical consumed in a reaction;Determines the quantity of
aspects of the structure and changes of matter. products formed
Excess Reagent-The reactant that does not get
completely consumed;
Some is left over after a reaction
You might also like
- CHEM (no formula)Document4 pagesCHEM (no formula)palacioaya28No ratings yet
- Stem Lesson 1 Gen Chem Pure SubsDocument15 pagesStem Lesson 1 Gen Chem Pure SubsYvonne CuevasNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistryhehe xdNo ratings yet
- Chem (Lec)Document2 pagesChem (Lec)Dalgom's WifeNo ratings yet
- Compilation Report in Science: Submitted byDocument24 pagesCompilation Report in Science: Submitted byHan ONo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument2 pagesChemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 - Gen. Chem Engg. 3rd QTR SY2015-2016Document4 pagesLec 4 - Gen. Chem Engg. 3rd QTR SY2015-2016CeceNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerJohn Nicolo P. GurangoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Sas 1 Sas 5Document25 pagesLecture Notes Sas 1 Sas 5Louise Nicole CastroNo ratings yet
- LEX-115-01 Chemical Technology ClassDocument4 pagesLEX-115-01 Chemical Technology ClassMARLY DAYANARA CASADO CABRALNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Chemistrybangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Week 1Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Week 1Wayne AngeloNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemistry ExplainedDocument52 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemistry ExplainedjabNo ratings yet
- All VocabDocument34 pagesAll Vocabapi-294055859No ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument8 pagesSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryJatinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry Reviewerback upNo ratings yet
- C15 Notes CH1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesC15 Notes CH1 IntroductionArnieNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances and MixturesDocument1 pagePure Substances and MixturesRebishara CapobresNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Chapter Description Review and Add-OnsDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Chapter Description Review and Add-OnsJesieBoyLlanesNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentAntonella MabasaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- Gen Chem - Matter ReviewerDocument2 pagesGen Chem - Matter Reviewerjellyjelly458No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Chemistry concepts explained in 11 pointsDocument2 pagesChemistry concepts explained in 11 pointsIan BelenNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGrade 7 ReviewerHunger StealSMPNo ratings yet
- Solution Topic 1Document1 pageSolution Topic 1NovyCendianNo ratings yet
- Physics and Chemistry Unit 3Document3 pagesPhysics and Chemistry Unit 3sērgîö :DNo ratings yet
- CH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)Document43 pagesCH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)James FrancisNo ratings yet
- CH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)Document43 pagesCH 4. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (Chem +1)Dipin Preet SinghNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry QuesDocument40 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistry QuesSaadiya HussainNo ratings yet
- Matter and Chemical Change: Topic 1Document16 pagesMatter and Chemical Change: Topic 1ardusias100% (1)
- Free Study Materials for All Classes & BoardsDocument10 pagesFree Study Materials for All Classes & BoardsAnkit kumarNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document10 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!sarwath sultanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in ChemistryDocument3 pagesLecture Notes in ChemistryDaryllNo ratings yet
- 1 ChemistryDocument13 pages1 ChemistryAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- My Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesMy Chemistry Notess2023100462No ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument14 pagesProperties of MatterCharlz BombalesNo ratings yet
- Review Matter, Atoms, Elements and MixturesDocument3 pagesReview Matter, Atoms, Elements and MixturesMarco Antonio MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Science ReportDocument5 pagesScience Reportjelai anselmoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1 ReviewDocument3 pagesChemistry Chapter 1 ReviewMarcia MurilloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Vocabulary-1Document2 pagesChemistry Vocabulary-1api-535412468No ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Chapter SummaryDocument4 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Chapter SummaryAnirudhNo ratings yet
- Classification of Matter ScienceDocument5 pagesClassification of Matter Sciencenina jannaNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade - Week 2 Mixing SubstancesDocument12 pages5th Grade - Week 2 Mixing Substancesapi-254428474100% (1)
- Chemistry For EngineersDocument5 pagesChemistry For EngineersErgie PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ChemistryDocument2 pagesFundamentals of ChemistryKahlil Kaimo MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Chemistrylecturewps OfficeDocument12 pagesChemistrylecturewps Officeniconiconii BANGTANXARMYNo ratings yet
- Chemistry BasicsDocument12 pagesChemistry BasicsJanna EchavezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Firstsem GenchemDocument7 pagesReviewer Firstsem GenchemChricellFNo ratings yet
- NMAT - Must Know-ChemistryDocument45 pagesNMAT - Must Know-ChemistryElise TraugottNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument7 pagesGen Chem Reviewersophia rimandoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Matter and Its ClassificationDocument56 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Matter and Its ClassificationLiezel Brillantes100% (1)
- Chemistry NotesDocument60 pagesChemistry Noteshcv7cptvs6No ratings yet
- Chemistry For EngineersDocument21 pagesChemistry For Engineersjustnothing010100No ratings yet
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5Ann Margaret Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry FundamentalsDocument33 pagesGeneral Chemistry FundamentalsrenataNo ratings yet
- XI ChemistryDocument86 pagesXI Chemistryadvietiya.fiverrNo ratings yet
- CHM101 - Chapter 1Document26 pagesCHM101 - Chapter 1masoodaamna705No ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument28 pagesClassification of MatterLawrence LongcopNo ratings yet
- Fyp CT 1406758 DTDocument156 pagesFyp CT 1406758 DTKath GarletNo ratings yet
- CE Board Exam ChecklistDocument6 pagesCE Board Exam ChecklistSherlyn BesasNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine Worksheet KeyDocument2 pagesSimple Machine Worksheet KeyKath GarletNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument4 pages3 PDFRohith100% (1)
- Backus FortranDocument11 pagesBackus FortranKath GarletNo ratings yet
- Ogale's Do and Discover Science Kit Experiment BookletDocument16 pagesOgale's Do and Discover Science Kit Experiment BookletUdita Ogale100% (1)
- Separation of Substances - Questions - PPTDocument45 pagesSeparation of Substances - Questions - PPTRahul RajNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade - Week 2 Mixing SubstancesDocument12 pages5th Grade - Week 2 Mixing Substancesapi-254428474100% (1)
- Specification Patent NZ 743350Document57 pagesSpecification Patent NZ 743350Isabela BalanNo ratings yet
- Water NotebookDocument3 pagesWater NotebookosamaNo ratings yet
- MixturesDocument11 pagesMixturesAvigail Joyce AndradeNo ratings yet
- Concept Note:: Eastern Tayabas College, IncDocument4 pagesConcept Note:: Eastern Tayabas College, IncRENA LAICA ESTEBANNo ratings yet
- Describe The Appearance and Uses of ColloidsDocument20 pagesDescribe The Appearance and Uses of ColloidsLuisa Jamero Regalado50% (2)
- Tea Worth of RsDocument11 pagesTea Worth of RsAnkit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Pure and Impure BookletDocument7 pagesPure and Impure BookletOokieNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures Particulate NatureDocument5 pagesSeparating Mixtures Particulate NatureStruggl1ngNo ratings yet
- Article of PDLCDocument7 pagesArticle of PDLCMuhammad RamzanNo ratings yet
- Support Material Class 9thDocument49 pagesSupport Material Class 9thJashn RakhechaNo ratings yet
- Matter: Properties and ChangesDocument48 pagesMatter: Properties and ChangesRichionNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of The Pillar College-Cauayan Reina Mercedes Vocational and Industrial School Tallungan, Reina Mercedes, IsabelaDocument6 pagesOur Lady of The Pillar College-Cauayan Reina Mercedes Vocational and Industrial School Tallungan, Reina Mercedes, IsabelaLena Beth Tapawan YapNo ratings yet
- ASTM-D3230-19 Salinidad en CrudoDocument7 pagesASTM-D3230-19 Salinidad en CrudoAngel MurilloNo ratings yet
- QCVN 07 2009btnmt - Quy Chuan Nguong CTNHDocument30 pagesQCVN 07 2009btnmt - Quy Chuan Nguong CTNHanon_416094192No ratings yet
- Siyavula Textbooks Grade 10 Physical Science 3.1Document336 pagesSiyavula Textbooks Grade 10 Physical Science 3.1AshelyNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and SolutionsDocument19 pagesMixtures and SolutionsMelissa Favila PanagaNo ratings yet
- Classifying Matter and Its PropertiesDocument5 pagesClassifying Matter and Its PropertiesJohannah SuraitNo ratings yet
- Y7 Separating MixturesDocument2 pagesY7 Separating Mixturesellen mae GonatoNo ratings yet
- Mixtures in Two or More Phases Are Heterogeneous Mixtures. Examples Include Ice Cubes in A Drink, SandDocument2 pagesMixtures in Two or More Phases Are Heterogeneous Mixtures. Examples Include Ice Cubes in A Drink, SandJinky Verano CortezNo ratings yet
- BOOK IntroductoryChemistry 1st Ed Key 2011 PDFDocument974 pagesBOOK IntroductoryChemistry 1st Ed Key 2011 PDFArturo Limachi DiazNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Midterm Exam ReviewDocument27 pagesChemistry Midterm Exam Reviewkayla behlerNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Teacher Reference Term 1 - Introduction To Science and ChemistryDocument2 pagesYear 7 Teacher Reference Term 1 - Introduction To Science and Chemistryapi-350319898No ratings yet
- Ingredients: Dispersing Agent and Acid Buffer For Polyester Dyeing Production Process - 1Document6 pagesIngredients: Dispersing Agent and Acid Buffer For Polyester Dyeing Production Process - 1Juthi Rahman100% (1)
- Turkey ImportDocument14 pagesTurkey ImportMani 1No ratings yet
- Study Material Chemistry-1 PDFDocument340 pagesStudy Material Chemistry-1 PDFYash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Learn about SolutionsDocument7 pagesLearn about SolutionsLIEZEL C DELA PENANo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingDocument28 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingPrabodh GuptNo ratings yet
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice)From EverandChemistry: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice)No ratings yet
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)