Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem (Lec)
Uploaded by
Dalgom's Wife0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
CHEM (LEC)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesChem (Lec)
Uploaded by
Dalgom's WifeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
INORGANIC & ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LECTURE)
1ST YEAR SEMESTER 1
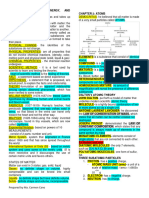
CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS Fundamental Chemical Laws
Chemistry John Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Study of matter and the changes it 1. All matter is composed of very tiny
undergoes particles called atoms.
Matter 2. All atoms of the same element have the
- Anything that occupies space and has same chemical properties. Atoms of
mass different elements have different
- Divided into pure substances and chemical properties.
mixtures 3. In a chemical reaction, no atom of any
Pure Substances element disappears or is changed into
- Fixed composition an atom of another element.
- Cannot be further purified 4. Compounds are formed by the chemical
- Divided into elements and compounds combination of two or more of the same
Elements or different kinds of atoms.
- Cannot be subdivided by chemical or 5. Molecules are a tightly bound
physical means combination of two or more atoms that
Compounds acts as a single unit.
- Elements united in fixed ratios
Mixtures Law of conservation of mass
- Combination of two or more pure - Antoine Lavoisier (1743-1794)
substances - matter can neither be created nor
- Physically separable into pure substances destroyed
- Divided into homogeneous matter and
heterogeneous matter Law of constant consumption
Homogeneous matter - Joseph Proust (1754-1826)
- Uniform composition throughout - Any compound is always made up of
Heterogeneous matter elements in the same proportion by
- Non uniform composition mass.
Classification of matter Law of multiple proportions
Substance - John Dalton
- has a definite composition and distinct - Different compounds made up of the
properties same element differ in the number of
Element atoms of each kind that combine.
- Consists of identical atoms
Compound CHEMICAL REACTIONS
- Made up of 2 or more elements in a fixed Chemical Reaction
ratio by mass - process in which one or more substances
are converted into one or more new
Elements substances
Monoatomic - single atom Chemical Equation
Diatomic - H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (7) - shorthand notation to describe a
Polyatomic - 3 or more atoms per molecule (O3, chemical reaction.
P4, S8) ex. diamond - symbolic representation of a chemical
reaction that shows:
Molecular formula - letters a. reactants on left side of reaction
Structural formula - lines b. products on right side of equation
Ball-and stick model - balls and stick c. relative amounts of each using
Space-filling model - size stoichiometric coefficient
- reactants produce/yield the product
-
*triangle - heat
*H2O - water
*U.V. - sunlight
*catalyst
*always treat the polyatomic ion as one unit
Precipitation reaction
-
You might also like
- CHEM (No Formula)Document4 pagesCHEM (No Formula)palacioaya28No ratings yet
- CHEM1003 Lecture 1 & 2Document5 pagesCHEM1003 Lecture 1 & 2Eli FalzunNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesDocument2 pagesLesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Chemistrybangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- 1 ChemistryDocument13 pages1 ChemistryAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Gen Science)Document3 pagesReviewer (Gen Science)Sophia LantinNo ratings yet
- STEM 3 (Chem) Definition of TermsDocument1 pageSTEM 3 (Chem) Definition of TermsBilly JamesNo ratings yet
- Llogers - General Chemistry m1-m6Document18 pagesLlogers - General Chemistry m1-m6api-639087356No ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument3 pagesChem ReviewerShane PangatoNo ratings yet
- Biochem LecDocument10 pagesBiochem LecRachell Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument46 pagesScience Reviewerrowannenicole.jaudianNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument12 pagesGen ChemGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notesbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- GENCHEM ReviewerDocument6 pagesGENCHEM ReviewerChricellFNo ratings yet
- C15 Notes CH1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesC15 Notes CH1 IntroductionArnieNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4695793937270644090Document6 pagesInbound 4695793937270644090joshuatimothylaoNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistryhehe xdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- Chem 16 Long Exam 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesChem 16 Long Exam 1 Reviewerdesperateboy100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Chemistrylecturewps OfficeDocument12 pagesChemistrylecturewps Officeniconiconii BANGTANXARMYNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic Theory: Indivisible Indestructible Basic Particles Atoms Atoms of A Given Element IdenticalDocument2 pagesDalton's Atomic Theory: Indivisible Indestructible Basic Particles Atoms Atoms of A Given Element IdenticalJohn RandyNo ratings yet
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesMatter and Its Properties Properties of MattermiahNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Stoichiometric Relationships PDFDocument7 pagesTopic 1 Stoichiometric Relationships PDFAshwinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Matter - Its Properties and MeasurementDocument54 pagesChapter 1: Matter - Its Properties and MeasurementJan Rovyn Javier100% (1)
- Environmental Science - Module 2Document3 pagesEnvironmental Science - Module 2mashihoNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument13 pagesChemAngelica Marie DiegoNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Key Terms Collection by Saya Minn ThantDocument8 pagesBasic Chemistry Key Terms Collection by Saya Minn ThantMinn ThantNo ratings yet
- 201Document15 pages201RosheenNo ratings yet
- Ust Shape ReviewerDocument28 pagesUst Shape ReviewerkNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 2 NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry Chapter 2 Notesvolleycrew818No ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Year MTDocument12 pagesChemistry 1st Year MTENo ratings yet
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5Ann Margaret Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Formulas & Notes - Basic Chem & Envi Engg Jun2013Document7 pagesFormulas & Notes - Basic Chem & Envi Engg Jun2013Bhabi BarrugaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1 - P1 - MatterDocument21 pagesChemistry Unit 1 - P1 - MatterMelina BazarNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic: Classifying MatterDocument11 pagesAtoms and The Periodic: Classifying MattercharlieNo ratings yet
- Sections 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4,1.5Document17 pagesSections 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4,1.5gchanjrNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument7 pagesGen Chem Reviewersophia rimandoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYPrincess Diane AgripaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Science and TechnologyDocument4 pagesFaculty of Science and TechnologyMARLY DAYANARA CASADO CABRALNo ratings yet
- Science ReportDocument5 pagesScience Reportjelai anselmoNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFICATION - OF - MATTER-week 2-pptshwDocument31 pagesCLASSIFICATION - OF - MATTER-week 2-pptshwAlyssa Crizel CalotesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document3 pagesChapter 2rhymeNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesGen Chem 2 ReviewerDrake AlzonaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerNishka CarabeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry Reviewerback upNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Components - 1Document6 pagesMatter and Its Components - 1TenacityNo ratings yet
- 2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument6 pages2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument7 pagesREVIEWERrhymeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument14 pagesChemistry ReviewerZildjian ApudNo ratings yet
- I. Matter Matter - Anything That Has Mass and Takes Up Mass - Amount of Matter The Object Contains A. Physical States of Matter - Conditions ofDocument15 pagesI. Matter Matter - Anything That Has Mass and Takes Up Mass - Amount of Matter The Object Contains A. Physical States of Matter - Conditions ofBhoxs Joey CelesparaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer-ZaraDocument7 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer-ZaraMara LaoNo ratings yet
- Matter Exist In: (Examples) : Molecules and CompoundsDocument2 pagesMatter Exist In: (Examples) : Molecules and CompoundsprincessmagpatocNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerJohn Nicolo P. GurangoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYkhayceemeade2No ratings yet
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument10 pagesAtoms Molecules and IonsLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Practice Question Separating and Purifying MixtureDocument5 pagesPractice Question Separating and Purifying MixtureRyan PurnamanNo ratings yet
- Cl-7 (Ch3 and 4)Document4 pagesCl-7 (Ch3 and 4)Sureshkumar DevanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry A Molecular Approach Tro 2nd Edition Test BankDocument32 pagesChemistry A Molecular Approach Tro 2nd Edition Test BankAlbert Seale100% (29)
- Chihhao Fan, Ya-Zhen Huang, Jhen-Nan Lin, Junwei Li: Article InfoDocument10 pagesChihhao Fan, Ya-Zhen Huang, Jhen-Nan Lin, Junwei Li: Article InfoMichal Braverman FinkelshteinNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances Mixtures and SolutionsDocument18 pagesPure Substances Mixtures and SolutionsJoanna Angela LeeNo ratings yet
- QCX AutoSampling - ENDocument9 pagesQCX AutoSampling - ENtonyNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual PDFamess.trias.xpuax100% (12)
- Construction and Building Materials: Zhengqi Zhang, Jianhua Yang, Ying Fang, Yaofei LuoDocument14 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Zhengqi Zhang, Jianhua Yang, Ying Fang, Yaofei LuoAlejandro MorenoNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Construction Materials: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesCase Studies in Construction Materials: SciencedirectAmin ZuraiqiNo ratings yet
- A A Chemistry Model Exam 2012Document13 pagesA A Chemistry Model Exam 2012Kerod MohamedNo ratings yet
- August 2022 (Test Paper)Document17 pagesAugust 2022 (Test Paper)Jhuanna Marie CabalteraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Round 3 (Problem of The Day)Document3 pagesChemistry Round 3 (Problem of The Day)ASIEDU BOADU KWAKUNo ratings yet
- Dr. Teresa Curtin (Room: MSG 015) : General Chemistry 1 / Chemistry For EngineersDocument21 pagesDr. Teresa Curtin (Room: MSG 015) : General Chemistry 1 / Chemistry For EngineersTadhg O'ShaughnessyNo ratings yet
- Tyrosinase Inhibition From Green Tea (Camellia Sinensis (L.) Kuntze) GelDocument7 pagesTyrosinase Inhibition From Green Tea (Camellia Sinensis (L.) Kuntze) GelSandra MegantaraNo ratings yet
- ASTM D6307.2019 Determination of Asphalt Content by Ignition MethodDocument5 pagesASTM D6307.2019 Determination of Asphalt Content by Ignition Methodjitendra100% (1)
- Additional Exercises Separation TechniquesDocument12 pagesAdditional Exercises Separation TechniquesBaiye RandolfNo ratings yet
- Naming Ionic CompoundsDocument20 pagesNaming Ionic CompoundsMegan Sarah100% (1)
- Shopping For Colloids: Science-VIDocument15 pagesShopping For Colloids: Science-VIEvelynNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Elements & Compounds - AnswersDocument12 pagesWorksheet - Elements & Compounds - AnswersJohn Michael Ditchon100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed LP in Science 4 For CODocument4 pagesSemi-Detailed LP in Science 4 For CORonalyn Rugayan BalangatNo ratings yet
- Science7 q1 Mod3 Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures FINAL08122020Document32 pagesScience7 q1 Mod3 Two Worlds Apart Pure Substances vs. Mixtures FINAL08122020Hector PantiNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Test in Science 6 Read and Understand The Sentences and Questions. Choose The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument6 pagesFirst Quarter Test in Science 6 Read and Understand The Sentences and Questions. Choose The Letter of The Correct AnswerJENNIFER LUMBRESNo ratings yet
- Is The Homogeneity of Your Dry Mix Acceptable - Chemical ProcessingDocument9 pagesIs The Homogeneity of Your Dry Mix Acceptable - Chemical Processingaswar teknikNo ratings yet
- Notes - Mixtures and Pure SubstancesDocument32 pagesNotes - Mixtures and Pure Substancesapi-326942798No ratings yet
- Chemistry Contexts PreliminaryDocument377 pagesChemistry Contexts PreliminaryEshayz111100% (3)
- Year 10 Chemistry End of Year Exam Revision BookletDocument34 pagesYear 10 Chemistry End of Year Exam Revision Bookletrespectawesome1801No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Chemistry Principles and Reactions 7th Edition William L Masterton DownloadDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry Principles and Reactions 7th Edition William L Masterton Downloadliterarysyncline63wjwpNo ratings yet
- SDA Primary School Grade 5 Science TestDocument3 pagesSDA Primary School Grade 5 Science TestAj MuwindwaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Test ReviewDocument9 pagesProperties of Matter Test ReviewAngel PeayNo ratings yet
- Monlab OperationsDocument4 pagesMonlab OperationsJulieAnne DelaCruzNo ratings yet