Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemistry Mind Map
Uploaded by
Bhavna BeniwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrochemistry Mind Map
Uploaded by
Bhavna BeniwalCopyright:
Available Formats
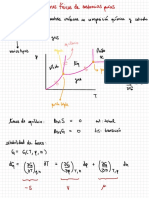
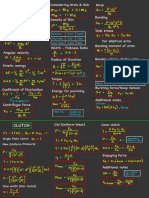
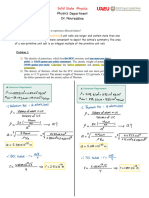
Conductivity Debye-haeckel onsager equation Galvanic cell
k-i-g-tr.la →
spontaneous mean
for strong electrolytes occurs on = ne
-
R = Gx G*
Current Anode
flow to
→
Molar conductance
✗
m= Amos -
b. To
cathode
Xm = K ✗
M
1000
,
^
>
↳ ( internat )
Cathode to anode
( external )
Equivalent conductance
✗
ey=
K ✗✓ = KX 1000 Electrochemistry
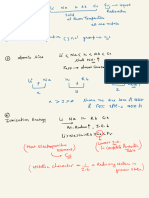
N Electrolytic cell
>
→ Non
Kohlraush law <
-
spontaneous redonrean
→ oh > 0
✓
XD m
=
Ninfa tyimp Nernst equation
→ Cathode -
reduction
→ Anode → onidateon
RI enc Product]
ka={÷,(
E= Eo
)
→ source → direct current
-
✗ < 5%
[Reactant ]
at
nf
Efficiency In )=%u= -1¥
7=298 K
Ñm =
KX 1000
E=E° 0.0591 [Product]
s
logio[ Faradays law
-
n
reactant ]
1st law → w=zxixt
Cell
representation for concentration cell
2nd Exixt
ELu= Wynn law → w =
/ / / Wrote /
Anode Anode
half cathode 9050°
oxidising Power
all
✗ srpsnysop
electrolyte electrolyte ¥ __W§z=Y§= constant .
Reducing Power So PL YSRP ,
✗
-> Primary cells cannot be charged. Eg- dry cell,mercury cell.
->Secondary cells can be recharged. Eg- Ni-Cd cell & lead storage battery.
->Fuel cell produce energy from the combustion of fuels which can be converted into electrical
energy. Eg- H2O2 fuel cell.
Name of cell/ Anode Cathode Electrolyte
battery
Dry cell Zinc Graphite; MnO2 + C NH4Cl + ZnCl2 (touching
(touching cathode) anode)
Mercury cell (used in Zinc- Paste of HgO & Paste of KOH &
watches,hearing aids) mercury carbon ZnO
amalgum
Lead storage battery Lead Lead dioxide PbO2 H2SO4 (38%)
Ni-Cd cell Cadmium [Ni(OH)3] KOH solution
H2O2 Fuel cell Porous carbon Porous carbon Conc. Aq. NaOH
containing catalysts containing catalysts solution
(H2 passed) (O2 passed)
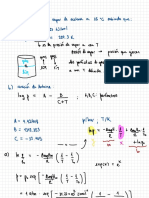
Reactions in lead storage battery during discharge:
At anode:- Pb ) -1 505
(s Pbsoycs] -12 e-
>
At cathode:- 4Mt Pboz (g) +5042 > Pbsoy ( )
-
-1
2h20
-
+ + Ze s
Complete reaction: Pts , -1 Pboz ( ) -1 24250g s Zpbsoycs, -12420
→
You might also like
- TK3082 - HomeWork HT - 12221065 - Jovita Vala Maritza MaharaniDocument1 pageTK3082 - HomeWork HT - 12221065 - Jovita Vala Maritza MaharanijovitaNo ratings yet
- ConductionDocument2 pagesConduction503-10-Pattarachanok JunthipNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesAtomic StructureHems MadaviNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Mind MapDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure Mind Maplakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- 12th May ITCM921E01 PDFDocument13 pages12th May ITCM921E01 PDFNanaiNo ratings yet
- T.284xlobmaxwell-Slots - In: Direct GeneratorDocument7 pagesT.284xlobmaxwell-Slots - In: Direct GeneratorFelix Mar Colipano EspejoNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Notes - Ii: Amit Kumar Jha (Iitian)Document15 pagesQuantum Mechanics Notes - Ii: Amit Kumar Jha (Iitian)Tiasha DevNo ratings yet
- HVACDocument85 pagesHVACAbner PramanaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Mind MapDocument1 pageChemical Kinetics Mind MapSamridhi MoudgilNo ratings yet
- Clase 20220526 FQDocument10 pagesClase 20220526 FQJeshNo ratings yet
- S BlockDocument23 pagesS BlockskyrusttyyNo ratings yet
- Parapet Connection DesignDocument24 pagesParapet Connection DesignShivaranjan HJNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Voltage and Output Speed of A DC Motor-1Document8 pagesRelation Between Voltage and Output Speed of A DC Motor-1Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Equation Sheet HeatDocument5 pagesEquation Sheet HeatNoor GoldNo ratings yet
- 電動力學 L1Document18 pages電動力學 L1盧郁傑No ratings yet
- Trigonometry NotesDocument1 pageTrigonometry NotesRainbow100% (1)
- Notes - Quantum Chemistry ReviewDocument11 pagesNotes - Quantum Chemistry ReviewTrecy Jane RicabordaNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document26 pagesCH 4林孟群No ratings yet
- Ncert Kaksha Formula Sheets Chemistry Class 11thDocument18 pagesNcert Kaksha Formula Sheets Chemistry Class 11thABCD Play school100% (4)
- Unit 11 Reading NotesDocument14 pagesUnit 11 Reading Notes陳洪翊No ratings yet
- U&D To NLM (RY)Document277 pagesU&D To NLM (RY)Chashan DeepNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium (IITian Notes - Kota)Document24 pagesChemical Equilibrium (IITian Notes - Kota)UndRratedNo ratings yet
- Upd C11 CHM EngDocument18 pagesUpd C11 CHM EngArinjoy Mervyn GomesNo ratings yet
- 0223微積分A二Document9 pages0223微積分A二江品萱No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Document1 pageElectromagnetic Waves - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024newideasanuragNo ratings yet
- Suhu Dan Teori Kinetik GasDocument8 pagesSuhu Dan Teori Kinetik GasCarrisa Ferly WidjayaNo ratings yet
- Deber 1 TMI 2018 ADocument8 pagesDeber 1 TMI 2018 AMilenka Naomi Rosado FloresNo ratings yet
- Dual Atom NuclieDocument25 pagesDual Atom NuclieDeepika VNo ratings yet
- Crash Course PDFDocument8 pagesCrash Course PDFSatvik SinghNo ratings yet
- Reaction: 50 Absorbed)Document1 pageReaction: 50 Absorbed)zyzy6527No ratings yet
- Chapter 15, Principle of Physics, Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 15, Principle of Physics, Lecture NotesBushraNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diodes: NiharDocument8 pagesSemiconductor Diodes: NiharMyzoNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diodes: NiharDocument8 pagesSemiconductor Diodes: NiharMyzoNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument39 pagesMachine DesignJp G PeterosNo ratings yet
- Clase 20220530 FQDocument11 pagesClase 20220530 FQJeshNo ratings yet
- 高微筆記 Chapter 3Document37 pages高微筆記 Chapter 3magicfrank030801No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Electrochemistry (Classroom Notes)Document60 pagesUnit 3 Electrochemistry (Classroom Notes)vihas bNo ratings yet
- Magnetic: CoverageDocument128 pagesMagnetic: CoverageAishwarya RajaputNo ratings yet
- HW 12Document2 pagesHW 12haiNo ratings yet
- Formula Cheat Sheet 2023Document3 pagesFormula Cheat Sheet 2023Hardik NarangNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 - Take HomeDocument2 pagesExam 2 - Take Hometim kanzNo ratings yet
- เคมีเพิ่มDocument5 pagesเคมีเพิ่มPavaridNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Notes (Transition Metals)Document3 pagesIB Chemistry Notes (Transition Metals)hyunjinp0107No ratings yet
- EMA3050 Oct 17Document5 pagesEMA3050 Oct 17Alicina DaleNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics and The AtomDocument1 pageQuantum Mechanics and The AtomMarciaNo ratings yet
- hw1 5Document3 pageshw1 5Abdullah RashidNo ratings yet
- CerculDocument5 pagesCerculMarianaNo ratings yet
- Bevlangsreng BRP: LajurxDocument3 pagesBevlangsreng BRP: Lajurxbella graciaNo ratings yet
- Coordinating Comp XC12 & A11+Document12 pagesCoordinating Comp XC12 & A11+Krish TomarNo ratings yet
- Fined: OfmdesofdedrDocument9 pagesFined: OfmdesofdedrAkash.SNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAssignment 9 SolutionsClerry SamuelNo ratings yet
- Week 05 BDocument5 pagesWeek 05 BhawulikemenawNo ratings yet
- Power and Distribution NotesDocument8 pagesPower and Distribution NotesgrayditorNo ratings yet
- F-Riviera: AlishaDocument5 pagesF-Riviera: AlishaFalisha RivienaNo ratings yet
- Elektronika Dasar Electronic Circuit Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument4 pagesElektronika Dasar Electronic Circuit Bipolar Junction TransistorAnti Gaptek -AGA-No ratings yet
- Solutions & Colligative PropertiesDocument14 pagesSolutions & Colligative PropertiesPoonam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Waves 2Document1 pageWaves 2fghhfgfNo ratings yet
- Ejemplos Diseño Muros SDPWS-NCh1198Document8 pagesEjemplos Diseño Muros SDPWS-NCh1198Ignacio A. GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Ap Academy 3Document3 pagesAp Academy 3José Luis Bolívar AguilarNo ratings yet
- Imagining the Nation in Nature: Landscape Preservation and German Identity, 1885–1945From EverandImagining the Nation in Nature: Landscape Preservation and German Identity, 1885–1945No ratings yet
- ChemhhwDocument12 pagesChemhhwHarshit MalikNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument9 pagesHuman Health and DiseaseBhavna BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Oct 04, 2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan Oct 04, 2023Bhavna BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Poster DraftingDocument14 pagesPoster DraftingBhavna BeniwalNo ratings yet
- MCQ Laws-Of-Motion-McqsDocument7 pagesMCQ Laws-Of-Motion-McqsBhavna BeniwalNo ratings yet
- QP Eng XiDocument9 pagesQP Eng XiBhavna BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Glass, Brittle Plastic and Ceramic Materials Control: BRC Global StandardsDocument8 pagesGlass, Brittle Plastic and Ceramic Materials Control: BRC Global StandardsNavaneethanNo ratings yet
- TransmissionDocument3 pagesTransmissionamitsaharulzNo ratings yet
- Building A HA SmartConnector Cluster-V2.0.6Document35 pagesBuilding A HA SmartConnector Cluster-V2.0.6Ranadeep BhattacahrayaNo ratings yet
- Test Method of Flammability of Interior Materials For AutomobilesDocument17 pagesTest Method of Flammability of Interior Materials For AutomobilesKarthic BhrabuNo ratings yet
- Real Estate License AgreementDocument2 pagesReal Estate License AgreementRocketLawyerNo ratings yet
- 46GA On Designers For CEED, UCEED and NID - Stuff You LookDocument3 pages46GA On Designers For CEED, UCEED and NID - Stuff You LookReshmi Varma100% (1)
- H2S Personal Gas MonitorDocument14 pagesH2S Personal Gas Monitormaher mansiNo ratings yet
- Date CalcDocument8 pagesDate CalcPaolaNo ratings yet
- 777rsec3 PDFDocument36 pages777rsec3 PDFAlexander Ponce VelardeNo ratings yet
- Youth Worker Course Gold CoastDocument6 pagesYouth Worker Course Gold Coastf5dq3ch5100% (2)
- Nef Upper Endtest ADocument8 pagesNef Upper Endtest AVera Stojnova100% (3)
- Europe MapDocument13 pagesEurope MapNguyên ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Snowflake Schema - JennyDocument2 pagesSnowflake Schema - JennyJennyNo ratings yet
- Swash Plate Leveling Tool Instructions: Trex 600 Electric & NitroDocument3 pagesSwash Plate Leveling Tool Instructions: Trex 600 Electric & NitroEdinal BachtiarNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Lesson Plan 3Document4 pagesSocial Studies Lesson Plan 3api-260708940No ratings yet
- Cavinkare Private LimitedDocument4 pagesCavinkare Private LimitedRohit TrivediNo ratings yet
- EN Paper-5Document11 pagesEN Paper-5isabellemdelmasNo ratings yet
- Sample From Cambridge AssessmentDocument2 pagesSample From Cambridge AssessmentVinicius GomesNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Manual 6vem eDocument67 pagesMotherboard Manual 6vem eAri Ercilio Farias FereirraNo ratings yet
- Publication PDFDocument20 pagesPublication PDFBhaumik VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Cheats BFG Doom 3Document5 pagesCheats BFG Doom 3screw_x3No ratings yet
- PIRCHLDocument227 pagesPIRCHLapi-3703916No ratings yet
- Server Preparation Details LinuxDocument9 pagesServer Preparation Details Linuxbharatreddy9No ratings yet
- Sokkia MagnetDocument9 pagesSokkia Magnetbbutros_317684077No ratings yet
- 3.3 Cell MembraneDocument19 pages3.3 Cell MembraneHanaa WazzanNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas AeruginosaDocument26 pagesPseudomonas AeruginosaNur AzizahNo ratings yet
- Phy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb31 Architectures Ver43 PDFDocument99 pagesPhy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb31 Architectures Ver43 PDFRaj Shekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- The Baldur's Gate Series 1 - Baldur GateDocument125 pagesThe Baldur's Gate Series 1 - Baldur GateJustin MooreNo ratings yet
- 2 - ARM Cotex-M3 - IntroductionDocument124 pages2 - ARM Cotex-M3 - IntroductionNghĩa VũNo ratings yet
- RAB PLTS Hybrid 1kWp-ScheneiderDocument4 pagesRAB PLTS Hybrid 1kWp-ScheneiderilhamNo ratings yet