0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6K views5 pagesCE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Answer Key)
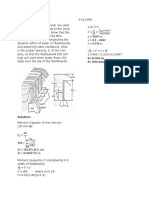
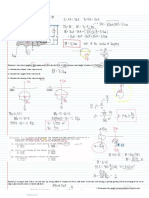
This document provides a 20-question practice exam on principles of geotechnical engineering and hydraulics for the civil engineering licensure exam. The questions cover topics like fluid pressure, fluid flow, centrifugal force, and fluid dynamics problems involving rotating or accelerating containers of water. Correct answers are to be marked on an answer sheet.
Uploaded by
Angelice Alliah De la CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6K views5 pagesCE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Answer Key)
This document provides a 20-question practice exam on principles of geotechnical engineering and hydraulics for the civil engineering licensure exam. The questions cover topics like fluid pressure, fluid flow, centrifugal force, and fluid dynamics problems involving rotating or accelerating containers of water. Correct answers are to be marked on an answer sheet.
Uploaded by
Angelice Alliah De la CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Exam: This section contains a comprehensive set of exam questions focusing on hydraulics and geotechnical engineering principles.