Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xymon Raine S
Uploaded by
Rence SalduaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Xymon Raine S
Uploaded by
Rence SalduaCopyright:
Available Formats
Xymon Raine S.
Bacunata Grade 7 –
Copernicus
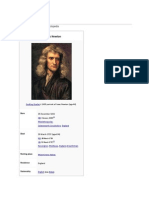
Sir Isaac Newton
(25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27)
He was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author who was described in his
time as a natural philosopher
His most famous contribution to science is the formulation of The Three Laws of Motion. He was a key figure in the
Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His pioneering book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia
Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, consolidated many previous
results and established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with
German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific
viewpoint for centuries until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of
gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, accounting for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the
equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the
motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that
the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and
others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.
Newton built the first practical reflecting telescope and developed a sophisticated theory of colour based on the
observation that a prism separates white light into the colours of the visible spectrum. His work on light was collected in
his highly influential book Opticks, published in 1704. He also formulated an empirical law of cooling, made the first
theoretical calculation of the speed of sound, and introduced the notion of a Newtonian fluid. In addition to his work on
calculus, as a mathematician Newton contributed to the study of power series, generalised the binomial theorem to
non-integer exponents, developed a method for approximating the roots of a function, and classified most of the cubic
plane curves.
You might also like
- IFÁ Order, Wisdom and DeathDocument97 pagesIFÁ Order, Wisdom and DeathAwo Alfredo Rodriguez100% (1)
- Isaac NewtonDocument29 pagesIsaac NewtonShelly JohnNo ratings yet
- Biography of Isaac NewtonDocument7 pagesBiography of Isaac NewtonReyna Avila Ramírez-Arellano100% (1)
- Intro To Philosophy-Module 2Document38 pagesIntro To Philosophy-Module 2binnieNo ratings yet
- Steps in Research ProcessDocument11 pagesSteps in Research ProcessImtiaz Ahmad80% (5)
- Chisholm, Swartz - Empirical Knowledge. Readings From Contemporary Sources PDFDocument600 pagesChisholm, Swartz - Empirical Knowledge. Readings From Contemporary Sources PDFKrisztián PeteNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument21 pagesIsaac Newtonbhaskara the mathematicianNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: The Fluxional MethodDocument3 pagesIsaac Newton: The Fluxional MethodJajaNo ratings yet
- Summary of The God Equation: by Michio Kaku - The Quest for a Theory of Everything - A Comprehensive SummaryFrom EverandSummary of The God Equation: by Michio Kaku - The Quest for a Theory of Everything - A Comprehensive SummaryNo ratings yet
- Birth of A Body, Origin of A History Piera AulagnierDocument31 pagesBirth of A Body, Origin of A History Piera AulagnierGabriela AviñaNo ratings yet
- Sir Isac Newton - BiographyDocument12 pagesSir Isac Newton - BiographyscoutjohnyNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: Lawrence D. Rivera VI-KatapatanDocument1 pageIsaac Newton: Lawrence D. Rivera VI-KatapatankaateviNo ratings yet
- Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Isaac NewtonDocument9 pagesPhilosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Isaac NewtonPedro Soto CruzNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia MathematicaDocument1 pageSir Isaac Newton: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia MathematicaFerrariNo ratings yet
- Colorful Flat Graphic Fact Sheet Isaac Newton Physics WorksheetDocument1 pageColorful Flat Graphic Fact Sheet Isaac Newton Physics Worksheetf.ckthesecretNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument1 pageNewtonaarav.parekh29No ratings yet
- Gladays R. TanesDocument17 pagesGladays R. TanesTanes Peña Rebosura GladaysNo ratings yet
- Biography Isaac NewtonDocument3 pagesBiography Isaac NewtonMyron BrandwineNo ratings yet
- Saac Newton: Early Life and EducationDocument9 pagesSaac Newton: Early Life and EducationGabriel André AlvesNo ratings yet
- Taller Lec 3Document2 pagesTaller Lec 3tallysluciaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper of NewtonDocument7 pagesResearch Paper of Newtonfzfgkws3100% (1)
- Text I: Classical Mechanics Describes The Motion of Macroscopic Objects, From Projectiles ToDocument22 pagesText I: Classical Mechanics Describes The Motion of Macroscopic Objects, From Projectiles ToCaraiman GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Lectura Isaac NewtonDocument2 pagesLectura Isaac NewtonCESAR MAURICIO RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Sir Isaac NewtonDocument1 pagePhilosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Sir Isaac NewtonCharles SalinasNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia MathematicaDocument1 pageSir Isaac Newton: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia MathematicanagavishnuNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument4 pagesHomeworkalabhya singhNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument4 pagesIsaac Newtonalabhya singhNo ratings yet
- Physics Group PresentionDocument3 pagesPhysics Group Presentionapi-285379169No ratings yet
- VrushaliDocument4 pagesVrushaliPriyadarshan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia MathematicaDocument1 pageIsaac Newton: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia MathematicaBibin K NairNo ratings yet
- Issac Newton With PICDocument1 pageIssac Newton With PICusunomNo ratings yet
- Power PointDocument15 pagesPower PointMuhammed RafivithuraNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument6 pagesIsaac NewtonDreamNuance AnutzaNo ratings yet
- Newton, Isaac (1642-1727) : EuclidDocument4 pagesNewton, Isaac (1642-1727) : EuclidHugo Cesar GNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27 Newton Saint of ScienceDocument12 pagesLecture 27 Newton Saint of SciencePathumavathy RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Cap 1Document11 pagesCap 1Elena DimitriuNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac NewtonDocument29 pagesSir Isaac NewtonGladie Ann Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- The Celestial Mechanics of Newton: Dipankar BhattacharyaDocument10 pagesThe Celestial Mechanics of Newton: Dipankar BhattacharyaAlexander AlekhineNo ratings yet
- Tugas Teks Recount Berupa Biografi Tokoh TerkenalDocument3 pagesTugas Teks Recount Berupa Biografi Tokoh Terkenalilhamzulkarnain604No ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: BiographyDocument4 pagesIsaac Newton: BiographychelseyNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument15 pagesIsaac NewtonSamanNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument2 pagesNewtonvaranpreetNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument2 pagesNewtonappoplexian rathNo ratings yet
- Young EinsteinDocument10 pagesYoung EinsteinkaubreyNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument1 pageIsaac NewtonAnandadeva. BNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton (164-1727) A Scientific GeniusDocument4 pagesSir Isaac Newton (164-1727) A Scientific GeniusKim PowellNo ratings yet
- Birth of Modern PhysicsDocument27 pagesBirth of Modern PhysicsA-Mark Gabriel PesanteNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: BibliografiaDocument8 pagesIsaac Newton: BibliografiaAbraham ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Sir Isaac NewtonDocument1 pagePhilosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Sir Isaac NewtonSyed Anas SohailNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac NewtonDocument16 pagesSir Isaac NewtonSean CoxNo ratings yet
- Scientist in Scientific RevolutionDocument2 pagesScientist in Scientific RevolutionRc RcNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws & His System of The World: Part CDocument53 pagesNewton's Laws & His System of The World: Part CAkhmadTaufikIsmailNo ratings yet
- Sir Isaac Newton, PRS, (4 January 1643 - 31 March 1727)Document6 pagesSir Isaac Newton, PRS, (4 January 1643 - 31 March 1727)bookpalNo ratings yet
- Quantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsFrom EverandQuantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsNo ratings yet
- Essay About Isaac NewtonDocument1 pageEssay About Isaac NewtonMarko MedinNo ratings yet
- Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Sir Isaac NewtonDocument1 pagePhilosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica: Sir Isaac NewtonsatvikNo ratings yet
- Information About Isaac Newton - A4Document4 pagesInformation About Isaac Newton - A4johnreybayoguingNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument14 pagesIsaac Newton11Toán1-06-Phạm Lê Bá DươngNo ratings yet
- The Road To Reality: A Complete Guide To The Laws of The UniverseDocument6 pagesThe Road To Reality: A Complete Guide To The Laws of The UniverseKaustubhNo ratings yet
- Who Is Isaac Newton - Act 4Document3 pagesWho Is Isaac Newton - Act 4Cati-an AnalynNo ratings yet
- Contribution and Postulate of Famous AstronomersDocument2 pagesContribution and Postulate of Famous AstronomersRj YanesNo ratings yet
- Quantum in EdDocument9 pagesQuantum in EdmoonthinkerNo ratings yet
- Saac NewtonDocument4 pagesSaac NewtonMohit GaharanaNo ratings yet
- Annus Mirabilis Papers - WikipediaDocument47 pagesAnnus Mirabilis Papers - Wikipediaminsara madtNo ratings yet
- Documentary Research Method New DimensionsDocument15 pagesDocumentary Research Method New Dimensionsvictorvallejo3529No ratings yet
- APSCHE Curriculum For Engineering UG ProgrammesDocument44 pagesAPSCHE Curriculum For Engineering UG ProgrammesGodavari KurisunaNo ratings yet
- Sociology and Common Sense Andre BeteilleDocument6 pagesSociology and Common Sense Andre BeteilleM SNo ratings yet
- Research QuestionsDocument2 pagesResearch QuestionsFrances Gallano Guzman AplanNo ratings yet
- Engendering The Social PDFDocument234 pagesEngendering The Social PDFJuan Antonio Duque-Tardif100% (1)
- Human Biology Y11 Syllabus ATAR - GDDocument25 pagesHuman Biology Y11 Syllabus ATAR - GDparty100% (1)
- 4 Argumenta Philippe Huneman and Marion Vorms Is A Unified Account of Conspiracy Theories PossibleDocument7 pages4 Argumenta Philippe Huneman and Marion Vorms Is A Unified Account of Conspiracy Theories PossiblesikedbruhNo ratings yet
- Tom 2020Document5 pagesTom 2020pacoto livingstoneNo ratings yet
- ED 106 MidtermDocument2 pagesED 106 MidtermRazyl EdioNo ratings yet
- CAPUTOL Activity 2.1 - PhysicsDocument4 pagesCAPUTOL Activity 2.1 - PhysicsCaputol CrystalNo ratings yet
- Group-2 05 Lab Worksheet 1Document1 pageGroup-2 05 Lab Worksheet 1Pauline OcampoNo ratings yet
- Viva-Vice Examinations For PH.D StudentsDocument15 pagesViva-Vice Examinations For PH.D StudentsDr.Umakant.G.DevaramaniNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Marketing Research A Hands-On Orientation 1st Edition Malhotra Test Bank 1Document24 pagesEssentials of Marketing Research A Hands-On Orientation 1st Edition Malhotra Test Bank 1robin100% (39)
- Dark Intentions Sidharth Soundararajan 14630Document2 pagesDark Intentions Sidharth Soundararajan 14630Sidharth SoundararajanNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Media Pembelajaran Matematika Menggunakan Software Geogebra Dengan Pendekatan Scientific Pada Materi Prisma Dan Limas Di Tingkat SMPDocument16 pagesPengembangan Media Pembelajaran Matematika Menggunakan Software Geogebra Dengan Pendekatan Scientific Pada Materi Prisma Dan Limas Di Tingkat SMPSugeng SungkonoNo ratings yet
- IOP2601_ASSESSMENT 3 SEMESTER 1 2024Document4 pagesIOP2601_ASSESSMENT 3 SEMESTER 1 2024onelam.ndenganeNo ratings yet
- 1 Review Guide For The Final Exams Educational ResearchDocument13 pages1 Review Guide For The Final Exams Educational ResearchNia CervantesNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument10 pages1 SMAnindita GaluhNo ratings yet
- How Far Have We Come With The Study of Artificial Intelligence For Recruitment ProcessDocument7 pagesHow Far Have We Come With The Study of Artificial Intelligence For Recruitment ProcessAyaz SultanNo ratings yet
- Root,+journal+manager,+15 IJEFI 10458 IC24Document5 pagesRoot,+journal+manager,+15 IJEFI 10458 IC24Josué Mercado ZagacetaNo ratings yet
- 1-Sample Hypo TestDocument34 pages1-Sample Hypo TestChong ChongNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Research Methods PGDocument77 pagesCH 1 Research Methods PGabrehamNo ratings yet
- Materials: Design of Industrial Standards For The Calibration of Optical MicroscopesDocument22 pagesMaterials: Design of Industrial Standards For The Calibration of Optical MicroscopesVikram BillalNo ratings yet
- Role of Bioinformatics in Medical LaboratoryDocument9 pagesRole of Bioinformatics in Medical LaboratoryEmmanuel Kings100% (2)
- Unit 2 Understanding H-H RelationshipDocument66 pagesUnit 2 Understanding H-H RelationshipONLINE hapurNo ratings yet