Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class Ix - Science - Biology - Chapter 6 - Tissues (Animal Tissues) - Notes
Uploaded by
Vipul TehlanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class Ix - Science - Biology - Chapter 6 - Tissues (Animal Tissues) - Notes
Uploaded by
Vipul TehlanCopyright:
Available Formats
“Happiness is a matter of choice”
.
CLASS: IX
SECTION: ALL
SUBJECT: SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
SESSION: 2023-24
CHAPTER 6: TISSUES
NOTES (PART 2)
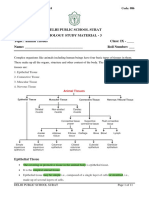
ANIMAL TISSUES
ANIMAL TISSUES
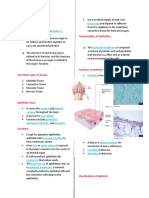
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
✓ Characteristics: Tightly packed without intercellular spaces and form a continuous sheet.
The cells are generally flat or cuboidal or columnar cells.
The tissueus have a small amount of cementing material between them
✓ Location: Covers the whole body surface and most organs and cavities within the body.
✓ Function: Protection, absorption, secretion, mechanical support etc
TYPES OF EPITHELIAL TISSUE
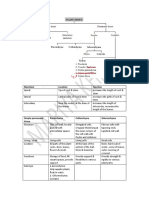
Type Characteristics Location Function
Simple squamous Cells are large, extremely Lining of blood vessels, Exchange and transport
thin and flat on a basement lung alveoli, of substances through a
mebrane oesophagus, the lining of selectively permeable
the mouth and cheek membrane
Stratified squamous Cells are arranged in a Outer protective Provides protection to
pattern of layers covering all over the underlying tissues
body surface
Columnar Cells are tall and cylindrical Inner lining of the Absorption of nutrients
epithelium (pillar-like) stomach and intestines from the digested food
Ciliated columnar Cells possess fine hair-like Inner lining of the In the respiratory tract,
cilia trachea, lungs, the movement of cilia
(respiratory system) and pushes the mucus
buccal chambers forward to clear it
Cuboidal epithelium Cells are cube-shaped and Lining of the kidney Gives mechanical
are placed on a basement tubules as well as in the support and helps in the
membrane ducts of the salivary absorption of useful
glands
www.queensvalleyschool.in Sector-8, Phase-I, Dwarka, New Delhi-110077
“Happiness is a matter of choice”
.
material from urine
before it is passed out
Glandular Epithelial tissue which folds Present in the stomach, Secretion of substances
epithelium inwards to form a intestine, pancreas and at the epithelial surface
multicellular gland other glands
Fig: Simple Squamous epithelium
Fig: Types of Epithelial tissues
Fig: Ciliated Columnar epithelium
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
✓ Characteristics: Consists of a matrix and the cells are embedded in it.
✓ Location: Found in the deeper parts of the body, between the skin and muscles.
✓ Function: Connects various organs and keeps them in place.
TYPES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Type Characteristics Location Function
Blood Red-coloured fluid matrix Present throughout the Connects different parts of
which consists of plasma body and flows through the body and establishes
and cells such as RBCs, blood vessels. continuity within the body.
WBCs and platelets. Blood flows and transports
gases, digested food,
The plasma contains hormones and waste
proteins, salts and materials to different parts
hormones. of the body.
Bone Hard, strong and non- Forms a part of the Forms the supporting
flexible tissue. skeletal system framework of the body .
Bone cells (osteocytes) It also anchors the muscles
are embedded in a hard and supports the main
matrix that is composed organs of the body. Gives
of calcium and shape and rigidity to the
phosphorus compounds. body
Tendons Great strength but Found in the spaces Tendons help to attach
(Fibrous tissue- Mainly limited flexibility between the bones and muscles to the bones.
formed of fibre-forming muscles
cells)
www.queensvalleyschool.in Sector-8, Phase-I, Dwarka, New Delhi-110077
“Happiness is a matter of choice”
.
Ligaments Elastic and has Between bones Ligaments connect bones
(Fibrous tissue- Mainly considerable strength. with bones and serve to
formed of fibre-forming They contain very little hold the structures
cells) matrix. together and keep them
strong and stable.
Cartilage Elastic tissue with widely Present in the nose, Smoothens the bone
spaced cells. external ear, trachea, surface at joints, allowing
Cells (Chondrocytes) are larynx, ends of the long smooth movement of these
embedded in the solid bones and between the joints
matrix composed of vertebrae
proteins and sugars.
Areolar tissue Made of gelatinous Found between the skin Fills the space inside the
matrix containing cells and muscles, around the organs,
and irregularly arranged blood vessels, nerves Helps in repair of tissues.
fibres and in the bone marrow Supports and strengthens
the internal organs
Adipose tissue Cells are filled with fat Found beneath the skin, Stores fat.
globules around the kidneys and Act as an insulator and
other internal organs prevents the loss of heat.
such as intestines
MUSCLE TISSUE
✓ Characteristics : Consists of elongated, narrow, muscle cells called muscle fibres;
✓ contain special proteins called contractile proteins, which contract and relax to cause movement.
✓ Location: Mostly attached to the bones; found in heart as the cardiac muscles.
✓ Function : Contract and relax to cause the movement of the body.
TYPES OF MUSCLE TISSUE
Type Characteristics Location Function
Striated/skeletal/ Muscle fibres are long, Found attached to the Help in voluntary
striped/voluntary muscles cylindrical, unbranched bones movement and
and multinucleate locomotion.
www.queensvalleyschool.in Sector-8, Phase-I, Dwarka, New Delhi-110077
“Happiness is a matter of choice”
.
Non-striated/ Muscle fibres are smooth Found in the uterus, Helps to carry out
smooth/non-striped/ and without striations digestive tract, urinary involuntary movements
involuntary muscles bladder, iris of the eye, (which cannot be carried
bronchi of the lungs and out by our conscious will)
other internal organs
Cardiac/heart muscles Muscle cells are short, Found only in the walls Rhythmic contraction
cylindrical and have a of the heart and relaxation of cardiac
single, centrally placed muscles help to pump
nucleus and distribute the blood
to various parts of the
body
Differences between the Skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles
Skeletal Smooth Cardiac
1. Striated 1. Unstriated 1. Striated
2. Cylindrical 2. Spindle-shape 2. Cylindrical
3. Not branched 3. Not branched 3. Branched
4. Nuclei - peripheral 4. Nucleus - central 4. Nuclei - central
5. Voluntary 5. Involuntary 5. Involuntary
NERVOUS TISSUE
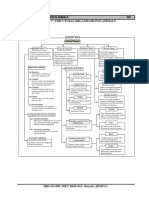
Characteristics : Made up of elongated cells called neurons.
Each neuron consists of the following parts—
1. Dendrites 2.Cell Body 3. Axon and 4.Nerve endings.
Many nerve fibres bound together by connective tissue make
up a nerve.
The signals that passes along the nerve fibre is called a nerve
impulse. Nerve impulses allow us to move our muscles
Location : Component of the nervous system and
encompasses the brain, spinal cord and nerves.
Function: Nerve cells help in the transmission of messages
from the brain to different parts of the body and vice versa.
www.queensvalleyschool.in Sector-8, Phase-I, Dwarka, New Delhi-110077
You might also like
- UntitledDocument41 pagesUntitledDion AdalaNo ratings yet
- Tissue of The BodyDocument12 pagesTissue of The BodyJuliet Aira Cabero Quibilan100% (1)
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Document28 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Linati Dawedi100% (1)
- Anatomy - TissuesDocument43 pagesAnatomy - TissuesGleceree Filomeno100% (1)
- HUMAN TISSUE PRESENTATIONDocument47 pagesHUMAN TISSUE PRESENTATIONAngelo Cadenas75% (4)
- Introduction to HistologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction to HistologyMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis LectureDocument29 pagesNeonatal Sepsis LectureElton Ndhlovu100% (3)
- PTT Gas Separation Plant Fire Proofing StandardDocument18 pagesPTT Gas Separation Plant Fire Proofing StandardKanjana LeardrakNo ratings yet
- Planets that rule over different parts of the body and their effectsDocument6 pagesPlanets that rule over different parts of the body and their effectsmurthyy55% (11)
- Static Var CompensatorDocument12 pagesStatic Var CompensatorBengal Gaming100% (1)
- EpidemiologyDocument26 pagesEpidemiologymohildasadiaNo ratings yet
- Mercaptans Removal From Gases by Absorption Into Amines and CausticDocument8 pagesMercaptans Removal From Gases by Absorption Into Amines and Causticgopal100% (1)
- Answer Key EXAM DRILL 2 - Community Health Nursing Nursing Practice Ii - CHN and Care of The Mother and ChildDocument24 pagesAnswer Key EXAM DRILL 2 - Community Health Nursing Nursing Practice Ii - CHN and Care of The Mother and Childbetiful83% (6)
- Policy and Procedures For Hiring, PromotionsDocument2 pagesPolicy and Procedures For Hiring, PromotionsRazel Ann ElagioNo ratings yet
- Biolis 24i PDFDocument43 pagesBiolis 24i PDFMohamed Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- IX-BIODocument4 pagesIX-BIOkartikvarshney98No ratings yet
- Handout-Animal-Tissues-2023-2024Document4 pagesHandout-Animal-Tissues-2023-2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- Fact Sheets Animal Cell TypesDocument4 pagesFact Sheets Animal Cell Typessamsung picturesNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Tissues - Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab 5 Tissues - Lab ReportbrittNo ratings yet
- BIO 9 SM3 23-24pDocument11 pagesBIO 9 SM3 23-24pNandini Pritesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue TypeDocument7 pagesEpithelial Tissue Typevaynegod5No ratings yet
- Animal Tissues ExplainedDocument9 pagesAnimal Tissues ExplainedAlfred CariñoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Biology ReviewerDocument8 pagesModule 2 Biology ReviewerDeirdre dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andDocument5 pagesChapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andMonika MehanNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument4 pagesTissuesjisoo kimNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissues - ObjectivesDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Tissues - ObjectivesSyedrijal AkberNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL TISSUES AND ORGAN SYSTEMSDocument7 pagesANIMAL TISSUES AND ORGAN SYSTEMSKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- Tissues Part 2Document4 pagesTissues Part 2Monika Mehan100% (1)
- Mind Tissues: A Summary of Plant and Animal Tissue TypesDocument1 pageMind Tissues: A Summary of Plant and Animal Tissue TypesAbhishek NarwariyaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument32 pagesAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueSarveshrau MagentharauNo ratings yet
- Module3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyDocument11 pagesModule3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyJahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsDocument16 pagesCH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsREENA GULERIANo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument61 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- AP Module4 Trans DiazDocument18 pagesAP Module4 Trans DiazJohn Rafael DiazNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Types, Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: Types, Structure and FunctionsL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Tissue Types and FunctionsDocument16 pagesTissue Types and FunctionsMeruthulaNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesDocument3 pagesStructural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesHadiya FatimaNo ratings yet
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- 5689794613Document4 pages5689794613DEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Structural OrganizationDocument119 pagesStructural OrganizationAVS CONo ratings yet
- ANIMAL-CELL group 2Document35 pagesANIMAL-CELL group 2mjecbjNo ratings yet
- Answers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsDocument7 pagesAnswers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsKatznjammrNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Document11 pagesBIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Tonya Oliver100% (1)
- 649539f145572900183c11f2 ## Structural Organisation in Animals ShortDocument4 pages649539f145572900183c11f2 ## Structural Organisation in Animals Shorts.yagyan prasad acharyNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Cell Biology and Organisation: 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsDocument47 pages2.0 Cell Biology and Organisation: 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsFHATIN AMIRA BINTI MUSA MoeNo ratings yet
- Answers of Histology SlidesDocument38 pagesAnswers of Histology SlidesJiyaa PatelNo ratings yet
- Tissues Level OrganizationDocument60 pagesTissues Level OrganizationHilman YusriNo ratings yet
- GENERAL-BIOLOGY-R-Q3Document16 pagesGENERAL-BIOLOGY-R-Q3Maysheil GalarceNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue TypesDocument17 pagesAnimal Tissue TypesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Tissue Types and FunctionsDocument31 pagesTissue Types and Functionsaliyyah aswinanda100% (1)
- GEN BIO 2 Final ReviewerDocument12 pagesGEN BIO 2 Final ReviewerJemuel Luc JavierNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisation NotesDocument15 pagesCell Organisation Notessylent gohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 or 4 - Body Tissues and GlandsDocument11 pagesChapter 3 or 4 - Body Tissues and GlandsAlthea BayolaNo ratings yet
- What Is Tissue and What Are The Different Types of Animal Tissue?Document6 pagesWhat Is Tissue and What Are The Different Types of Animal Tissue?Shahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue ReportDocument29 pagesConnective Tissue ReportSheina UdaundoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument2 pagesTissuesDinesh0% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- CH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument8 pagesCH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsLaxmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- Human TissueDocument6 pagesHuman TissueRence GuerraNo ratings yet
- 2.2.2 Cell Specialisation in Multicellular OrganismsDocument18 pages2.2.2 Cell Specialisation in Multicellular Organismsche sal100% (1)
- Tissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsDocument4 pagesTissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsRyan Cadorna FontanillaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch07 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes Ch07 Structural Organisation in AnimalsSham PhadtareNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- May 2 Homework Solutions: S M X CDocument3 pagesMay 2 Homework Solutions: S M X CClerry SamuelNo ratings yet
- Ark of The Covenant Montessori Chamber of Learning PoblacionDocument3 pagesArk of The Covenant Montessori Chamber of Learning PoblacionMaiAce Sean Shawn SynneNo ratings yet
- 2022 EDCS Weekly Surveillance Report No 5Document22 pages2022 EDCS Weekly Surveillance Report No 5Aesthetics MinNo ratings yet
- Anesthesiology GuideDocument4 pagesAnesthesiology GuideGeorge Wang100% (1)
- Mineral Resources, Uses and Impact of MiningDocument4 pagesMineral Resources, Uses and Impact of MiningShakti PandaNo ratings yet
- iSF EClassRecord - NewNormal AdviserDocument254 pagesiSF EClassRecord - NewNormal AdviserYanara Delarama DayapNo ratings yet
- IDSA Guias Infeccion de Tejidos Blandos 2014 PDFDocument43 pagesIDSA Guias Infeccion de Tejidos Blandos 2014 PDFyonaNo ratings yet
- WiNmaster 2: Intelligent LV Air Circuit BreakerDocument62 pagesWiNmaster 2: Intelligent LV Air Circuit Breakerabdul karimNo ratings yet
- Kyocera Fs 1118mfpKm1820Document200 pagesKyocera Fs 1118mfpKm1820Jane VinuyaNo ratings yet
- Rigatoni With Beef and Onion RaguDocument3 pagesRigatoni With Beef and Onion RagumadduxdavidNo ratings yet
- ADPKDDocument75 pagesADPKDVenkataramanan KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Imaging-Guided Chest Biopsies: Techniques and Clinical ResultsDocument10 pagesImaging-Guided Chest Biopsies: Techniques and Clinical Resultsweni kartika nugrohoNo ratings yet
- KAP COVIDDocument4 pagesKAP COVIDIndahNo ratings yet
- Project PPT Spot WeldingDocument19 pagesProject PPT Spot WeldingMehul BariyaNo ratings yet
- Is 228 (Part 1) : 1987 Methods For Chemical Analysis Of: (Reaffirmed 2008)Document5 pagesIs 228 (Part 1) : 1987 Methods For Chemical Analysis Of: (Reaffirmed 2008)Indira BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- RPLB Trip Kit Index and Airport InformationDocument22 pagesRPLB Trip Kit Index and Airport InformationMeta learnNo ratings yet
- Genetic Recombination and Linkage MappingDocument47 pagesGenetic Recombination and Linkage MappingTony BernardNo ratings yet
- Climate Responsive ArchitectureDocument32 pagesClimate Responsive ArchitectureNikhila CherughattuNo ratings yet
- Buy Lizol Floor Cleaner 5000 ML Online - GeMDocument4 pagesBuy Lizol Floor Cleaner 5000 ML Online - GeMHimanshu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- What Exactly Are Period PantiesDocument2 pagesWhat Exactly Are Period PantiesJay Jay KamgaNo ratings yet