Professional Documents
Culture Documents
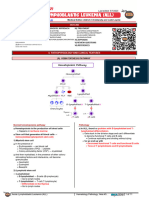
Hematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Illustrations - Key)
Uploaded by
hasanatiya41Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Illustrations - Key)
Uploaded by
hasanatiya41Copyright:
Available Formats
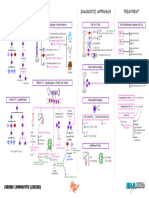
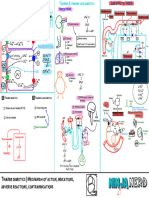
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TREATMENT
Hematopoiesis Pathway Effects of ↑↑ Leukocytes (Chronic Phase) CBC w/ P.B.S. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
80-85%
Agents: Imatinib
Chronic Phase
Splenomegaly CP-CML → normal
No symptoms
Hemocytoblast N/V M.S.C. (Accelerated Phase)AP/BP-CML → ↓↓RBC's
Anorexia CP-CML → ↑↑PLT's
Fullness ↑ No effect on RBS's
↑ AP/BP-CML → ↓↓PLT's
in this phase
M.S.C. L.S.C.
Thrombocytosis (increase number of PL ) C/P/AP ± BP-CML WBC↑↑
Deposition Leukocytosis↑↑
BCR-ABL
P.B.S. ↑neutrophils
TPO CSF EPO
Extramedullary Neutrophils↑↑ Pathophysiology
hematopoiesis CP-CML ↑eosinophils
Basophils↑↑ IL-1 ↓↓Blast cells (<10%) ↑basophils
Lymphoblasts increase produce bld cell Mature
Eosinophils INF-Alpha ↑↑Granulocytes AP/BP-CML Granulocutes
↑PLT’s Myeloblast RBC’s
Fevers + night sweats ↑↑Blast cells ↓↓Blast cells
↓↓Cell prolifiration ↑↑Apoptosis
B-cells T-cells
P.M.C.
Effects of ↑↑ Leukocytes (Accelerated Phase) Bone Marrow Biopsy
Bone Marrow Transplant
Splenomegaly Expand R.B.M. Bone Trigger Definitive Dx
Blast cells
Myelocyte pain 2/2 Failure of TKI’s
Splenic (9;22)t <10% → CP-CML
rupture 10-19% → AP-CML
↑ 2/2 BCR-ABL gene >20% → BP-CML
Metamyelocyte ↑ Cytoreduction
Deposition ↓Space ↑Cell prolif. ↓Apoptosis Granulocytes (↑↑Diff)
Hematopoiesis Refractory Thrombocytopenia Functional Symptomatic
(extra) Leukocytosis Bruising ↓Space Granulocytes↑↑ ↑↑WBC’s
↑↑Neutrophil ↑↑Eosinophil ↑↑Basophil Myelocytes CML >> AML
Basophils↑↑ Anemia Mut.
Bleeding Blast cells↑↑ Metamyelocytes ↑↑PLT’s
Pruritus Fatigue (10-19%)
bcz basophil produce a
Pallor Agent: Hydroxyurea
Causes of ↑↑ Leukocytes lot of histamin Space in
Dyspnea R.B.M. Genetic Studies
red bone marrow
1
Ionizing Radiation Effects of ↑↑ Leukocytes (Blast Phase) Cytogenetics PCR
Mutation ↑Mortality (+) Phil.
↑Cell prolif. chromosome
Oncogenes (9;22)t
M.S.C. (9;22)t
T. Suppressor ↓Apoptosis CML BCR-ABL (+)
genes Bone pain
AML TKI’s TKI’s
M.B.
2
Genetic Dx (9;22)t Additional Tests
↑Blast ↓Functional ↑↑Anemia
↑↑Replication P.M.C.
cells WBC's
Chromosomal Translocation
tyrosin kinase ↑↑Thrombocytopenia
↑↑Mutations 90% BCR-ABL T.K. CML VS Leukemoid Reaction
M.C.
gene Receptor ↑↑Infections ↑↑Cell prolif.
(9;22)t (9;22)t
↓↓Diff. M.S.C. ↓↓Apoptosis 2/2 (9;22)t 2/2 Infection
↓Apoptosis Time
M.M.C. Leukostasis ↑↑WBC (>50K) 2/2 Stress
CML ALL
Time ↑Cell prolifiration Mutations
(90%) (20%) T.L.S. LAP ↓↓LAP ↑↑WBC (<50%)
Tumor lysis syndrome ↓Diff. leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
↑↑LAP
↑↑ ↑↑ ↑↑ ↑↑Blast cells (>20%)
Splenic uls or CT abdomen
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
You might also like
- Hematology Pathology - 004) Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageHematology Pathology - 004) Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageHematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- EMD1 Pc1 PATOFISIOLOGI SEPSISDocument5 pagesEMD1 Pc1 PATOFISIOLOGI SEPSISRasyid RidhaNo ratings yet
- Sec2 G8Document2 pagesSec2 G8อัมพกา ทองแท้No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 005) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageHematology Pathology - 005) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- DR Anna Mira Lubis - Diagnostic Approach of ThrombocytopeniaDocument36 pagesDR Anna Mira Lubis - Diagnostic Approach of Thrombocytopeniayosua simarmataNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument4 pagesPath o PhysiologyDorinna Rizada BagaNo ratings yet
- CBC (Complete Blood Count)Document38 pagesCBC (Complete Blood Count)yeshitla amsaluNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Flow Chart: Drug/Medication Started DiscontinuedDocument4 pagesTherapeutic Flow Chart: Drug/Medication Started DiscontinuedJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Flow Chart: Drug/Medication Started DiscontinuedDocument4 pagesTherapeutic Flow Chart: Drug/Medication Started DiscontinuedJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- RBC DisordersDocument8 pagesRBC DisordersDavid JohnNo ratings yet
- 2 Main Anemia in PregnancyDocument8 pages2 Main Anemia in PregnancyParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 007) Cushing's Syndrome (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageEndocrinology Pathology - 007) Cushing's Syndrome (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Anemia: Myelodysplastic SyndromeDocument1 pageAnemia: Myelodysplastic SyndromeFidesha Nurganiah SiregarNo ratings yet
- Anemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic MacrocyticDocument1 pageAnemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic Macrocyticمحمد عقيلي100% (1)
- 13-Komplikasi Jantung Terapi Lung CancerDocument19 pages13-Komplikasi Jantung Terapi Lung CancersukiyantoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal FBC 1.16 Feb 2016Document5 pagesAbnormal FBC 1.16 Feb 2016jyothi vallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- CC2 TransDocument12 pagesCC2 TransAnathalea ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anemia DX TXDocument2 pagesAnemia DX TXProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- How I Treat Polycythemia VeraDocument12 pagesHow I Treat Polycythemia VeraMayra AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Bloodbld 2018834044 CDocument12 pagesBloodbld 2018834044 CFrancieudo SampaioNo ratings yet
- 19-Laboratory RequestDocument1 page19-Laboratory RequestMisale HaileNo ratings yet
- Conditions That Cause Interference On Most Hematology AnalyzersDocument2 pagesConditions That Cause Interference On Most Hematology AnalyzersSamantha IsabelNo ratings yet
- CC Serum Protein FractionsDocument6 pagesCC Serum Protein FractionsmendoxastarNo ratings yet
- Mr. S/67 Yo/bengawan Solo WardDocument27 pagesMr. S/67 Yo/bengawan Solo WardMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Basic HematologyDocument69 pagesBasic HematologyDimas Bayu FirdausNo ratings yet
- Chart - WBC DisordersDocument1 pageChart - WBC DisordersSamuel RothschildNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids & CirculationDocument5 pagesBody Fluids & CirculationSipranjali SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Anemia Workup - Approach Considerations, Investigation For Pathogenesis, Evaluation For Blood LossDocument14 pagesAnemia Workup - Approach Considerations, Investigation For Pathogenesis, Evaluation For Blood LossRahul SahadevanNo ratings yet
- (M3) Approach To Full Blood Count (FBC)Document93 pages(M3) Approach To Full Blood Count (FBC)azs8t1No ratings yet
- EUROFLOW ANTIBODY PANELS Cytognos BrochureDocument1 pageEUROFLOW ANTIBODY PANELS Cytognos Brochure82lauNo ratings yet
- MS NTBKDocument10 pagesMS NTBKARIANE DOLINONo ratings yet
- KAKAKDocument5 pagesKAKAKMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Anemia in PregnancyDocument5 pagesDiagnosis of Anemia in PregnancyKlaraNo ratings yet
- 3304 37128 Anemia DefisiensiDocument36 pages3304 37128 Anemia DefisiensifatihahannisahumairaNo ratings yet
- Hematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsDocument55 pagesHematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsAmorrita Puspita Ratu100% (1)
- XN-Series Clinical Case Report Vol. 2Document71 pagesXN-Series Clinical Case Report Vol. 2Görünmez gorunur100% (2)
- CML DX TX PatholDocument47 pagesCML DX TX PatholMarthinoNo ratings yet
- 05.012.002.0045-2 Finecare IiDocument2 pages05.012.002.0045-2 Finecare IiAinun Jariah100% (1)
- RBC AnomaliesDocument5 pagesRBC AnomaliesThe16LoverrNo ratings yet
- 3304 37128 Anemia DefisiensiDocument36 pages3304 37128 Anemia DefisiensifatihahannisahumairaNo ratings yet
- Piis0025619611615681 PDFDocument14 pagesPiis0025619611615681 PDFMaryJoy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anaemia and Oncology NotesDocument57 pagesAnaemia and Oncology Notesgirlcub789No ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISMTAPSEMDocument2 pagesHEMATOPOIESISMTAPSEMDarwin AlejosNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology DiagramDocument3 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology DiagrammonishaNo ratings yet
- 2F MEDICINE 2 Hypoproliferative Anemias (Dr. Kua)Document4 pages2F MEDICINE 2 Hypoproliferative Anemias (Dr. Kua)herrerachaimNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Clinpath Le1Document7 pagesShanz - Clinpath Le1Petrina XuNo ratings yet
- My Important DocumentsDocument12 pagesMy Important DocumentsNivein's BiG WolrdNo ratings yet
- 9anemia Due To Increased Destruction of ErythrocytesDocument43 pages9anemia Due To Increased Destruction of ErythrocytesanonacadsNo ratings yet
- Leukemia ?Document1 pageLeukemia ?7ussain7aliNo ratings yet
- Armand Et Al. - 2013 - Detection of Circulating Tumour DNA in Patients With Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma PDFDocument4 pagesArmand Et Al. - 2013 - Detection of Circulating Tumour DNA in Patients With Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma PDFflashjetNo ratings yet
- Clinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesDocument55 pagesClinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesShiv Sookun100% (1)
- Khaled Khalilia: Normocytic Microcytic Macrocytic HemolyticDocument12 pagesKhaled Khalilia: Normocytic Microcytic Macrocytic HemolyticrupNo ratings yet
- 1.BC 5800 PrincipleDocument37 pages1.BC 5800 PrinciplekiryNo ratings yet
- CBE - Platelet AbnormalitiesDocument3 pagesCBE - Platelet AbnormalitiesRuxandra MesarosNo ratings yet
- Over Weight / Obesity Stress Smoking Cocaine Use / Abuse Sedentary Lifestyle Diet in Fats, Na, CholesterolDocument4 pagesOver Weight / Obesity Stress Smoking Cocaine Use / Abuse Sedentary Lifestyle Diet in Fats, Na, Cholesterollouije_mombael2000No ratings yet
- Electrolytes FinalDocument22 pagesElectrolytes Finalfaiza anwerNo ratings yet
- Hematology 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesHematology 2 ReviewerAnn YeongNo ratings yet
- Acute Ischemic Stroke Concept MapDocument6 pagesAcute Ischemic Stroke Concept MapMoonyeen Jann Casera Balic100% (2)
- Endocrine Physiology) 15. Adrenal Medulla - Catecholamines - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology) 15. Adrenal Medulla - Catecholamines - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Neurology LectureDocument48 pagesNeurology Lecturehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla CatecholaminesDocument4 pages051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla Catecholaminesیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 007) Cushing's Syndrome (Notes)Document7 pagesEndocrinology Pathology - 007) Cushing's Syndrome (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Reumato and EndocrineDocument106 pagesReumato and Endocrinehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Orthopedic DisordersDocument15 pagesOrthopedic Disordershasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 009) Pheochromocytoma (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageEndocrinology Pathology - 009) Pheochromocytoma (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology& Onco LectureDocument66 pagesHematology& Onco Lecturehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 010 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular Cardiac CycleDocument3 pages010 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular Cardiac Cyclehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Development & Growth Nutrition & Behavioral DisordersDocument27 pagesDevelopment & Growth Nutrition & Behavioral Disordershasanatiya41No ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument43 pagesCardiologyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology) 09 Thiazide Diuretics - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology) 09 Thiazide Diuretics - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- ACE I & ARBs Mechanism of Action AtfDocument3 pagesACE I & ARBs Mechanism of Action AtfAmir mohammad moori MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 057 - Endocrinology Physiology) OvulationDocument4 pages057 - Endocrinology Physiology) Ovulationhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Notes)Document8 pagesHematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Notes)Document11 pagesHematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Vasculitis PPT NotesDocument14 pagesVasculitis PPT Noteshasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 342 - Hematology Physiology) Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationDocument6 pages342 - Hematology Physiology) Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell Formationhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Renal Pathology Acute Kidney Injury AKIDocument14 pagesRenal Pathology Acute Kidney Injury AKIPranav PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Legal Education BoardDocument25 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Legal Education BoardPam NolascoNo ratings yet
- Laser For Cataract SurgeryDocument2 pagesLaser For Cataract SurgeryAnisah Maryam DianahNo ratings yet
- National Geographic Traveller India - July 2016-P2PDocument104 pagesNational Geographic Traveller India - July 2016-P2PPeter100% (2)
- Business Research Chapter 1Document27 pagesBusiness Research Chapter 1Toto H. Ali100% (2)
- Reinforcing Steel and AccessoriesDocument4 pagesReinforcing Steel and AccessoriesTheodore TheodoropoulosNo ratings yet
- Quiz MicrobiologyDocument65 pagesQuiz MicrobiologyMedShare98% (51)
- 6 Special Favors Given To Muhammad ( ) by Allah (Notes) - AuthenticTauheed PublicationsDocument10 pages6 Special Favors Given To Muhammad ( ) by Allah (Notes) - AuthenticTauheed PublicationsAuthenticTauheedNo ratings yet
- Use Case Diagram ShopeeDocument6 pagesUse Case Diagram ShopeeAtmayantiNo ratings yet
- Chelsea Bellomy ResumeDocument1 pageChelsea Bellomy Resumeapi-301977181No ratings yet
- Plessy V Ferguson DBQDocument4 pagesPlessy V Ferguson DBQapi-300429241No ratings yet
- 00000000Document4 pages00000000GagoNo ratings yet
- The Best John Green QuotesDocument10 pagesThe Best John Green Quotesapi-586467925No ratings yet
- Teaching English in The Elementary Grades (Language Arts)Document21 pagesTeaching English in The Elementary Grades (Language Arts)RENIEL PABONITANo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 5.2 Concept ReviewDocument4 pagesLearning Activity 5.2 Concept ReviewJames CantorneNo ratings yet
- HDFCDocument60 pagesHDFCPukhraj GehlotNo ratings yet
- 4TES-9Y 20KW With InverterDocument4 pages4TES-9Y 20KW With InverterPreeti gulatiNo ratings yet
- 9 Electrical Jack HammerDocument3 pages9 Electrical Jack HammersizweNo ratings yet
- TestertDocument10 pagesTestertjaiNo ratings yet
- Malware Reverse Engineering HandbookDocument56 pagesMalware Reverse Engineering HandbookAJGMFAJNo ratings yet
- The Foundations of Ekistics PDFDocument15 pagesThe Foundations of Ekistics PDFMd Shahroz AlamNo ratings yet
- Model United Nations at Home Code of ConductDocument3 pagesModel United Nations at Home Code of ConductAryan KashyapNo ratings yet
- NetEco Commissioning Guide (V200R003C01 - 01) (PDF) - enDocument116 pagesNetEco Commissioning Guide (V200R003C01 - 01) (PDF) - enabdo elmozogyNo ratings yet
- Robbins FOM10ge C05Document35 pagesRobbins FOM10ge C05Ahmed Mostafa ElmowafyNo ratings yet
- TM201 - Session 1-2 Paper - Introduction To The Field of Technology Management - AFVeneracion - 201910816Document1 pageTM201 - Session 1-2 Paper - Introduction To The Field of Technology Management - AFVeneracion - 201910816Nicky Galang IINo ratings yet
- Bruce and The Spider: Grade 5 Reading Comprehension WorksheetDocument4 pagesBruce and The Spider: Grade 5 Reading Comprehension WorksheetLenly TasicoNo ratings yet
- War: Causation of War, Total War, Limited War, Strategic Culture: Determinants of Strategic Culture Deterrence: Theory and Practice With SpecialDocument52 pagesWar: Causation of War, Total War, Limited War, Strategic Culture: Determinants of Strategic Culture Deterrence: Theory and Practice With SpecialMazhar HussainNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Turnaround Management Concepts Applied in The Agribusiness Environment in RomaniaDocument6 pagesLeadership and Turnaround Management Concepts Applied in The Agribusiness Environment in RomaniaLoredana PredaNo ratings yet
- MKTG4471Document9 pagesMKTG4471Aditya SetyaNo ratings yet
- 2 - (Accounting For Foreign Currency Transaction)Document25 pages2 - (Accounting For Foreign Currency Transaction)Stephiel SumpNo ratings yet
- Adressverificationdocview Wss PDFDocument21 pagesAdressverificationdocview Wss PDFabreddy2003No ratings yet