Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mod 1
Uploaded by
pubgmobilekr77220 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesKtu mpmc notes module 1
Original Title
mod 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKtu mpmc notes module 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesMod 1
Uploaded by
pubgmobilekr7722Ktu mpmc notes module 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
• Industrial safety is primarily a management Terminology 1. The personal injury (final domino) occurs only as ❖Embrace consistency.
(final domino) occurs only as ❖Embrace consistency. Be consistent in all areas
activity which is concerned with • Safety: Control over hazards or Freedom from a result of accident. of your responsibilities as consistency leads to
reducing, controlling and eliminating hazards from unacceptable risk of harm. 2. An accident occurs only a result of a sustainable habits regardless of your role.
the industries or industrial units. • Accident: Undesirable event that arises to injury, personal/mechanical hazard. Common Responsibilities of the Safety Team…
• The danger of life of human being is increasing fatality, ill health, property damage or 3. Personal/mechanical hazard exist only through ❖Be understanding and tolerant. People will make
with advancement of scientific development in combination of these. the fault of careless persons or poorly mistakes. An error can be an opportunity to
different fields. • The importance of industrial • Hazard: Source, situation, or act with a potential designed or improperly maintained equipment. identify safety gaps and improve working
safety was realized because every millions of for harm in terms of human injury or ill health or 4. Fault of persons are inherited or acquired as a behaviours.
industrial accidents occur which result in property damage or a combination of these all. result of their social environment or ❖Have patience. Even attitude and behaviour
✓ death • Reportable injury: If a person sustained injury & acquired by ancestry. changes require patience. Change takes time.
✓ temporary or permanent disablement of unable to resume his duty within 48 hours. 5. Environment is where and how a person was
❖Follow through. If you say you are going to do
employees Terminology… raised and educated.
something, do it; that proves you mean what you
✓ large amount of losses resulting from danger to • Risk: Combination of Probability & severity of • On safety audits and inspections, when the risk
say and helps build trust
property and wasted man hours. specific hazardous event occurring. of an accident has been identified,
Common Responsibilities of Executive and
Need for Safety • Non Conformance: Any deviation from work possible event chain should be investigated and
Operations Management
1. Social Need standards, practices, procedure, Regulations, action taken to remove potential cause.
1.Respond to failure.
• The accident causes social loss in great Management System requirements etc, that could • Domino Theory – Corrective Action Sequence
• Put in the work to determine the causes of a
magnitude in form of suffering, loss of be either directly or indirectly lead to injury or (The three “E”s)
failure, no matter the severity or consequence.
earning capacity and cost due to disturbance to illness, damage or loss to property or combination 1. Engineering
• You may identify gaps that could lead to
economic efficiency. The economic costs are more of these. • Control hazards through product design or
improved working conditions and/or management
tangible. • Dangerous occurrence: Any occurrence of process change
abilities.
2. Management Need serious nature which could have caused injury/ 2. Education
2.Lead with the appropriate demeanour.
• Management bear huge loss due to accident. death to person but did not, is called Dangerous • Train workers regarding all facets of safety –
• As a manager, how you respond to safety
Cost of accident is of two typeDirect & Indirect occurrence. Impose on management that attention to
requirements – whether verbally or physically
cost. Indirect cost is several times more than • Near Miss: A narrow escape of injury or any safety pays off
through facial
Direct Cost. Direct cost include medical expenses, harm 3. Enforcement
expressions and body language – communicates
compensation to the injured or their • Insure that internal and external rules,
your interest in safety to those you lead.
families. Unsafe Act regulations, and standard operating procedures
• It also gives those you lead permission to
3. Legal Need • Committing mistake by person or Any act that are followed by workers as well as management.
respond in a like manner. Choose your demeanour
• As per The Building & other construction Act may lead to accident is 2. Human Factors Theory
wisely.
1996, Factories Act 1948 and known as unsafe act. • Heinrich posed his model in terms of a single
3.Celebrate victories of all sizes.
several other related Acts & rules the general duty Following are example of unsafe act: domino leading to an accident. The premise
• Doing so encourages and inspires those you lead
of the employer is to 1. Working without wearing safety helmet & here is that human errors cause accidents. These
to continue the effort to meet safety expectations.
ensure Health & Safety of his employee & protect safety shoes errors are categorized broadly as:
• Always keep an eye out for opportunities to
the Environment. 2. Working at height without wearing full body ❖Overload – applaud employee efforts.
4. Humanitarian Need harness. • The work task is beyond the capability of the
• The Humanitarian reason for prevention of 3. Taking rest in working areas worker Executive Management Responsibilities
accidents is based on notion that it 4. Working or taking rest below Hanging Load • Includes physical and psychological factors 1.Care
is duty of every person to ensure safety of his 5. Over speeding • Influenced by environmental factors, internal • Before anything else, you must care about those
fellow men Unsafe Act… factors, and situational factors who work for and with you. There is a
6. Operating equipment without qualification or ❖Inappropriate Worker Response – difference between an employee and a person.
Safety and productivity authorization. • To hazards and safety measures (worker’s fault) • When you consider someone an employee, the
• In the world of manufacturing and construction, 7. Lack of/or improper use of PPE • To incompatible work station (management, implication is that they are replaceable, like a
there are mainly 8. Operating equipment at unsafe speeds environment faults) tool or machine.
three pillars 9. Failure to warn ❖Inappropriate Activities • When you consider someone a person, you are
1. Safety 2. Quality 3. Productivity 10. Bypass or removal of safety devices • Lack of training and misjudgement of risk. more likely to see them as an individual who
• These three are interlinked with each other. 11. Using defective equipment 3. Accident/Incident Theory has value and meaning.
1. Safety improves quality and productivity. • Extension of human factors theory. • Humans are not replaceable, and they deserve a
• When operations are unsafe, they aren’t well- Unsafe condition • Here the following new elements are safe working environment – which an
managed. • Any sources or situation or condition that have introduced: employer, by law, is required to provide.
• Employees will not be motivated nor mindful. potential to create accident • Ergonomic traps – component of the design 2.Culture.
• Quality and productivity both suffer when is known as unsafe condition. contributes to an accident. • Setting the organization’s cultural expectations
Following are example of unsafe condition:
employees are under stress, unsatisfied, or ✓These are incompatible work stations, tools or means establishing the overall expectations
unable to complete their mission. 1. Damage welding cable
expectations (management failure) for safety within the organization, and then
• But when businesses are safe, it frees up 2. Mechanical guard not provided on rotating
• Decision to err – Unconscious or conscious providing the means for maintaining those
employees to focus on their quality and parts
(personal failure) expectations.
their productivity. 3. Defective sling or lifting equipment.
• Systems failure – Management failure (policy,
• The safer the organization is, the less frequently 4. Defective work platform
training, etc.) Operations Management Responsibilities
the organization will experience 5. Floor or platform opening, pits etc.
1.Evaluate.
large scale disruption. 6. Poor housekeeping
Common Responsibilities of the Safety Team • Keep production, quality and safety in mind
2. Quality improves safety and productivity. 7. Defective tools, equipment or supplies
Following are seven common responsibilities of when planning a job or task.
• Safety is a measure of conscientiousness and 8. Inadequate supports or guards
the safety team • Observe the people you lead to make sure they
9. Congestion in the workplace
proactiveness. ❖Focus on learning. There should be a understand their jobs and can perform them
• High quality work means better results and 10. Inadequate warning systems
continuous, conscious effort to learn and effectively. • Confirm they have the appropriate
better products. 11. Hazardous atmospheric conditions etc
improve. We learn from four distinct areas: training before any work begins.
• The higher quality the work, the fewer reworks 1. Failure: This is one of the most common ways 2.Ensure.
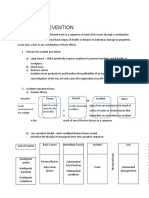
are needed, and the 1. Domino Theory…
we learn because when something goes wrong, • Make sure the people you supervise understand
greater overall productivity is. • Heinrich related these five stages to five
we must fix it. the hazards associated with the work to be
• When quality is high for a business, it can be dominoes standing on edge in a line
2. Near misses: A near miss can be defined as an performed, the safety requirements that apply,
assumed that standards next to each other, so that when the first domino
unexpected event that occurred outside the the proper procedures to be followed and the
for the business are generally high, including falls it automatically knocks
identified hazards and planned work procedure, appropriate equipment needed to safely
safety equipment, safety down its neighbour which in turn knocks down its
but during which no one was injured and no perform the work.
software, and safety processes. neighbour and so on. • Removal of any one of the
property was damaged. Operations Management Responsibilities…
3. Productivity improves safety and quality. first four will break the sequence and so prevent
3. Positive work experiences: These occur when 3. Engage.
• Carelessness is often what results in safety the injury.
employees work within the established and known • Communicate effectively and consistently so
issues. • Heinrich suggested that accident prevention
safety expectations, getting the job done without that the people you lead fully understand
• With the appropriate (and productive) safety should aim to remove or eliminate
incident. what is expected of them.
processes, safety can be the middle or third domino, representing the
4. Observations: During observations, attention is • Create an environment in which everyone is
improved, and quality can be improved as well. unsafe act, mechanical or physical
paid to work habits and management abilities, empowered to ask questions, make
• The more productive employees are, the less hazard, thus preventing the accident.
including attitude and behaviour. recommendations and respectfully remind other
likely they are to cut • The five factors or stages in the sequence of
Common Responsibilities of the Safety Team… employees, including managers, when a safety
corners on things like safety processes. events are:
❖Be committed. Each member of the safety team correction needs to be made.
• The more productive they are, the more likely 1. Ancestry and social environment, leading to
must be committed to being the leader they are 4. Enforce.
they are to put extra noble
expected to be, which includes consistently • It means making sure the people you lead are
attention into the quality of their work. 2. Fault of person, constituting the proximate
demonstrating a good attitude and appropriate following all safety expectations.
reason for
behaviour as well as being transparent and • If they are not, it is your obligation to work with
3. An unsafe act and/or mechanical hazard, which
accountable. them to make the necessary corrections.
results in
4. The accident, which leads to ❖Communicate. Effective communication leads to
5. The injury learning, understanding and improvement by all
parties.
Worker Responsibilities
1.Determine.
• They must be sure that they fully understand
their tasks before starting, especially any
associated hazards.
2.Decide.
• They must decide if they have the training,
knowledge, tools, PPE, equipment and time to
complete their tasks safely.
3.Do.
• They must use the right tools and equipment
and follow the appropriate safety procedures to
complete their tasks.
• Workers are obligated to communicate when
necessities for safety are not available, when
they have ideas for improvement and when they
identify opportunities for correction.
You might also like
- Topic 2 - Accident Theories (Student)Document54 pagesTopic 2 - Accident Theories (Student)Siti KhadijahNo ratings yet
- Health & Safety: Implementation ofDocument14 pagesHealth & Safety: Implementation ofharikeshmn09No ratings yet
- LCM Element 3Document58 pagesLCM Element 3Vincent Anthony MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Pre-Fabricated Metal Building Manufacturing: Information and ChecklistDocument10 pagesPre-Fabricated Metal Building Manufacturing: Information and ChecklistKishan MauryaNo ratings yet
- Hazard What Is Being Done Already? Workstation Design Who Might Be Harmed and How?Document8 pagesHazard What Is Being Done Already? Workstation Design Who Might Be Harmed and How?MAHESH SHAWNo ratings yet
- WSH Training Slides For WoodworkingDocument54 pagesWSH Training Slides For WoodworkingRajNo ratings yet
- SG Top-Up Textbook - 230830 - 162821Document10 pagesSG Top-Up Textbook - 230830 - 162821Luchian IonutNo ratings yet
- Accident Causes Theories Risk AssessmentDocument29 pagesAccident Causes Theories Risk AssessmentFAHD SALAH HASAN LAHMDI / UPMNo ratings yet
- Safety Management: Definition of TermsDocument4 pagesSafety Management: Definition of TermsPrincess SamianoNo ratings yet
- 2. WHAT IS RISKDocument11 pages2. WHAT IS RISKGaudencio BoniceliNo ratings yet
- 30-Hour Construction Safetey - Updated (2017 - 09 - 04 12 - 51 - 06 UTC)Document393 pages30-Hour Construction Safetey - Updated (2017 - 09 - 04 12 - 51 - 06 UTC)nuhNo ratings yet
- Risks and Risk Management Insurance Life Insurance Need and Analysis Analysis of An Insurance Policy Agent Regulation Claims HandlingDocument89 pagesRisks and Risk Management Insurance Life Insurance Need and Analysis Analysis of An Insurance Policy Agent Regulation Claims HandlingShweta ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The Swiss Cheese Model of Accident CausationDocument10 pagesThe Swiss Cheese Model of Accident CausationNazlıcan MUTLUNo ratings yet
- Construction Safety Training-CreativeDocument19 pagesConstruction Safety Training-CreativeJinu Saji100% (1)
- RM SynthèseDocument46 pagesRM SynthèseCéline LazzeriniNo ratings yet
- Risk Mgmt & Insurance OverviewDocument131 pagesRisk Mgmt & Insurance Overviewpparty aanimalzNo ratings yet
- Accident Prevent IonsDocument13 pagesAccident Prevent IonsSusweta GuhaThakurtaNo ratings yet
- Eurocontrol White Paperon Resilience EngineeringDocument17 pagesEurocontrol White Paperon Resilience EngineeringVikki KalilNo ratings yet
- 1. WHAT IS RISKDocument11 pages1. WHAT IS RISKGaudencio BoniceliNo ratings yet
- Risk & Disaster Management Plan for Limestone MineDocument22 pagesRisk & Disaster Management Plan for Limestone MineBrijgopal YadavNo ratings yet
- Safety Management Plan: For Limestone Mine of Ultratech Cement LimitedDocument22 pagesSafety Management Plan: For Limestone Mine of Ultratech Cement LimitedsunilsinghmNo ratings yet
- Basic Safety Procedures ModuleDocument5 pagesBasic Safety Procedures ModuleAljon AvilaNo ratings yet
- Insect Rodent - ControlDocument8 pagesInsect Rodent - ControlMuhammad RidhoNo ratings yet
- Hazard Register ConstructionDocument15 pagesHazard Register ConstructionMohd ObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Lecture 6 - Accident Causes and InvestigationsDocument48 pagesWeek 5 - Lecture 6 - Accident Causes and InvestigationsAbdoukadirr SambouNo ratings yet
- Hse For Engineers-PresentDocument30 pagesHse For Engineers-PresentMalayalam musical CollectionNo ratings yet
- CSS - Hazards and RisksDocument1 pageCSS - Hazards and RisksRowell MarquinaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 ReportDocument2 pagesGroup 3 ReportJireh Saratorio EliotNo ratings yet
- Total'S Golden Rules: Safety at WorkDocument16 pagesTotal'S Golden Rules: Safety at WorkShahzada Shahzeb BaigNo ratings yet
- 01 - IG2 Form-V5.1Document47 pages01 - IG2 Form-V5.1Mohamed Adel0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction.Document38 pagesChapter 1 Introduction.yaqoobNo ratings yet
- 5218 CIRS White Paper 08062014Document7 pages5218 CIRS White Paper 08062014Helen VicenteNo ratings yet
- Risk Evaluation Sheet: 1 Internal Workers Comp Injuries, Medical Costs, and Lost ProductivityDocument6 pagesRisk Evaluation Sheet: 1 Internal Workers Comp Injuries, Medical Costs, and Lost ProductivityAbhijitNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and Health (Osh) Management HRM3033: Topic 2: Accident TheoriesDocument31 pagesOccupational Safety and Health (Osh) Management HRM3033: Topic 2: Accident TheoriesNurulFatihah01No ratings yet
- Cosh ReviewerDocument6 pagesCosh ReviewerFOEBE MARREY MANUELNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Safety ManagementDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Safety Managementprecious maningasNo ratings yet
- TRcKQfGiqjfTJ0jB - WbQBErcXKOcA0TjR Osha 10 Construction Module 12 Study GuideDocument7 pagesTRcKQfGiqjfTJ0jB - WbQBErcXKOcA0TjR Osha 10 Construction Module 12 Study GuideBelkacem BouazzaNo ratings yet
- Incident Prevention and Risk ManagementDocument14 pagesIncident Prevention and Risk ManagementYusdie YasimilNo ratings yet
- Risk Managment or Copy 1Document10 pagesRisk Managment or Copy 1M.K.PereraNo ratings yet
- Tot SrampDocument23 pagesTot SrampBrhane WeldegebrialNo ratings yet
- Improving Workplace Safety Through Behavior Based SafetyDocument39 pagesImproving Workplace Safety Through Behavior Based SafetyJack Frost0% (1)
- Chapter 7-UpdatedDocument59 pagesChapter 7-UpdatedElena MeghanNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 Persepsi Tentang Risiko PDFDocument53 pagesBab 2 Persepsi Tentang Risiko PDFDaffa JNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Total Loss ControlDocument29 pagesIntroduction to Total Loss ControlStanley Muchemedzi33% (3)
- Risk ManagementDocument16 pagesRisk ManagementJeng AlferezNo ratings yet
- Construction Manpower SafetyDocument30 pagesConstruction Manpower SafetyMaridel Gacos Berioso100% (1)
- Accident Investigation ReportDocument9 pagesAccident Investigation ReportKeinth JosephNo ratings yet
- Safety Chapter 2Document33 pagesSafety Chapter 2linsiejoyaNo ratings yet
- Hand Out Maintenance Course For EngineersDocument109 pagesHand Out Maintenance Course For EngineersGauravNo ratings yet
- Additional Topic (May 2022 Civil Engineers Board Exam)Document3 pagesAdditional Topic (May 2022 Civil Engineers Board Exam)Crischouel Radovan AlimorongNo ratings yet
- She News Letter 22-10-2017Document5 pagesShe News Letter 22-10-2017ponnada shanmukha pavan kumarNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 5 - Health: Health Safety in ConstructionDocument12 pagesBuilding Utilities 5 - Health: Health Safety in ConstructionMelaine A. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- ISE-Module 1Document84 pagesISE-Module 1Norah ElizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Risk ManagementDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Risk ManagementfidyaqonitaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Vulnerable AdultsDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment Vulnerable AdultsAyu Wanda SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- 6 Hazard AvoidanceDocument22 pages6 Hazard AvoidancefirahliyanaNo ratings yet
- Building Envelope Security GuideDocument17 pagesBuilding Envelope Security GuideDave InghamNo ratings yet
- Ar Bradley Info CurveDocument1 pageAr Bradley Info Curverizki muhammad PercekaNo ratings yet
- Security Leader Insights for Business Continuity: Lessons and Strategies from Leading Security ProfessionalsFrom EverandSecurity Leader Insights for Business Continuity: Lessons and Strategies from Leading Security ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive DRRM in Schools AssessedDocument4 pagesComprehensive DRRM in Schools Assessedjuliamark78% (9)
- Asm Risk Assesment fv2 PDFDocument3 pagesAsm Risk Assesment fv2 PDFshijadNo ratings yet
- PHA Material MSDSDocument3 pagesPHA Material MSDSjituniNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Plan T.L.EDocument3 pagesLesson - Plan T.L.Eariezan2023No ratings yet
- Offshore PDFDocument10 pagesOffshore PDFsubhashNo ratings yet
- SmartLogger3000 User ManualDocument350 pagesSmartLogger3000 User ManualPavel LaurinecNo ratings yet
- Ig2 Forms Electronic Submission V5.1saharDocument7 pagesIg2 Forms Electronic Submission V5.1saharbalanced balancedNo ratings yet
- Fairgrounds tcm4-22894 PDFDocument74 pagesFairgrounds tcm4-22894 PDFFaiz BokhadiNo ratings yet
- Secretary Module - IDocument100 pagesSecretary Module - IBe YourselfNo ratings yet
- Hazard HuntDocument6 pagesHazard HuntasuNo ratings yet
- Manual de Asfaltadora 1000F PDFDocument184 pagesManual de Asfaltadora 1000F PDFAlvin Smith100% (1)
- Process and Plant Safety HazardsDocument71 pagesProcess and Plant Safety Hazardsapi-2614241788% (17)
- IB Sciences Experimentation GuidelinesDocument10 pagesIB Sciences Experimentation GuidelinesAdan SherNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management Strategies in ChennaiDocument4 pagesDisaster Management Strategies in ChennaiMuthu KumaarrNo ratings yet
- Hse Regulation Geothermal PDFDocument10 pagesHse Regulation Geothermal PDFferry ferdiansyah pradanaNo ratings yet
- Application of Hirarc at Unimap Laboratory: December 2009Document6 pagesApplication of Hirarc at Unimap Laboratory: December 2009AmyNo ratings yet
- Tle Ict Cy9 W3 PDFDocument4 pagesTle Ict Cy9 W3 PDFMichelle DaurogNo ratings yet
- Phast 3D Explosions Flier Tcm8 56732Document2 pagesPhast 3D Explosions Flier Tcm8 56732Dedy PriambodoNo ratings yet
- CDP+ GuidelinesDocument124 pagesCDP+ GuidelinesRheii Estandarte100% (1)
- HSE-RA-036 Working at Night - Rev 0Document11 pagesHSE-RA-036 Working at Night - Rev 0عمروNo ratings yet
- TD 3 - Philippine Vulnerability AssessmentDocument23 pagesTD 3 - Philippine Vulnerability AssessmentChan VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Mosca Point of Work Risk AssessmentDocument1 pageMosca Point of Work Risk AssessmentBryanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Geography (0460) Case Study Past Paper QuestionsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Geography (0460) Case Study Past Paper Questionssafwan12100% (9)
- TLE Lesson Identifies Workplace HazardsDocument3 pagesTLE Lesson Identifies Workplace HazardsRose CasugaNo ratings yet
- Foreing Part-145 Smsag 0Document21 pagesForeing Part-145 Smsag 0Polydoros BourdaniotisNo ratings yet
- DRRR ModuleDocument53 pagesDRRR ModuleWina MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sediment Transport: Methodology and its Application to Flood Risk AnalysisDocument10 pagesSediment Transport: Methodology and its Application to Flood Risk Analysislittle projectNo ratings yet
- SEW Motor Brake BMGDocument52 pagesSEW Motor Brake BMGPruthvi ModiNo ratings yet
- Dictionary For Tunnel WorksDocument165 pagesDictionary For Tunnel WorksFaruk AtalarNo ratings yet
- X12 4010 DictionaryDocument21 pagesX12 4010 DictionaryJogador Dois SteamNo ratings yet