Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IGCSE Physics Data & Formulae v02
IGCSE Physics Data & Formulae v02
Uploaded by
bernicewpyhkOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IGCSE Physics Data & Formulae v02
IGCSE Physics Data & Formulae v02
Uploaded by
bernicewpyhkCopyright:
Available Formats
CONCORD COLLEGE PHYSICS
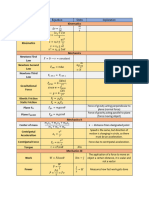
IGCSE PHYSICS DATA & FORMULAE
FORMULAE PRESSURE IN A LIQUID
DENSITY, MASS AND VO LUME pressure = density×𝑔×depth
mass 𝑝 = 𝜌𝑔ℎ
density =
volume TEMPERATURE
𝑚
𝜌= Kelvin temperature = temperature in °C + 273
𝑉
SPEED COMPRESSING GASES
distance moved pressure1 ×volume1 = pressure2 × volume2
average speed =
time taken 𝑝1 𝑉1 = 𝑝2 𝑉2
ACCELERATION WORK
change in velocity distance moved
average acceleration = work done = force×
time taken in direction of force
𝑣−𝑢
𝑎= 𝑊 = 𝐹𝑑
𝑡
FORCE, MASS AND ACCE LERATION GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY
force = mass×acceleration gravitational potential energy = mass×𝑔×height
𝐹 = 𝑚𝑎 PE = 𝑚𝑔ℎ
MOMENTUM KINETIC ENERGY
momentum = mass×velocity 1
kinetic energy = ×mass×velocity 2
𝑝 = 𝑚𝑣 2
IMPULSE 1
KE = 𝑚𝑣 2
2
change in momentum = resultant force×time
ENERGY AND TEMPERATU RE CHANGE
impulse = 𝐹𝑡
energy specific heat temperature
WEIGHT = mass× ×
transferred capacity change
weight = mass×𝑔
𝐸 = 𝑚𝑐Δ𝑇
𝑊 = 𝑚𝑔
ENERGY AND STATE CHA NGE
MOMENT OF A FORCE
energy transferred = mass×specific latent heat
moment of a force perpendicular
= force × 𝐸 = 𝑚𝐿
about a point distance from point
POWER
STRETCHED SPRING
work done energy transformed
load = spring constant×extension power = =
time taken time taken
𝐹 = 𝑘𝑥 EFFICIENCY
PRESSURE AND FORCE
useful work done
efficiency =
force total energy input
pressure =
area useful energy output
=
𝐹 total energy input
𝑝=
𝐴 useful power output
=
total power input
DR L GARLAND IGCSE Physics Data & Formulae PAGE 1 OF 4
CONCORD COLLEGE PHYSICS
WAVES TRANSFORMERS
speed = frequency×wavelength output voltage output turns
=
𝑣 = 𝑓𝜆 input voltage input turns
𝑉2 𝑁2
FREQUENCY AND PERIOD =
𝑉1 𝑁1
1
frequency = FOR 100% EFFICIENT TRANSFORMER
period
1 power input = power output
𝑓=
𝑇 𝑉1 𝐼1 = 𝑉2 𝐼2
REFRACTION OF LIGHT PREFIXES
sine of angle of incidence
refractive index = Prefix Meaning 𝟏𝟎𝒙 notation
sine of angle of refraction
T (tera) 1,000,000,000,000 1012
sin 𝑖
𝑛= G (giga) 1,000,000,000 109
sin 𝑟
M (mega) 1,000,000 106
TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION
k (kilo) 1,000 103
1 d (deci) 1⁄10 10−1
sine of critical angle =
refractive index c (centi) 1⁄100 10−2
1 m (milli) 1⁄1,000 10−3
sin 𝑐 =
𝑛
μ (micro) 1⁄1,000,000 10−6
CHARGE AND CURRENT n (nano) 1⁄1,000,000,000 10−9
charge = current×time p (pico) 1⁄1,000,000,000,000 10−12
𝑄 = 𝐼𝑡 SI BASE UNITS
RESISTANCE, PD (VOLT AGE) AND CURRENT
Quantity Name Symbol
PD length metre m
resistance =
current
mass kilogram kg
𝑉
𝑅= time second s
𝐼
current ampere A
RESISTORS IN SERIES... temperature kelvin K
total resistance 𝑅 = 𝑅1 + 𝑅2 amount of substance mole mol
...AND IN PARALLEL SI DERIVED UNITS
1 1 1
= +
𝑅 𝑅1 𝑅2
Quantity
Symbol
Name
Units
ELECTRICAL POWER
power = PD×current
force newton N
𝑃 = 𝑉𝐼 pressure pascal Pa N m−2
ELECTRICAL ENERGY energy joule J Nm
energy transformed = power×time power watt W J s −1
frequency hertz H𝑧
= PD×current×time
PD, EMF volt V W A−1
𝐸 = 𝑉𝐼𝑡
resistance ohm Ω V A−1
charge coulomb C
capacitance farad F C V −1
temperature ° Celsius °C
DR L GARLAND IGCSE Physics Data & Formulae PAGE 2 OF 4
CONCORD COLLEGE PHYSICS
ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS
A V
wires joining wires crossing lamps ammeter voltmeter
+ terminal
+ −
switch cell battery (several cells) DC power supply AC power supply
resistor variable resistors thermistor light-dependent resistor
heater fuse transformer diode light-emitting diode
M G
earth motor generator relay coil and switch bell
DR L GARLAND IGCSE Physics Data & Formulae PAGE 3 OF 4
CONCORD COLLEGE PHYSICS
COMMAND WORDS AND PHRASES MEANT (WHAT IS MEANT…)
See ‘Understand’
CALCULATE
MEASURE
A numerical answer is needed. You should show any
working, especially when there are two or more steps in a You are expected to find a quantity by using a measuring
calculation e.g. calculate the refractive index. instrument e.g. length (by using a ruler), volume (by using
a measuring cylinder).
DEDUCE
OUTLINE
This may be used in two ways:
State the main points briefly e.g. outline a method of
(i) You find the answer by working out the patterns in the
magnetising an iron bar.
information given to you and drawing logical
conclusions from them. You may need to use PREDICT
information from tables and graphs and do This can be used in two ways:
calculations e.g. deduce what will happen to velocity of (i) You find the answer by working out the patterns in the
the vehicle if… information provided and drawing logical conclusions
(ii) You have to refer to a Law or scientific theory or give a from this. You may need to use information from
reason for your answer e.g. use your knowledge of the tables and graphs and do calculations. e.g. predict
kinetic theory to deduce what will happen when… what will happen to the direction of the resultant force
DEFINE if…
(ii) It may also mean giving a short answer to a question
You need to state the meaning of something e.g. define
stating what might happen next e.g. predict what
speed.
effect an increase in temperature will have on the
DESCRIBE resistance.
You need to state the main points about something using SKETCH
labelled diagrams if it helps you e.g. describe a rotating-
(i) When drawing graphs, this means that you may draw
coil generator.
the approximate shape and/or position of the graph
You may also be asked to describe
BUT you need to make sure that important details,
• observations e.g. describe the ways in which a force such as the line passing through the origin or finishing
may change the motion of a body. at a certain point, are drawn accurately.
• how to do particular experiments e.g. describe an (ii) When drawing apparatus or other diagrams, a simple
experiment to determine resistance using a voltmeter line drawing is all that is needed, but you must make
and an ammeter. sure that the proportions are correct and the most
DETERMINE important details are shown. You should always
You are expected to use a formula or method that you remember to label your diagrams.
know to calculate a quantity e.g. determine graphically STATE
the resultant of two vectors. You should give a short answer without going into any
DISCUSS detail e.g. state the hazards of damaged electrical
You have to write down points for and against an insulation BUT: ‘state the meaning of…’ is different. It is
argument e.g. discuss the energy loss in cables. more like ‘understand’.
ESTIMATE SUGGEST
Suggest an approximate value for a quantity based on This may be used in two ways:
reasons and data. You may need to make some (i) There may be more than one correct answer e.g.
approximations e.g. estimate the volume of a test tube. suggest a precaution to improve the accuracy of the
experiment.
EXPLAIN
(ii) You are being asked to apply your general knowledge
You have to give reasons for your answer OR refer to a of physics or reasoning skills to a topic area that is not
particular theory on the syllabus e.g. applying ideas about moments to
FIND the stability of a vehicle.
This is a general term meaning several similar things such UNDERSTAND (WHAT DO YOU UNDERS TAND…)
as calculate, measure, determine etc. You should
LIST (i) define something and
(ii) make a more detailed comment about it.
Write down a number of separate points. Where the
number of points is stated in the question, you should not The amount of detail depends on the number of marks
write more than this number e.g. list three uses of awarded e.g. what do you understand by the term total
converging lenses. internal reflection
DR L GARLAND IGCSE Physics Data & Formulae PAGE 4 OF 4
You might also like
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetJereme Cheong93% (56)
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheeteltytanNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Thamesmead.surrey - Sch.ukwp Contentuploads201909AQA Physics Equations PDFDocument1 pageHTTPSWWW - Thamesmead.surrey - Sch.ukwp Contentuploads201909AQA Physics Equations PDFMariam HossamNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics EquationsDocument1 pageIGCSE Physics Equationsgamer eliteNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation Sheet AQA 2023Document2 pagesPhysics Equation Sheet AQA 2023HazzaYT HicksNo ratings yet
- Equation Sheet: Combined / PhysicsDocument1 pageEquation Sheet: Combined / PhysicsKza1No ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Physics - Equations & Formulae: Higher Tier Only Separate Physics OnlyDocument2 pagesAQA GCSE Physics - Equations & Formulae: Higher Tier Only Separate Physics OnlyLuisNo ratings yet
- All Physics Formulas For O Levels Physics by Ethan Wu: Celsius To KelvinDocument6 pagesAll Physics Formulas For O Levels Physics by Ethan Wu: Celsius To KelvinReuben CachiaNo ratings yet
- Equations To Learn (Combined) Year 10 VersionDocument1 pageEquations To Learn (Combined) Year 10 VersionSteve RamseyNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Combined Science Equation SheetDocument5 pagesAQA GCSE Combined Science Equation SheetJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Physics IGCSE Equations A4 VersionDocument1 pageEdexcel Physics IGCSE Equations A4 Versionlelon81No ratings yet
- General Physics 1 (W5)Document5 pagesGeneral Physics 1 (W5)Kim SeungminNo ratings yet
- Physics AS Unit 1 04 Energy and PowerDocument9 pagesPhysics AS Unit 1 04 Energy and PowerAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- Physics A LevelDocument38 pagesPhysics A LevelThoon Nadi NaiNo ratings yet
- List of FormulasDocument1 pageList of FormulasKenzy Waleed SolimanNo ratings yet
- Gcse Physics Equations: ForcesDocument1 pageGcse Physics Equations: ForcesRanjan SharmaNo ratings yet
- All GCSE Physics Equations (Editable)Document3 pagesAll GCSE Physics Equations (Editable)will hayNo ratings yet
- Work and Kinetic EnergyDocument9 pagesWork and Kinetic EnergyChan LieslNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - Science Notes For End of Year 9 AssessmentDocument6 pagesPHYSICS - Science Notes For End of Year 9 AssessmentJenny DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel Physics GCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel Physics GCSEAli AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Dimensions and Units Measures of Amount or SizeDocument5 pagesDimensions and Units Measures of Amount or SizennbNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument12 pagesPhysics Formula SheetGiulia CostantiniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Gravity Field of The EarthDocument56 pagesUnit 2 Gravity Field of The EarthndrwmilletNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Work Energy Power and MomentumDocument3 pages2.3 Work Energy Power and MomentumEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes (G - 11) (ch-4)Document7 pagesPhysics Notes (G - 11) (ch-4)Khin Khin ThanNo ratings yet
- 5 Hydraulics Toolbox 2Document4 pages5 Hydraulics Toolbox 2Ocir Kram AdlawonNo ratings yet
- Physics equations sheet: W=mg W=Fs F=ke s=vt a = Δ v t F=ma p=mv Ek = 1 m v 2 Ep=mgh P = E T P = W tDocument2 pagesPhysics equations sheet: W=mg W=Fs F=ke s=vt a = Δ v t F=ma p=mv Ek = 1 m v 2 Ep=mgh P = E T P = W tUtkarsh IngleNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Lesson 1 2 MidtermDocument6 pagesHydraulics Lesson 1 2 MidtermAs ReNo ratings yet
- Advanced Placement Physics 1 Equations PDFDocument5 pagesAdvanced Placement Physics 1 Equations PDFjohn smithNo ratings yet
- Derived Quantities: Density Mass Velocity Displacement TimeDocument1 pageDerived Quantities: Density Mass Velocity Displacement TimeLuke SuouNo ratings yet
- w73621 Int Gcse Physics 4ph1 4sd0 Exam AidDocument4 pagesw73621 Int Gcse Physics 4ph1 4sd0 Exam AidjenifaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument10 pagesWork Energy PowerMarvin AndradeNo ratings yet
- E XMXV: Gravitational Potential Energy Mass X Gravitational Field Strength X HeightDocument3 pagesE XMXV: Gravitational Potential Energy Mass X Gravitational Field Strength X HeightKryptosNo ratings yet
- Power in Electric CircuitsDocument1 pagePower in Electric CircuitsDanKimberleyNo ratings yet
- AQA Style Physics Equation SheetDocument1 pageAQA Style Physics Equation SheetBilaal SohailNo ratings yet
- Equations From Module 1-8: Submitted By: Amante, Denzey B. 12 STEM - BoyleDocument19 pagesEquations From Module 1-8: Submitted By: Amante, Denzey B. 12 STEM - BoyleJaydee GalahadNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument2 pagesGravitational Potential EnergyHarry WangNo ratings yet
- Energy Work and PowerDocument35 pagesEnergy Work and PowerFabian ClarkeNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Physics Equation Sheet - No UnitsDocument5 pagesAQA GCSE Physics Equation Sheet - No UnitsAbishake VimNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetPREM OfFiCiAlNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetMomin BabarNo ratings yet
- O' Level Physics Formula Sheet: MeasurementsDocument2 pagesO' Level Physics Formula Sheet: MeasurementsXOXOuser39938No ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetAukasha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet For OlevelsDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet For OlevelsMomin BabarNo ratings yet
- Topics III - Thermo 1Document20 pagesTopics III - Thermo 1warren carozcaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Fluid MechanicsDocument1 pageGeneral Physics 1 Fluid MechanicsJam JungNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Thermodynamics UpdatedDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Thermodynamics UpdatedLia HamadaNo ratings yet
- Formula ListDocument2 pagesFormula ListFong Jun YangNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics FormulasDocument5 pagesIgcse Physics Formulasmohammad affan merchantNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2D: Magnetic Matter, Elasticity, Fluids, & Curved SpacetimeFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2D: Magnetic Matter, Elasticity, Fluids, & Curved SpacetimeNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Bold Visionary Portrait Coral Sticker BookDocument28 pagesBold Visionary Portrait Coral Sticker BookbernicewpyhkNo ratings yet
- November 2018 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CIE Economics IGCSEDocument5 pagesNovember 2018 (v2) QP - Paper 1 CIE Economics IGCSEbernicewpyhkNo ratings yet
- Vocab Task 2Document1 pageVocab Task 2bernicewpyhkNo ratings yet
- News - Content PageDocument1 pageNews - Content PagebernicewpyhkNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-05 at 3.00.45 PMDocument28 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-05 at 3.00.45 PMbernicewpyhkNo ratings yet
- M24 Assignment CorrectionDocument14 pagesM24 Assignment CorrectionbernicewpyhkNo ratings yet
- Banana Milk Notebook - Boxed Header, Boxed Lined PaperDocument163 pagesBanana Milk Notebook - Boxed Header, Boxed Lined PaperbernicewpyhkNo ratings yet
- Img 2996-06Document11 pagesImg 2996-06bernicewpyhkNo ratings yet
- Physics Imp Mind MapDocument15 pagesPhysics Imp Mind MapShubhansh Nigam 43No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Differential Calculus IntroductionDocument73 pagesLesson 1 Differential Calculus IntroductionAngelica Marie DiegoNo ratings yet
- Avalanche Transit Time DevicesDocument40 pagesAvalanche Transit Time DevicespapanyameNo ratings yet
- Clark Inflatable Supersonic Tension ConeDocument9 pagesClark Inflatable Supersonic Tension ConenaraNo ratings yet
- 1.5 HPHT Testing PDFDocument6 pages1.5 HPHT Testing PDFHATEMNo ratings yet
- Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor Aptasensors For Estrogen Detection in LiquidsDocument9 pagesCarbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor Aptasensors For Estrogen Detection in LiquidsNilashis RoyNo ratings yet
- What Was Albert Einstein's IQ BiographyDocument1 pageWhat Was Albert Einstein's IQ BiographyIlaria PuiuNo ratings yet
- Asco - Jkh8551g401mmsDocument4 pagesAsco - Jkh8551g401mmsBiến tần MICNONo ratings yet
- Icon 2000 Electric Actuators Metric English en Us 2378990Document48 pagesIcon 2000 Electric Actuators Metric English en Us 2378990NanDo Wandi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Basic Metallurgy - A WalkthroughDocument129 pagesBasic Metallurgy - A WalkthroughPrasanth M CoolNo ratings yet
- Review Module 22 Geotechnical 3 Nov 2020Document4 pagesReview Module 22 Geotechnical 3 Nov 2020Ma Ella Mae LogronioNo ratings yet
- PDFsam - BIOBASE Part 1.1Document68 pagesPDFsam - BIOBASE Part 1.1cuma mencobaNo ratings yet
- Rbi-Episode 8 (Q1) Science 8 Learning Competency: Infer The Relationship Between Current and VoltageDocument3 pagesRbi-Episode 8 (Q1) Science 8 Learning Competency: Infer The Relationship Between Current and VoltageTrexie AliaNo ratings yet
- Experiment #2 - Plotting A Stress-Strain DiagramDocument13 pagesExperiment #2 - Plotting A Stress-Strain DiagramAzooNo ratings yet
- Automatic Testing For The Undervoltage Dependent Directional Reactive Power Protection FunctionDocument4 pagesAutomatic Testing For The Undervoltage Dependent Directional Reactive Power Protection FunctionFava yavarNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Steam Turbine Rotor: M. Chandra Sekhar ReddyDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Steam Turbine Rotor: M. Chandra Sekhar ReddyPinank PatelNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Separator Learning System 8094289 (3535-10) : Labvolt SeriesDocument22 pagesThree-Phase Separator Learning System 8094289 (3535-10) : Labvolt Seriesleonardo morenoNo ratings yet
- AEMT Yearbook 2020 OptDocument424 pagesAEMT Yearbook 2020 OptChandramohan MuruganNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 1Document6 pagesQuarter 1 Week 1GhghaaaNo ratings yet
- Fields and Currents SummaryDocument1 pageFields and Currents SummaryBill WhiteNo ratings yet
- SIFI-131 Fire Protection in Electrical Equipment RoomsDocument8 pagesSIFI-131 Fire Protection in Electrical Equipment RoomsemiljanlazeNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Activation of Synthetic Gehlenite Glasses: by J. DejaDocument14 pagesAlkaline Activation of Synthetic Gehlenite Glasses: by J. DejaomarnajimNo ratings yet
- Geo QuestionDocument6 pagesGeo QuestionYordanosNo ratings yet
- T1070 Tswell Packer - BEDocument1 pageT1070 Tswell Packer - BECristian BarbuceanuNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual: 0 Series PumpDocument31 pagesInstallation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual: 0 Series PumpTim WorkmanNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion: PSI AP Physics 1Document6 pagesUniform Circular Motion: PSI AP Physics 1Boldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- Extreme Temperature, Flexible Cable Assembly: Model 3076ADocument3 pagesExtreme Temperature, Flexible Cable Assembly: Model 3076Ashibu TNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.2 Numericals on Equivalent Drive ParametersDocument11 pagesUnit 2.2 Numericals on Equivalent Drive ParametersShnzak GiriNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii MCB and ElcbDocument26 pagesUnit-Ii MCB and ElcbArshad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chimney Seismic AnalysisDocument9 pagesChimney Seismic AnalysisStructural SpreadsheetsNo ratings yet