Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cor 001 2ND QTR
Cor 001 2ND QTR
Uploaded by
Kassandra Gayle Olmodo Sardoncillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThis document provides an overview of communication, including its definition, levels, types, and key concepts. It discusses intrapersonal and interpersonal communication, verbal and non-verbal communication, and linear, interactive, and transactional communication models. It also summarizes speech styles, speech acts, communication strategies, purposes of speeches, types of speeches, and speech delivery methods.
Original Description:
Original Title
COR 001 2ND QTR
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of communication, including its definition, levels, types, and key concepts. It discusses intrapersonal and interpersonal communication, verbal and non-verbal communication, and linear, interactive, and transactional communication models. It also summarizes speech styles, speech acts, communication strategies, purposes of speeches, types of speeches, and speech delivery methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesCor 001 2ND QTR
Cor 001 2ND QTR
Uploaded by
Kassandra Gayle Olmodo SardoncilloThis document provides an overview of communication, including its definition, levels, types, and key concepts. It discusses intrapersonal and interpersonal communication, verbal and non-verbal communication, and linear, interactive, and transactional communication models. It also summarizes speech styles, speech acts, communication strategies, purposes of speeches, types of speeches, and speech delivery methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
COR 001 1st Quarter
Tuesday, 20 September 2022 10:29 am
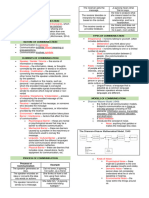
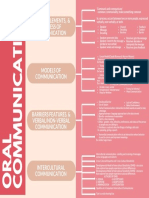
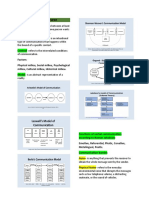
Communication transmission of thoughts from one mind to others Levels of Communication:
*Intrapersonal - takes place within a single person
Sender The person giving out information; encodes the message - purpose: clarifying and/or analyzing a situation
Message The information being communicated Internal discourse Thinking, concentration, and analysis
Medium The format where the information is conveyed Solo Vocal communication Talking to oneself
Listener The person receiving the information; interprets the message Solo Written Communication Writing not intended for others
Feedback The reaction given by the receiver
Interference Barriers in the communication process *Interpersonal - involves a direct face-to-face relationship from sender to receiver
*Internal Interference - hunger / wandering thoughts Dyadic Communication Involves two people
*External Interference - noise
Small group discussion Involves three or more persons
Public Communication Involves a large group of people; one-way communication
Communication skills:
- Listening Mass Communication Through television, radio, news, books, etc.
- Straight talking
- Stress Management According to Martin Joos (1959), there are several types of speech style of communicating, to which
- Emotion Control these are:
- Non-verbal Communication
Intimate Non-public speech; uses private vocabulary
Linear: Speaker -> Listener Casual Speech style used to friends
- No feedback Consultativ Two-way participation; used among people who do not share common
- One-way process; e experiences
- Speaker encodes the message, Listener decodes Formal Used for imparting information
Interactive Speaker -> Listener; Listener -> Speaker Frozen A formal style whose quality is static, ritualistic, and may even be archaic
- Has feedback
- a two-way communication process
Speech Act - an utterance that serves a function in communication
Transactional Speaker -> Speaker; Speaker <- Speaker
- Has all parties involved Types of Speech Acts:
Locutionary Speech Act When speaker performs an utterance
Types of Communication: *Utterance - when something is said and may not have meaning
*Propositional - where a particular reference is made
Verbal - uses words, spoken, or written
Illocutionary Speech Act The performance of the act of saying something with specific
Formal Uses pre-defined words to transmit information intention
Informal Does not follow a pre-defined channel to transmit information
Oral Face-to-face communication Communication Strategies - plans/ways/means of sharing information
^lectures, phone calls Nomination Presenting a particular topic clearly, truthfully, and saying what's relevant
Written ^letters, E-mails, SMS Restriction Constraining the response/reaction within a set of categories
Turn-taking Recognizing when and how to speak because it's one's turn
Non-verbal - sending of messages without using words; uses signals; hand -signals
Topic Control Keeping the interaction going by asking questions and eliciting a response
Chronemics Punctuality/speed
Repair Overcoming communication breakdowns to send more comprehensive
Vocalics Volume/tone/pitch messages
Haptics Touch Termination Using verbal and non-verbal signals to end the interaction
Kinesis Gestures/posture/facial expressions
Proxemics Distance between the speaker and the listener 4 basic purposes of speeches:
- To inform
Artifacts Clothing/lifestyle/fashion - To instruct
- To entertain
7C's of Effective Communication: - To persuade
Clear Make objectives clear
TYPES OF SPEECH ACCORDING TO PURPOSE:
Concise Straight to the point
Informative Serves to provide interesting and useful information to your
Concrete Be specific audience
Correct Avoid typos Demonstrative Speeches Teaches you with something including a demo
Coherent Make your message have any sense Persuasive Works to convince people to change in some way
Complete Contains everything Entertaining Where the speaker provides enjoyment to the audience
Courteous Be polite
4 TYPES OF SPEECH DELIVERY:
Manuscript Used as a reference during speeches
Intellectual Communication The communication "between" people from different backgrounds Memorization Involves memorizing a speech word for word
Enculturation One learns the traditional content of a culture and its practices and values Impromptu Speeches with little to no time of preparation
Ethnocentrism Believing that "one" of your own race is better than others Extemporaneous Has more preparation time than impromptu
Stereotyping One's thought about someone that is wrong
PRINCIPLES OF EFFECTIVE SPEECH DELIVERY
FUNCTIONS OF COMMUNICATIONS: Articulation Pronouncing words or speaking with clear diction
Regulation and Control Control others by managing their behaviour Modulation Capability to adjust vocal tone
Social Interaction Allows people to be connected with one another Stage presence The ability to own the stage
Motivation When one wants to persuade one's thoughts or actions Facial Expressions, gestures, and w/o these speaker may be judged as boring
Information Enables one to get to know and understand the world movements
Emotional Expression Appeal to one's feelings and emotions Audience Appeal Able to appeal and connect to the audience
COR 001 Page 1
COR 001 - 2nd quarter
Tuesday, 25 October 2022 6:46 pm
TYPES OF SPEECH ACCORDING TO PURPOSE:
Informative Serves to provide interesting and useful information to your
audience
Demonstrative Teaches you with something including a demo
Speeches
Persuasive Works to convince people to change in some way
Entertaining Where the speaker provides enjoyment to the audience
TYPES OF SPEECH ACCORDING TO MANNER OF DELIVERY
Manuscript Used as a reference during speeches
Memorization Involves memorizing a speech word for word
Impromptu Speeches with little to no time of preparation
Extemporaneous Has more preparation time than impromptu
makes it hard to make a mistake
PRINCIPLES OF EFFECTIVE SPEECH DELIVERY
Articulation Pronouncing words or speaking with clear diction
Modulation Capability to adjust vocal tone
Stage presence The ability to own the stage
Facial Expressions, gestures, and w/o these speaker may be judged as boring
movements
Audience Appeal Able to appeal and connect to the audience
PRINCIPLES OF SPEECH WRITING: ANALYZING THE AUDIENCE
Audience analysis studies your audience along three primary dimensions:
Demographic Audience Aims to discover who you are speaking to
Analysis
Psychological Audience Aims to discover what your audience may be thinking before and
Analysis during your presentation
Contextual Audience Aims to discover how the speaking event itself may influence your
Analysis audience's state of mind
COR 001 Page 2
You might also like
- Base Form Past Simple Past Participle 3rd Person Singular Present Participle / GerundDocument14 pagesBase Form Past Simple Past Participle 3rd Person Singular Present Participle / GerundRonokanAshNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Document6 pagesOral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Katleya Balitaan75% (8)
- Hand Out For Midterm Exam in Oral CommDocument4 pagesHand Out For Midterm Exam in Oral CommRoland John MarzanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral Com 22 23Document4 pagesReviewer in Oral Com 22 23Melody BatoNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing Handbook For Philosophy StudentsDocument14 pagesEssay Writing Handbook For Philosophy StudentsLance KirbyNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Reviewer 1Document3 pagesOral Communication Reviewer 1Rlly Jay70% (10)
- ORAL-COMM Reviewer 1st-QuarterDocument5 pagesORAL-COMM Reviewer 1st-QuarterJohn Marithe Putungan100% (1)
- Din 929 Decembre 2013Document10 pagesDin 929 Decembre 2013Franck SavignardNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Simple Future Tense-1Document7 pagesPresentasi Simple Future Tense-1Mursyid JailNo ratings yet
- S2 OralCom ReviewerDocument11 pagesS2 OralCom ReviewerArabella MejoradaNo ratings yet
- Dofollow Edu Backlinks ListDocument2 pagesDofollow Edu Backlinks ListArmin CivoTemhaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Complete Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesPurposive Communication Complete Lecture NotesShiela Mae CasNo ratings yet
- How to Deliver an Effective Speech: Speak and speak before a mirrorFrom EverandHow to Deliver an Effective Speech: Speak and speak before a mirrorNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document13 pagesCH 3api-325935419No ratings yet
- Purp CommDocument5 pagesPurp CommKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4Document16 pagesChapter 1-4SJ SuingNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication PrelimDocument2 pagesOral Communication PrelimAngelika ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Purcom MidtermDocument1 pagePurcom MidtermNene OcampoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer CommunicationJaimNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesOral CommunicationScythe RyuNo ratings yet
- Grammatical - Morphology and Syntax Discourse - Connection of Sentences of Utterance. Sociolinguistic - Interaction of Language To Society or ToDocument2 pagesGrammatical - Morphology and Syntax Discourse - Connection of Sentences of Utterance. Sociolinguistic - Interaction of Language To Society or ToysaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication LectureDocument18 pagesPurposive Communication LectureRandolf MartinezNo ratings yet
- Jerilyn Rafols Activity 2Document5 pagesJerilyn Rafols Activity 2Danica RafolsNo ratings yet
- 1st Semester Q1 Oral Communication (Notes)Document4 pages1st Semester Q1 Oral Communication (Notes)vince.resultay07No ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument8 pagesOral CommunicationAlliah ManilaNo ratings yet
- Communis Which Means "Common" and Communico Which Means "To Confer"Document8 pagesCommunis Which Means "Common" and Communico Which Means "To Confer"Angelica TañedoNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument5 pagesCommunicationEman D. PangcatanNo ratings yet
- Sanchez (2017) : Non-Verbal Cues - Make TheDocument11 pagesSanchez (2017) : Non-Verbal Cues - Make TheLei Yunice NorberteNo ratings yet
- Green Concept Map Chart PDFDocument1 pageGreen Concept Map Chart PDFCassy BulataoNo ratings yet
- Green Concept Map ChartDocument1 pageGreen Concept Map ChartCassy BulataoNo ratings yet
- Module 1&2 (Oral Comm)Document5 pagesModule 1&2 (Oral Comm)Lory TenorioNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument15 pagesPurcom ReviewerJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Reviewer 1ST QuarterDocument10 pagesOral Com Reviewer 1ST QuarterRaian PaderesuNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument9 pagesOral CommunicationLiah ManilaNo ratings yet
- Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesCommunication ReviewerJESTON AMBUNANNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDA SulitNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Purposive CommunicationKiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Syntactic, Pragmatic, Semantic: Public Speaking and Persuasion Effective Speech and Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesSyntactic, Pragmatic, Semantic: Public Speaking and Persuasion Effective Speech and Oral CommunicationAndrea Nicole TaguinesNo ratings yet
- Humss 11 B1 Oral Comm Reviewer Unit 1Document2 pagesHumss 11 B1 Oral Comm Reviewer Unit 1JANIS ESPEJONo ratings yet
- Communication: Completeness Conciseness Clarity Correctness Consideration Courtesy ConcretenessDocument7 pagesCommunication: Completeness Conciseness Clarity Correctness Consideration Courtesy ConcretenessPuloma Singh RaghavNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Nonverbal Communication: Speaker WriterDocument4 pagesKinds of Nonverbal Communication: Speaker WriterAUBREI GOULD SIABABANo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument9 pagesREVIEWERAtty Joven Allen AsidoNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive CommunicationPearl NoconNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument2 pagesPurcom Reviewergimboongaling489No ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesOral CommunicationKaith Ashlee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationsDocument2 pagesPurposive Communicationsviannametharam30No ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument2 pagesCOMMUNICATIONwannabeeurzNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PURC111Document10 pagesReviewer PURC111priya garciaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication (Reviewer)Document2 pagesPurposive Communication (Reviewer)blainechloeNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument10 pagesOral CommunicationCee Jay GerongcoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communcation ReviewerDocument7 pagesPurposive Communcation ReviewerGirlie VillamerNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument6 pagesOral CommunicationABM - TOLENTINO, JOANNA MARIE DC.No ratings yet
- Purposive ComDocument7 pagesPurposive ComAlliah Mickah GallegaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document6 pagesOral Communication Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- Small Group Communication - When: Jmba2019Document2 pagesSmall Group Communication - When: Jmba2019Maverick AlviarNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Topic 5Document3 pagesOral Communication Topic 5jaja rumbaoaNo ratings yet
- Purcom Midterm Exam NotesDocument18 pagesPurcom Midterm Exam NotesShaina TelenNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument5 pagesOral ComVenise RevillaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument14 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerKrisselyn ReigneNo ratings yet
- PurCom MidtermsDocument5 pagesPurCom MidtermshaneenamaedediosNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument13 pagesOral CommunicationAlliah ManilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document1 pageLecture 1shirleymcoronaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2nd GradingDocument26 pagesReviewer 2nd GradingRj PangaNo ratings yet
- Speaker Speech Audience: Which Channel To, Whom and With WhatDocument2 pagesSpeaker Speech Audience: Which Channel To, Whom and With WhatLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocument3 pagesOral Comm Reviewerdingomez01No ratings yet
- The Complete Communication & People Skills Training: Master Small Talk, Charisma, Public Speaking & Start Developing Deeper Relationships & Connections- Learn to Talk To AnyoneFrom EverandThe Complete Communication & People Skills Training: Master Small Talk, Charisma, Public Speaking & Start Developing Deeper Relationships & Connections- Learn to Talk To AnyoneNo ratings yet
- VocabDocument32 pagesVocabAnmolNo ratings yet
- Find The Number of Triangles in The Given Figure Count The Number of TrianglesDocument5 pagesFind The Number of Triangles in The Given Figure Count The Number of TrianglesSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- Lesson 25Document2 pagesLesson 25api-263677727No ratings yet
- J2EE 5 Architect Exam Study GuideDocument270 pagesJ2EE 5 Architect Exam Study GuideaalmoshaigahNo ratings yet
- Sap Smartforms v3 en Us PDFDocument52 pagesSap Smartforms v3 en Us PDFShashank NimeshNo ratings yet
- Data ModelingDocument4 pagesData ModelingJesse LinebergerNo ratings yet
- Heroic Ethnocentrism: The Idea of Universality in LiteratureDocument3 pagesHeroic Ethnocentrism: The Idea of Universality in LiteratureNoshaba QureshiNo ratings yet
- What Is Character MapDocument2 pagesWhat Is Character MapCiel QuimlatNo ratings yet
- Antony and CleopatraDocument257 pagesAntony and Cleopatrasanjay ktNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 StringsDocument16 pagesLecture1 StringsFoainaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Groups: The 8051 Has 255 Instructions - Every 8-Bit Opcode From 00 To FF Is Used Except For A5.Document30 pagesInstruction Groups: The 8051 Has 255 Instructions - Every 8-Bit Opcode From 00 To FF Is Used Except For A5.VLC350ZNo ratings yet
- Ell Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesEll Lesson Planapi-240597767No ratings yet
- This Is A Heading 1 Title For Your StoryDocument2 pagesThis Is A Heading 1 Title For Your Storyshaunte williamsNo ratings yet
- DBMS Complete NoteDocument89 pagesDBMS Complete NoteSan DipNo ratings yet
- Abhi 2Document146 pagesAbhi 2Gayatri HegadeNo ratings yet
- Love and Time - Version2Document3 pagesLove and Time - Version2elenaorNo ratings yet
- CharakDocument8 pagesCharakchauhan_892277982No ratings yet
- Sensing History - Eric's ArticleDocument18 pagesSensing History - Eric's ArticlePastor Eric BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- 21stCenturyLit Lesson 3 Introduction To The Literary Contributions of Ilocos RegionsDocument1 page21stCenturyLit Lesson 3 Introduction To The Literary Contributions of Ilocos RegionsJay Reyes De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Programming Techniques - PG (New 2009)Document202 pagesProgramming Techniques - PG (New 2009)Vikas SinglaNo ratings yet
- American Life and InstitutionsDocument8 pagesAmerican Life and InstitutionsEsma KaraçNo ratings yet
- Renewed For The New YearDocument26 pagesRenewed For The New YearJairah BausaNo ratings yet
- Press Brake Idea1Document11 pagesPress Brake Idea1Vishnu VardhanNo ratings yet
- Sentence Patterns: Let's Analyse The Sentence Patterns and Understand How They Are FormedDocument5 pagesSentence Patterns: Let's Analyse The Sentence Patterns and Understand How They Are FormedSITI SALWANI BINTI SAAD MoeNo ratings yet