Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Cell Project
Uploaded by
731728Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Animal Cell Project
Uploaded by
731728Copyright:
Available Formats
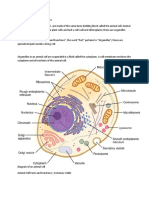
Cell Functions - Seeret
Cell Membrane The cell membrane is the outer layer of the
cell. It is semi-permeable, which means that it
allows some things to pass through into the
cell.
Cytoplasm (also known as cytosol) This is a jelly-like fluid inside the cell, which
helps the organelles to float. The substance
is cytosol, which is mostly made up of water.
Cytoplasm acts as a cushion and road
system to transport materials.
Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton helps the cell maintain the
structure it has, and how it’s organized on the
inside.
Nucleus This is referred to as the “brain” of the cell. It
holds the necessary information that’s
needed to perform and conduct the cell’s
functions. It’s the largest and most important
organelle in the cell. It contains Chromatin,
which are tightly wound strands of DNA. The
genetic information gets passed down when
the cell’s reproduce.
Nucleolus It creates ribosomal RNA, which reads and
carries out the instructions that are given from
the DNA.
Ribosomes It’s a very small organelle that produces
proteins. They make the protein based on the
information given by the organism’s nucleic
acids.
Centrioles The centrioles organize microtubules and
serve as the cell’s skeletal system.
Mitochondria It is one of the most critical organelles for an
organism, and the cell in general. It’s also
known as the “cell’s powerhouse”. In this
organelle, oxygen and sugars react in
chemical reactions to create energy for the
body. Muscle cells need the most energy, so
they have the most mitochondria, but blood
cells have none.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum The rough endoplasmic reticulum helps
produce proteins for the rest of the cell to
function. It’s rough, due to the ribosomes all
over the surface.
Cell Functions - Seeret
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum The smooth endoplasmic is largely for the
lipid (fat), steroid and hormone production. It
also detoxifies the body. For example, it helps
to detoxify drugs, alcohol, etc.
Golgi Apparatus This organelle stores proteins, puts them in
packages called vesicles, and they carry
proteins to the surface, and release them.
Lysosomes They contain special proteins, which help
break down large molecules. They can also
kill other harmful bacteria, such as bacteria
and viruses.
Vacuoles The vacuole helps the cell to hold water and
nutrients for future use, or emergency use.
Cell Functions - Seeret
References
Brown , M. (2021). Everything You Need To Ace Biology in One Big Fat Notebook. Workman
Publishing.
Centriole. Genome.gov. (n.d.). Retrieved February 13, 2023, from
https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Centriole
Endoplasmic Reticulum (rough and smooth). British Society for Cell Biology. (n.d.). Retrieved
February 13, 2023, from
https://bscb.org/learning-resources/softcell-e-learning/endoplasmic-reticulum-rough-and-smooth
/
Endoplasmic Reticulum (rough). Genome.gov. (n.d.). Retrieved February 13, 2023, from
https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Endoplasmic-Reticulum-rough
Nature Publishing Group. (n.d.). Nature news. Retrieved February 13, 2023, from
https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/microtubules-and-filaments-14052932/
You might also like
- 2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e FunctionDocument14 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e Functionwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Body PartsDocument1 pageAnimal Cell Body Partsnako simpNo ratings yet
- FB - Sevilla - Module 4Document5 pagesFB - Sevilla - Module 4Joyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Act 2CDocument3 pagesAct 2CCHARLIENE FAYE ASPRERNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- Foundation - 1 RecapDocument15 pagesFoundation - 1 RecapSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Infografia de BiologiaDocument4 pagesInfografia de BiologiafrancosebastianbcNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDocument28 pagesAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNo ratings yet
- Bio Ncert GistDocument96 pagesBio Ncert GistrrphysicsinstituteNo ratings yet
- Found-1 Science NotesDocument15 pagesFound-1 Science NotesSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- 8 - 2 BiologyDocument5 pages8 - 2 Biologyminda.eslteacherNo ratings yet
- LAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsDocument7 pagesLAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsJeanne RanielleNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument10 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionAngelique VeteNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Animal in Cells: Definition & FunctionsDocument2 pagesAnimal in Cells: Definition & FunctionsJonesJunker66No ratings yet
- CELL OrganellesDocument5 pagesCELL OrganellesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (2.1)Document13 pagesChapter 2 (2.1)mrtheunknownNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsJonathan MayoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Organisation of The OrganismDocument6 pages2 - Organisation of The OrganismAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Biology Y10 Ch2Document7 pagesBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Only Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The CytoplasmDocument14 pagesOnly Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The Cytoplasmrakan ilyasNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Isnain - Biochem Lec - Assignment 1Document4 pagesIsnain - Biochem Lec - Assignment 1Erich IsnainNo ratings yet
- ADOCS1002 - Course NotesDocument12 pagesADOCS1002 - Course NotesMostafa MansourNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyKent TediosNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell BIOLOGYDocument43 pagesParts of A Cell BIOLOGYSam Ferbyn LomotanNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDocument16 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- JetDocument14 pagesJetAnnie Lyn VillamorNo ratings yet
- Bio 221 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBio 221 Lecture NotesMuhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Cell Organelles 1Document4 pagesThe Cell and Cell Organelles 1Wennie Fe MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cell+WSDocument3 pages2 - Cell+WSRohan SoniNo ratings yet
- Basic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"Document12 pagesBasic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"cbseiscNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- Gen Bio (Definitions) - Cell StructureDocument3 pagesGen Bio (Definitions) - Cell StructureMary Vhenn SamonteNo ratings yet
- "Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology IDocument23 pages"Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology ITeacher Ella MorillaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- CellDocument11 pagesCellNicole ArangurenNo ratings yet
- Module 1-2Document21 pagesModule 1-2Edel Ruth Pal-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- What Is A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesWhat Is A MicroscopeMcj TeeNo ratings yet
- O Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsDocument10 pagesO Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsTakudzwa ZvidzaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgA SX2Document7 pagesACFrOgA SX2Nadhine MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organisation 2021Document17 pagesLevels of Organisation 2021ronalNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organisation 2021Document17 pagesLevels of Organisation 2021ronalNo ratings yet
- Premedication: Moderator: DR - Dinesh Kaushal Presentsd By: DR Rajesh Raman & DR Gopal SinghDocument60 pagesPremedication: Moderator: DR - Dinesh Kaushal Presentsd By: DR Rajesh Raman & DR Gopal Singhramanrajesh83No ratings yet
- Session #8 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document5 pagesSession #8 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G INo ratings yet
- Pex 05 01Document5 pagesPex 05 01Wijoyo KusumoNo ratings yet
- Sangat StudioDocument5 pagesSangat Studiosanja9balerNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain - 1Document7 pagesElectron Transport Chain - 1Manash SarmahNo ratings yet
- VO Basics of Neuroscience WS 22Document4 pagesVO Basics of Neuroscience WS 22Sina HsNo ratings yet
- William R. Uttal - The Neuron and The Mind - Microneuronal Theory and Practice in Cognitive Neuroscience-Routledge (2016)Document221 pagesWilliam R. Uttal - The Neuron and The Mind - Microneuronal Theory and Practice in Cognitive Neuroscience-Routledge (2016)gfrtbvhNo ratings yet
- The Rice Glycine-Rich Protein 3 Confers Drought ToDocument20 pagesThe Rice Glycine-Rich Protein 3 Confers Drought Toyustina_183741565No ratings yet
- Microbiology 1st Edition Wessner Dupont Charles Solution ManualDocument8 pagesMicrobiology 1st Edition Wessner Dupont Charles Solution Manuallorraine100% (23)
- 1) Varaz Chaniago 2) Vicka Zahara Firdaus 3) Vina Nur Sholikhah 4) Zidan Abdul GaniDocument22 pages1) Varaz Chaniago 2) Vicka Zahara Firdaus 3) Vina Nur Sholikhah 4) Zidan Abdul GaniFikri RamaNo ratings yet
- Delapaz, John Benedict (Performance Task 2)Document1 pageDelapaz, John Benedict (Performance Task 2)John Eric D. WongNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active Transport-2Document33 pagesPassive and Active Transport-2api-505212257No ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument5 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- SNS2023 BookletDocument44 pagesSNS2023 BookletAryan FeryNo ratings yet
- Omd551 Bbi Unit4Document63 pagesOmd551 Bbi Unit4Karthikeyan GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Nur 322 Gi Anatomyand Physiology and DiagnosticprocedureDocument59 pagesNur 322 Gi Anatomyand Physiology and DiagnosticprocedureLovelights ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Depression 3Rd Edition Edition Raymond W Lam Full ChapterDocument67 pagesDepression 3Rd Edition Edition Raymond W Lam Full Chapterruby.nicholson732100% (16)
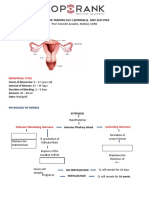
- Unit 3. (Group 16) Fertilization of Ovum, Embedding of The Blastocyst, Development and Growth of The FetusDocument80 pagesUnit 3. (Group 16) Fertilization of Ovum, Embedding of The Blastocyst, Development and Growth of The FetusKu NiniNo ratings yet
- MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY PRAKTIKUM.2020docxDocument17 pagesMEDICAL TERMINOLOGY PRAKTIKUM.2020docxEvangeline EngieNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Competency (2019)Document7 pagesAnatomy Competency (2019)Isha RaghuNo ratings yet
- DopplerDocument56 pagesDopplerEsraa AlmassriNo ratings yet
- Edema Cerebral TratamientoDocument16 pagesEdema Cerebral TratamientoLuis octavio carranzaNo ratings yet
- GLYCOLYSISDocument6 pagesGLYCOLYSISHAZEL SANDRONo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Biological Nitrogen FixationDocument5 pagesMechanism of Biological Nitrogen Fixationmymimi100% (1)
- The Pathophysiology of Sepsis - 2021 Update - Part 2, Organ Dysfunction and AssessmentDocument13 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Sepsis - 2021 Update - Part 2, Organ Dysfunction and AssessmentValerie ZimmermannNo ratings yet
- 911Document1 page911Cj Nicole SuriagaNo ratings yet
- Revised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDocument15 pagesRevised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Different Light Intensities On Carbohydrate Accumulate and Distribution in Three Native Broad-Leaved Tree Species of TaiwanDocument12 pagesEffects of Different Light Intensities On Carbohydrate Accumulate and Distribution in Three Native Broad-Leaved Tree Species of TaiwanJosephine ChiuNo ratings yet
- 03.immune InflamationDocument11 pages03.immune InflamationVARUN BHARADWAJ .MNo ratings yet
- 5.0 LeukopoiesisDocument37 pages5.0 LeukopoiesisJunior SataNo ratings yet