Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Closer Look at The Phil. Curriculum
Uploaded by
beaquincena180 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
A CLOSER LOOK AT THE PHIL. CURRICULUM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesA Closer Look at The Phil. Curriculum
Uploaded by
beaquincena18Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
A CLOSER LOOK AT THE PHIL.
CURRICULUM
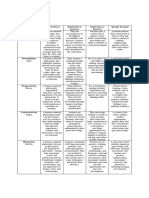
Educational Philosophy Beliefs/Perspectives %of influence Evidences
1.Essentialism A teacher-centered
philosophy that holds
that all students should
have the same set of
abilities and
knowledge that well-
educated people ought
to possess. It
emphasizes deferring
to authority, cultivating
good mental habits and
instruction in the
essentials.
2.Progressivism Progressivism 80% of influence Student-centered
encourages hands-on, methods, in which
active learning that teachers adapt their
involves students in lessons to their
dealing with and students' interests,
solving problems from skills, and learning
the real world. preferences, are highly
valued in many
contemporary
classrooms. This
method encourages
students to take charge
of their education,
which boosts
motivation and
develops students'
capacity for
independent study. In
order to help students
feel at ease in the
classroom, teachers
encourage in-class
discussion and thought
sharing.
3. Existentialism It involves fostering
uniqueness and
accountability for
oneself. It emphasizes
self-discovery and the
formation of a distinct
identity while
encouraging pupils to
investigate their own
values, ideas, and
decisions.
4. Perennialism It claims that these
ideas are necessary for
a well-rounded
education that
emphasizes critical
thinking and the
development of a
feeling of cultural
heritage.
5. Linguistic Philosophy It is the idea that
language is the
fundamental basis of
all learning since
language is how we
learn best.
6.Behaviorism It concentrates on
looking at and studying
how a controlled
environment affects
behavior. The pupils'
behavior in the
classroom may have an
impact.
7.Constructivism Instead of just passively
absorbing information,
learners actively
generate knowledge.
The information and
comprehension of the
pupils are derived from
their own personal
experiences.
You might also like
- Philosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: The Seven Philosophies of EducationDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: The Seven Philosophies of EducationJohn RaymondNo ratings yet
- The Seven Philosophies of Education PhilDocument2 pagesThe Seven Philosophies of Education PhilArnold C. LasitNo ratings yet
- Kapu YaaaaDocument6 pagesKapu YaaaaJenny Rose BaculadNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Part 1Document9 pagesModule 1 Part 1Maria Nicole M. ClerigoNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUTIVISMDocument4 pagesCONSTRUTIVISMAlama,Shenna Mea OroscoNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument4 pagesFinal ExamjhoerielNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophies of EducationErica LeysonNo ratings yet
- Unit One - Learner-Centered Teaching - Foundations and CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesUnit One - Learner-Centered Teaching - Foundations and CharacteristicsCarina Margallo CelajeNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To TeachDocument4 pagesPhilosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To TeachAMABELLE MITZI S. NO-OTNo ratings yet
- Table TEFL METHODOLOGYDocument3 pagesTable TEFL METHODOLOGYSantiago JarrinNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed 13 - The Teaching Profession Modular Lesson No. 2Document4 pagesProf. Ed 13 - The Teaching Profession Modular Lesson No. 2Mish LimNo ratings yet
- NRepublic Act No. 9293Document6 pagesNRepublic Act No. 9293JAY TAGBUYAWANNo ratings yet
- Tpeh Output 5Document5 pagesTpeh Output 5Shaira Colleen Merano VillamorNo ratings yet
- FLCT Review Material For Distribution 2024 2Document9 pagesFLCT Review Material For Distribution 2024 2danllyodangelo.sambajonNo ratings yet
- The Seven Philosophies of Education PhilDocument2 pagesThe Seven Philosophies of Education PhilJohn Patrick ArciteNo ratings yet
- Seven Philosophies - Rocel NavajaDocument3 pagesSeven Philosophies - Rocel NavajaRocel NavajaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 3 LECTURE SEVEN PHILOSOPHIES of EDUCATIONDocument5 pagesEDUC 3 LECTURE SEVEN PHILOSOPHIES of EDUCATIONAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument36 pagesPhilosophies of EducationNorman De VeraNo ratings yet
- Educ 2Document5 pagesEduc 2Jhonalyn ManubagNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of Education MatrixDocument4 pagesPhilosophies of Education MatrixCesar Patac100% (1)
- Inquiry-Based LearningDocument2 pagesInquiry-Based Learningapi-465646946No ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning: Today's Student Is Tomorrow's ColleagueDocument3 pagesTeaching and Learning: Today's Student Is Tomorrow's ColleagueAldren BeliberNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning: Today's Student Is Tomorrow's ColleagueDocument3 pagesTeaching and Learning: Today's Student Is Tomorrow's ColleagueAldren BeliberNo ratings yet
- Scarlet Educ 109 Mam BambicoDocument6 pagesScarlet Educ 109 Mam BambicoScarlet Elgamo GalantoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Evaluation PhiloDocument4 pages3rd Evaluation PhiloBerlin Tingson LabianoNo ratings yet
- Philo of Educ Learning Output 2Document4 pagesPhilo of Educ Learning Output 2Zeke Gabrielle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Elaborate NotesDocument3 pagesElaborate NotesJannine CatalanNo ratings yet
- The 7 Philosophies of EducationDocument23 pagesThe 7 Philosophies of EducationJonamay CarantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document19 pagesChapter 8NesreenNo ratings yet
- Challenge 3 Philophies of EducationDocument3 pagesChallenge 3 Philophies of EducationDiane RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14:: Our Philosophical Heritage: Philosophies of EducationDocument15 pagesLesson 14:: Our Philosophical Heritage: Philosophies of EducationMary Grace ApinadoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.4 (33-34)Document3 pagesActivity 1.4 (33-34)Jessa Mae GomezNo ratings yet
- Exercise #1 Educational Philosophies: Prof. Ed. 533 - The Teaching Profession and Social Dimension of EducationDocument3 pagesExercise #1 Educational Philosophies: Prof. Ed. 533 - The Teaching Profession and Social Dimension of EducationLouise salesNo ratings yet
- Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: EssentialismDocument2 pagesWhy Teach What To Teach How To Teach: EssentialismSunako Claes0% (1)
- Asyncronous Assignment TTP...Document17 pagesAsyncronous Assignment TTP...Kim alexandraNo ratings yet
- ProEd 6Document1 pageProEd 6Jirah Joy PeañarNo ratings yet
- Weakness and Interventions OnlyDocument5 pagesWeakness and Interventions OnlyKRISTEL JOY MANCERANo ratings yet
- Different Type of Educ PhilosophyDocument6 pagesDifferent Type of Educ PhilosophyThet SalazarNo ratings yet
- Philosophical MatrixDocument3 pagesPhilosophical MatrixIvy Jean Amadora FelicianoNo ratings yet
- My Teaching PhilosophyDocument1 pageMy Teaching PhilosophyMichelle “Chelle”No ratings yet
- Philosophies in TeachingDocument1 pagePhilosophies in TeachingArielle Ariane NacarNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism vs. EssentialismDocument5 pagesBehaviorism vs. EssentialismJamill BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT #3 - Matrix of The Different PhilosophiesDocument6 pagesASSIGNMENT #3 - Matrix of The Different Philosophiesngitngit.jjtNo ratings yet
- Constructivist Learning and TeachingDocument7 pagesConstructivist Learning and TeachingZackNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY - Comparison of Western and Eastern PhilosophiesDocument4 pagesACTIVITY - Comparison of Western and Eastern PhilosophiesChanie Baguio PitogoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Implications of Learning Theories ForDocument11 pagesWhat Are The Implications of Learning Theories ForzieryNo ratings yet
- Production of Social Studies: Prepared By: Iciah Jesalva Bse Major in Social StudiesDocument22 pagesProduction of Social Studies: Prepared By: Iciah Jesalva Bse Major in Social StudiesICIAH ALANA NADINE JESALVANo ratings yet
- CurriculumDocument19 pagesCurriculumIlene Rose BuencochilloNo ratings yet
- The 7 Philosophies of EducationDocument4 pagesThe 7 Philosophies of EducationJonamay CarantoNo ratings yet
- Instructional ApproachDocument1 pageInstructional ApproachJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- Mangahas, James Moses (Bped 3-A)Document49 pagesMangahas, James Moses (Bped 3-A)James Sanchez MangahasNo ratings yet
- Teaching ProfessionDocument10 pagesTeaching ProfessionAna Mae MaruNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Part 1 PDFDocument3 pagesModule 1 Part 1 PDFLouise salesNo ratings yet
- Morato DLL For Ipcrf With AnnotationDocument8 pagesMorato DLL For Ipcrf With AnnotationJessie MarieNo ratings yet
- Comparing Learning TheoriesDocument8 pagesComparing Learning Theoriesfimmee2006No ratings yet
- The 7 Philosophies of EducationDocument25 pagesThe 7 Philosophies of EducationJonamay CarantoNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of A Student - Centered Instruction On Philippine History Class in Developing Higher Order Thinking Skills HOTSDocument7 pagesEffectiveness of A Student - Centered Instruction On Philippine History Class in Developing Higher Order Thinking Skills HOTSAlmie CostillasNo ratings yet
- Teaching Profession Activity 1 - Realyn D. TanecaDocument5 pagesTeaching Profession Activity 1 - Realyn D. TanecaEya Delos Santos TañecaNo ratings yet
- How To Be a Great Teacher: Your Step-By-Step Guide To Teach Students EffectivelyFrom EverandHow To Be a Great Teacher: Your Step-By-Step Guide To Teach Students EffectivelyNo ratings yet
- Educational Perennial IsmDocument9 pagesEducational Perennial IsmJo BernabeNo ratings yet
- LCP Sample (Domrac)Document4 pagesLCP Sample (Domrac)Chris John TenorioNo ratings yet
- Should Teachers Give Homework Over The WeekendDocument7 pagesShould Teachers Give Homework Over The Weekendafnaoabfuddcdf100% (1)
- Subtraction With Regrouping Lesson Plan 2014Document5 pagesSubtraction With Regrouping Lesson Plan 2014api-299488464No ratings yet
- 2 Types of CurriculumDocument20 pages2 Types of Curriculumirene apiladaNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Answers To Complete The Following Short PassageDocument4 pagesChoose The Correct Answers To Complete The Following Short PassageMaria Angelica Moreno O.No ratings yet
- Understanding The Gmat Exam PDFDocument13 pagesUnderstanding The Gmat Exam PDFileaders04No ratings yet
- Pamantayan Sa Pagbibigay NG MarkaDocument6 pagesPamantayan Sa Pagbibigay NG MarkaMarry DanielNo ratings yet
- List ReferenceDocument44 pagesList ReferenceSERNOR CHERRYL GATCHALIANNo ratings yet
- Tegr 110 Module 1Document33 pagesTegr 110 Module 1Cathy Anne Alcones GarnaceNo ratings yet
- 03.materi Presentasi Sync - SPIRIT Value For Binusian - Rev1Document20 pages03.materi Presentasi Sync - SPIRIT Value For Binusian - Rev1Random GuyNo ratings yet
- Daily English Language Lesson Plan: Skills Pedagogy (Strategy/Activity)Document4 pagesDaily English Language Lesson Plan: Skills Pedagogy (Strategy/Activity)Aimi Syafiqah100% (3)
- Unit 1 8626Document28 pagesUnit 1 8626Neelam ZahraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2023 International Trade ECS3702 Semesters 1 and 2 Department of EconomicsDocument14 pagesTutorial Letter 101/3/2023 International Trade ECS3702 Semesters 1 and 2 Department of Economicsdalron pedroNo ratings yet
- Comparative EducationDocument67 pagesComparative Educationrimsha aminNo ratings yet
- Ge4 - Mathematics-In-The-Modern-WorldDocument14 pagesGe4 - Mathematics-In-The-Modern-WorldJohn Paul Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Summary-Nursing As A TeacherDocument1 pageSummary-Nursing As A Teacherphlanxx_07No ratings yet
- Tugasan 1 - KPD 3016Document17 pagesTugasan 1 - KPD 3016Sandra MeruNo ratings yet
- SOPDocument1 pageSOPshuxuelaoshiNo ratings yet
- Pda-Programa de Actividades-La-Abuela PDFDocument17 pagesPda-Programa de Actividades-La-Abuela PDFpatricia floresNo ratings yet
- PROJECT-mobile LaboratoryDocument6 pagesPROJECT-mobile LaboratoryMarilyn M. SolimanNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Engineer Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesMachine Learning Engineer Interview QuestionsANKIT MITTALNo ratings yet
- Norval Morrisseau Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesNorval Morrisseau Lesson Planapi-309886947No ratings yet
- 7 Days Dolpa Training ReportDocument20 pages7 Days Dolpa Training ReportRishi Kesh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Paradigm Shift in Nursing AdministrationDocument63 pagesParadigm Shift in Nursing AdministrationJenn Botal Baguidudol100% (1)
- PPSTDocument37 pagesPPSTmia saraba bazar75% (4)
- The Teaching Profession: MARCH 24, 2021Document14 pagesThe Teaching Profession: MARCH 24, 2021Alondra SiggayoNo ratings yet
- Educational Game Design Conceptualisation and EvaluationDocument12 pagesEducational Game Design Conceptualisation and EvaluationAnonymous Lk40y4eDozNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus UTS - (DM)Document14 pagesCourse Syllabus UTS - (DM)Mayeyean TaguibalosNo ratings yet
- Participant Evaluation Form (Ms Word)Document1 pageParticipant Evaluation Form (Ms Word)Ruel Apostol IINo ratings yet