Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Predisposing-Factors 20231129 134609 0000
Uploaded by
Mary Mathel Del Rosario0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageOriginal Title
Predisposing-Factors_20231129_134609_0000
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pagePredisposing-Factors 20231129 134609 0000
Uploaded by
Mary Mathel Del RosarioCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
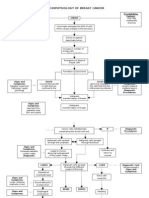
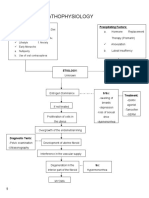
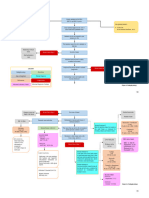
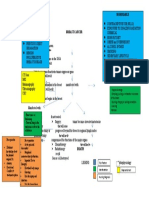
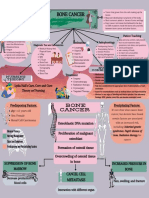
Precipitating Factors:
Hx of taking oral contraceptives
Immunosuppression
Predisposing Factors:
Diet
Gender (Female) Etiology:
Radiation exposure
Age (50 yrs old ↑) Unknown
Cigarette smoking
Family history (first line in family)
Obesity
Genetics
Alcohol use
Early menarche ate menopause
Virus
Hormonal therapy
Increasing age at first pregnancy
Permanent damage to DNA
Genetic mutation on the DNA
(BRCA1 and BRCA2)
Activation of growth promoting oncogenes Inactivation of tumor suppressor genes Alteration in Apoptopic genes
Breast
Neoplasm formation in the breast
Lump (1 cm growth)
Nipple inversion
Orange peel dimpling
Nipple discharge
Breast examination Primary tumor begins in the breast
Mammogram
Ultrasound
MRI
Scintimammography
Biopsy
Tumor becomes invasive
-Chemotherapy
If treated: -Hormone therapy
-Surgery -Radiation therapy
-Chemotherapy -Targeted therapy
-Radiotherapy -Surgery
Progressed beyond the breast to regional node.
Blood tests (CBC, Comprehensive metabolic panel)
Cancer cell destroyed Whole-body bone scan
CT scan
MRI of the spine or brain
Travel to the other organs PET scan
( through lymphatic system, bloodstream or local invasion ) X-ray
Death
Ultrasound of abdomen or chest
Bronchoscopy
Biopsy of any suspicious area
If not treated: Compromised the functions of the major organs. Tap (thoracentesis, spinal tap, paracentesis)
Lungs
Liver
Bones
Brain
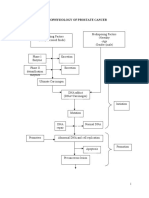
Bone Metastases Brain Metastases
Pain Lung Metastases Liver Metastases Headache
Visual change (double or loss of
Pathological fracture Obstruction of the airway vision)
Jaundice (Yellowing of skin
Dizziness
or white of the eyes)
Seizure
Spinal cord compression Confusion
Malignant Pleural Effusion Weakness on one side of the body
Bleeding
Problem with coordination
Itching and rash
Personality change
Hypercalcemia Pneumonia Abdominal pain
Numbness
Increased abdominal girth
Early on, this may cause: Swelling of foot and hand
Nausea and vomiting Pulmonary hemorrhage
Increased thirst
Legends:
Weakness Cough Steroids
Muscle aches Fever Complication
Liver function test Whole- brain radiation
It can progress into serious Difficulty/ labored breathing PET scan
symptoms, including: Acute respiratory failure
Risk Factor
Confusion
Mechanism
Abnormal hearth rhythm
Shortness of breath
Coma Chemotherapy
Treatment
Hormonal therapy
Targeted therapy Signs/ Symptoms
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy General treatments for
Diagnostic /
Strontium 89 metastatic cancer
Laboratory test
Surgery Pleural drainage
Bone- modifying medication (
Zometa, Xgeva )
You might also like
- Breast Cancer Risk Factors and PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Risk Factors and PathophysiologyDianne Kate CadioganNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer: Unkno Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancer: Unkno Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsKevin Ercia100% (1)
- JF Nov 04 Web VersionDocument8 pagesJF Nov 04 Web VersionAndrew GrazianoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Prostate Cancer Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Prostate Cancer Risk Factorsmkho100% (1)
- Cancer Pathophysiology To Be EditedDocument5 pagesCancer Pathophysiology To Be EditedEyySiEffVeeNo ratings yet
- Patho of CA & Breast CaDocument3 pagesPatho of CA & Breast CaAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Types of Cancer Risk Factors Screenings TreatmentsDocument4 pagesTypes of Cancer Risk Factors Screenings TreatmentsEffie Cloe Marie BitengNo ratings yet
- Breast CA PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesBreast CA Pathophysiologylyn valerieNo ratings yet
- Modifiedpatho ToyodaDocument4 pagesModifiedpatho ToyodaCaneEscabarteNo ratings yet
- 07.systemic Therapy For Metastatic Breast CancerDocument20 pages07.systemic Therapy For Metastatic Breast CancerDIVISI HOM FK ULMNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Aaron Arce BSN 3 DDocument7 pagesCase Analysis - Aaron Arce BSN 3 DAaron ArceNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer: If Not TreatedDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Breast Cancer: If Not TreatedsteffiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsRalph GeraldNo ratings yet
- DPatho ProstateDocument2 pagesDPatho Prostateshujin_samaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Precipitating FactorsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Larygeal CancerDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Larygeal CancerAra Shian OdinerNo ratings yet
- 4 ConceptDocument1 page4 ConceptStacey GarciaNo ratings yet
- Diagram Myoma IDocument1 pageDiagram Myoma IJoann100% (12)
- Pheochromocytoma DPDocument1 pagePheochromocytoma DPRosemarie HagnaNo ratings yet
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 pagesProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Patho of Invasive Duct CarcinomaDocument3 pagesPatho of Invasive Duct CarcinomaBESA JERIC FLORESNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of H MoleDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of H MoleHenzbely JudeNo ratings yet
- PRINT 3Document2 pagesPRINT 32080500No ratings yet
- Myoma PathoniixDocument1 pageMyoma PathoniixRendel FernandezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cancer of the Male Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Cancer of the Male Reproductive SystemDinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomavssarcomaDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomavssarcomaJustin AlejoNo ratings yet
- Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment OptionsDocument30 pagesMetastatic Breast Cancer Treatment OptionslagundaNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma PDFDocument3 pagesOsteosarcoma PDFkc andrea torresNo ratings yet
- Mammaprint in IndonesiaDocument52 pagesMammaprint in IndonesiaYuliaji Narendra PutraNo ratings yet
- Rostate Ancer: Symptoms, Risk Factors and TreatmentsDocument6 pagesRostate Ancer: Symptoms, Risk Factors and TreatmentsKomal KhanNo ratings yet
- Tumor Markers Common Manifestations Therapy/Treatment Others: Male CancersDocument9 pagesTumor Markers Common Manifestations Therapy/Treatment Others: Male CancersErica DagdagNo ratings yet
- Bhavesh Patel, Radhika Patel, Hasti Patel, Henil Patel Submitted To: Dr. Sandesh Lodha SirDocument1 pageBhavesh Patel, Radhika Patel, Hasti Patel, Henil Patel Submitted To: Dr. Sandesh Lodha Sirradhika patelNo ratings yet
- Ass DrugDocument1 pageAss Drug2080315No ratings yet
- Oncology PresentationDocument31 pagesOncology Presentationonkar.expg23383No ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 ChecklistDocument16 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Checklistmariana PeraltaNo ratings yet
- BreastCancer PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBreastCancer PathophysiologyClaudineNo ratings yet
- Greater Sciatic NotchDocument1 pageGreater Sciatic NotchTogaju KuboyeNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Screening: Screening Management:: A. DciDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Screening: Screening Management:: A. DciCharlie65129No ratings yet
- Anatomi dan Etiologi Kanker PayudaraDocument55 pagesAnatomi dan Etiologi Kanker PayudaraatyNo ratings yet
- Molecular basis of cancer: Carcinogenesis & Regulator genesDocument52 pagesMolecular basis of cancer: Carcinogenesis & Regulator genesFenny Cienta Damai ClaluNo ratings yet
- Critical Apraisal For EbpDocument4 pagesCritical Apraisal For EbpBagaz Riyuzha'ky BoyzzNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer PathophysiologyJM Andrade100% (3)
- Female Precocious Puberty AlgorithmDocument1 pageFemale Precocious Puberty AlgorithmRICHI ADITYANo ratings yet
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 pagesMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument1 pageCervical CancerMasarrah AlchiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: - Hematuria - Frequency - Urgency - Lower Abdominal Pain - Rectal DiscomfortDocument1 pagePathophysiology: - Hematuria - Frequency - Urgency - Lower Abdominal Pain - Rectal DiscomfortEarlvin JavierNo ratings yet
- Medical Brochure Templates Blue White Clean Modern Hospital Services TrifoldDocument1 pageMedical Brochure Templates Blue White Clean Modern Hospital Services TrifoldNadjaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Abortion Case Study (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Document4 pagesPathophysiology of Abortion Case Study (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- CONCEPT MAP Malignant Breast CancerDocument1 pageCONCEPT MAP Malignant Breast CancerIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Hepatoblastoma PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesHepatoblastoma Pathophysiologyjennachristy03100% (1)
- Richard Chumbiauca Munares EndometriosisDocument14 pagesRichard Chumbiauca Munares Endometriosis01OrietammNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Concept MapKeepItSecret100% (1)
- BONE CANCER CASE STUDY: 61-YEAR-OLD FEMALEDocument2 pagesBONE CANCER CASE STUDY: 61-YEAR-OLD FEMALEJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Road To MDDocument1 pageRoad To MDEcel AggasidNo ratings yet
- 66 - Prevention and Early Detection of CancersDocument1 page66 - Prevention and Early Detection of CancersRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument22 pagesBreast CancerCasey Vergara TañedoNo ratings yet
- S5. Diseases of the Male Genital SystemDocument11 pagesS5. Diseases of the Male Genital Systemkp9cbkzj9vNo ratings yet
- Hormone Therapy in The Postmenopausal Years - Considering Benefits and Risks in Clinical PracticDocument36 pagesHormone Therapy in The Postmenopausal Years - Considering Benefits and Risks in Clinical PracticPaloma PeñaNo ratings yet
- Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Pathology, Volume 1From EverandBreast Disease: Diagnosis and Pathology, Volume 1Adnan AydinerNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Cancer: A Comprehensive Resource for Patients and FamiliesFrom EverandEndometrial Cancer: A Comprehensive Resource for Patients and FamiliesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics ACTIVITY 8Document3 pagesNursing Informatics ACTIVITY 8Mary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Preboard 33BDocument11 pagesPreboard 33BMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument4 pagesNursing InformaticsMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Population Growth RateDocument1 pagePopulation Growth RateMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION ONG EditedDocument21 pagesCASE PRESENTATION ONG EditedMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Kohlberg's Theory of Moral DevelopmentDocument3 pagesKohlberg's Theory of Moral DevelopmentMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- The Subject Is A Nurse Giving The Mother Her Newborn Child.: Scribbling SoulDocument4 pagesThe Subject Is A Nurse Giving The Mother Her Newborn Child.: Scribbling SoulMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument1 pageBiochemistryMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Predisposing and precipitating factors of pneumoniaDocument1 pagePredisposing and precipitating factors of pneumoniaMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Nurse'S Notes (Fdar Method) : Displayed No Expression of PainDocument3 pagesNurse'S Notes (Fdar Method) : Displayed No Expression of PainMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- NCM103Activity 1 NCPDocument2 pagesNCM103Activity 1 NCPMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Arsitektur Resnet50 Dan Resnet101 Dalam Klasifikasi Kanker Serviks Pada Citra Pap SmearDocument8 pagesPerbandingan Arsitektur Resnet50 Dan Resnet101 Dalam Klasifikasi Kanker Serviks Pada Citra Pap SmearJamil Al-idrusNo ratings yet
- 1 Lines EsofagoDocument33 pages1 Lines EsofagoClaudia MartínezNo ratings yet
- STUDENT CASE SSS WEEK 2 (Case Kelamin Student)Document7 pagesSTUDENT CASE SSS WEEK 2 (Case Kelamin Student)girvNo ratings yet
- Ca MammaeDocument19 pagesCa Mammaeelika dwiNo ratings yet
- Eating For Energy NEWDocument272 pagesEating For Energy NEWCARLOSWAR101100% (4)
- Discharge Plan FinalDocument6 pagesDischarge Plan Finalfidc_0428No ratings yet
- LT Governor Re Patricia Wright 6.12.2020Document5 pagesLT Governor Re Patricia Wright 6.12.2020Ethan BrownNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumor Epidemiology: Consensus From The Brain Tumor Epidemiology ConsortiumDocument16 pagesBrain Tumor Epidemiology: Consensus From The Brain Tumor Epidemiology ConsortiumscrugnlorNo ratings yet
- Actualización de Inmunoterapia en CáncerDocument13 pagesActualización de Inmunoterapia en CáncerAli BelloNo ratings yet
- Principles of Cancer TreatmentDocument1 pagePrinciples of Cancer TreatmentRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Final 2021 Benefit Year Final HHS Risk Adjustment Model CoefficientsDocument26 pagesFinal 2021 Benefit Year Final HHS Risk Adjustment Model CoefficientsJ CHANGNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Gemcitabine: Synonym (S) : Common Trade Name (S) : ClassificationDocument8 pagesDrug Name Gemcitabine: Synonym (S) : Common Trade Name (S) : ClassificationOka Robi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Onion Phytochemical and Health PropertiesDocument24 pagesOnion Phytochemical and Health PropertiesPépé DiopNo ratings yet
- Active Ingredients PomegranateDocument91 pagesActive Ingredients Pomegranatekennitaharyati100% (1)
- Neoplasma Lecture For FKG''Document62 pagesNeoplasma Lecture For FKG''ginulNo ratings yet
- Male Breast Pathology: Understanding Gynecomastia and Other LesionsDocument27 pagesMale Breast Pathology: Understanding Gynecomastia and Other LesionsNenad DjokicNo ratings yet
- Ulangan Akhir Semester Ganjil Bhs InggrisDocument7 pagesUlangan Akhir Semester Ganjil Bhs InggrisWhilda BayuNo ratings yet
- Oral Oncology: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesOral Oncology: SciencedirectafissaNo ratings yet
- Wu 2019 JCODocument9 pagesWu 2019 JCOluNo ratings yet
- Esophageal CarcinomaDocument34 pagesEsophageal Carcinomaapi-19916399100% (1)
- India Research Paper TopicsDocument8 pagesIndia Research Paper Topicsafnkyarofeepzh100% (1)
- Cytotoxicity of Vitex NegundoDocument35 pagesCytotoxicity of Vitex NegundoDean Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- RK PandeyDocument211 pagesRK PandeyNirdeshKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- Nano TechnologyDocument31 pagesNano Technologysruthireddy12y100% (2)
- Jco 20 03282Document10 pagesJco 20 03282AKNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Review ArticleDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Review ArticleNazim ThakranNo ratings yet
- Covid Self Declaration Form Visitor PDFDocument3 pagesCovid Self Declaration Form Visitor PDFTipu BabuNo ratings yet
- Oral CancerDocument29 pagesOral CancerBijen LangpoklakpamNo ratings yet
- Role of CT Virtual Colonoscopy Versus Conventional Colonoscopy in The Evaluation of Colonic PolypsDocument8 pagesRole of CT Virtual Colonoscopy Versus Conventional Colonoscopy in The Evaluation of Colonic PolypsPari Pengda BaliNo ratings yet