Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Current Electricity
Uploaded by
aadiv20120060 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesjee mind map
Original Title
current electricity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentjee mind map
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesCurrent Electricity
Uploaded by
aadiv2012006jee mind map
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
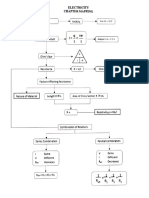
Ohm’s Law: V = IR
Resistivity: Electrical resistivity is the reciprocal of electrical
Current Electricity conductivity. It is the measure of the ability of a material to
oppose the flow of current.
Dependence of resistivity on various parameter:
● It does not depend upon material dimensions.
● It depends upon temperature as well as material.
Electric Current: The rate of flow of electric charge per unit
time across any cross-section. Variation in Resistivity wrt. Temperature: T ↑ 𝝉↓ = ρ ↑
Current Density: Current density has a magnitude equal to
current per unit perpendicular area in the region surrounding
Kirchhoff’s Current Law
that point.
Drift Velocity: The average velocity attained by charged
particles, (eg. electrons) in a material due to an electric field is
known as Drift Velocity.
Relation with Electric Current I = neAvd
The drift velocity of an electron for a unit electric field is
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law
known as the mobility of the electron.
Current Electricity
Combination of Resistors
NOTE- In series combination,
current through each resistor is
same.
P = VI
NOTE- In Parallel combination,
Potential difference across each P = V2/R
resistor is same
P = I 2R
You might also like
- Current Electricity: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF FormatDocument4 pagesCurrent Electricity: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF FormatYug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06 Mar 2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 06 Mar 2022Jitender GuptaNo ratings yet
- Current and ElectricityDocument10 pagesCurrent and ElectricitySiddanta PoudelNo ratings yet
- CH 12 ElectricityDocument10 pagesCH 12 ElectricityMohammed SafwanNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Definition Sem 2Document3 pagesSTPM Physics Definition Sem 2OMFNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Electricity: ChargeDocument6 pagesRevision Notes On Electricity: ChargeJahnavi MeharNo ratings yet
- X Class Physics ElectricityDocument7 pagesX Class Physics ElectricityPaarth BansalNo ratings yet
- A6 CurrentsummaryDocument1 pageA6 CurrentsummaryZainabNo ratings yet
- Su4c9 by Adel KhamisDocument8 pagesSu4c9 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNo ratings yet
- Electricity : R V RaDocument8 pagesElectricity : R V RastapleNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity: B.E. (Me) Iiest, ShibpurDocument9 pagesCurrent Electricity: B.E. (Me) Iiest, ShibpurshubhamNo ratings yet
- 3 Current ElectricityDocument31 pages3 Current ElectricityPallavi PalluNo ratings yet
- 2 Current ElectricityDocument17 pages2 Current ElectricityHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law: Presented byDocument18 pagesOhms Law: Presented byMirayl iveNo ratings yet
- A Level Electric Current Slides 001Document43 pagesA Level Electric Current Slides 001markwelly367No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument1 pageElectricityShajeena Abdul NasarNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument7 pagesElectricityWalia FatimaNo ratings yet
- Current-Electricity NotesDocument4 pagesCurrent-Electricity NotesPiyush RoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Network Theory - Study NotesDocument16 pagesBasic Concept of Network Theory - Study NotesBORN TO DIENo ratings yet
- Physics Ch5 NotesDocument20 pagesPhysics Ch5 NotesAli GorganiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document7 pagesLesson 5Stephen Maina NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Ohm Law, Resistance, Conductance - 07.04.2022Document14 pagesOhm Law, Resistance, Conductance - 07.04.2022Arasan ArasanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 ElectricityDocument16 pagesClass 10 ElectricityTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument18 pagesCurrent ElectricityTasawar Hussain DayoNo ratings yet
- 10 ElectricityDocument4 pages10 ElectricitySunil SeerviNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY Imp NotesDocument2 pagesELECTRICITY Imp Notesq-tipNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - IDocument72 pagesCurrent Electricity - IAjaya KumarNo ratings yet
- SCM X Physics 202122 Term 1 and 2Document86 pagesSCM X Physics 202122 Term 1 and 2Evilzen GamingNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument13 pagesCurrent Electricityreshma1917singhNo ratings yet
- UnitNo1DCCircuitspptx 2022 10 08 15 08 30pptx 2022 11 03 21 34 27Document66 pagesUnitNo1DCCircuitspptx 2022 10 08 15 08 30pptx 2022 11 03 21 34 27DUSHIMIMANA ROBIN mefgiNo ratings yet
- Study Material and Notes of CH 12 Electricity Class 10th. Topics in The ChapterDocument5 pagesStudy Material and Notes of CH 12 Electricity Class 10th. Topics in The ChapterSavita ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectricityDocument7 pagesChapter 3 ElectricityNilaksh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - IDocument13 pagesCurrent Electricity - IjaindevanshNo ratings yet
- Bansal Current ElectricityDocument27 pagesBansal Current Electricitysudhanva mattupalli100% (1)
- Bansal Current Electricity PDFDocument27 pagesBansal Current Electricity PDFUttiya SangiriNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledArnab DasNo ratings yet
- Electricity Notes For CBSE Class 10 PhysicsDocument5 pagesElectricity Notes For CBSE Class 10 Physicssadiyaarchive22No ratings yet
- Phy 061 Electrodynamics (Circuits - Series and Parallel)Document8 pagesPhy 061 Electrodynamics (Circuits - Series and Parallel)Angel Lou LiwagonNo ratings yet
- S2 Module 3 NotesDocument16 pagesS2 Module 3 NotesAjmi JudsonNo ratings yet
- APC CircuitsDocument6 pagesAPC CircuitsRana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitsDocument52 pagesElectrical CircuitsPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document46 pagesChapter 27varpaliaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electric CircuitDocument81 pagesIntroduction To Electric Circuitkaushallyaa navindranNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity: Key Concepts Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise-Iii Answer KeyDocument15 pagesCurrent Electricity: Key Concepts Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise-Iii Answer KeyRoNNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thDocument24 pagesElectricity - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thsyedyaseen39375No ratings yet
- Electricity Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesElectricity Knowledge OrganiserJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Its Heating and Chemical EffectsDocument7 pagesElectricity and Its Heating and Chemical EffectsManish Kedawat50% (2)
- Ohm'S Law and Its Derivation: V Ir V-Voltage I-Current R-ResistanceDocument9 pagesOhm'S Law and Its Derivation: V Ir V-Voltage I-Current R-ResistancemanuNo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity NotesCarlos KasambiraNo ratings yet
- Electricity Notes Class 10THDocument8 pagesElectricity Notes Class 10THNeha BansalNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentChris LauNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 Electricity - CreateDocument24 pagesChapter - 12 Electricity - CreateVatsal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Aakash 02 - Current ElectricityDocument14 pagesAakash 02 - Current ElectricityAshish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesCurrent Electricitymohitverma303No ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: ElectricityDocument9 pagesElectric Circuits: ElectricityFernanda VillacísNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and EngineersDocument48 pagesPhysics For Scientists and EngineersĐức HuyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12.1 - Current, Resisitivity, and ResistanceDocument13 pagesLesson 12.1 - Current, Resisitivity, and ResistanceLaihcaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Current ElectricityDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Current ElectricitySajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument5 pagesCurrent ElectricityKamesh RajputNo ratings yet