Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leach in GGGG
Uploaded by
Alan Winston SedzeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Leach in GGGG
Uploaded by
Alan Winston SedzeCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Properties
• Physical state – Except mercury and gallium, all metals are solids at room temperature.
• Lustre – Metals possess a high lustre.
• Hardness – Resistance to indentation.
• Melting point – The temperature at which the state of a substance changes from solid to liquid.
• Boiling point – The temperature at which the substance vaporize.
• Density – It is the measure of mass per unit volume.
• Ductility – The ability of a material which can be deformed plastically without failure or fracture.
• Malleability – The ability of a material which can be rolled or pressed without failure or fracture.
• Conduction of heat – The ability of the transfer of heat.
• Conduction of electricity – The ability of the transfer of electricity.
• Solubility – The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent to form a solution.
Chemical Properties
• Valence electrons – Electrons in an outermost shell in an atom that may participate in the
formation of a chemical bonding.
• Formation of ions – The addition or removal of electrons from the neutral atom forms the ions.
Metals losses the electrons to form Positive ions. Hence they are electro positive.
• Discharge of ions – At cathode metals get discharged during the electrolysis process.
• Atomicity – Total number of atoms that constitute a molecule.
• Nature of oxides – Oxides of metals are usually basic.
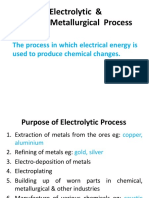
In metal mining, sulfuric acid is used to leach copper oxide minerals. In one process, a solution of
sulfuric acid laden with copper sulfate is stripped of copper via a solvent extraction and electro
winning with the used sulfuric acid recycled back into the process.
You might also like
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument23 pagesMetals and Non Metalsshaunchinu patilNo ratings yet
- Earths Processes PowepointDocument282 pagesEarths Processes PowepointRufo Daskeo Jr.No ratings yet
- Solidification and Crystalline Imperfection Part 1Document25 pagesSolidification and Crystalline Imperfection Part 1Aiman MutallidNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument12 pagesMetallic Bonding: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenAngelica Maeriz MindoroNo ratings yet
- Matter and Change1Document62 pagesMatter and Change1cynthiambwasiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Lecture by Nur Aini, M.Si: Picture Credite: GCSE ScienceDocument28 pagesChemical Bonding Lecture by Nur Aini, M.Si: Picture Credite: GCSE ScienceSilvia UsmaniaNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument17 pagesClassification of MatterAshmyra ManaloNo ratings yet
- Structure and Properties of Water: General Chemistry 2Document38 pagesStructure and Properties of Water: General Chemistry 2Cielo GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Science MetalsDocument5 pagesScience Metalsalnajdawisewar2No ratings yet
- Ikatan Logam 2Document26 pagesIkatan Logam 2laelatul mutoharohNo ratings yet
- Metal Nonmetal Metalloid 1Document3 pagesMetal Nonmetal Metalloid 1Andre Miguel LlanesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. Properties of SolidsDocument27 pagesLecture 4. Properties of SolidsAcademe HelperNo ratings yet
- Equlibrium DiagramsDocument42 pagesEqulibrium DiagramsAVINASH KAMBLENo ratings yet
- Metal AlloysDocument114 pagesMetal AlloysRudra VermaNo ratings yet
- Some Properties Between Metals and NonmetalsDocument2 pagesSome Properties Between Metals and Nonmetalsanon-632572No ratings yet
- Matter and Minerals: Geology For EngineersDocument61 pagesMatter and Minerals: Geology For EngineersLinh VoNo ratings yet
- Crystalline SolidsDocument10 pagesCrystalline SolidsoracleNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Singh's Kingdom: Prepared by Jeevendar SinghDocument7 pagesWelcome To Singh's Kingdom: Prepared by Jeevendar SinghNandishwara ThonthanalNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Metals 2023Document26 pagesCH 4 Metals 2023Heidi VagueNo ratings yet
- Metals and AlloysDocument73 pagesMetals and AlloysmahaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Periodic Table (Compatibility Mode)Document18 pagesLecture 4 Periodic Table (Compatibility Mode)Ahmed MinhazNo ratings yet
- PT TrendsandpropertiesDocument49 pagesPT TrendsandpropertiesshizukesakeitoNo ratings yet
- Alloy - Systems - PPTM Filename - UTF-8''Alloy Systems-1Document95 pagesAlloy - Systems - PPTM Filename - UTF-8''Alloy Systems-1Adriel JohnNo ratings yet
- General Properties of MetalsDocument15 pagesGeneral Properties of Metalsdona merinNo ratings yet
- 5 - Metallurgy and The Chemistry of Metals: Week 7 - Topic 5 Chemistry For EngineersDocument24 pages5 - Metallurgy and The Chemistry of Metals: Week 7 - Topic 5 Chemistry For EngineersClarkNo ratings yet
- M 1 Electrolytic ProcessDocument12 pagesM 1 Electrolytic ProcessVeena BhatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1A Metals G11Document55 pagesLesson 1A Metals G11Jodell CampbellNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Matter and MineralsDocument52 pagesChapter II Matter and MineralsCaig UsachNo ratings yet
- Metals and Their Properties PDFDocument10 pagesMetals and Their Properties PDFafoo1234100% (1)
- Metals: PropertiesDocument20 pagesMetals: PropertiesReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- METALDocument76 pagesMETALBenilda ArazasNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry - States of MatterDocument25 pagesAS Chemistry - States of MatterwilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Electrolysisrheanna0076No ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 - Engineering Materials and Their Properties - Part 1 - Sem 1 - 2022 - 2023Document67 pagesLECTURE 3 - Engineering Materials and Their Properties - Part 1 - Sem 1 - 2022 - 2023Idham NasrulNo ratings yet
- Lec 5-6Document136 pagesLec 5-6sm shikderNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Drug MoleculeDocument57 pagesPhysical Properties of Drug MoleculeNoorul AlamNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of MatterDocument18 pagesBuilding Blocks of MatterPaul AckermannNo ratings yet
- Learning - The - Periodic - Table First LessonDocument30 pagesLearning - The - Periodic - Table First LessonjehanNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements, and Minerals: Physical Geology 13/e, Chapter 2Document15 pagesAtoms, Elements, and Minerals: Physical Geology 13/e, Chapter 2Toto MaloNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Acid Base Metal Non MetalDocument35 pagesPart 2 Acid Base Metal Non MetalCay C. CordovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Matter and Energy)Document65 pagesChapter 3 (Matter and Energy)Raynan TabaldoNo ratings yet
- Metals, Polymers, Ceramics and CompositesDocument80 pagesMetals, Polymers, Ceramics and Compositestharushisewwanndi43No ratings yet
- Groups of The Periodic TableDocument15 pagesGroups of The Periodic Tablefieli924No ratings yet
- Bonding Ionic CRGDocument13 pagesBonding Ionic CRGCharlotte GoodeNo ratings yet
- 02.matter and MineralsDocument33 pages02.matter and MineralsJ AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 Elements: Introduction To The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesChapter 1.3 Elements: Introduction To The Periodic TableLaura SimonsNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy CHAPTER 1$2Document77 pagesMetallurgy CHAPTER 1$2Ermias GuragawNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Properties of Materials: WWW - Carsparefinder.co - UkDocument28 pagesThe Nature and Properties of Materials: WWW - Carsparefinder.co - UkYash JainNo ratings yet
- Deformation of Solids AsDocument14 pagesDeformation of Solids AsWaseem AminNo ratings yet
- Classifying MatterDocument53 pagesClassifying MatterTanya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Classification of Metals: - Metals Can Be Classified As Ferrous or Non Ferrous MetalsDocument11 pagesClassification of Metals: - Metals Can Be Classified As Ferrous or Non Ferrous MetalsSara Ben AmaraNo ratings yet
- METALSDocument24 pagesMETALSKillua ZoldyckNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2018-19 CHY1701 ETH TT208 VL2018195004060 Reference Material I Alloy Coatings-1Document24 pagesWINSEM2018-19 CHY1701 ETH TT208 VL2018195004060 Reference Material I Alloy Coatings-1Akshat TiwariNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23Document37 pagesMetals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406100% (1)
- What Is A Mineral: Chapter 3 Minerals of Earth's CrustDocument28 pagesWhat Is A Mineral: Chapter 3 Minerals of Earth's Crustallison_burkhardtNo ratings yet
- Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument39 pagesProperties of Engineering Materialsdaisyclare vernyuyNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Materials in The EnvironmentDocument19 pagesDiversity of Materials in The EnvironmentMarjorie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- GLT 101 MinearlogyDocument67 pagesGLT 101 MinearlogyMaksuda HossainNo ratings yet
- Full Detailed Notes (All Syllabus) 2Document42 pagesFull Detailed Notes (All Syllabus) 2EveNo ratings yet
- Comprehension g4 2020Document6 pagesComprehension g4 2020Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- GEO P1 GR10 MEMO NOV2019 - EnglishDocument12 pagesGEO P1 GR10 MEMO NOV2019 - EnglishAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- WSC Gr4 Sci Forms of Energy ws1Document4 pagesWSC Gr4 Sci Forms of Energy ws1Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- OceanofPDF - Com Milkshakes For Sale - Olive ChaudhuriDocument121 pagesOceanofPDF - Com Milkshakes For Sale - Olive ChaudhuriAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- 16 November Times TablesDocument1 page16 November Times TablesAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Instructions: TASK 10: Creative Writing: ProjectDocument2 pagesInstructions: TASK 10: Creative Writing: ProjectAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- (Untitled) 2Document10 pages(Untitled) 2Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- LFM Profile 2024..Document11 pagesLFM Profile 2024..Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- TASK 9: Oral: Presentation of Project: Task 2023 G04 English Home LanguageDocument2 pagesTASK 9: Oral: Presentation of Project: Task 2023 G04 English Home LanguageAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument4 pagesSubject Verb AgreementAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Life Skills ChrisssDocument5 pagesLife Skills ChrisssAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Rewrites-Open 2024Document1 pageRewrites-Open 2024Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Business Partnershippp With MR DosantosDocument4 pagesBusiness Partnershippp With MR DosantosAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Brainline DetailssDocument4 pagesBrainline DetailssAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Linda Mkhanyiseli JOJO TERM 4Document3 pagesLinda Mkhanyiseli JOJO TERM 4Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Online Time TableDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Online Time TableAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Business Partnership With MR F.G. MakunikeDocument4 pagesBusiness Partnership With MR F.G. MakunikeAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Sphiwe Natural ScienceDocument3 pagesSphiwe Natural ScienceAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Rorisang RamagoshingDocument1 pageRorisang RamagoshingAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Invigilator Registration Form Eng Afr v2020.1Document6 pagesInvigilator Registration Form Eng Afr v2020.1Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Creative Arts gr6Document3 pagesCreative Arts gr6Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Stationery List For 2023Document2 pagesGrade 4 Stationery List For 2023Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Stationery List 2023Document1 pageGrade 4 Stationery List 2023Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 4 Task 6: Test 3 EXAMINER: S. Müller TIME: 1 Hour Moderator: K. Britz TOTAL: 35 InstructionsDocument6 pagesMathematics Grade 4 Task 6: Test 3 EXAMINER: S. Müller TIME: 1 Hour Moderator: K. Britz TOTAL: 35 InstructionsAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Business For AllenDocument4 pagesBusiness For AllenAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- 2023 Fee Structuree G10Document2 pages2023 Fee Structuree G10Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Laser Focus Mind Academy 2023 Enrollment Form Home School 2023 - 2024Document11 pagesLaser Focus Mind Academy 2023 Enrollment Form Home School 2023 - 2024Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 4 Task 3: Test 2 EXAMINER: S. Müller TIME: 1 Hour Moderator: K. Britz TOTAL: 35 InstructionsDocument6 pagesMathematics Grade 4 Task 3: Test 2 EXAMINER: S. Müller TIME: 1 Hour Moderator: K. Britz TOTAL: 35 InstructionsAlan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- Updated C.V.Document3 pagesUpdated C.V.Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet
- APPLICATION FORM FOR HOME EDUCATION x-1Document5 pagesAPPLICATION FORM FOR HOME EDUCATION x-1Alan Winston SedzeNo ratings yet