Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lewis Structures
Uploaded by
Канат Тютенов0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pages1. The document provides instructions on writing Lewis structures, including how to determine the number of valence electrons and draw Lewis dot symbols for various elements.
2. It describes how covalent bonds form through the overlap of atomic orbitals, with hydrogen using its 1s orbital and other atoms using their valence p orbitals.
3. The octet rule states that atoms are surrounded by 8 electrons, though some exceptions exist for atoms that are too small or can expand their octet.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document provides instructions on writing Lewis structures, including how to determine the number of valence electrons and draw Lewis dot symbols for various elements.
2. It describes how covalent bonds form through the overlap of atomic orbitals, with hydrogen using its 1s orbital and other atoms using their valence p orbitals.
3. The octet rule states that atoms are surrounded by 8 electrons, though some exceptions exist for atoms that are too small or can expand their octet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesLewis Structures
Uploaded by
Канат Тютенов1. The document provides instructions on writing Lewis structures, including how to determine the number of valence electrons and draw Lewis dot symbols for various elements.
2. It describes how covalent bonds form through the overlap of atomic orbitals, with hydrogen using its 1s orbital and other atoms using their valence p orbitals.
3. The octet rule states that atoms are surrounded by 8 electrons, though some exceptions exist for atoms that are too small or can expand their octet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Westminster H.S.
AP Chemistry Name _________________________________
Period ___ Date ___/___/___
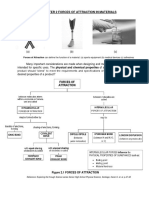
8 Bonding: General Concepts
LEWIS STRUCTURES
1. A bond forms when two orbitals ____________ 5. You should be able quickly to state the number
allowing electrons to be close to two nuclei at of valence electrons any atom has based on its
the same time. When two H atoms bond, they position on the periodic table. Write it.
overlap electrons in their ______ orbitals.
P Ca F As
2. As two H atoms approach each other, the
potential energy ____________ because of the C Na K H
electron-proton attractions. The potential
energy __________ because of electron-electron Si O B Mg
and proton-proton repulsions.
6. Draw the Lewis electron-dot symbol for each
3. Consider this diagram: of the following elements.
P Ca F As
C Na K H
Si O B Mg
7. In writing Lewis structures, the rule is that only
Two separate atoms have an energy of ___J. valence electrons are included.
The equilibrium bond distance is ______ nm.
The bond energy is ______ Joules which is the Atom Ion Atom Ion
amount of energy you need to add to break the
bond (i.e. separate the two atoms). K Br
4. Consider this diagram again: Al N
8. You should be able to recognize the type of
bond that forms between two atoms based on
the atoms involved. Classify each of the
following bonds as Ionic or Covalent.
SO KI
If two He atoms approach, their bond distance
NaCl HCl
is 0.500 nm and bond energy is 100 J. Sketch
the energy curve for He2. The two atoms do not
CaBr SiO
get close enough for the electrons to be close to
both nuclei at the same time… no bond forms.
XeF MgCl
We generalize: two _____________ orbitals
CAN make a bond. CO NI
Two ________ orbitals cannot make a bond.
9. Lewis symbols are generally used with covalent 13. The Lewis symbol for O can be drawn two
bonds, but they CAN be used with ionic bonds. ways, so the Lewis symbol for H2O can be
Draw the Lewis symbols for these ions: drawn two ways. Draw them:
cation anion Lewis symbols for compound
Na+ Cl-
Ca2+ O2-
Which one is correct? ________________
Li+ F- (Consider the picture of water.)
Mg2+ F- 14. Not all atoms follow the octet rule.
Elements ___ through ___ are too small.
Na+ S2- Families ___, ___, and ___ also do not follow
the octet rule when forming covalent bonds.
However, these families are USUALLY
10. All of the negative ions (anions) above are
involved in ionic bonds.
surrounded by ___ electrons. For the positive
ions (cations) we show ____ electrons, but we
Some atoms have MORE than an octet, too, this
know that there is a full shell one level below.
is called the “extended valence shell”.
The _________ rule is a recognition of the fact
that atoms are often (not always) surrounded by
15. Each of the diatomic elements involves a
8 electrons.
covalent bond.
Draw the Lewis symbol for each one.
11. When a covalent bond forms, two ______ -
Which one does not follow the octet rule? ___
__________ orbitals overlap. Hydrogen only
Diatomic Lewis
uses one orbital, the _____ orbital.
Molecule Symbol
Draw and label oxygen’s valence orbitals:
Oxygen:
H2 H H
Consider the two H atoms and the O atom in a
water molecule. N2 N N
How many bonds are shown? _____
O2 O O
F2 F F
For each bond, the hydrogen orbital uses its
____ orbital. The oxygen atom uses its two
Cl2 Cl Cl
half-filled ____ orbitals to overlap each of the
hydrogen’s half-filled orbitals.
Br2 Br Br
12. Draw the Lewis dot symbol for H2O.
I2 I I
The oxygen atom is surrounded by ____ e-‘s.
16. The Lewis Structure of a molecule shows how 17. The rules we have used for Lewis structures
the valence electrons are arranged among the apply to most molecules, but there are
atoms in the molecule. exceptions.
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures: Incomplete Octet:
a. Sum the valence electrons from all the Boron, for example, tend to form compounds in
atoms. Do not worry about keeping track of which the boron atom as fewer than 8 electrons.
which electrons come from which atoms. It
is the total number of electrons that is BF3
important.
b. Use a pair of electrons to form a bond
between each pair of bound atoms.
c. Arrange the remaining electrons to satisfy
the duet rule for hydrogen and the octet rule
for the second-row elements. Expanded Octet:
Some atoms exceed the octet rule. This behavior
Example: Give the Lewis structure for each of the is observed only for those elements in Period 3
following: of the periodic table and beyond.
a. HF
SF6
b. N2
c. NH3
Comments about the Octet Rule:
1. The second-row elements C,N,O, and F
should always be assumed to obey the octet
rule.
d. CH4 2. The second-row elements B and Be often
have fewer than 8 electrons around them in
their compounds. These electron-deficient
compounds are very reactive.
3. The second-row elements never exceed the
octet rule, since their valence orbitals (2s
e. CF4 and 2p) can accommodate only 8 electrons.
4. Third-row and heavier elements often satisfy
the octet rule but can exceed the octet rule
by using their empty valence d orbitals.
5. When writing the Lewis structure for a
molecule, satisfy the octet rule for the atoms
f. NO+ first. If electrons remain after the octet rule
has been satisfied, then place them on the
elements having available d orbitals
(elements in Period 3 or beyond).
You might also like
- POWERFUL MAGIC RING - GET POWER, WEALTH, PROTECTION, LOVE, HEALTH Etc Call/wattsapp +27717097145 MAMA LAKIADocument16 pagesPOWERFUL MAGIC RING - GET POWER, WEALTH, PROTECTION, LOVE, HEALTH Etc Call/wattsapp +27717097145 MAMA LAKIAProfmama Lakia0% (2)
- 4.0 ChemicalbondingDocument219 pages4.0 ChemicalbondingTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Speed - Miriam JosephDocument97 pagesSpeed - Miriam JosephLone Hansen100% (1)
- WORKSHEET Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesWORKSHEET Chemical BondingIsabel Del ValleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Chemical BondsDocument41 pagesChapter 6 - Chemical BondsDn ZackNo ratings yet
- 05 Chem Bond - Modul - ChemistryDocument11 pages05 Chem Bond - Modul - Chemistryrudi_z100% (1)
- Python Odoo 14 NRW Version Book PDFDocument22 pagesPython Odoo 14 NRW Version Book PDFTree loveNo ratings yet
- Hohner Accordions Nova III 96 Fingering ChartDocument4 pagesHohner Accordions Nova III 96 Fingering ChartFilipe Monteiro TavaresNo ratings yet
- Report Consumer Behaviour On SamsungDocument24 pagesReport Consumer Behaviour On Samsungeira50% (2)
- Introduction To SAP UI5Document11 pagesIntroduction To SAP UI5EugeneNo ratings yet
- Chem.g12 q2w7 Module3 PamplonaDocument16 pagesChem.g12 q2w7 Module3 PamplonaRaymalyn MalynNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Q2 Gen Chem I v.2Document10 pagesModule 3 Q2 Gen Chem I v.2ariinnggg onichaNo ratings yet
- Fayol General and Industrial Management PDFDocument2 pagesFayol General and Industrial Management PDFJennifer33% (6)
- Module 3 Q2 Gen Chem IIDocument10 pagesModule 3 Q2 Gen Chem IIMengieNo ratings yet
- General Inorganic ChemistryDocument28 pagesGeneral Inorganic ChemistryGIDEON TEMIDAYO JUDENo ratings yet
- Chemistry MergedDocument19 pagesChemistry Merged몰라나도No ratings yet
- Richard S. Moog - Chemistry - A Guided Inquiry, 7th Edition-Wiley (2017) - 85Document45 pagesRichard S. Moog - Chemistry - A Guided Inquiry, 7th Edition-Wiley (2017) - 85Siti SupriyantiNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument48 pagesBondingjacklinephilip745No ratings yet
- SGCH 09Document24 pagesSGCH 09belleblackNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument78 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDingetegna GodanaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 2Document10 pagesPhysical Science Module 2Mikaela AguilarNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesChemical BondingShashank BgNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: Formation of Covalent BondsDocument8 pagesCovalent Bonding: Formation of Covalent BondsRez CaitlinaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonds and Covalent BondsDocument19 pagesIonic Bonds and Covalent BondsLyndy PantaoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemistry RemedialDocument69 pagesUnit 2 Chemistry Remedialabdimoh7522100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document32 pagesChapter 8Danilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- Molecular Geometry: Presented By: Loreen Jane D. Abogado Maed Physical ScienceDocument65 pagesMolecular Geometry: Presented By: Loreen Jane D. Abogado Maed Physical ScienceLoreen Jane AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Solvation EnergyDocument18 pagesSolvation EnergyL. SHRUTHINo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument132 pagesChemical BondingKowser mahmud100% (1)
- General Chemistry q2 Week 7Document64 pagesGeneral Chemistry q2 Week 7Keisha Mae Custodio100% (1)
- Notes - Chemical BondingDocument14 pagesNotes - Chemical Bonding黄心盈No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Catalysis Thesis WoltersDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding and Catalysis Thesis WoltersBheim LlonaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingAmadeus BachNo ratings yet
- Get Ready For Organic Chemistry Excerpt Ch2Document12 pagesGet Ready For Organic Chemistry Excerpt Ch2yisixo8693No ratings yet
- Electronic Theory of Valency &bondingDocument12 pagesElectronic Theory of Valency &bondingshivakafle039No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter - 04Document35 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter - 04Harsh OthayothNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - (Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory-Not MO)Document45 pagesChapter 3 - (Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory-Not MO)PHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Ch09 - Lecture (Chemical Bonding)Document57 pagesCh09 - Lecture (Chemical Bonding)Shir0 NobiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument47 pagesUntitledchandrakanth maheshNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument36 pagesBondingmanish365No ratings yet
- 11 NCERT Book Chapter 4Document36 pages11 NCERT Book Chapter 4Pankaj MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding And: Molecular StructureDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding And: Molecular StructureAnanya MNo ratings yet
- Kech 104Document36 pagesKech 104Rogerio AndradeNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 ChemicalbondingDocument23 pagesChapter2 ChemicalbondingAbbyNo ratings yet
- 16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat SheetDocument1 page16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheetbooty holeNo ratings yet
- Differentiating AtomsDocument3 pagesDifferentiating AtomsChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Ikatan KimiaDocument91 pagesIkatan KimiaRomi IndayatiNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Lewis Sturcture 7th Ed PDFDocument90 pagesCH 3 - Lewis Sturcture 7th Ed PDFNora AounNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document2 pagesChemical Bonding 1Uniyals AcademyNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Leson 2Document90 pagesGen Chem Leson 2Jay-mee Claire V. DioNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember Class: XI Chapter Name: Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument15 pagesPoints To Remember Class: XI Chapter Name: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureaustinfru7No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSneh PatelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Unit 4Document35 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Unit 4Rajiv Sharma100% (1)
- Bonding Student Study GuideDocument15 pagesBonding Student Study GuideJohn Philip NapalNo ratings yet
- LONGTEST Science 9 (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesLONGTEST Science 9 (AutoRecovered)jerome CarpioNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 Q2 Module 3Document14 pagesGen Chem 1 Q2 Module 3lkNo ratings yet
- Chemistry I ASC 0304: Chemical BondsDocument35 pagesChemistry I ASC 0304: Chemical BondshadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: Gilbert N. Lewis 1875-1946Document36 pagesCovalent Bonding: Gilbert N. Lewis 1875-1946ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument34 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingAwais altafNo ratings yet
- CHM 171 Theme 3 Bonding and Molecular GeometryDocument91 pagesCHM 171 Theme 3 Bonding and Molecular Geometrycatman123123No ratings yet
- Chem 65 CH 10 - ELAC - Student PDFDocument24 pagesChem 65 CH 10 - ELAC - Student PDFAnonymous YsErc8jUdNo ratings yet
- A Lewis StructureDocument9 pagesA Lewis StructureSetch PalmaNo ratings yet
- Geometry BkgdroundDocument7 pagesGeometry Bkgdroundtanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- 7.1 Valence Electron and Lewis StructureDocument42 pages7.1 Valence Electron and Lewis StructureNURBALQIS BINTI ZAILAN KMNSNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestFrom EverandElectronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestNo ratings yet
- Station Review AnswersDocument5 pagesStation Review AnswersКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FULL PresentationDocument134 pagesChapter 7 FULL PresentationКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- IMF NotesDocument23 pagesIMF NotesКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Quick Check 1 and 2Document2 pagesQuick Check 1 and 2Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Two Points AnswersDocument2 pagesTwo Points AnswersКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Quick Check 1Document1 pageQuick Check 1Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- IMF WorksheetDocument3 pagesIMF WorksheetКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- IMF TrendsDocument1 pageIMF TrendsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Le Chateliers Principle PracticeDocument1 pageLe Chateliers Principle PracticeКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Le Chateliers Principle Practice 2Document2 pagesLe Chateliers Principle Practice 2Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Heating CurveDocument1 pageHeating CurveКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Hess S Law NotesDocument2 pagesHess S Law NotesКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EnergyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To EnergyКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Quick Check 3Document1 pageChapter 7 Quick Check 3Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Energies of Solution FormationDocument2 pagesEnergies of Solution FormationКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Study QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 13 Study QuestionsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- End Point CalculationsDocument2 pagesEnd Point CalculationsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Ch14 PH CalculationsDocument1 pageCh14 PH CalculationsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- End Point Calculations AnswersDocument2 pagesEnd Point Calculations AnswersКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Ch14 Quick Check 3Document1 pageCh14 Quick Check 3Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- AP PPT CH 9 AP OnlyDocument42 pagesAP PPT CH 9 AP OnlyКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- AP PPT CH 11Document68 pagesAP PPT CH 11Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- AP PPT CH 2 AP OnlyDocument26 pagesAP PPT CH 2 AP OnlyКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Buffer CalculationsDocument2 pagesBuffer CalculationsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- 5 RadiationDocument8 pages5 RadiationКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Boiling PointDocument2 pagesBoiling PointКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide To Large Language Mo-Ebook-Part1Document25 pagesA Beginner's Guide To Large Language Mo-Ebook-Part1John O'MearaNo ratings yet
- Puma OpenDocument5 pagesPuma Opencaliniclodean7737No ratings yet
- عتبات النص في التراث العربيDocument12 pagesعتبات النص في التراث العربيREZKALLAH OMARNo ratings yet
- Bitter Heart by Zee AviDocument2 pagesBitter Heart by Zee AviStephen YipNo ratings yet
- 12V 150ah (10hr) : Shenzhen Center Power Tech - Co.LtdDocument2 pages12V 150ah (10hr) : Shenzhen Center Power Tech - Co.Ltddarwin darioNo ratings yet
- Psycho LinguisticsDocument10 pagesPsycho Linguisticsyuvens gandasuliNo ratings yet
- Academic CV Working DraftDocument3 pagesAcademic CV Working Draftapi-548597996No ratings yet
- MarketingDocument73 pagesMarketingAse SharewNo ratings yet
- Ivan Rivera Visualcv ResumeDocument1 pageIvan Rivera Visualcv ResumeEdwin Reuben Jusino AldarondoNo ratings yet
- MFRD Assignment 2 Duc CuteDocument13 pagesMFRD Assignment 2 Duc CuteanfkrNo ratings yet
- AC Combiner Box Specification 400vac)Document7 pagesAC Combiner Box Specification 400vac)emilNo ratings yet
- Supplies Inventory Monitoring SheetDocument10 pagesSupplies Inventory Monitoring Sheetmharaynel.afableNo ratings yet
- 7395 398 WL Console RevA WebDocument7 pages7395 398 WL Console RevA WebSebastian Ezequiel Gomez GiuggioloniNo ratings yet
- Dim 1001Document7 pagesDim 1001Kokxing KkxNo ratings yet
- Version For Internet Nutrition Spreadsheet (With Workout Tracker)Document10 pagesVersion For Internet Nutrition Spreadsheet (With Workout Tracker)GeraldyneNo ratings yet
- Prasanna CV UltDocument3 pagesPrasanna CV UltPrasannaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Mini Project Slide (Currypuff Maker)Document24 pagesGroup 2 - Mini Project Slide (Currypuff Maker)Muhd Khairul AmriNo ratings yet
- Industrial Project GuidelinesDocument3 pagesIndustrial Project Guidelinesmohit punNo ratings yet
- Kojeve - Colonialism From A European PerspectiveDocument18 pagesKojeve - Colonialism From A European PerspectiveTetsuya MaruyamaNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resources Planning (ERP) 2610002Document2 pagesEnterprise Resources Planning (ERP) 2610002Virendra Arekar100% (1)
- Aggregate Planning and EOQDocument14 pagesAggregate Planning and EOQEngr Muhammad EhsanNo ratings yet
- MORRISON BUSINESS CLUB - RevisedDocument27 pagesMORRISON BUSINESS CLUB - RevisedAndrew HoNo ratings yet
- Afs Map Pes 2013 Ps2Document11 pagesAfs Map Pes 2013 Ps2Sergio GarciaNo ratings yet