Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8A Food and Digestion
8A Food and Digestion
Uploaded by
26apatel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThe document provides definitions and information about the digestive system and digestion. It defines key parts of the digestive system like the oesophagus, stomach, and small intestines. It explains the roles of enzymes, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals in digestion. Digestion is summarized as the breakdown of large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules using enzymes for absorption. Tests for identifying starches, sugars, and proteins in food are also outlined.
Original Description:
Original Title
8A-Food-and-Digestion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides definitions and information about the digestive system and digestion. It defines key parts of the digestive system like the oesophagus, stomach, and small intestines. It explains the roles of enzymes, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals in digestion. Digestion is summarized as the breakdown of large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules using enzymes for absorption. Tests for identifying starches, sugars, and proteins in food are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 page8A Food and Digestion
8A Food and Digestion
Uploaded by
26apatelThe document provides definitions and information about the digestive system and digestion. It defines key parts of the digestive system like the oesophagus, stomach, and small intestines. It explains the roles of enzymes, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals in digestion. Digestion is summarized as the breakdown of large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules using enzymes for absorption. Tests for identifying starches, sugars, and proteins in food are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
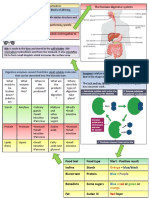
KS3 Food and Digestion
Definitions Test for food groups
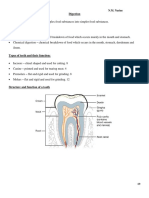
1 Oesophagus A muscular tube that squeezes food from 16 Starch test Iodine is orange. It will turn black in a positive test
the mouth to the stomach. (Also known as
the gullet.)
2 Stomach A muscular organ that churns up the food. 17 Sugar Benedicts solution is blue. When heated with sugar it will turn
Enzymes and stomach acid are added “brick red”.
here.
3 Small intestines Absorption of nutrients into the blood stream 18 Protein Biuret solution is blue. When heated with protein it will turn
happens here. purple.
4 Peristalsis The muscular contraction that squeezes Products of digestion
food down the oesophagus.
5 Protein Needed for growth and repair. 19 Amino acids Proteins are broken down into amino acids using protease
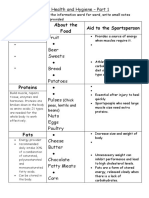
enzymes.
6 Carbohydrates Needed for energy. 20 Fatty acids Fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol using lipase
enzymes.
7 Fats Needed for insulation of nerve cells and 21 Simple sugars Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars using
body insulation. carbohydrase enzymes e.g Amylase in saliva.
8 Fibre Needed to provide the “bulk” for faeces
(poo). Keeps the intestines working properly.
9 Vitamins and Help maintain general health and fitness.
minerals
10 Enzymes Biological catalysts that speed up the rate
of a reaction. Enzymes help speed up
digestion.
11 Denatured Enzymes can be altered in shape if exposed
to high temperatures or pH.
12 Deficiency Diseases can be caused by a lack of
nutrients. E.g scurvy, anaemia.
13 Obesity Being excessively overweight. Can result in
type 2 diabetes, CHD, high blood pressure
14 Villi Finger like structures that line the small
intestines. These give a larger surface area
for absorption.
15 Digestion The break- down of large insoluble Diagram 1: Parts of the digestive system Diagram 2: Lock and Key theory.
molecules into smaller soluble molecules.
You might also like
- High Intensity Training - Mike MentzerDocument46 pagesHigh Intensity Training - Mike MentzerAl Stancu100% (3)
- Fun and Functional Workouts EbookDocument48 pagesFun and Functional Workouts EbookLuv Sachdeva100% (2)
- People Half Their Size March 2022Document102 pagesPeople Half Their Size March 2022janusz100% (1)
- Looksmaxxing GuideDocument6 pagesLooksmaxxing GuideStudy TipsNo ratings yet
- Inja Aesthethics: Upper Lower SplitDocument14 pagesInja Aesthethics: Upper Lower SplitIgor100% (1)
- Parts of The Digestive System Matching Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesParts of The Digestive System Matching Worksheet PDFMon Duray BalaniNo ratings yet
- The Liver Healing Diet: The Nutritional Plan to Fight Toxins, Reverse Fatty Liver Disease and Promote Good HealthFrom EverandThe Liver Healing Diet: The Nutritional Plan to Fight Toxins, Reverse Fatty Liver Disease and Promote Good HealthNo ratings yet
- Dante Trudel - Strait Down The LineDocument5 pagesDante Trudel - Strait Down The Linesupplychain789No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument52 pagesFundamentals of NursingRegie Rose Luna100% (1)
- Case Note 1 PDFDocument4 pagesCase Note 1 PDFRoseanne Mae Anioay50% (2)
- Digestion and Metabolism (6 Oct)Document15 pagesDigestion and Metabolism (6 Oct)api-19824406No ratings yet
- 8 Science - Obtaining Food AnswerDocument3 pages8 Science - Obtaining Food Answermichael tanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Human Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 14 - Human Digestive SystemChaw Wei HengNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Mechanical & Chemical Breakdown of Food For EnergyDocument26 pagesThe Digestive System: Mechanical & Chemical Breakdown of Food For EnergyRozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- Biology GCSE Unit 2 Part 4 Enzymes and DigestionDocument3 pagesBiology GCSE Unit 2 Part 4 Enzymes and DigestiontahamidNo ratings yet
- Tled13 PPTDocument15 pagesTled13 PPTjoyceannserra8No ratings yet
- Unit 8A Food and Digestion: Name: .Document14 pagesUnit 8A Food and Digestion: Name: .rickyNo ratings yet
- Food Digestion To PrintDocument44 pagesFood Digestion To PrintMindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - Book ExerciseDocument3 pagesCH 6 - Book ExerciseHarry LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Answer KeyzakiyaNo ratings yet
- Concise Selina Biology Part I Solution For Class 9 Biology Chapter 11Document6 pagesConcise Selina Biology Part I Solution For Class 9 Biology Chapter 11Nehaa MankaniNo ratings yet
- 8A NutrienDocument17 pages8A NutrienAron ProxyNo ratings yet
- Science HelpDocument5 pagesScience HelpDena AL-SHOWALINo ratings yet
- Nutrition AssignmentDocument11 pagesNutrition AssignmentAngela MorNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Nutrition Part 2Document10 pagesTopic 5 Nutrition Part 2AHMED AMR ABDELKHALEKNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Digestion in AnimalsDocument18 pagesNutrition and Digestion in Animalsmark smithNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument23 pagesHuman Digestive SystemJANo ratings yet
- Prelab Digestion of FatsDocument3 pagesPrelab Digestion of FatsTrina Rose AutidaNo ratings yet
- B2.5.1 Proteins - B2.5.2 Enzymes: No Higher Tier ContentDocument3 pagesB2.5.1 Proteins - B2.5.2 Enzymes: No Higher Tier ContentRekaNo ratings yet
- Digestion& Absorption and DegradationDocument16 pagesDigestion& Absorption and Degradationsuad aliNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Human BeingsDocument28 pagesNutrition in Human Beingssarrah asgarNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - AnimalDocument13 pagesNUTRITION - AnimalDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - The Digestive SystemDocument21 pages3.1 - The Digestive SystemJavierNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Digestion and The Digestive SystemDocument6 pages1.3 Digestion and The Digestive Systemj5nfng2zzxNo ratings yet
- Accessory Organs of The Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesAccessory Organs of The Digestive SystemMais MarwanNo ratings yet
- Biology 7 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition: An Adequate Diet Must Satisfy Three NeedsDocument8 pagesBiology 7 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition: An Adequate Diet Must Satisfy Three NeedsKevinZamudioNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Nutrition QuizDocument19 pagesDigestion & Nutrition QuizchalihflNo ratings yet
- Digestive Enzymes & BacteriaDocument13 pagesDigestive Enzymes & BacteriaEsraa BahaaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument25 pagesBiologycarlotarubioperez123No ratings yet
- Topic 2 OrganisationDocument31 pagesTopic 2 OrganisationMeriNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument7 pagesNutrition in AnimalsFX GeraldNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: VitaminsDocument29 pagesNutrition: Vitaminsrv5bcgywkpNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Biology Chapter1 AnswersDocument7 pagesActivate 2 Biology Chapter1 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Nurition in Mammals - 2Document3 pagesNurition in Mammals - 2Farzan ButtNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Animal NutritionDocument12 pagesUnit 6 Animal Nutritionulavan24No ratings yet
- Intestinal Phase of Digestion and AbsorptionDocument9 pagesIntestinal Phase of Digestion and AbsorptionRand ELABEDNo ratings yet
- 9-BIO-8 MCQs (Web)Document3 pages9-BIO-8 MCQs (Web)Shahbaz AnwarNo ratings yet
- PE FinalDocument26 pagesPE FinalCheryz Angel LabillesNo ratings yet
- General Science - BioDocument15 pagesGeneral Science - BioMY LADOONo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Digestion: Regents BiologyDocument64 pagesNutrition and Digestion: Regents BiologyzohaNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision NotesDocument34 pagesBiology Revision NotesFreakshow38No ratings yet
- Week 5 (B) Human and Social BiologyDocument5 pagesWeek 5 (B) Human and Social BiologyBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- Handout On Digestion, Respiration, Circulation and TransportDocument47 pagesHandout On Digestion, Respiration, Circulation and TransportNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- ANPS 020 Cornbrooks 02-14-14Document40 pagesANPS 020 Cornbrooks 02-14-14cadotillosNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceToh Yi KeeNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Nutrition ReviewDocument25 pagesDigestion & Nutrition ReviewISABELLA LEALNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Enteric (Gi)Document19 pagesThe Digestive System: Enteric (Gi)Carolina TanasNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Enteric (Gi)Document40 pagesThe Digestive System: Enteric (Gi)Ezekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Please Complete The Table. Why Should Avoid Fast Food? Discuss ThoroughlyDocument1 pagePlease Complete The Table. Why Should Avoid Fast Food? Discuss ThoroughlyKassandra Shayne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Enteric (Gi)Document40 pagesThe Digestive System: Enteric (Gi)Barbora PiatkováNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument14 pagesDigestioncmizalpccfuNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument7 pagesDigestionEthan RamdeenNo ratings yet
- Rev - Notes - ch06 - e Human NutritionDocument6 pagesRev - Notes - ch06 - e Human NutritionEsther WongNo ratings yet
- Prelim Oral Exam FinalDocument6 pagesPrelim Oral Exam FinalJP2001No ratings yet
- Food Type About The Food Carbohydrates FruitDocument2 pagesFood Type About The Food Carbohydrates FruitSNo ratings yet
- Starch Salivary Amylase Maltose: BrownDocument4 pagesStarch Salivary Amylase Maltose: BrownLetchumanan L MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Handout NRG201Document13 pagesHandout NRG201Kyle DoloritosNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Notes (Nutrition & Respiration) - 1Document6 pagesLife Processes Notes (Nutrition & Respiration) - 1ARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition Spreadsheet - Student GroupDocument9 pagesAnimal Nutrition Spreadsheet - Student GroupZoey LawNo ratings yet
- Teaching Slide Set 2019: Global Initiative For Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (Gold)Document135 pagesTeaching Slide Set 2019: Global Initiative For Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (Gold)zaimmuhtar100% (1)
- Nursing Theories 2023 Set - 103204Document7 pagesNursing Theories 2023 Set - 103204henri kaneNo ratings yet
- Marathon Garmin Connect PDFDocument12 pagesMarathon Garmin Connect PDFThomas VanderghoteNo ratings yet
- Nutrition-Module 230817 083933Document536 pagesNutrition-Module 230817 083933Romm JacobNo ratings yet
- Arguementative EassyDocument4 pagesArguementative Eassyrah tajNo ratings yet
- Role of Pa'S in Managing One'S StressDocument11 pagesRole of Pa'S in Managing One'S StressAntonio S. Binavice Jr.No ratings yet
- TFN Midterm Exam ReviewDocument21 pagesTFN Midterm Exam ReviewMayeee GayosoNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic ExercisesDocument3 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic ExercisesBonak na BataNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Physical Education and Health 1Document4 pagesPortfolio in Physical Education and Health 1Arnold Jr MontaNo ratings yet
- 7 Different Exercises: Stretching Before WorkoutDocument5 pages7 Different Exercises: Stretching Before Workoutcly espinosaNo ratings yet
- COLLEGE DEPARTMENT S.Y. 2021-2022 1 Semester: (2 Term)Document10 pagesCOLLEGE DEPARTMENT S.Y. 2021-2022 1 Semester: (2 Term)Raniel GalindoNo ratings yet
- Davidpol Nursing Diagnosis Nic NocDocument1 pageDavidpol Nursing Diagnosis Nic NocFreshyAndMessyNo ratings yet
- Research CapsuleDocument2 pagesResearch CapsuleNancy LantinganNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice.: Physical Education 12Document4 pagesMultiple Choice.: Physical Education 12cjNo ratings yet
- Sample Size in Qualitative Interview Studies: Guided by Information PowerDocument8 pagesSample Size in Qualitative Interview Studies: Guided by Information PowermohammedNo ratings yet
- Women's Weight Gain Program PDF-Book by Jayna DavisDocument41 pagesWomen's Weight Gain Program PDF-Book by Jayna DavisAnita SinghNo ratings yet
- Author:: Firdausi Ramadhani, Herman Hatta, Nuryani, Nirmala Yusuf, SuwignyoDocument9 pagesAuthor:: Firdausi Ramadhani, Herman Hatta, Nuryani, Nirmala Yusuf, SuwignyoyaniNo ratings yet
- Endline Grade 1 2022Document1 pageEndline Grade 1 2022JAIRAH BAUSANo ratings yet
- 14 Psychological Well Being Bagi Mahasiswa Jurusan Pendidikan Dokter Ditinjau Dari Dukungan Sosial Teman Sebaya Dan Internal Locus of ControlDocument21 pages14 Psychological Well Being Bagi Mahasiswa Jurusan Pendidikan Dokter Ditinjau Dari Dukungan Sosial Teman Sebaya Dan Internal Locus of ControlGrettaNo ratings yet
- Expositions Text - Analytical & Hortatory Exposition - Adverbial Phrases - Kumpulan Soal 2 (Sedang) - QuizizzDocument10 pagesExpositions Text - Analytical & Hortatory Exposition - Adverbial Phrases - Kumpulan Soal 2 (Sedang) - QuizizzAulia NurdinNo ratings yet
- EOT2 G12 Gen Boys HSDocument3 pagesEOT2 G12 Gen Boys HSHasan ShkoukaniNo ratings yet