Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
dan 123Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
dan 123Copyright:
Available Formats
Name Class Date
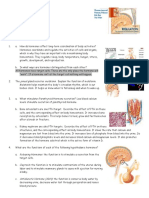
Section 39-1 The Endocrine System (pages 997-1002)
Key Concepts
• What is the function of the endocrine system?
• How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Introduction (page 997)
1. What makes up the endocrine system?
2. What do the products of the endocrine system do?
Hormones (page 997)
3. Chemicals released in one part of the body that travel through the bloodstream and
affect the activities of cells in other parts of the body are called
4. How do hormones affect the activities of other cells?
5. Cells that have receptors for a particular hormone are referred to as
6. Is the following sentence true or false? Cells without receptors are not affected by
hormones.
7. Is the following sentence true or false? Generally the body’s responses to hormones are
quicker and shorter lasting than the responses to nerve impulses.
Glands (page 998)
8. An organ that produces and releases a substance, or secretion, is called a(an)
9. What is an exocrine gland?
10. Glands that release sweat, tears, and digestive juices are considered
glands.
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
194
Name Class Date
5. What is the function of the parathyroid glands?
Match the endocrine gland with the hormone it produces.
Endocrine Gland Hormone It Produces
_______ 12. Pineal a. Glucagon
_______ 13. Thyroid b. Melatonin
_______ 14. Pancreas c. Epinephrine
_______ 15. Thymus d. Thyroxine
_______ 16. Adrenal e. Thymosin
_______ 17. Ovary f. Testosterone
_______ 18. Testis g. Estrogen
19. The hormone that regulates metabolism is______________________
Hormone Action (page 999)
20. List the two general groups into which hormones may be classified. a.
b.
21. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about steroid hormones.
a. They are lipids.
b. They cannot cross cell membranes.
c. They help regulate gene expression.
d. They can enter the nucleus.
22. Is the following sentence true or false? Steroid hormones are produced from
cholesterol.
23. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about nonsteroid hormones.
a. They are proteins, small peptides, or modified amino acids.
b. They can cross cell membranes.
c. They rely on secondary messengers.
d. They cannot enter the nucleus.
24. Is the following sentence true or false? Secondary messengers may include calcium
ions, cAMP, nucleotides, and fatty acids.
Prostaglandins (page 1000)
25. Hormonelike substances produced by other kinds of cells and tissues are called
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
195
Name Class Date
26. Why are prostaglandins known as “local hormones”?
27. Is the following sentence true or false? Some prostaglandins cause smooth muscles to
contract.
Control of the Endocrine System (pages 1000-1001)
28. When does feedback inhibition occur?
29. Fill in the missing labels in the diagram to show how the thyroid gland is regulated by
feedback controls.
Inhibition
Anterior
TRH pituitary Thyroid
30. Circle the letter of each event that occurs when core body temperature begins to drop.
a. The hypothalamus produces less TRH.
b. More TSH is released.
c. Less thyroxine is released.
d. Metabolic activity increases.
31. Is the following sentence true or false? As you lose water, the concentration of
dissolved materials in the blood falls.
Complementary Hormone Action (page 1002)
32. What is complementary hormone action?
33. Is the following sentence true or false? Calcitonin increases the concentration of
calcium in the blood.
34. If calcium levels drop too low, the parathyroid glands release
35. How does PTH increase calcium levels?
36. Why is the regulation of calcium levels so important?
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
196
You might also like
- MelatoninDocument16 pagesMelatoninJessica HuffNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Sum. TestfinalDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Science Sum. TestfinalHAIDEENo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMary Christelle100% (1)
- Problem Set 2 EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesProblem Set 2 EndocrinologyJessica EtieneNo ratings yet
- Hormones Endocrine System WorksheetDocument4 pagesHormones Endocrine System WorksheetRia LouNo ratings yet
- Exam Question Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesExam Question Endocrine SystemTumabang DivineNo ratings yet
- Drug & Cosmetic Act 1940Document23 pagesDrug & Cosmetic Act 1940AnuragMishra100% (3)
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument19 pagesAcute GastroenteritisJoy Jarin100% (1)
- Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFDocument12 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration PDFSanjana SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Lab WorksheetDocument7 pagesEndocrine System Lab WorksheetedwardNo ratings yet
- Drugs in The ElderlyDocument38 pagesDrugs in The ElderlyMyda Efron ArchuletaNo ratings yet
- Answerd FINAL EXAM STUDENT-1Document4 pagesAnswerd FINAL EXAM STUDENT-1Omar H100% (1)
- The Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesThe Endocrine SystemJonathan TabbunNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in ScienceDocument6 pagesSummative Test in ScienceRalph Rexor Macarayan BantuganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine System蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 1Document2 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 1Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument3 pagesEndocrine Glandsdan 123No ratings yet
- ICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)Document14 pagesICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)TAHMEENA ZAFARNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument23 pagesEndocrine SystemMichael DimasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System ORIGDocument5 pagesEndocrine System ORIGkimberly HoveNo ratings yet
- 1016MSC T1 2023 Module 5 Tutorial WorksheetsDocument21 pages1016MSC T1 2023 Module 5 Tutorial WorksheetsTina HussainiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnonymous -No ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 10 Endocrine SystemJamesanne DemetriaNo ratings yet
- Saladin 17.1Document6 pagesSaladin 17.11613405No ratings yet
- Review Chapter 16 EndocrineDocument11 pagesReview Chapter 16 EndocrineAkul MunjalNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Body Functions by Chemical MessengerDocument6 pagesCoordination of Body Functions by Chemical MessengerHorain FatimaNo ratings yet
- Bio f4 Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesBio f4 Endocrine SystemE-SKUUL ACADEMYNo ratings yet
- 3rdq Science 10 ExamDocument3 pages3rdq Science 10 ExamPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Assessment of The Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesMODULE 1 Assessment of The Endocrine SystemLorraine GambitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 45 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 45 Notessadaf_5No ratings yet
- Chapter 9. The Endocrine System: Short QuestionsDocument24 pagesChapter 9. The Endocrine System: Short QuestionsParardha DharNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Notes 1314Document9 pagesEndocrine System Notes 1314Adrianna LjubiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 10 Endocrine SystemAce ClaireNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32Document30 pagesChapter 32RovanNo ratings yet
- AP2 Unit 6 Exam Review CASDocument12 pagesAP2 Unit 6 Exam Review CASMarera DomnicNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 CommunicationIII 1Document30 pagesLecture10 CommunicationIII 1Liana Rose MeregildoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesThe Endocrine Systemapi-282601291No ratings yet
- Human Endocrine System - Grade 11 & 12Document29 pagesHuman Endocrine System - Grade 11 & 12Ishita SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy: Lesson 10: Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesBasic Human Anatomy: Lesson 10: Endocrine SystemIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Dulutalias - Chapter18-THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMDocument10 pagesDulutalias - Chapter18-THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMGwen Valerie DulutaliasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemNicholas FavourNo ratings yet
- CH 45 Guided ReadingDocument7 pagesCH 45 Guided ReadingmharirajNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument8 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationsuryababaNo ratings yet
- Lec No 3Document50 pagesLec No 3X And ZNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration: SolutionsDocument10 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration: SolutionsIhtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology IntroductionDocument43 pagesEndocrinology IntroductionDICKSONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - The Endocrine System - ReviewDocument11 pagesChapter 17 - The Endocrine System - ReviewAnonymous xTR2A3TfdhNo ratings yet
- Enr SaqsDocument4 pagesEnr SaqsMahnoor KhanNo ratings yet
- PH3. 2024. Endocrine Physiology Questions-1Document14 pagesPH3. 2024. Endocrine Physiology Questions-1School TeamNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3: WORKSHEET NO. 1 Name: Score: Section: Date Submitted The Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesQuarter 3: WORKSHEET NO. 1 Name: Score: Section: Date Submitted The Endocrine SystemPrincess RamoleteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesIntroduction To EndocrinologyBunny OzuNo ratings yet
- evaluatedSLK On The Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesevaluatedSLK On The Endocrine SystemMilagrosBautistaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine Systemfumiko.cruzNo ratings yet
- 3418 1701236940Document4 pages3418 1701236940SatnampreetNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 13Document18 pagesLaboratory Exercise 13Jessa SuacitoNo ratings yet
- Nervous and Hormonal Coordination Worksheet - AnswersDocument3 pagesNervous and Hormonal Coordination Worksheet - AnswersДамир КаримовNo ratings yet
- EXCI360 Ch75 IntroductionDocument19 pagesEXCI360 Ch75 Introduction5xfz6hjkpgNo ratings yet
- I. Learning Objective:: /endocrine-System-Lesson-Plan-Final-Na-FinalDocument10 pagesI. Learning Objective:: /endocrine-System-Lesson-Plan-Final-Na-FinalGabilan Rose JeanNo ratings yet
- M18 Mari2036 07 Ig C18 PDFDocument5 pagesM18 Mari2036 07 Ig C18 PDFJelian GraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter Practice Test: Home Chapter 16: The Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesChapter Practice Test: Home Chapter 16: The Endocrine SystemHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test Q3Document4 pages1st Summative Test Q3Jamiy QtNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Equilibrium: Navigating the Hormonal Seas: Navigating the Whispers of Hormones: A Delicate Dance of BalanceFrom EverandEndocrine Equilibrium: Navigating the Hormonal Seas: Navigating the Whispers of Hormones: A Delicate Dance of BalanceNo ratings yet
- Causes and Symptoms & The Oral Cancer ExamDocument4 pagesCauses and Symptoms & The Oral Cancer ExamAndykaYayanSetiawanNo ratings yet
- A Study of Classification Systems For Maxillectomy DefectsDocument8 pagesA Study of Classification Systems For Maxillectomy DefectsAnonymous LnWIBo1GNo ratings yet
- Cultural Belief SystemDocument21 pagesCultural Belief SystemMARK ANDY BRIONESNo ratings yet
- Im-Sq Skill Competency Grading Rubric - Student Rev Fall 19Document1 pageIm-Sq Skill Competency Grading Rubric - Student Rev Fall 19api-547300476No ratings yet
- Dental ALLDocument13 pagesDental ALLandyNo ratings yet
- Anticolinérgicos Morgan and Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology, 7th Edition 2022Document7 pagesAnticolinérgicos Morgan and Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology, 7th Edition 2022Lourdes RamírezNo ratings yet
- Plain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children: Hee Jung Lee, M.DDocument7 pagesPlain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children: Hee Jung Lee, M.DkishanNo ratings yet
- AdimeDocument2 pagesAdimeapi-276849892No ratings yet
- AknowledgementDocument3 pagesAknowledgementObaidullah MominNo ratings yet
- Closed Head Injury in AdultsDocument175 pagesClosed Head Injury in AdultsElfiraNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation For Thalassemia: Javid Gaziev and Guido LucarelliDocument14 pagesHematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation For Thalassemia: Javid Gaziev and Guido LucarelliRatna AzizahNo ratings yet
- Core Competencies-Perform Pre Lay and Lay Activities CO Ms. DianDocument6 pagesCore Competencies-Perform Pre Lay and Lay Activities CO Ms. Dianrobelyn veranoNo ratings yet
- Inpatient Handbook 2008-2009 UCLADocument275 pagesInpatient Handbook 2008-2009 UCLAartig44No ratings yet
- Orbitotomi MedscapeDocument9 pagesOrbitotomi MedscapeBonita AsyigahNo ratings yet
- 62 1LivelyIntroductionDocument36 pages62 1LivelyIntroductionhurqalyaNo ratings yet
- Role Play English Bu CintyaDocument5 pagesRole Play English Bu Cintyavarly psd997No ratings yet
- Albert Abrams For WebDocument7 pagesAlbert Abrams For Webapi-232178087100% (1)
- Peraturan Bpjs Poli GigiDocument11 pagesPeraturan Bpjs Poli GigitarikusumaNo ratings yet
- Soybean Glycine Max Allergy in Europe Gly M 5 Conglycinin and Gly M 6 Glycinin Are Potential Diagnostic Markers For Severe Allergic Reactions To Soy 2009 Journal of Allergy and CliDocument11 pagesSoybean Glycine Max Allergy in Europe Gly M 5 Conglycinin and Gly M 6 Glycinin Are Potential Diagnostic Markers For Severe Allergic Reactions To Soy 2009 Journal of Allergy and CliDiva Silva FirminoNo ratings yet
- Proton Pump Inhibitors - AMBOSSDocument3 pagesProton Pump Inhibitors - AMBOSSRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- MSDS HexaneDocument7 pagesMSDS HexaneThammarat PattanarungsanNo ratings yet
- WWW - Uhu.es Antonia - Dominguez Selectividad 2007-2008 INGLES 2007 P4 andDocument1 pageWWW - Uhu.es Antonia - Dominguez Selectividad 2007-2008 INGLES 2007 P4 andJanetNo ratings yet
- Nclex Group Care of PhsychatricDocument22 pagesNclex Group Care of Phsychatricsri rengganiNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Nuclear Medicine Part 2Document45 pagesGastrointestinal System Nuclear Medicine Part 2api-19916399No ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugSaleha YounusNo ratings yet
- Nutrients 10 01103 v2Document21 pagesNutrients 10 01103 v2Ida Ayu LitaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Needs in Hot EnvironmentsDocument393 pagesNutritional Needs in Hot EnvironmentsgeoNo ratings yet