Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Print Questions Answerstyuh
Uploaded by
adamgonoloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Print Questions Answerstyuh
Uploaded by
adamgonoloCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
1) Match each unit of measurement to its physical quantity on the left.
charge coulomb
potential energy ampere
current volt
resistance joule
electric potential watt
difference
ohm
power
Correct Answer
charge coulomb
potential energy joule
current ampere
resistance ohm
electric potential difference volt
power watt
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 1/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
2) Match each description to the items below.
the depiction of parallel
lightbulbs or heating
elements in a circuit current
diagram series
potential difference fuse
divided by resistance
ammeter
the instrument that
resistors
measures current
a circuit in which
there are several
current paths
the type of circuit in
which the equivalent
resistance is the sum
of the resistances of
each resistor
a safety device that
stops current through
a circuit
Correct Answer
the depiction of lightbulbs or heating elements in resistor
a circuit diagram s
potential difference divided by resistance current
the instrument that measures current ammeter
a circuit in which there are several current paths parallel
the type of circuit in which the equivalent
resistance is the sum of the resistances of each series
resistor
a safety device that stops current through a circuit fuse
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 2/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
3) The conservation of charge in a circuit implies that ______.
electrons cannot be created or destroyed
the total amount of charge is constant
electrons can move through the circuit
all of the above
Correct Answer
all of the above
4) A conventional current is the flow of ______.
electrons
alternating current
positive charge
electrons or ions
Correct Answer
positive charge
5) The potential difference between two points in space is 1000 V, and 2 coulombs of charge
is transferred from the point of lower potential to the point of higher potential. The
amount of work done is ______.
500 J
2000 J
2×10−3 J
1000 J
Correct Answer
2000 J
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 3/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
6) A 9-V battery is connected to a toy car, and the current produced is 2 A. The rate at which
energy is delivered to the toy car is ______.
4.5 W
4.5 J
18 J
18 W
Correct Answer
18 W
7) A 60-W lightbulb runs for 2 hours. The energy transformed is ______.
120,000 J
432,000 J
120 J
30 J
Correct Answer
432,000 J
8) A heater that operates at 220 W is connected to a 110-V outlet. The current through the
heater is ______.
2.2 A
2A
0.5 A
20 A
Correct Answer
2A
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 4/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
9) A lamp is connected to a battery of 50 V, and the current through the circuit is 2 A. The
resistance of the lamp is ______.
100 Ω
150 Ω
0.04 Ω
25 Ω
Correct Answer
25 Ω
10) The current through a resistor of 15 Ω is 5.0 A. The potential difference across the
resistor is ______.
45 V
0.33 V
75 V
3.0 V
Correct Answer
75 V
11) A series circuit has a power source of 120 V and a 150-Ω resistor. The power delivered by
the power source is ______.
96 W
96 kW
192 W
9.6 kW
Correct Answer
96 W
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 5/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
12) The rating of a lightbulb is 100 W and its resistance is 50 Ω. The current through the
lightbulb when it is on is ______.
2A
1.4 A
5000 A
0.5 A
Correct Answer
1.4 A
13) The amount of energy transformed by a 150-W lightbulb in 24 h is ______.
3.6 kWh
130,000 J
3.6 J
3×103 kWh
Correct Answer
3.6 kWh
14) A household’s electric bill is $56 for the month of February and the cost of electricity is
$0.12 per kilowatt-hour. The household used ______ of energy in this month.
467 kJ
6.7 kW
467 kWh
67 kJ
Correct Answer
467 kWh
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 6/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
15) A conducting wire has a resistance of 0.02 Ω/m. The power of this 100-m wire when it
carries a current of 20 A is ______.
8W
800 W
800 J
0.8 J/s
Correct Answer
800 W
16) If four electric devices are connected in a series circuit, the number of current paths is
equal to ____ .
four
three
one
two
Correct Answer
one
17) A series circuit contains four resistors. Each resistor has a different resistance. What is
the equivalent resistance of the circuit?
R/4
4R
R1 + R2 + R3 + R4
(R 1 + R 2 + R 3 + R 4)/4
Correct Answer
R1 + R2 + R3 + R4
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 7/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
18) In an electric circuit, ____ are switches that act as safety devices.
combined circuits
fuses and voltage dividers
ammeters
fuses and circuit breakers
Correct Answer
fuses and circuit breakers
19) If three resistors are connected in parallel, there are ____ current paths in the circuit.
four
one
three
two
Correct Answer
three
20) A series circuit has a 120-V generator, but requires a source that provides a potential
difference of only 60 V. To achieve the desired potential difference, a ____ can be used.
semiconductor
sensor
voltage divider
photoresistor
Correct Answer
voltage divider
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 8/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
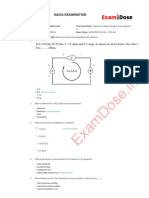
21) A closed circuit connects a 36-V battery, a potentiometer, an ammeter, a bulb, and
voltmeter. The voltmeter is connected in parallel across the potentiometer, and the other
components are connected in series. Suppose that the initial setting of the potentiometer
is 1 Ω. Fill in the missing values in the table below for the current in the lamp as the
resistance in the potentiometer increases from 1 Ω to 100 Ω, 200 Ω, and finally, 300 Ω.
Resistance (Ω) Current (A)
1
100
200
300
Correct Answer
Blank 1: 36
Blank 2: 0.4
Blank 3: 0.2
Blank 4: 0.1
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 9/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
22) Suppose an ammeter reads 1.0 A, 0.12 A, 0.18 A, and 0.36 A. Fill in the table below
showing the resistance of the potentiometer for each reading on the ammeter for a closed
circuit with a 36-V battery.
Current (A) Resistance (Ω)
1.0 36
0.12
0.18
0.36
Correct Answer
Blank 1: 300.0
Blank 2: 200.0
Blank 3: 100.0
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 10/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
23) A wire is connected to a 9-V battery and ammeter, and its resistance is measured. The
length of the wire is varied, and the values shown in the table are obtained. Complete the
table by filling in the missing values for resistance and current.
Length (m) Current (A) Voltage (V) Resistance (Ω)
1 12.7 9
2 6.4 9
3 4.3 9
4 3.2 9
5 2.6 9
Correct Answer
Blank 1: 0.7
Blank 2: 1.4
Blank 3: 2.1
Blank 4: 2.8
Blank 5: 3.5
24) To measure the current through a resistor, an ammeter should be connected in series
with the resistor.
True
False
Correct Answer
True
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 11/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
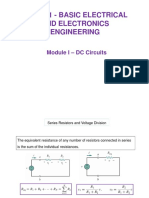
25) The equivalent resistance of a parallel circuit is always less than the resistance of any
resistor in the circuit.
True
False
Correct Answer
True
26) A voltmeter should have a very low resistance so that it causes the largest possible
changes in currents and potential differences in the circuit.
True
False
Correct Answer
False
27) The resistance of an ammeter should be as low as possible.
True
False
Correct Answer
True
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 12/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
28) To measure the potential difference across a resistor, connect a voltmeter in parallel with
the resistor.
True
False
Correct Answer
True
29) The increase in electric potential provided by the generator or other energy source is
equal to the sum of the drops in electric across the lamps in the
circuit.
Correct Answer
Blank 1: potential
30) The current produced in a given circuit hooked up to a given potential difference
depends on the of that circuit.
Correct Answer
Blank 1: resistance
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 13/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
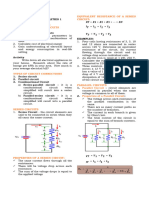
31) Complete the following statements about parallel electric circuits.
a. The potential difference across each path is .
b. The of the total resistance is the sum of the reciprocals of the
individual resistances.
c. In a parallel circuit, the total current is the of the currents
through each path.
d. enable a user to turn on some of the electric devices and not
others.
Correct Answer
Blank 1: the same, equal, or equivalent
Blank 2: reciprocal
Blank 3: sum
Blank 4: switches or switch
32) Current is represented by the symbol .
Correct Answer
Blank 1: I
33) A can measure the potential difference across a lightbulb.
Correct Answer
Blank 1: voltmeter
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 14/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
34) Current can only travel in a circuit—one in which all of the
switches are closed.
Correct Answer
Blank 1: complete or closed
35) To measure the potential drop across a resistor, a voltmeter is connected in
with the resistor.
Correct Answer
Blank 1: parallel
36) What would happen to the current in a circuit if a voltmeter were substituted for an
ammeter?
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 15/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
37) For the following experimental results, provide an explanation or theory.
a. The resistance of a wire increases as its length increases.
b. The resistance of a wire increases as its cross section decreases.
c. The resistance of a wire increases as its temperature increases.
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 16/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
38) What happens to resistance when a resistor is added in parallel to a circuit that already
has two resistors?
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
39) How is it possible to turn devices on and off independently of each other in a house?
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
40) Why is a ground-fault interrupter often required by law for electric outlets in bathrooms
and kitchens, but not in other rooms in a house?
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 17/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
41) Why does turning on additional appliances on the same circuit breaker increase the
current through that circuit breaker?
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
42) What happens to a series current if one device fails?
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
43) Two lamps are connected in parallel. If there are 6 V across one lamp, must there also be
6 V across the other lamp? Explain.
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 18/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
44) Household circuits are normally wired in parallel.
a. What would happen in a household if it were wired in series and one device failed?
b. What would happen in that same household when additional devices were turned on?
Correct Answer
Answers may vary.
45) Two resistors of 3.0 Ω and 8.0 Ω are connected in series across a 9.0-V battery.
What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? Ω
What is the current through the 3.0-Ω resistor? A
What is the current through the 8.0-Ω resistor? A
What is the potential difference across the 3.0-Ω resistor? V
What is the potential difference across the 8.0-Ω resistor? V
Correct Answer
Blank 1: 11.0
Blank 2: 0.82
Blank 3: 0.82
Blank 4: 2.5
Blank 5: 6.6
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 19/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
46) A 15-Ω bell and an 8.0-Ω lamp are connected in parallel and placed across a potential
difference of 42 V.
What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? Ω
What is the current in the circuit? A
What is the current through each resistor?
Ibell = A
Ilamp = A
What is the potential difference across each resistor?
Vbell = V
Vlamp = V
Correct Answer
Blank 1: 5.2
Blank 2: 8.1
Blank 3: 2.8
Blank 4: 5.3
Blank 5: 42
Blank 6: 42
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 20/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
Answer Key with Questions
Module Test: Electric Current and Circuits
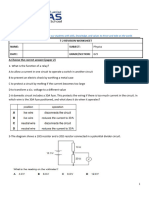
47) Refer to the diagram to answer the following questions.
a. What is the total current? A
b. What is the potential difference across the 20-Ω resistor? V
c. What is the potential difference across the 16-Ω resistor? V
d. What is the potential difference across each 8-Ω resistor? V
e. What is the current at the branch measured by ammeter 1? A
f. How much power is used by the 20.0-Ω resistor? W
g. How much power is used by the 16.0-Ω resistor? W
h. How much power is used by the 8.0-Ω resistor? W
Correct Answer
Blank 1: 3.0
Blank 2: 60
Blank 3: 48
Blank 4: 12
Blank 5: 1.5
Blank 6: 180
Blank 7: 140
Blank 8: 18
Copyright © 2024, McGraw-Hill Education. 21/21
This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students.
You might also like
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Kaha Se Shuru Karu BhaiDocument12 pagesKaha Se Shuru Karu Bhai;(No ratings yet
- Cea 223 Mod 2Document2 pagesCea 223 Mod 2PhoemelaNo ratings yet
- Electricity WorksheetDocument11 pagesElectricity Worksheetsrijankanduri14No ratings yet
- Det1013 - Electrical Technology: Introduction To Electric CircuitDocument118 pagesDet1013 - Electrical Technology: Introduction To Electric Circuitcaj7687No ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument107 pagesElectric CircuitsKristine Cris VenusNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument4 pagesElectric CircuitsThando zondiNo ratings yet
- Electricity Exam Type Questions 2017Document25 pagesElectricity Exam Type Questions 2017Muhammad Iqbal SamanNo ratings yet
- Q ElectricityDocument29 pagesQ Electricityvidhan tiwariNo ratings yet
- 10 Sci Electricity tp01Document6 pages10 Sci Electricity tp0142rwgwnjg5No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document117 pagesChapter 1badrilaminNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsDocument32 pagesIGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsSam JordanNo ratings yet
- Answers For Electricity In-Text and Book ExerciseDocument16 pagesAnswers For Electricity In-Text and Book ExerciseLorith Plays SMPNo ratings yet
- Current and Voltage in CircuitsDocument31 pagesCurrent and Voltage in CircuitsChalitha RanasingheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document117 pagesChapter 1badrilaminNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Direct Current Circuits1Document8 pagesLesson 5 Direct Current Circuits1AjzNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt-1 D.C. Circuits IDocument3 pagesAssignemnt-1 D.C. Circuits IDinesh MatlaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Las Week 7.1Document8 pagesGrade 8 Science Las Week 7.1michelleNo ratings yet
- Bal Bharati Public School, Dwarka Physics - Important Questions Chapter-ElectricityDocument4 pagesBal Bharati Public School, Dwarka Physics - Important Questions Chapter-ElectricityTrishyaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Energy, Power and Resistance - EMF and PD QPDocument14 pages4.2 Energy, Power and Resistance - EMF and PD QPwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- EASA Electrical Fundamentals 2Document33 pagesEASA Electrical Fundamentals 2Marty008100% (3)
- EE Lec 06Document24 pagesEE Lec 06adil11699611No ratings yet
- Gen Physics 2 - Las 3 - Allas - Version 4Document4 pagesGen Physics 2 - Las 3 - Allas - Version 4J-heart Basabas MalpalNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Questions: Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 10: Direct-Current CircuitsDocument25 pagesConceptual Questions: Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 10: Direct-Current CircuitsDaniel AntonioNo ratings yet
- سلايدات كهر201Document263 pagesسلايدات كهر201بدر الشهرانيNo ratings yet
- Bee Experiments: Pointers To FollowDocument35 pagesBee Experiments: Pointers To FollowPratik Mishra100% (1)
- EE Lec 05Document24 pagesEE Lec 05adil11699611No ratings yet
- Electric Current, Resistance and ResistivityDocument8 pagesElectric Current, Resistance and ResistivityPavan BoroNo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr10PhysicalSciences - 16 - Electric Circuits I - 27may2014Document3 pagesLXL - Gr10PhysicalSciences - 16 - Electric Circuits I - 27may2014zlmulaudzi42No ratings yet
- NPCIL Kaiga Previous QuestionDocument16 pagesNPCIL Kaiga Previous QuestionSuraj BauriNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- NPCIL Kaiga ST-SA ElectricalDocument16 pagesNPCIL Kaiga ST-SA ElectricalSuraj RaiNo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 24 - Electric Circuit Problems - 12aug2014Document5 pagesLXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 24 - Electric Circuit Problems - 12aug2014HNo ratings yet
- 10 Physics ch12 Electricity Ncert SolutioDocument19 pages10 Physics ch12 Electricity Ncert SolutiothemidnightismNo ratings yet
- Applied Electrical Notes Unit 1Document12 pagesApplied Electrical Notes Unit 1The STUDY koala happyNo ratings yet
- Revision ExerciseDocument20 pagesRevision ExerciseAlfred GaleaNo ratings yet
- Physics-Revision WS - Gr9-Mrs EsraaDocument17 pagesPhysics-Revision WS - Gr9-Mrs EsraaLemar AdelNo ratings yet
- 19.2 Using Electrical EnergyDocument16 pages19.2 Using Electrical EnergyHasan AlzaghalNo ratings yet
- 12 - Electricity: CLASS-10Document4 pages12 - Electricity: CLASS-10Kaustubh FFNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits and Internal Resistance (MCQ Only)Document12 pagesElectrical Circuits and Internal Resistance (MCQ Only)Ant Live100% (1)
- Current Electricity 23 - 24Document51 pagesCurrent Electricity 23 - 24Maryam ShahidNo ratings yet
- IFC Q & A 2 - ElectronicsDocument6 pagesIFC Q & A 2 - ElectronicsJohn Paul M. TubigNo ratings yet
- Physics: Senior Secondary School: ThirdDocument32 pagesPhysics: Senior Secondary School: ThirdAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- Current and ResistanceDocument42 pagesCurrent and ResistancehelsaNo ratings yet
- Act. Module 4 - Resonance, Bandwidth, Non-Sinusoidal WaveformDocument6 pagesAct. Module 4 - Resonance, Bandwidth, Non-Sinusoidal WaveformSherwin PagpaguitanNo ratings yet
- Allen: Subjective AssignmentDocument4 pagesAllen: Subjective AssignmentPiyush YadavNo ratings yet
- G8 Week5 6 WorksheetDocument5 pagesG8 Week5 6 WorksheetArvin RescatorNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab Manualdinuarslan86% (7)
- Lec 14 - Electric CircuitsDocument37 pagesLec 14 - Electric CircuitsNikky SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistance: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in Physics 2-4Document21 pagesElectrical Resistance: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in Physics 2-4Sam JordanNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law and Electric CircuitsDocument46 pagesOhm's Law and Electric CircuitsGabriel Carl Alpuerto100% (1)
- 3 Year Mechanical Power MPE 331: Dr. Mohamed Hammam 2019Document25 pages3 Year Mechanical Power MPE 331: Dr. Mohamed Hammam 2019Mohamed HammamNo ratings yet
- Interference Voltages Induced by Magnetic Fields of Simulated Lightning Currents in PV Modules & ArraysDocument4 pagesInterference Voltages Induced by Magnetic Fields of Simulated Lightning Currents in PV Modules & ArraysbitudayNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 24 ElectricalResistanceDocument21 pagesIGCSE 24 ElectricalResistanceHAMAD NoorNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: Department of Mechatronics and Control Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, LahoreDocument35 pagesElectric Circuits: Department of Mechatronics and Control Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, Lahoreabdullah javedNo ratings yet
- Is Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityDocument3 pagesIs Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (2) On Current ElectricityDocument7 pagesWorksheet (2) On Current ElectricitySrijit SahaNo ratings yet
- Ryan International School Class X Chapter: ElectricityDocument2 pagesRyan International School Class X Chapter: ElectricityAnnu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 4sd0 1p Rms 20230302Document18 pages4sd0 1p Rms 20230302adamgonoloNo ratings yet
- FSDFSDF 302Document15 pagesFSDFSDF 302adamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Fsdotor EffectDocument39 pagesFsdotor EffectadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Grade: Faculty Member: Date: Topic: Activity Time Warm - UpDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Grade: Faculty Member: Date: Topic: Activity Time Warm - UpadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2023: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Mathematics A (4MA1) Paper 1HRDocument24 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2023: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Mathematics A (4MA1) Paper 1HRadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2023: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Mathematics A (4MA1) Paper 1HDocument25 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2023: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Mathematics A (4MA1) Paper 1HadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz - Solar System: Match The Definition To The Correct Vocabulary WordDocument2 pagesScience Quiz - Solar System: Match The Definition To The Correct Vocabulary WordadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Grade: Faculty Member: Date: Topic: Activity Time Warm - UpDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Grade: Faculty Member: Date: Topic: Activity Time Warm - UpadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Rrrs of Matter LabDocument6 pagesRrrs of Matter LabadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Date 14 December 2017 Grade 6PDocument1 pageDate 14 December 2017 Grade 6PadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- DLP Week 4-p1Document3 pagesDLP Week 4-p1adamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet 1 AK: ReproductionDocument2 pagesScience Worksheet 1 AK: ReproductionadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Ars WorksheetDocument8 pagesArs WorksheetadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Picture Style Editor: Ver. 1.15 Instruction ManualDocument21 pagesPicture Style Editor: Ver. 1.15 Instruction ManualadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Forces: Mark Scheme 4Document4 pagesForces: Mark Scheme 4adamgonoloNo ratings yet
- The Complete Solution IELTS Writing - 2017 UpdateDocument159 pagesThe Complete Solution IELTS Writing - 2017 UpdateHoàng Đức Mạnh100% (1)
- Grade 8 Physics Booklet Answer Key: Unit 3 Lesson 2 (Interaction of Light Waves) Answer SectionDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Physics Booklet Answer Key: Unit 3 Lesson 2 (Interaction of Light Waves) Answer SectionadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Solar Smart Street Light SystemDocument26 pagesSolar Smart Street Light Systemmayank100% (1)
- Quick Comparison Between The DECS-200 and DECS-200N: Sep-05 Description DECS-200 DECS-200N Benefit Product DifferencesDocument1 pageQuick Comparison Between The DECS-200 and DECS-200N: Sep-05 Description DECS-200 DECS-200N Benefit Product DifferencesRamakrishnan AlagarsamyNo ratings yet
- Balun QEX Chris - Trask PDFDocument13 pagesBalun QEX Chris - Trask PDFNestor Alberto EscalaNo ratings yet
- 20150227080211Chp 5 InductionDocument17 pages20150227080211Chp 5 Inductionbatraz79No ratings yet
- Continuity, Conservation, Stokes, and MaxwellDocument16 pagesContinuity, Conservation, Stokes, and MaxwellShahil AzmayishNo ratings yet
- Maximum Reliability and Minimal Maintenance: Pantograph Disconnectors Upto 550kV - GW54Document2 pagesMaximum Reliability and Minimal Maintenance: Pantograph Disconnectors Upto 550kV - GW54Han Huang100% (1)
- EEE 315 ELECTRICAL MACHINES III Supplementary EXAM - 2017Document5 pagesEEE 315 ELECTRICAL MACHINES III Supplementary EXAM - 2017Abkul KunniNo ratings yet
- Over All Drawings of PMCC-4 Panel-R0Document27 pagesOver All Drawings of PMCC-4 Panel-R0GreenOlive ControlsNo ratings yet
- KV-29C3 CH - Ae-4Document71 pagesKV-29C3 CH - Ae-4luigigerulaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument55 pagesReportArpitSemwalNo ratings yet
- Testing Procedure For Switch Yard Equipments 1Document9 pagesTesting Procedure For Switch Yard Equipments 1d_kabulpuria100% (2)
- Horn AntennaDocument2 pagesHorn Antennaprashant4455No ratings yet
- Base Modul ETAPDocument2 pagesBase Modul ETAPhrstgaNo ratings yet
- 9020-0618 MCS Multi-Criteria SensorDocument2 pages9020-0618 MCS Multi-Criteria SensorGUZMANNo ratings yet
- (Sanfoundry) Power Electronics 1. Questions & Answers On DiodesDocument7 pages(Sanfoundry) Power Electronics 1. Questions & Answers On Diodeszelin99No ratings yet
- Standard Abbreviation List by Siemens 20Document1 pageStandard Abbreviation List by Siemens 20Pendl PendlNo ratings yet
- Newage Mx341 Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocument6 pagesNewage Mx341 Automatic Voltage RegulatoredgarcooNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: 1. Write Short Notes On Travelling Wave Antenna? AnsDocument14 pagesUnit 4: 1. Write Short Notes On Travelling Wave Antenna? AnsPoornima ChinthalaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Substation - 97Document26 pagesWhat Is A Substation - 97Justin Sam MathewsNo ratings yet
- FR-E800 Instruction Manual - Function Ib0600868engeDocument534 pagesFR-E800 Instruction Manual - Function Ib0600868engeNguyễn Quang HảoNo ratings yet
- Sa Max700 PDFDocument124 pagesSa Max700 PDFAngeler Jp100% (1)
- RectifierDocument5 pagesRectifierpreethiNo ratings yet
- Modelo Bobinas de HelmholtzDocument12 pagesModelo Bobinas de HelmholtzJuan Luis Palacio BedoyaNo ratings yet
- Sony Kvhr34m91Document257 pagesSony Kvhr34m91socket1155No ratings yet
- WEG SSW 06 Soft Starter Usassw06 Brochure EnglishDocument6 pagesWEG SSW 06 Soft Starter Usassw06 Brochure EnglishBujar IbrahimiNo ratings yet
- Nepsi SpreadsheetDocument38 pagesNepsi SpreadsheetAnonymous CO7aaHrNo ratings yet
- Samsung Ue65ks9000t Chassis Uwq60 Suhd TVDocument92 pagesSamsung Ue65ks9000t Chassis Uwq60 Suhd TVkevinalleinNo ratings yet
- Design of Single and Three Phase Transformer Using MATLABDocument6 pagesDesign of Single and Three Phase Transformer Using MATLABDevesh JayaswalNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 10: Prepare Circuit of Automatic Emergency Light Using IC-LM317Document3 pagesExperiment - 10: Prepare Circuit of Automatic Emergency Light Using IC-LM317ArjunAgharaNo ratings yet