Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 11 Physics Practicals Notes
Uploaded by
Iflah SameenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 11 Physics Practicals Notes
Uploaded by
Iflah SameenCopyright:
Available Formats
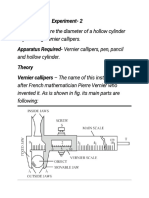
VERNIER CALIPERS
Expt No. ……Date:…………
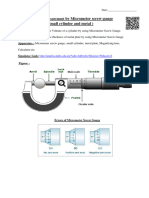
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS Aim: To find the volume of the given cylinder using vernier
Magnitude of 1 main scale division, 1 msd = …………mm calipers
Number of divisions on the vernier , n = …….. Apparatus: Vernier calipers, cylinder, etc
Least count , LC = 1msd = …………mm = …………cm
n
To find the volume of the given cylinder
Principle: Using vernier calipers
Sl. Total reading
Dimension
No.
MSR VSD VSD x LC MSR + (VSD x Mean Least count, L C = magnitude of 1 main scale division
LC) No. of divisions on the vernier scale
cm div cm cm cm
Total reading = M S R + (VSD x L C )
1
Length of 2 where MSR – Main Scale Reading
the 3 . VSD – Vernier Scale Devision
Beaker 4 Volume of the cylinder = πr2l
(l) 5 where r – radius of the cylinder
6 . l – length of the cylinder
1
2
Diameter
3 Result: Volume of the cylinder = …………… m3
of the
4
Beaker
5 PRECAUTIONS:
(d) • If the vernier scale is not sliding smoothly over the main scale,
6
apply machine oil/grease.
• Screw the vernier tightly without exerting undue pressure to avoid
any damage to the threads of the screw.
Diameter of the cylinder, d = …………….cm SOURCES OF ERROR:
Radius of the cylinder , r = d/2 = ………cm = …………….m • the zero error in the instrument placed is not accounted for; and
• the Vernier Callipers is not in a proper position with respect to the body,
Length of the cylinder, l = ………….cm = ………………m avoiding gaps or undue pressure or both.
Volume of the cylinder = Π r2l = …………… cm3 …………..m3
Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
SCREW GAUGE
Expt No. ……Date:…………
Aim: To find the volume of the given wire using screw gauge
Apparatus: Screw Gauge, wire, etc
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS
Principle: Using screw gauge,
Distance moved for 6 rotations = ………………mm
Pitch = Distance moved = …………….mm Least Count, LC = Pitch .
No. of rotations No. divisions on the head scale
No. of divisions on the head scale = ……………
Least Count (LC) = Pitch . . Corrected HSR = observed HSR + zero correction
No. divisions on the head scale
= ………………mm
Zero correction = …………..…..divisions Total reading = PSR + (corrected HSD x LC )
To find the volume of the wire
where PSR – Pitch Scale Reading
Corrected Total reading = HSD – Head Scale Devision
Dimension
Sl.
No.
PSR
Observed
HSD
Corrected
HSD
HSD
x
PSR + (
corrected HSD x
Volume of the wire = π r l
2
LC LC) where r – radius of the wire
mm div div mm mm . l – length of the wire
1
2
3
Diameter
of the wire
4
5
Result: The volume of the given wire = …………… m3
6
PRECAUTIONS:
• Move the screw in one direction else the screw may develop “play”.
• Screw should move freely without friction.
Mean diameter of the wire = ……….mm
SOURCES OF ERROR:
• The wire may not be of uniform cross-section.
Radius of the wire = ………………mm = …………………. m
Length of the wire = ………………cm = …………………….m
• Error due to backlash though can be minimized but cannot be eliminated.
Volume of the wire = Π r2l = ………………. m3
Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
Parallelogram Law
CONCURRENT FORCES
Expt No. ……Date:…………
Aim: To find the weight of the given body using parallelogram law of vectors
Apparatus: A vertical wooden board with two pullies, slotted weights, the given
body etc
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS Principle
To find the weight of the given body by measuring the length of the diagonal Using parallelogram law of vectors
Scale chosen: 1 cm = 20 gm Weight of the body = OD x scale chosen
Diagonal Weight of the body
Forces (OD) = OD x Scale chosen Mean where OD is the length of the diagonal
Trial P Q
no. gmwt gmwt cm gmwt gmwt Scale chosen: 1 cm = 50 gm
Result: The weight of the given body by measuring the length of the diagonal = …..kgwt.
PRECAUTIONS:
• Board of Gravesend’s apparatus is perpendicular to table on which it is placed,
The weight of the given body = ………..gmwt………….. kgwt by its construction. Check up by plumb line that it is vertical. If it is not,
make table top horizontal by putting packing below appropriate legs of table.
• Take care that pulleys are free to rotate, i.e.,
have little friction between pulley and its axle.
SOURCES OF ERROR:
• Friction at the pulleys may persist even after oiling.
• Slotted weights may not be accurate.
• Slight inaccuracy may creep in while marking the position of thread.
Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
HELICAL SPRING I
Expt No. ……Date:…………
Aim: (1) To find the spring constant of the given helical spring
by load – extension method
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS Apparatus: The given helical spring, stand, slotted weights etc
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2
Principle: According to Hookes law,
Dead load W0 = ……….. gm
Scale reading for W0 , r0 = ……………. cm for a spring, load is directly proportional to extension produced.
Scale reading
Mass On On Extension m Therefore
Trial No.
producing loading unloading Mean l = r - r0 l 𝒎
extension (cm) (cm) r cm gm/cm Spring constant, K = load = g
𝒍
m (gm) (cm) extension
1 50
where m - the mass producing the extension l
2 100 g – acceleration due to gravity
3
150
4
200
Result: (1) The spring constant of the given helical spring
by load – extension method = ………...N/m
Mean m = …………gm/cm = …………… kg/m PRECAUTIONS:
l
• Loading and unloading of weight must be done gently.
𝒎 • Reading should be noted only when tip of pointer comes to rest.
Spring constant, K = g = ……….. N/m • Pointer tip should not touch the scale surface.
𝒍 • Loading should not be beyond elastic limit.
SOURCES OF ERROR:
• The support may not be rigid
• The slotted weights may not have correct weight.
Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
(Note: The length of the pendulum is the distance THE SIMPLE PENDULUM
between point of suspension and centre of the bob)
Expt No. ……Date:………….
Aim: To findverify
(i) To the acceleration
the relationdue to gravity
between at the
period andplace
length of a simple
(ii) Using a Simple Pendulum plot a graph between L & T2
Apparatus: Simple Pendulum, stop watch, metre scale etc
Principle: For small oscillation of a simple pendulum
l = a constant
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS T2
where l - length of the pendulum
T – period of the pendulum
Radius of the bob = ………..cm
Length Time for 20 The acceleration due to gravity is given by
Trial no.
Period of
of the oscillations l
oscillation T2 g = 4Π2 l
pendulum
T = t/20 T2
s T2
(l) 1 2 Mean s cm/s2
cm s s (t) s
65
70 Result:
75 Acceleration due to gravity at the place by calculation = …… m/s2
85 PRECAUTIONS:
90
• The thread should be very light and strong.
• The point of suspension should be reasonably rigid.
• The pendulum should oscillate in the vertical plane without any spin motion.
Mean value of l/ T2 = ………. cm/s2………. m/s2
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 4 Π 2 l = …………. m/s2 SOURCES OF ERROR:
T2
• The string may not be weightless and in extensible.
• Point of suspension may not be rigid.
• The amplitude may not be small
Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
You might also like
- Assetto Corsa Physics Pipeline 0.8 PUBLICDocument49 pagesAssetto Corsa Physics Pipeline 0.8 PUBLICTao-Wei HuangNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalsDocument86 pagesPhysics PracticalsGvns Reddy100% (1)
- Ditch Witch RT40 ManualDocument165 pagesDitch Witch RT40 ManualJhonny Rodriguez100% (1)
- Homemade Paintball GunDocument8 pagesHomemade Paintball GunAinis Štelemėkas0% (1)
- M73loc View BMW 750 IL 1995Document110 pagesM73loc View BMW 750 IL 1995locochakaNo ratings yet
- Practical 123Document16 pagesPractical 123tbf06720No ratings yet
- Applied Physics Lab ManualDocument28 pagesApplied Physics Lab ManualJulie MaxNo ratings yet
- Phy Lab ManualDocument18 pagesPhy Lab Manualkaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- Lab MannualDocument28 pagesLab Mannualsoumya ranjan ParidaNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Physics Solved Scheme PDFDocument7 pagesHsslive Physics Solved Scheme PDFReemasalamNo ratings yet
- Ver Cal Cyl SphereDocument2 pagesVer Cal Cyl SphereYash JhaNo ratings yet
- Grade Xi Physics Manual-22-23Document18 pagesGrade Xi Physics Manual-22-23Poop MasterNo ratings yet
- Class 11 ExperimentsDocument25 pagesClass 11 ExperimentsSoham Nag100% (1)
- Vernier Calipers-I-BCJDocument2 pagesVernier Calipers-I-BCJtrail7488No ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual BY: Muhammad Hassan MaqsoodDocument32 pagesPhysics Lab Manual BY: Muhammad Hassan MaqsoodMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Objective: Vernier Callipers, A Spherical Body (It Can Be A Pendulum Bob), A Beaker or A CalorimeterDocument2 pagesExperiment No. 1 Objective: Vernier Callipers, A Spherical Body (It Can Be A Pendulum Bob), A Beaker or A CalorimeterShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 VernierDocument13 pagesExpt 1 VernierIbrahim Ali RizviNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical LabmanualDocument11 pagesPhysics Practical LabmanualVishnupriya SurajNo ratings yet
- X Icse Physics Practicals 2021-2022Document32 pagesX Icse Physics Practicals 2021-2022Andhra Pros GamingNo ratings yet
- Experiments (1 - 4)Document8 pagesExperiments (1 - 4)Aditya YadavNo ratings yet
- I PUC Revised Physics MannualDocument83 pagesI PUC Revised Physics MannualSankirth PNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Physics - Practical - Booklet - 2022-23Document40 pagesGR 11 Physics - Practical - Booklet - 2022-23Hunter OfficialNo ratings yet
- 1 PUC Manual-17Document22 pages1 PUC Manual-17shyla100% (1)
- Phy Lab ReadingsDocument31 pagesPhy Lab ReadingsMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Determine The Density & VolumeDocument4 pagesDetermine The Density & Volumeimniloybhattacharjee15No ratings yet
- Class Xi - Practicals - R - RecDocument26 pagesClass Xi - Practicals - R - RecDivyashekogNo ratings yet
- Veriner CaliperDocument2 pagesVeriner CaliperUmesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Labs at Puc-1Document79 pagesLabs at Puc-1yerrinaidu.gallaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi - Practicals 2024Document24 pagesClass Xi - Practicals 2024pillisathwik2No ratings yet
- Grade - 11 - Study Material - Practical Exam - 23-24Document17 pagesGrade - 11 - Study Material - Practical Exam - 23-24monishchess2468No ratings yet
- PHY 107 Experiment 1Document6 pagesPHY 107 Experiment 1Aisha AwaisuNo ratings yet
- Vernier Calipers-2Document4 pagesVernier Calipers-2warriorNo ratings yet
- 2micrometer Screw - Copy 2Document5 pages2micrometer Screw - Copy 2fearlessshaikh007No ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2bhagwatsunil100No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 2Document4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 2Me Being RandomNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Lab Manual 2023Document57 pagesB.Tech Lab Manual 2023sonamthakur1419No ratings yet
- I Pu Physics ManualDocument65 pagesI Pu Physics ManualSamiksha SainiNo ratings yet
- Phy PraDocument19 pagesPhy PraAfnaan AmeerNo ratings yet
- Practical Experiments 1 To 7Document9 pagesPractical Experiments 1 To 7Moses Samuel SukdularyNo ratings yet
- Practical Physics For XI and XIIDocument36 pagesPractical Physics For XI and XIIRameshkumar Ramanathan100% (1)
- M E S Indian School, Doha-Qatar Boys' Section Experiments For Class Xi (Cbse) 2016-17 Experiment No:1 Vernier Callipers Aim: Apparatus: TheoryDocument9 pagesM E S Indian School, Doha-Qatar Boys' Section Experiments For Class Xi (Cbse) 2016-17 Experiment No:1 Vernier Callipers Aim: Apparatus: TheorySimran MaheyNo ratings yet
- XI Physics ManualDocument10 pagesXI Physics Manualkiranpatel0100% (3)
- Lab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperDocument3 pagesLab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- Physics - Practical Record Writing - Class XIDocument83 pagesPhysics - Practical Record Writing - Class XISara Wolf100% (1)
- Physics Lab Manual For Mechanical Branches FinalDocument26 pagesPhysics Lab Manual For Mechanical Branches FinalSuresh Kumar A PNo ratings yet
- Newtons Ring Experiment1Document4 pagesNewtons Ring Experiment1Mahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Manual Class Xi-1Document32 pagesPhysics Practical Manual Class Xi-1Debajyoti SunariNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Computer Laboratory ManualDocument34 pagesApplied Physics: Computer Laboratory ManualYousha AbbasNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual Class XIDocument42 pagesPhysics Lab Manual Class XIn62284164No ratings yet
- Lab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperDocument4 pagesLab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- Vernier - ActivityDocument9 pagesVernier - ActivityCherry LimNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document2 pagesExperiment 1ISMART STUDY POINTNo ratings yet
- Screw GaugeDocument2 pagesScrew GaugeRony ThomasNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Practicals - Expts 1&2Document7 pagesClass 11 Practicals - Expts 1&2ARAVIND SANTHOSHNo ratings yet
- Anik Sarkar - Lab Manual XI PDFDocument34 pagesAnik Sarkar - Lab Manual XI PDFKousik SarkarNo ratings yet
- Vernier CalipersDocument6 pagesVernier CalipersRani JahnaviNo ratings yet
- Vernier Callipers-Sphere VolumeDocument1 pageVernier Callipers-Sphere Volumejarvis007No ratings yet
- Experiment 1 AIM To Find The Volume of Given Cylinder Using Screw Gauge APPARATUS Screw Gauge, Cylinder PrincipleDocument39 pagesExperiment 1 AIM To Find The Volume of Given Cylinder Using Screw Gauge APPARATUS Screw Gauge, Cylinder PrincipleRoshan RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Physics Ver CalDocument2 pagesHsslive XI Physics Ver CalSaajan MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Practical Hand Book 2 2022Document10 pagesPractical Hand Book 2 2022rugaikwad1736No ratings yet
- Lab 4Document5 pagesLab 4Tawsif ahmedNo ratings yet
- CPP Report 2020-1Document20 pagesCPP Report 2020-1UnmayNo ratings yet
- Sheet #6Document2 pagesSheet #6AHMED BAKRNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Machinery SystemDocument86 pagesAuxiliary Machinery SystemChristian Cañon GenterolaNo ratings yet
- Automated Tugger AGV's For Factory AutomationDocument2 pagesAutomated Tugger AGV's For Factory Automationservice9046No ratings yet
- Lpile Group ModuleDocument2 pagesLpile Group ModuleMUHAMMAD ALINo ratings yet
- CSMD Al SD Tt4rev05Document48 pagesCSMD Al SD Tt4rev05lubangjarumNo ratings yet
- IPBR Flush Bottom Ball ValveDocument2 pagesIPBR Flush Bottom Ball Valvedevang asherNo ratings yet
- 05 FS GduDocument18 pages05 FS GduAnonymous O0lyGOShYGNo ratings yet
- DFX-244 ManualDocument108 pagesDFX-244 Manualviero widyantoNo ratings yet
- TKC40升降机维修说明书TKC Man Lift Maintenance ManualDocument36 pagesTKC40升降机维修说明书TKC Man Lift Maintenance Manualkiên phạm trungNo ratings yet
- New Twist On Interpreting Vibration Analysis FaultsDocument11 pagesNew Twist On Interpreting Vibration Analysis FaultsSérgio CruzNo ratings yet
- The Actively Stressed Soil Nail System With Corrosion Protection Barley Mothersille Conference On Slope Engineering Malaysia 2006Document9 pagesThe Actively Stressed Soil Nail System With Corrosion Protection Barley Mothersille Conference On Slope Engineering Malaysia 2006Kenny CasillaNo ratings yet
- MarioniDocument45 pagesMarionifarmakisdNo ratings yet
- Mmscience - 2019 12 - Design of CNC Milling Machine As A Base of Industry 4 0 EnterpriseDocument6 pagesMmscience - 2019 12 - Design of CNC Milling Machine As A Base of Industry 4 0 EnterpriseKadir ŞUATAMANNo ratings yet
- ASPE PSD - Fire Pump InstallationDocument4 pagesASPE PSD - Fire Pump InstallationNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Iae V2500 Engine Questions: TH THDocument12 pagesIae V2500 Engine Questions: TH THRafael SantosNo ratings yet
- CNCDocument31 pagesCNCPravin DeshmaneNo ratings yet
- Vicat Test: Report1Document5 pagesVicat Test: Report1Khalid MohammadNo ratings yet
- Pump System Labby 2015Document6 pagesPump System Labby 2015Azril DahariNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument6 pagesCentrifugal Pumpkadar AhmedNo ratings yet
- SaeDocument8 pagesSaeahmadNo ratings yet
- Intermot - Iam Complete CatalogueDocument111 pagesIntermot - Iam Complete CatalogueChristian StalinNo ratings yet
- Edm-760 Quick Reference Guide: How To Use Leanfind (Page 13)Document59 pagesEdm-760 Quick Reference Guide: How To Use Leanfind (Page 13)jpzemogNo ratings yet
- Twisted ThermowellDocument16 pagesTwisted ThermowellpuchuuNo ratings yet
- Industrial RoboticsDocument77 pagesIndustrial RoboticsIslam Fouad100% (4)
- Nox RustDocument7 pagesNox RustBhuvanesh KumarNo ratings yet