Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dokumen PDF 21
Dokumen PDF 21
Uploaded by
Farhan FarhanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dokumen PDF 21
Dokumen PDF 21
Uploaded by
Farhan FarhanCopyright:
Available Formats
less gravitational potential energy than it did in its upright position, and thus,
it is more stable. Unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation in a spon-
Radiation Protection taneous process (a process that does not require energy) called radioactive
Technician decay. Unstable radioactive atoms undergo radioactive decay until they form
Do you like the idea of protect- stable nonradioactive atoms, often of a different element. Several types of
ing the health of others?
Would you enjoy the challenge
radiation are commonly emitted during radioactive decay.
of removing contaminated
materials? If so, consider a
career as a radiation protection
Types of Radiation
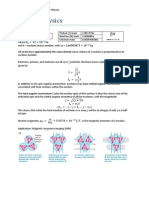
technician. Scientists began researching radioactivity in the late 1800s. By directing radi-
Radiation protection techni- ation from a radioactive source between two electrically charged plates,
cians use radiation measuring scientists were able to identify three different types of radiation. As you can
instruments to locate and see in Figure 4-19, some of the radiation was deflected toward the negatively
assess the risk posed by con-
taminated materials. Then they charged plate, some was deflected toward the positively charged plate, and
decontaminate the area with some was not deflected at all.
high-pressure cleaning equip-
ment and remove the radioac- Alpha radiation Scientists named the radiation that was deflected toward
tive materials. The work often the negatively charged plate alpha radiation. This radiation is made up of
requires the technicians to
wear protective suits. The phys- alpha particles. Each alpha particle contains two protons and two neutrons,
ically demanding work is care- and thus has a 2+ charge. As you know, opposite electrical charges attract.
fully planned and carried out, So the 2+ charge explains why alpha particles are attracted to the negatively
with an emphasis on safety.
charged plate shown in Figure 4-19. An alpha particle is equivalent to a
helium-4 nucleus and is represented by 42He or !. The alpha decay of radioac-
tive radium-226 into radon-222 is shown below.
226 Ra 0 222 Rn " 4 He
88 86 2
radium-226 radon-222 alpha particle
Note also that a new element, radon (Rn), is created as a result of the alpha
decay of the unstable radium-226 nucleus. The type of equation shown above
is known as a nuclear equation because it shows the atomic number and mass
number of the particles involved. It is important to note that both mass num-
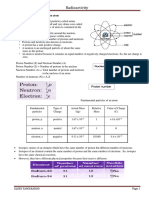
Figure 4-19 ber and atomic number are conserved in nuclear equations. The accounting
Because alpha, beta, and of atomic numbers and mass numbers below shows that they are conserved.
gamma radiation possess differ- 226 Ra
ent amounts of electrical charge, 88 0 222 4
86 Rn " 2 He
they are affected differently by Atomic number: 88 0 86 " 2
an electric field. Gamma rays,
which carry no charge, are not
Mass number: 226 0 222 " 4
deflected by the electric field.
Beta
Positive plate particles
(1" charge) $
Lead block Hole !
Gamma rays
(no charge)
#
Alpha
particles !
Radioactive "
(2! charge)
source Negative plate
Zinc sulfide
coated screen
106 Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom
You might also like
- Your English Pal ESL Lesson Plan Nuclear Power Student v1Document4 pagesYour English Pal ESL Lesson Plan Nuclear Power Student v1Yulia Petrishak100% (1)
- Nuril Trisnawati Te2Document3 pagesNuril Trisnawati Te2Nuril Trisnawati83% (6)
- Physics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics Cheat SheetmifewpmfewpoNo ratings yet
- 2922radioactivity Summary Cheat Sheet..Aidan MatthewsDocument3 pages2922radioactivity Summary Cheat Sheet..Aidan MatthewsSyed Mairaj Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document47 pagesSession 2Manish YadavNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity: by T.H. MusondelaDocument11 pagesRadioactivity: by T.H. MusondelaGrace jereNo ratings yet
- Rutherford Model of The AtomDocument17 pagesRutherford Model of The AtomChris Kevin LubgubanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 RadioactivityDocument64 pagesLecture 2 RadioactivityKakon AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Atomic - Physics NotesDocument10 pagesAtomic - Physics Notesrheanna.bartonNo ratings yet
- 02a LASERs Session 2 (ND YAG Laser, He-Ne Laser and Semiconductor Laser)Document7 pages02a LASERs Session 2 (ND YAG Laser, He-Ne Laser and Semiconductor Laser)Bibaswan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Radioactive C5 F5 PhysicsDocument22 pagesRadioactive C5 F5 PhysicsMrinaliniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 RadioactivityDocument21 pagesChapter 29 RadioactivityAlicia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity and NuclearDocument7 pagesRadioactivity and NuclearmustafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document10 pagesChapter 7DUIN 1o1 VlogsNo ratings yet
- SOLA2060 Introduction To Electronic Devices Semester 1, 2019Document43 pagesSOLA2060 Introduction To Electronic Devices Semester 1, 2019Marquee BrandNo ratings yet
- 16 RadioactivityDocument66 pages16 RadioactivityKashish AroraNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 22Document1 pageDokumen PDF 22Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- ScitslidDocument80 pagesScitslidNick kNo ratings yet
- 11 Atoms and NucleiDocument13 pages11 Atoms and NucleiHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Space Power Systems-Teofilo-2008Document52 pagesAdvanced Space Power Systems-Teofilo-2008AndyNo ratings yet
- F5 CH 5 TeacherDocument12 pagesF5 CH 5 Teachersekolah-1152No ratings yet
- Na Ion Comparison With Lion Cells 16 11 16Document22 pagesNa Ion Comparison With Lion Cells 16 11 16venugopalan srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Silver Oxide Battery: Parts: UsesDocument1 pageSilver Oxide Battery: Parts: UsesGino AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 Kertas 1 Tenaga NuklearDocument7 pagesBab 6 Kertas 1 Tenaga Nuklearnorhazilah ghazaliNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 7Document1 pageDokumen PDF 7Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Fizik Bab 8Document12 pagesFizik Bab 8ee9999No ratings yet
- Chapter 29 RadioactivityDocument21 pagesChapter 29 RadioactivityReef WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry EM Minimum Study Material English Medium PDF DownloadDocument8 pages11th Chemistry EM Minimum Study Material English Medium PDF Downloadjencys16No ratings yet
- 43 DecayDocument9 pages43 DecayMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Properties of Alpha, Beta and Gamma Rays and DifferencesDocument2 pagesProperties of Alpha, Beta and Gamma Rays and Differencesمنیر بلوچNo ratings yet
- RPO Mind MappingDocument8 pagesRPO Mind MappingAjimKe'enNo ratings yet
- 26 RadioactivityDocument117 pages26 Radioactivityrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Ut2 EPII (QB SOLN)Document21 pagesUt2 EPII (QB SOLN)otherwork3757No ratings yet
- Lab4 F15 Si DiodeDocument15 pagesLab4 F15 Si DiodeJohn MarkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Paper 1 Vle SCDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Paper 1 Vle SCsharinhanumNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument22 pagesRadioactivitymerezemenike272No ratings yet
- Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument70 pagesAtomic and Nuclear PhysicsGiovanni SlackNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety TrainingDocument118 pagesRadiation Safety TrainingZibiao SunNo ratings yet
- 13.3 RadioactivityDocument117 pages13.3 RadioactivityHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Radioactive EmissionDocument23 pagesRadioactive EmissionbreanacolmanNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Introduction To Nuclear RadioactivityDocument45 pages7.1 Introduction To Nuclear RadioactivityReyzhel Mae MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Bab 8 Notes and Latihan Form 3 PtsiDocument15 pagesBab 8 Notes and Latihan Form 3 PtsiShanti Guna0% (1)
- Form 5 Chapter 5 RadioactivityDocument54 pagesForm 5 Chapter 5 RadioactivityJr LiuNo ratings yet
- As Radioactivity 2016Document21 pagesAs Radioactivity 2016Lawrence OnthugaNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Decay and Half LifeDocument30 pagesRadioactive Decay and Half LifeM Imran SheikhNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Nuclear ChemistryDocument58 pagesLecture On Nuclear Chemistrysadia SultanaNo ratings yet
- Ian Appelbaum: Electrical and Computer Engineering University of DelawareDocument39 pagesIan Appelbaum: Electrical and Computer Engineering University of DelawareLIAKMANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-5 PDFDocument355 pagesChapter 1-5 PDFShakhawat Hossain ShovonNo ratings yet
- IB PHYSICS 7.1 and 12.2 RadioactivityDocument52 pagesIB PHYSICS 7.1 and 12.2 RadioactivityJustCallMeLarryNo ratings yet
- Studyguide-5 - Radioactivity and Nuclear EnergyDocument20 pagesStudyguide-5 - Radioactivity and Nuclear EnergyytNo ratings yet
- Basics of Radiation LeafletDocument2 pagesBasics of Radiation LeafletAhmed shabanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 N and P Type SemiconductorsDocument19 pagesLecture 2 N and P Type SemiconductorsTaahir YousafNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Inorganic Chemistry - Part 2Document5 pagesIntroduction To Inorganic Chemistry - Part 2Mohamad AzaniNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Aakash NeetDocument64 pagesAtomic Structure Aakash NeetPrashanthPatroNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument15 pagesModern PhysicsDr. Unoma OkoraforNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RadioactivityDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Radioactivitydeshmukhradhika146No ratings yet
- Deleted Portion Physics - 042Document2 pagesDeleted Portion Physics - 042Keval PatelNo ratings yet
- Surface Analysis by Accelerated Ion BeamsDocument53 pagesSurface Analysis by Accelerated Ion BeamsIatephysicsNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity - 2023 EditedDocument25 pagesRadioactivity - 2023 EditedLIZ HELENA A/P SUBRAMANIAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Basic Nuclear Physics 3 - Rad. DisintegrationDocument42 pagesLecture 3 - Basic Nuclear Physics 3 - Rad. DisintegrationDidik Setyawarno 198810132015041004No ratings yet
- RADIOACTIVITYDocument12 pagesRADIOACTIVITYAlusine BasmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Atomic Structure & Periodic Table: El-WakilDocument17 pagesUnit 2: Atomic Structure & Periodic Table: El-Wakilmaryamhaitham805No ratings yet
- Structure and Application of Galvanomagnetic Devices: International Series of Monographs on SemiconductorsFrom EverandStructure and Application of Galvanomagnetic Devices: International Series of Monographs on SemiconductorsNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 38Document1 pageDokumen PDF 38Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 45Document1 pageDokumen PDF 45Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 36Document1 pageDokumen PDF 36Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 42Document1 pageDokumen PDF 42Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 32Document1 pageDokumen PDF 32Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 26Document1 pageDokumen PDF 26Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 46Document1 pageDokumen PDF 46Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 28Document1 pageDokumen PDF 28Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 17Document1 pageDokumen PDF 17Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 16Document1 pageDokumen PDF 16Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 9Document1 pageDokumen PDF 9Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 58Document1 pageDokumen PDF 58Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 12Document1 pageDokumen PDF 12Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 4Document1 pageDokumen PDF 4Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 2Document1 pageDokumen PDF 2Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 3Document1 pageDokumen PDF 3Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - RadioactivityDocument28 pagesChapter 12 - RadioactivityAljoša GraovacNo ratings yet
- FC Rad Onc (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2012 Mar 28-4-2014Document6 pagesFC Rad Onc (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2012 Mar 28-4-2014matentenNo ratings yet
- Course-Guide EnggchemDocument13 pagesCourse-Guide EnggchemAereal MariNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument8 pagesNuclear Physics NotesCai Peng Fei100% (1)
- Physical Science: Modules From Central OfficeDocument12 pagesPhysical Science: Modules From Central OfficeR TECHNo ratings yet
- 27h Radiography PermitDocument1 page27h Radiography PermitMohammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-2d-3d-nmrDocument104 pagesChapter 3-2d-3d-nmrMELVINDO JACOBNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1 BackgroundDocument16 pagesChapter One 1.1 BackgroundHorllyNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 WS Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesActivity 2 WS Atomic StructureIshaan (Sparkz Гига товарищ)No ratings yet
- Electron Spin Orbital Angular Momentum Total Angular Momentum Nuclear Magnetic MomentDocument3 pagesElectron Spin Orbital Angular Momentum Total Angular Momentum Nuclear Magnetic MomentSURESH SURAGANINo ratings yet
- Laporan Unit 3Document48 pagesLaporan Unit 3Nisma yantiNo ratings yet
- CHEM 418 Quiz 1-1Document12 pagesCHEM 418 Quiz 1-1hengyu muNo ratings yet
- 42 11997 3239 469 PDFDocument27 pages42 11997 3239 469 PDFFlávio Augusto SoaresNo ratings yet
- Iesis: Synt StarsDocument108 pagesIesis: Synt StarsDhruv DharamshiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam of Nuclear Medicine Physics: 1) Choose The Correct AnswerDocument4 pagesFinal Exam of Nuclear Medicine Physics: 1) Choose The Correct AnswerabdulfatahalhemeryNo ratings yet
- STUDENT ChemTourWorkbook2022v01Document22 pagesSTUDENT ChemTourWorkbook2022v01Dhyey PatelNo ratings yet
- Appendix I: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument38 pagesAppendix I: Multiple Choice Questionsmukul sidhqueNo ratings yet
- Brachytherapy: Physical and Clinical AspectsDocument163 pagesBrachytherapy: Physical and Clinical AspectsmarwaziwajiNo ratings yet
- WWW Indiabix Com General Knowledge General Science 039001Document3 pagesWWW Indiabix Com General Knowledge General Science 039001iraj shaikhNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics and Nuclear PhysicsDocument8 pagesAtomic Physics and Nuclear Physicskaranubhab3No ratings yet
- Chapter 002Document2 pagesChapter 002Zaid jutt100% (1)
- MemonDocument5 pagesMemonvamsi NathNo ratings yet
- Trends in The Periodic TableDocument34 pagesTrends in The Periodic TableCaribelatinaNo ratings yet
- Help For Rad Pro CalculatorDocument21 pagesHelp For Rad Pro CalculatorNikolić MladenNo ratings yet
- Exercise - V: JEE-ProblemsDocument3 pagesExercise - V: JEE-ProblemsAshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A-LEVEL PHY1 June 2001 QPDocument2 pagesEdexcel A-LEVEL PHY1 June 2001 QPapi-3726022No ratings yet