Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Biology
Uploaded by
ParshvaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Biology
Uploaded by
ParshvaCopyright:
Available Formats
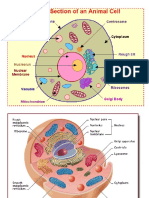
Chapter 2: Organisation of the organism
Definitions:
1. Cell: smallest unit from which all organisms are made.
2. Tissue: a group of similar cells that work together to perform a particular
function.
3. Organ: a group of tissues that work together to perform a particular function.
4. Organ system: several organs that work together to perform a particular
function.
5. Organism: a living thing
Important pointers:
● Cell wall: supports cell, gives structure
● Cell membrane: controls what enters and exits a cell based on the size of the
hole in it.
● Cytoplasm:
● Ribosomes: protein synthesis
● Mitochondria: site of aerobic respiration
● Chloroplast: contains chlorophyll which captures energy from sunlight which is
necessary for
● Nucleus: contains genetic information
● Flagilm: Allows movement (and/or swimming)
● Plasmids: Contains genetic information (also used in biotechnology)
● Animal cells contain cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, mitochondria and
nucleus.
● Plant cells contain cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuoles,
mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus and usually chloroplasts.
● Bacterial cells contain cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, circular
DNA and plasmids.
● Cell theory
○ All organisms are composed of cells
○ They are the structural and functional units of all organisms
○ All cells arise from pre-existing cells
○ Every organisms starts life as a single cell
● Specialised cells
○ Ciliated cells: adapted for movement of mucus in bronchi and trachea
and ovule in fallopian tube.
○ Root hair cells: adapted for absorption.
○ Palisade mesophyll cell: adapted for photosynthesis.
○ Neurones: adapted for conducting electrical impulses.
○ Red blood cells: adapted for transport of oxygen
○ Sperm and egg cells (gametes) : adapted for reproduction
● Magnification = image / actual
You might also like
- Cell Types & Cell ModificationDocument41 pagesCell Types & Cell ModificationShane Marcande Calicdan78% (18)
- General Biology 2Document13 pagesGeneral Biology 2Iren Castor MabutinNo ratings yet
- Genetics Module 2ADocument9 pagesGenetics Module 2ACelest KnightwalkerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeDocument38 pagesLesson 5.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeJENNILYN CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cell: Sri Guru Ram Das Instituite of Dental Sciences and Research Sri AmritsarDocument61 pagesSeminar On Cell: Sri Guru Ram Das Instituite of Dental Sciences and Research Sri AmritsarKomal MittalNo ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellDocument18 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Week 3: Cells and Tissues-Part 1 Cells - Structure and FunctionDocument27 pagesWeek 3 Week 3: Cells and Tissues-Part 1 Cells - Structure and FunctionJEANNo ratings yet
- Unite 3 CellsDocument44 pagesUnite 3 CellsJo AnNo ratings yet
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Biology - Exam #2Document14 pagesBiology - Exam #2Juliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsAmabelle DorothyNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Its OrganellesDocument21 pagesThe Cell and Its OrganellesKP DizonNo ratings yet
- Grade 12-General Biology (Cells)Document11 pagesGrade 12-General Biology (Cells)angeliaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsapi-95529788100% (1)
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- The Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesThe Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveHershell ContaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeDocument39 pagesLesson 5.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeMarjorie CaneteNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Guide Test 2Document9 pagesBiology Study Guide Test 2sharrone halimNo ratings yet
- 3cell Structure FunctionDocument51 pages3cell Structure FunctionenccaNo ratings yet
- Cells As The Basis of Life 1Document40 pagesCells As The Basis of Life 1Singh Gurleen100% (1)
- General-Biology ReviewerDocument24 pagesGeneral-Biology ReviewerBulbasaur NyaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.1 Cell Structure and Organisation FDocument34 pagesUnit 2.1 Cell Structure and Organisation FqdxtcmvzgzNo ratings yet
- CELLS BiologyDocument8 pagesCELLS BiologyKYLENE ABELLANANo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 CIE Biology A-LevelDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 CIE Biology A-LeveloqypooNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument8 pagesScience Notesfecol32501No ratings yet
- Summary Notes CH 2Document4 pagesSummary Notes CH 2Wee Too LoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument22 pagesCellrapidalerthubNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CAIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CAIE Biology IGCSE PDFZaid Bin salmanNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CIE Biology IGCSECarola Bogezi100% (1)
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument45 pagesCell Theoryjustine caintoyNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument41 pagesAnimal and Plant CellSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Biology Midterms 2021Document13 pagesBiology Midterms 2021Keano GelmoNo ratings yet
- Post Lab - Activity 1 Cell BioDocument32 pagesPost Lab - Activity 1 Cell Bioraphael100% (1)
- Cell OrganellesDocument42 pagesCell OrganellesTrisha OxalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson#4 - Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesLesson#4 - Cell Biologyjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Biology Sem1 - Chap1Document78 pagesBiology Sem1 - Chap1kotaknotaku100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Biology NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 1 - Biology Noteshuman tie lineNo ratings yet
- In Focus CSS: GSA Lecture 2 DR Bushra Javed SiddiquiDocument40 pagesIn Focus CSS: GSA Lecture 2 DR Bushra Javed SiddiquiBushra JavedNo ratings yet
- Cells: BIO100 Sumaiya Afrin SohaDocument27 pagesCells: BIO100 Sumaiya Afrin SohaNafees Hasan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Class 1 - Cell StructureDocument19 pagesClass 1 - Cell StructureSukanta SabatNo ratings yet
- 01-The CellDocument25 pages01-The Cellfordgt989No ratings yet
- CELLDocument8 pagesCELLRajendra Chikkamath100% (1)
- Biology Class Notes: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesBiology Class Notes: Cell Structure and FunctionAndre WelsNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument1 pageCell Biology Noteslog.pfoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesDocument35 pagesChapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesFairview PenangNo ratings yet
- Forest Botany For Forestry StudentsDocument39 pagesForest Botany For Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- L.3 - The CellDocument3 pagesL.3 - The CellJari JariNo ratings yet
- Aravinth Pandian BioDocument28 pagesAravinth Pandian BioThalapathi AravinthNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsDocument121 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsJoan Ano CaneteNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument33 pagesCell Structure and FunctionFahim Abid100% (1)
- Biology Basic ConceptsDocument6 pagesBiology Basic ConceptsAhsni128No ratings yet
- 1..cell Structure and FunctionDocument53 pages1..cell Structure and FunctionAminath MeesanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 BioDocument39 pagesTopic 3 BioTsukiNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pages8 Cell The Unit of Lifebikram keshari pradhanNo ratings yet
- Se Mi N Nhóm 1Document87 pagesSe Mi N Nhóm 1Trịnh Bảo MinhNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet