0% found this document useful (0 votes)
664 views2 pagesATP-sheet Worksheet
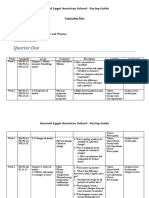
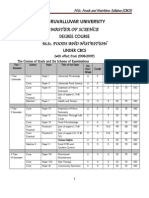
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate. It provides energy for many cellular processes through its hydrolysis into ADP and inorganic phosphate. ATP is synthesized from ADP through the addition of phosphate groups, catalyzed by the enzyme ATP synthase, either through photosynthesis, cellular respiration, or substrate-level phosphorylation. ATP is a better immediate energy source than glucose because it releases energy in smaller amounts through a single reaction, while glucose breakdown requires multiple reactions. Cells can also contain AMP, which is similar to ATP but with only one phosphate group.
Uploaded by
Valentina RumhizhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
664 views2 pagesATP-sheet Worksheet
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate. It provides energy for many cellular processes through its hydrolysis into ADP and inorganic phosphate. ATP is synthesized from ADP through the addition of phosphate groups, catalyzed by the enzyme ATP synthase, either through photosynthesis, cellular respiration, or substrate-level phosphorylation. ATP is a better immediate energy source than glucose because it releases energy in smaller amounts through a single reaction, while glucose breakdown requires multiple reactions. Cells can also contain AMP, which is similar to ATP but with only one phosphate group.
Uploaded by
Valentina RumhizhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd