Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ángulos 4
Uploaded by
Ana GuardianiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ángulos 4
Uploaded by
Ana GuardianiCopyright:
Available Formats
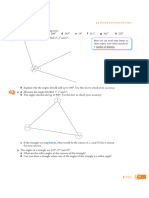
Desktop revision – Angles
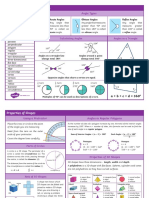
Acute – less than 90° Remember to give reasons and/or A right angle is 90°.
Obtuse – greater than workings for your answers!
90°, less than 180°
1. Calculate the value of a.
Reflex – greater than
Angles at a point add
180°, less than 360°
up to 360°.
35° a
Angles on a straight
2. Calculate the value of b. Angles in a triangle
line add up to 180°.
add up to 180°.
b
75° 35°
Corresponding angles Alternate angles are
are equal. 3. Calculate the value of c. equal.
c
125° 135°
4. Calculate the value of d.
d
130°
Allied/interior angles
Base angles in an
5. Calculate the value of e. sum to 180°.
isosceles triangle are
equal.
e
120°
6. Calculate the value of f.
20° 3f 2f Opposite angles are
equal.
7. Calculate the bearing from A to B and
the bearing to A from B.
In regular shapes:
N
1. all angles are equal
2. all sides are equal. B 55°
A
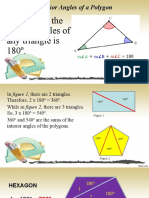
For any polygon,
For any polygon, the 8. Calculate the value of one interior corresponding interior
sum of interior angle in a regular decagon. and exterior angles
angles is sum to 180°.
(sides – 2) × 180. 9. Four interior angles in a pentagon are
100. What is the value of the fifth angle?
10. Here is part of a regular polygon. Bearings are always:
In any polygon, How many sides does this shape have?
1. measured c/w from
exterior angles sum North
to 360°. 162° 2. given in 3 figures.
3 triangle | 4 quadrilateral | 5 pentagon | 6 hexagon | 7 heptagon | 8 octagon | 10 decagon
© www.teachitmaths.co.uk 2013 20852 Page 1 of 2
Desktop revision – Angles
Teaching notes
This resource contains a selection of questions accompanied by revision notes.
Suggested uses
- Use as an individual revision sheet, homework, cover work, open book test, etc.
- Photocopy onto A3 and use as a poster during revision season.
- Laminate and tape to the desk for small group revision. You could create ‘revision
stations’ with other Desktop revision resources on www.teachitmaths.co.uk (quick
search: ‘desktop’).
Answers
1. 55° (angles on a straight line sum to 180°)
2. 70° (angles in a triangle sum to 180°)
3. 100° (angles at a point sum to 360°)
4. 80° (base angles in an isosceles triangle are equal (50° each), and angles in a triangle
sum to 180°)
5. 120° (alternate angles are equal)
3f + 2f + 20 = 180
6. 5f = 160 (angles on a straight line sum to 180°)
f = 32 o
7. A to B = 305° (bearings are measured c/w from North)
B to A = 125° (for return bearings, ±180°)
8. Angles in a decagon = (10 – 2) × 180 = 1440°
1440
One angle = = 144°
10
9. Angles in a pentagon = (5 – 2) × 180 = 540°
Fifth angle = 540 – 400 = 140°
10. One exterior angle = 180 – 162 = 18°
360
= 20 sides
18
© www.teachitmaths.co.uk 2013 20852 Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Angles in Parallel Lines (Print)Document7 pagesAngles in Parallel Lines (Print)Lionel Ronaldo100% (1)
- Angles - Exam Revision and QuestionsDocument10 pagesAngles - Exam Revision and Questionsben chordNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Geometry - UnlockedDocument42 pagesChapter 6 - Geometry - UnlockedAlyssa L100% (2)
- 6.1 - Radian Measure and Arc Length Math 30-1Document14 pages6.1 - Radian Measure and Arc Length Math 30-1Math 30-1 EDGE Study Guide Workbook - by RTD LearningNo ratings yet
- Airbus GlossaryDocument32 pagesAirbus GlossaryLuís Rodrigues100% (2)
- Angles RevisionDocument4 pagesAngles RevisionViet Hoang Quoc100% (1)
- Mathematics-Form 3-Chapter 1, 2, 3 & 4 by KelvinDocument10 pagesMathematics-Form 3-Chapter 1, 2, 3 & 4 by KelvinKelvin33% (3)
- Unit 5Document24 pagesUnit 5christal100% (1)
- Sum of The Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonDocument15 pagesSum of The Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonMaricel Balbuena100% (1)
- MathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14From EverandMathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14No ratings yet
- MiG 21Document29 pagesMiG 21Zoran Vulovic100% (2)
- Rules of Angles in Parallel Lines and Polygons (7-9Document6 pagesRules of Angles in Parallel Lines and Polygons (7-9Nancy RadwanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3Document6 pagesLesson Plan 3darlene bianzon67% (9)
- Deductive Geometry: This Chapter at A GlanceDocument46 pagesDeductive Geometry: This Chapter at A Glancesquishyapply100% (1)
- Dialysis PrescriptionDocument23 pagesDialysis PrescriptionMercy Juliana Jacqualine100% (1)
- II PUC PHYSICS - Previously Appeared Questions and Answers For 2021 Exam by MANJUNATH BDocument52 pagesII PUC PHYSICS - Previously Appeared Questions and Answers For 2021 Exam by MANJUNATH BVishal Ramesh100% (1)
- Referencia 8Document130 pagesReferencia 8Kimiko SullonNo ratings yet
- DL Throughput Improvement with Aperiodic CQI ReportingDocument10 pagesDL Throughput Improvement with Aperiodic CQI ReportingAqeel HasanNo ratings yet
- Grade 7: Applications of PolygonDocument9 pagesGrade 7: Applications of PolygonMa Teneza BarberoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Revision Summary 4: Angle Types Key VocabularyDocument2 pagesGeometry Revision Summary 4: Angle Types Key VocabularyPol PogbaNo ratings yet
- Angles in Polygons (Print)Document6 pagesAngles in Polygons (Print)Suchaya AngsakulNo ratings yet
- Geometry Quick Guide 1: Angles: Angle Types Angle RulesDocument1 pageGeometry Quick Guide 1: Angles: Angle Types Angle RulesROSLINA BINTI ABDUL RASHID MoeNo ratings yet
- Digital Text BookDocument12 pagesDigital Text BookBindu Vinu100% (1)
- Polygons: Plane and Solid GeometryDocument37 pagesPolygons: Plane and Solid GeometryMarjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Angles of RotationDocument34 pages13.2 Angles of RotationKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- formula angle chpter 5Document1 pageformula angle chpter 5AidaNo ratings yet
- Junior78 Oct14-SolnsDocument13 pagesJunior78 Oct14-SolnsEva KardhashiNo ratings yet
- PRECAL Final Module 1 4Document41 pagesPRECAL Final Module 1 4Glen MillarNo ratings yet
- Junior78 - Oct14 QDocument13 pagesJunior78 - Oct14 QMahisa AgniNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK6 INTERIOR and EXTERIOR ANGLES of A CONVEX POLYGONDocument82 pagesQ3 WEEK6 INTERIOR and EXTERIOR ANGLES of A CONVEX POLYGONlito77No ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About PolygonsDocument13 pagesEverything You Need to Know About PolygonsSameh SalahNo ratings yet
- Angles in Parallel Lines PowerPointDocument27 pagesAngles in Parallel Lines PowerPointxq86tqyhwhNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Classifying AnglesDocument4 pagesMeasuring and Classifying AnglesMUDABBIR HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals: AB, BC, CD, and DA Are Sides andDocument5 pagesQuadrilaterals: AB, BC, CD, and DA Are Sides andAlliah Mae CastilNo ratings yet
- Polygons Matching Pairs AnswersDocument2 pagesPolygons Matching Pairs AnswersKAVITHA CHANDRANNo ratings yet
- PPT2 Unit CircleDocument34 pagesPPT2 Unit CircleJejuvs TgmelyNo ratings yet
- Angle PropertiesDocument2 pagesAngle PropertiesGEGENo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: AnglesDocument66 pagesLearning Objectives: AnglesKhan AfghanNo ratings yet
- COT1 Polygon CLAROSDocument42 pagesCOT1 Polygon CLAROSShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument28 pagesPolygonsKENO MARTIN ADVIENTONo ratings yet
- FSMQ Angles RemovedDocument3 pagesFSMQ Angles RemovedDj GNo ratings yet
- 8-1 Measurement of Arcs (Presentation)Document13 pages8-1 Measurement of Arcs (Presentation)Sandra Miller100% (1)
- Exterior AngleDocument20 pagesExterior Angledrky2mms5qNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5. Angle Measurement Unit Circle Circular FunctionsDocument10 pagesLesson 5. Angle Measurement Unit Circle Circular FunctionsDiane MorosNo ratings yet
- Angle.MathsDocument1 pageAngle.Mathstranthihuong205No ratings yet
- Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument12 pagesUnderstanding QuadrilateralsWai MarNo ratings yet
- Quarter3 - Module - Week5Document1 pageQuarter3 - Module - Week5JAMAICA PAULA REGALANo ratings yet
- Coterminal AnglesDocument19 pagesCoterminal AnglesfafafaNo ratings yet
- 5.3-5.4 Calculating Angles Calculating Angles Task 1: Angles About A PointDocument2 pages5.3-5.4 Calculating Angles Calculating Angles Task 1: Angles About A PointSarwat El MarwanyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 5Document4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 5Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Page 1Document3 pagesWorksheet 1 Page 1Nathaniel PascuaNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT 2.1 (Module 1) : Name: Roszel Anne Carina I. Cardino Grade & Section: 11-Banzon ScoreDocument3 pagesASSESSMENT 2.1 (Module 1) : Name: Roszel Anne Carina I. Cardino Grade & Section: 11-Banzon ScoreRoszel Anne Carina CardinoNo ratings yet
- Precal ModuleeeeeeeDocument18 pagesPrecal ModuleeeeeeeCaila AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Polygons2Document26 pagesChapter 3 Polygons2Jonard G. TrajanoNo ratings yet
- Learn trigonometry fundamentals with the unit circleDocument5 pagesLearn trigonometry fundamentals with the unit circleBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Unit 23.5 HomeworkDocument1 pageUnit 23.5 HomeworkCHEW YE-HAUR IAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Department of EducationDocument16 pagesDepartment of EducationJulie Ann DefitaNo ratings yet
- LeaP Math G7 Week 6 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Math G7 Week 6 Q3Azenith CastroNo ratings yet
- TJP Top Tips: Igcse Shape & SpaceDocument24 pagesTJP Top Tips: Igcse Shape & SpaceChrystal BrownNo ratings yet
- Polygons - Classifying by Properties and TheoremsDocument5 pagesPolygons - Classifying by Properties and TheoremsJulia Ricel DomingoNo ratings yet
- Aw 02Document7 pagesAw 02abigail MallariNo ratings yet
- Geometrical ProofDocument4 pagesGeometrical ProofKristie CorpusNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems: Key PointsDocument9 pagesCircle Theorems: Key PointsTalha AzanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Shape SpaceDocument24 pagesIGCSE Shape Spacedemiyang030No ratings yet
- Angles & Parallel LinesDocument20 pagesAngles & Parallel LinesMansoor MithaiwalaNo ratings yet
- Sui Gas Connection FormsDocument1 pageSui Gas Connection Formsare50% (2)
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerFrank Jomari MurilloNo ratings yet
- CRRT (RVS) One Day TrainingDocument46 pagesCRRT (RVS) One Day TrainingwantoNo ratings yet
- Aisladores Polimericos vs. Aisladores Ceramicos Unmsm PDFDocument22 pagesAisladores Polimericos vs. Aisladores Ceramicos Unmsm PDFvgcasasNo ratings yet
- Skin LesionDocument5 pagesSkin LesionDominic SohNo ratings yet
- Ic F3022SDocument36 pagesIc F3022SEfren.galNo ratings yet
- Ymfc Al SetupDocument18 pagesYmfc Al SetupredaNo ratings yet
- Cancer EssayDocument4 pagesCancer EssayCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Book Review - Water, Ecosystems and Society A Confluence of Disciplines. by Jayanta BandyopadhyayDocument2 pagesBook Review - Water, Ecosystems and Society A Confluence of Disciplines. by Jayanta BandyopadhyayPDNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized Title for Quantitative Techniques for Business-II Exam DocumentDocument4 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for Quantitative Techniques for Business-II Exam DocumentEthan WillsNo ratings yet
- Usg Iom PDFDocument56 pagesUsg Iom PDFAnonymous 7xHNgoKE6eNo ratings yet
- Model146C DynamicGasCal 156file - 18125Document150 pagesModel146C DynamicGasCal 156file - 18125api-26966403100% (1)
- Incremental and Newton Methods Lab ReportDocument10 pagesIncremental and Newton Methods Lab ReportAbde RrahimNo ratings yet
- Bitterness Compounds in Coffee Brew Measured by Analytical Instruments and Taste Sensing SystemDocument34 pagesBitterness Compounds in Coffee Brew Measured by Analytical Instruments and Taste Sensing SystemSolisNo ratings yet
- Sunningdale School Notes Summer 2022Document12 pagesSunningdale School Notes Summer 2022sunningdaleschoolNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Week 1 ActivitiesDocument4 pagesPhysical Education Week 1 ActivitiesTummys TummieNo ratings yet
- AmadiDocument18 pagesAmadijawad bello aNo ratings yet
- Process Modeling in The Pharmaceutical Industry Using The Discrete Element MethodDocument29 pagesProcess Modeling in The Pharmaceutical Industry Using The Discrete Element MethodRonaldo MenezesNo ratings yet
- 3 Uscg BWM VRPDocument30 pages3 Uscg BWM VRPdivinusdivinusNo ratings yet
- July 17, 2015 Strathmore TimesDocument32 pagesJuly 17, 2015 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- Analyzing the Effects of Changing the Values of a, b, and c in the Equation of a Quadratic Function on Its GraphDocument13 pagesAnalyzing the Effects of Changing the Values of a, b, and c in the Equation of a Quadratic Function on Its GraphRamil NacarioNo ratings yet
- Hoist by TechnologyDocument6 pagesHoist by TechnologyAnonymous ntE0hG2TPNo ratings yet
- D.K.Pandey: Lecture 1: Growth and Decay of Current in RL CircuitDocument5 pagesD.K.Pandey: Lecture 1: Growth and Decay of Current in RL CircuitBBA UniversityNo ratings yet
- Atoms & Ions Worksheet 1 /63: Atomic Number and Mass NumberDocument4 pagesAtoms & Ions Worksheet 1 /63: Atomic Number and Mass Numbercate christineNo ratings yet