Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Job Safety Analysis For Confined Space Work
Uploaded by
69housepartyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Job Safety Analysis For Confined Space Work
Uploaded by
69housepartyCopyright:
Available Formats
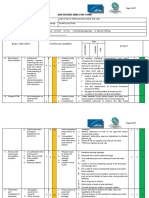
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS
Job description: Confined space entry Location: Workshop Date: 15/10/2023
No Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Selected Comments
1 Hard Hat Y
2 Air Purifying Respirator Y
3 Supplied Air Respirator - SCBA Y
4 Gloves Y
5 Safety Footwear Y
6 Proper PPE per company Guidelines Y
7 Gas Monitor Y Based on results of Hazard Assessment
8 Other Y Coveralls appropriate to job
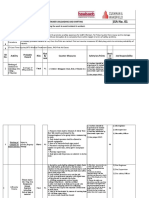
Job Steps
No Job Steps Potential Hazard Critical Actions
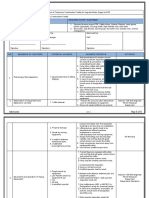
1 1. Ensure description of work identifies the
specific type of confined space: pit, tank,
1. Lack of hazard awareness of the specific
excavation, pipe, tunnel, etc. and that
confined space leading to injury or fatality.
Identify need to conduct confined space entry competent personnel conduct the hazard
during job planning. assessment.
2. Confirm the entry/work location, and
2. Loss of time, potential injury or fatality if wrong
communicate work intentions to appropriate
location is identified, assessed or entered.
personnel.
2
Prepare Work Permit and Confined Space 1. Potential confined space hazards not identified 1. Follow the Confined Space Entry SAFE
Entry Form. may cause injury or incident. WORK PRACTICES Standard instructions.
3 1a. Include competent persons in JSA
1. Hazardous energy sources affecting confined
Conduct job site and equipment preparation. development to ensure identification of all
space not properly identified or positively isolated.
sources of hazardous energy.
2. Unauthorized access of personnel to work area 1b. Identify and isolate sources of hazardous
leading to injury. energy.
3
3. Evacuation routes not identified leading to 2. Place barricades and signs to restrict
workers confusion in an emergency. access to work site.
4. Previous contents of confined space not 3a. Identify evacuation routes during site
evaluated for hazards leading to injury. assessment.
5. Equipment with internal combustion engines in
close proximity to the confined space may cause 3b. Develop contingency and emergency
accumulation of carbon monoxide (CO) inside the rescue plans. Include the following in the
space or create a source of ignition for flammable Rescue Plan:
vapors venting from the confined space.
6. Gas detector not calibrated, not properly
maintained (faulty sensors, battery not fully
· Procedures for reporting emergencies
charged, etc.) or not fitted with sensors for the
suspected leading to erroneous readings.
7. Competent personnel not identified or not
· Emergency escape routes
available leading to poor decision quality.
8. Improper access to entry and exit point
· Rescue equipment required
openings leading to injury.
9. Toxic or flammable vapors released by
· The designated emergency assembly
disturbing sludge product inside tanks leading to
area
fire, injury or fatality.
10. Slips, trips and falls due to poor housekeeping · Rescue and first aid procedures and
leading to injury. duties
4. Review existing information about the
previous contents, including material safety
11. Delay in work beginning due to a lack of or data sheets (MSDS) and other relevant
incorrect work permit documentation for the job. information. If sufficient information does not
exist, get help from the appropriate subject
matter experts.
5. Locate equipment with internal combustion
12. Inadequate ventilation and/or cooling which
engines at least 50 feet (15 meters) away
could result in a build up of hazardous vapors
from entry openings and ensure their
and/or heat resulting in suffocation, poisoning
exhausts are directed away from entry
and/or heat stress.
points.
6. Review gas detector records, including
annual calibration record sheet, monthly
calibration sheet and daily field response
sheet. Also verify that the correct sensor for
the gas being detected is installed in the
monitor.
7. Review personnel training records to verify
that they have the competencies to perform
their roles (e.g. Gas Testers, Entry Watch,
Fire Watch, Entrants, Rescue Workers,
excavation competent person, etc.).
8a. Provide secured ladders or stairs to
elevated entry/egress points to verify that
proper fall protection controls are in place.
8b. Evaluate the size and shape of the entry
opening and potential obstacles at entry
point. Review drawings of the space, if
available, to select best location for entry to
avoid awkward entry and obstacles.
8c. Designate a standby person assist with
safe entry and egress of work crew.
9. Review MSDSs to identify precautions and
appropriate PPE. Perform continuous gas
monitoring while sludge is present in the
space.
10. Review housekeeping and correct
deficiencies.
11. Plan the work with competent personnel
and the appropriate subject matter experts
(SMEs) to prepare the correct documentation
per the schedule. Examples of
documentation include work permits with the
required gas testing readings, signatures,
and hazard mitigation and PPE
requirements.
12. Provide adequate ventilation and cooling
equipment (if necessary). Verify that the
equipment is functioning as intended.
4
1. Gas Tester not qualified to test the atmosphere
1. Verify that the Gas Tester is qualified to
Gas test the work site and/or equipment. and interpret the readings leading to incorrect
perform the testing.
readings that may cause injury or fire.
2a. Gas test initially at the opening of the
confined space after the ventilation has been
turned off for a minimum of 15 minutes. If the
2. Readings taken at confined space opening may readings indicate that it is safe to do so, test
not be representative of the internal atmosphere further inside the confined space before
of the confined space. allowing work to start. Note: A separate
permit and Confined Space Entry form is
required if the Gas Tester needs to enter and
test inside the confined space.
3. Failure to test for specific toxic or flammable 2b. Entry Watch must be present for all
gases and vapors may cause injury or fatality. confined space entries.
3. Conduct gas testing for oxygen (O2), toxic
4. Failure to conduct follow-up or continuous gas
and flammable gases and vapors and record
tests (as appropriate) could result in injury or
the results on the permit along with date,
fatality.
time and Gas Tester’s signature.
4. Implement continuous or periodic gas
testing (as specified in the permit) to verify
that the confined space atmosphere remains
5. Not wearing the required PPE or wearing the
safe for entry. Record gas testing results on
incorrect PPE could result in injury or fatality.
the permit or applicable form (example: if
entrants are out of confined space for more
than one hour).
5. Identify the correct PPE and require that
personnel wear it before they enter into the
confined space. Note: When the Gas Tester
must enter into the confined space to
6. Undetected hazardous gases due to
conduct internal gas tests, the PPE must be
malfunctioning of gas detection equipment may
specified on the permit and the Gas Tester
cause injury or fire.
must put it on prior to entering the confined
space. PPE may include supplied air
respirator, coveralls, rubber boots and
personal monitor.
6. Confirm that the gas testing equipment is
calibrated and bump tested.
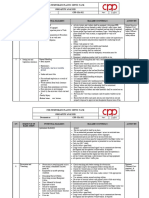
5 1. Entry Watch does not recognize hazards and 1a. Verify that the Entry Watch is competent
react appropriately. for the task.
1b. Provide the Entry Watch with a
communication device to raise the alarm if
there is an emergency.
2. Entry Watch could be overcome by gases or 2. Ensure Entry Watch is up wind from any
Position dedicated Entry Watch personnel at vapors originating from work in confined space potential gas or vapor hazard and is wearing
the confined space. leading to injury or fatality. the appropriate PPE.
3. Monitor the Entrants and their work and
3. Other unit/equipment may be or become a look for potential hazards arising from and to
source of flammable or combustible material nearby operations/work. Confirm that the
which may cause personal injury or fire. Entry Watch has the knowledge and ability to
contact operations personnel.
6
1. Entrants unaware of the hazards, not wearing 1a. Involve the affected personnel in the pre-
the correct personal protective equipment (PPE) job briefing to review the JLA, associated
or not following JLAs, procedures, standards or hazards and controls, including PPE
instructions for work tasks being performed could requirements. Consult and follow JLAs,
result in injury or fatality. procedures, standards and instructions.
2. Personnel unaware of emergency procedures 1b. Before personnel enter the confined
could result in injury or fatality (e.g. space, the Permit Issuer, the Entry Watch
communication between entry-watch and entrants and operating personnel must check the
unclear or does not occur). work location/conditions and the controls
1c. Conduct LPSA before starting work tasks
3. Constricted entry points could result in injury.
and each time there is a change.
2. Review the Rescue or Emergency Plan
4. Inadequate lighting in a confined space can
and facility emergency procedures (including
make it difficult to see and could result in injury or
evacuation routes, rally points and alarms)
fatality.
with personnel.
3. Be aware of surroundings and hazards by
5. Temperatures inside the confined spaces can
looking inside the confined space and
become hot due to the weather conditions or due
planning body position during entry. Pay
Enter the confined space and begin work. to the work occurring inside the space and may
attention to sharp edges, protrusions,
result in heat-related injury or fatality.
scaffold, etc.
6. Personal injury or fatality due to unauthorized 4. Use approved lighting to perform work
entries or entrants not accounted for. task.
7. Entrants may exit from an un-monitored egress
5a. Verify that personnel maintain adequate
point that would compromise the entry log and
hydration and ensure that they take breaks
could result in inadequate communications of
to avoid heat stress.
hazards to entrants in the confined space.
5b. Use ventilation to cool the confined
space or provide the appropriate PPE, such
as cooling vests.
6. Establish an Entry Watch and keep an
entry log of all entries and exits.
7. Instruct entrants to communicate
intentions with all Entry Watches if vessel
entry/egress points are different (example:
column top entry and column bottom egress).
7 1. Conditions change during work that may
1. Stop work and cancel the work permit if
introduce new hazards causing potential injuries
the work scope or condition changes.
or incidents.
2. Inadequate gas testing (proper intervals, 2. Ensure that the confined space
continuous testing when required, etc.) may atmosphere is tested with the frequency
cause injuries or fires. specified in the permit.
Work is in progress. 3. Confirm that communication equipment is
3. Faulty communication equipment may lead to
working correctly. Fully recharge radio
potential losses.
batteries prior to work beginning.
Work is in progress.
4. Changes in atmospheric conditions outside the 4. Verify that PPE is identified in hazard
confined space and/or inside the confined space assessment and that personnel know the
may result in asphyxiation and/or introduction of Rescue/Emergency Plan. Confirm that the
fuel to an ignition source that may cause a Rescue Personnel are on site and are
fire/explosion. available to perform a rescue, if needed.
8
Complete the work and clean up the job site.
Development Team
S/N Development Team Member Name Primary Contact Position
1
2
3
4
You might also like
- JOB HAZARD ANALYSIS - Cable PullingDocument7 pagesJOB HAZARD ANALYSIS - Cable PullingJayson Escamillan100% (2)
- Risk Assessment of Testing and Commissioning of Fire Alarm SystemDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment of Testing and Commissioning of Fire Alarm Systemfidgety67% (3)
- IG2 Project Risk Assessment RoughDocument21 pagesIG2 Project Risk Assessment RoughRemya80% (5)
- Aircraft Safety: Accident Investigations, Analyses, & Applications, Second EditionFrom EverandAircraft Safety: Accident Investigations, Analyses, & Applications, Second EditionRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Job Safety Analysis: 1 Confined Space Entry JSA ExampleDocument7 pagesJob Safety Analysis: 1 Confined Space Entry JSA Examplerashid zamanNo ratings yet
- Ansi Aga B109 1 2000Document43 pagesAnsi Aga B109 1 2000Ihab El-SaftawiNo ratings yet
- Sealcoating /crack Repair Parking Lots: Job Safety AnalysisDocument3 pagesSealcoating /crack Repair Parking Lots: Job Safety AnalysisRetselisitsoe0% (1)
- Jsa Dismantling The Wooden Framework-NewDocument3 pagesJsa Dismantling The Wooden Framework-NewHow Chin Engineering Sdn BhdNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - Rebar Installation/steel Fixing DateDocument1 pageJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - Rebar Installation/steel Fixing DatenabeelNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Lifting and RiggingDocument17 pagesJob Safety Analysis Lifting and RiggingSam Seed100% (1)
- SEO For Growth: The Ultimate Guide For Marketers, Web Designers & EntrepreneursDocument7 pagesSEO For Growth: The Ultimate Guide For Marketers, Web Designers & EntrepreneursJoyce M LaurenNo ratings yet
- Session 12. Facilities layout-IIDocument34 pagesSession 12. Facilities layout-IIsandeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Jsa Confined Space EntryDocument11 pagesJsa Confined Space EntryNii AshiiiNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis WorksheetDocument7 pagesJob Safety Analysis WorksheetMohamedSaidNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis WorksheetDocument57 pagesJob Safety Analysis WorksheetMohamedSaidNo ratings yet
- Job Hazards AnalysisDocument1 pageJob Hazards AnalysisJane RoNo ratings yet
- Job Activity Hazard Effect Control Measures: Project in ChargeDocument3 pagesJob Activity Hazard Effect Control Measures: Project in Chargeperquino oasanNo ratings yet
- XX - PTW 575283 Doc1Document46 pagesXX - PTW 575283 Doc1JeffersonDeGuiaNo ratings yet
- JOB HAZARD ANALYSIS - ConduitDocument9 pagesJOB HAZARD ANALYSIS - ConduitJayson Escamillan100% (2)
- JSA-002 JSA For TCFDocument4 pagesJSA-002 JSA For TCFRafeeq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- JOB HAZARD ANALYSIS - Cable TrayDocument10 pagesJOB HAZARD ANALYSIS - Cable TrayJayson Escamillan100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis: JSA Reference #: DateDocument3 pagesJob Safety Analysis: JSA Reference #: DateLi QiNo ratings yet
- 1-JHA - ExcavationDocument2 pages1-JHA - ExcavationAnna Marie Filipinas RajilNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Paving JsaDocument2 pagesAsphalt Paving Jsanabeel100% (1)
- JHSA Water Supply and Sewer InstallationDocument4 pagesJHSA Water Supply and Sewer InstallationAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- JHADocument8 pagesJHARayyan ramosNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Installation of Cable Trays & DCAC CablesDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment - Installation of Cable Trays & DCAC CablesIbrahim Esmat100% (1)
- Job Hazard Analysis - TubingsDocument9 pagesJob Hazard Analysis - TubingsJayson Escamillan100% (1)
- Jsa-007 PaintingDocument14 pagesJsa-007 PaintingDamien Monize100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - Night Work DateDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - Night Work Datenabeel100% (2)
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - Painting DateDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - Painting DatenabeelNo ratings yet
- TGN-W-03 Job Safety Analysis (Jsa) For The Water IndustryDocument8 pagesTGN-W-03 Job Safety Analysis (Jsa) For The Water Industryworlds funNo ratings yet
- JHSA For Temporary Plastic Septic TankDocument4 pagesJHSA For Temporary Plastic Septic TankAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- (JSA) Concreting in FoundationDocument2 pages(JSA) Concreting in FoundationGunjan Sinha AdityaNo ratings yet
- JSA ExcavationDocument6 pagesJSA ExcavationidreisNo ratings yet
- 002 Job Safety Analysis For Excavation, Backfilling and Compaction Activities at SAOO GOSPs Rev 03 PDFDocument8 pages002 Job Safety Analysis For Excavation, Backfilling and Compaction Activities at SAOO GOSPs Rev 03 PDFHaleemUrRashidBangash100% (1)
- 002 Job Safety Analysis For Excavation, Backfilling and Compaction Activities at SAOO GOSPs Rev 03Document8 pages002 Job Safety Analysis For Excavation, Backfilling and Compaction Activities at SAOO GOSPs Rev 03Haleem Ur Rashid Bangash100% (2)
- JSA Pipeworks - UEM - RAPID PETRONAS - Common FacilitiesDocument10 pagesJSA Pipeworks - UEM - RAPID PETRONAS - Common FacilitiesNazreen AzriNo ratings yet
- How Chin Engineering: Job Safety AnalysisDocument5 pagesHow Chin Engineering: Job Safety AnalysisHow Chin Engineering Sdn BhdNo ratings yet
- Hydro TestDocument8 pagesHydro Testmozzammil saqibNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - Carpentry Works DateDocument1 pageJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - Carpentry Works DatenabeelNo ratings yet
- Safe Work Procedure Working at Height Rescue PlanDocument13 pagesSafe Work Procedure Working at Height Rescue PlanChris BonningtonNo ratings yet
- JHA (85T Crawler Crane & Drill Rig Machine Assembling and Inspection)Document2 pagesJHA (85T Crawler Crane & Drill Rig Machine Assembling and Inspection)Armando AballeNo ratings yet
- JSA Hot Work Indospace RajpuraDocument2 pagesJSA Hot Work Indospace RajpuraGuri PreetNo ratings yet
- Kapoor Enterprises Jha-1Document3 pagesKapoor Enterprises Jha-1Dwitikrushna RoutNo ratings yet
- Attachment 7505Document11 pagesAttachment 7505Charles DoriaNo ratings yet
- Activity Hazard Analysis: Well DiggingDocument1 pageActivity Hazard Analysis: Well DiggingarjunkoiralaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assesment Project VimalDocument7 pagesRisk Assesment Project VimalHASHIM TKNo ratings yet
- Omn01ard - Jsa-Installation of Light Sensor at Top of JS and SS SkidsDocument3 pagesOmn01ard - Jsa-Installation of Light Sensor at Top of JS and SS Skidshechame TamerhouletNo ratings yet
- RCC Safety Supervisor: CivilDocument7 pagesRCC Safety Supervisor: CivilDwitikrushna RoutNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment RT Marine West Pier (Ok)Document29 pagesRisk Assessment RT Marine West Pier (Ok)jeyesbelmenNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis: Amichand Technological Pvt. LTDDocument6 pagesJob Hazard Analysis: Amichand Technological Pvt. LTDSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Siddhivinayak Jsa-004-Work in ShaftDocument5 pagesSiddhivinayak Jsa-004-Work in Shaftyogeshraut1910No ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure SOP - NO.-01 Joda Date:-19.09.2020Document6 pagesStandard Operating Procedure SOP - NO.-01 Joda Date:-19.09.2020Dwitikrushna Rout0% (1)
- Form JSA Lifting CraneDocument6 pagesForm JSA Lifting CraneYeti Srinurhayati100% (1)
- Bat (Rams)Document10 pagesBat (Rams)sodiqismail11No ratings yet
- Tuaman Engineering Limited: Job Safety Analysis (Jsa)Document6 pagesTuaman Engineering Limited: Job Safety Analysis (Jsa)abhijit janaNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis - Work SheetDocument4 pagesJob Safety Analysis - Work Sheetrickie7809No ratings yet
- JOB HAZARD ANALYSIS - Electrical WorksDocument9 pagesJOB HAZARD ANALYSIS - Electrical WorksJayson Escamillan100% (1)
- JSA For Hydrotesting of 24 Production HeaderDocument4 pagesJSA For Hydrotesting of 24 Production HeaderjavithNo ratings yet
- Jsa No-01 Container UnloadingDocument4 pagesJsa No-01 Container Unloadingsumith s100% (1)
- Scrap Material Handling & Loading Jha - 1Document2 pagesScrap Material Handling & Loading Jha - 1Dwitikrushna Rout100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - HVAC Ducting DateDocument1 pageJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - HVAC Ducting DatenabeelNo ratings yet
- 10039030M00 - PB560 System Final Test Procedure PDFDocument12 pages10039030M00 - PB560 System Final Test Procedure PDFDaniel MarquesNo ratings yet
- H07RN-F - (LTC) - 4Document6 pagesH07RN-F - (LTC) - 4Faizal AzwaryNo ratings yet
- Rattan Pole BendingDocument21 pagesRattan Pole Bendingcintamore_jos355No ratings yet
- Prime Vision Security Solutions - Company ProfileDocument11 pagesPrime Vision Security Solutions - Company ProfileAbdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Braking System of Mine WindersDocument53 pagesMechanical Braking System of Mine WindersAJEET YADAV100% (6)
- SeparatorsDocument50 pagesSeparatorsCVACAPNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Writing An EmailDocument1 pageReading and Writing Writing An EmailferfonsegonNo ratings yet
- Api-1169 Pipeline Construction Inspector: Body of KnowledgeDocument9 pagesApi-1169 Pipeline Construction Inspector: Body of KnowledgeKhalilahmad KhatriNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Buying A Better Used Car in MalaysiaDocument2 pagesChecklist For Buying A Better Used Car in MalaysiaSurendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Siklus RankineDocument26 pagesSiklus RankineArialdi Almonda0% (1)
- Autohex Ii BMW: Beyond The Edge of ImpossibleDocument2 pagesAutohex Ii BMW: Beyond The Edge of ImpossibleJuank MrtNo ratings yet
- Pass Transistor LogicDocument36 pagesPass Transistor LogicMuneza NaeemNo ratings yet
- VEDST003 - Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Specification SheetDocument23 pagesVEDST003 - Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Specification SheetyuganterNo ratings yet
- SAP Brazil Localization PortfolioDocument31 pagesSAP Brazil Localization Portfoliosatishkr14No ratings yet
- Creative Industries Journal: Volume: 1 - Issue: 1Document86 pagesCreative Industries Journal: Volume: 1 - Issue: 1Intellect BooksNo ratings yet
- BOOKDocument681 pagesBOOKMohamad ShafeyNo ratings yet
- Catalog of NIMS Creep Data Sheets: Science and Technology of Advanced MaterialsDocument31 pagesCatalog of NIMS Creep Data Sheets: Science and Technology of Advanced MaterialsTrushar ParmarNo ratings yet
- New Horizons and Opportunities of Modular Constructions and Their TechnologyDocument9 pagesNew Horizons and Opportunities of Modular Constructions and Their TechnologyPhD. Arch. Klodjan XhexhiNo ratings yet
- Bisskey ThaicomDocument8 pagesBisskey Thaicomazroy86No ratings yet
- Gravity Analog Dissolved Oxygen Sensor SKU SEN0237 DFRobot Electronic Product Wiki and Tutorial Arduino and Robot WikiDocument8 pagesGravity Analog Dissolved Oxygen Sensor SKU SEN0237 DFRobot Electronic Product Wiki and Tutorial Arduino and Robot WikihipolitoNo ratings yet
- Aa1a32 02Document3 pagesAa1a32 02MramirezNo ratings yet
- Collapsible Steering ColumnDocument2 pagesCollapsible Steering ColumnKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Information For New CustomersDocument1 pageInformation For New CustomersOctavian P TodirasNo ratings yet
- Fire Risk Assessment ChecklistDocument10 pagesFire Risk Assessment Checklistm. absiyeNo ratings yet
- Bittorrent-Like P2P NetworkDocument41 pagesBittorrent-Like P2P NetworkNguyễn Ngọc GiàuNo ratings yet
- Fauzan Ariq Santoso From Marine Electrical Engineering ShipsDocument11 pagesFauzan Ariq Santoso From Marine Electrical Engineering ShipsFauzan Ariq SantosoNo ratings yet
- ICBC Motorcycle Handbook (British Columbia)Document212 pagesICBC Motorcycle Handbook (British Columbia)BNo ratings yet