Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(English) (English)
Uploaded by
GREEN BOXCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(English) (English)
Uploaded by
GREEN BOXCopyright:
Available Formats
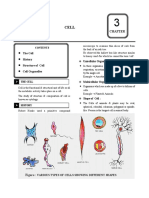
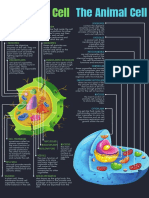
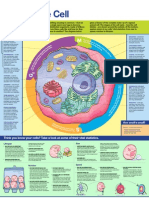
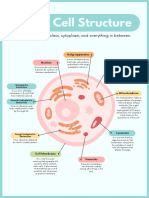
Plant cell Organelles and cellular structures that
differentiate it from the animal cell
Cellular wall It is a rigid structure that surrounds the
They do not have a plasma membrane, and gives the plant
developed cytoskeleton,
All living organisms are composed of structural and functional units that we call cells, and plants it is rather simple, nor
cell a prism-like shape.
Its main functions are to protect the cell,
are no exception. Although their cells share similar characteristics with animal cells, they are centrioles (unlike the providing rigidity and support, and to
animal cell), which are regulate relationships with its
characterized by having a defined shape thanks to having a rigid cell wall, and specific organelles environment.
hollowed cylindrical
called chloroplasts, where photosynthesis occurs. structures, which are AF cellulose fibrils
LI
TTE
involved in cell division.
N RI
cellulose microfibril
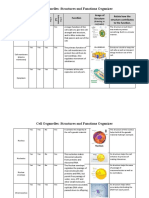
Organelles and cellular structures
that they share with the animal cell
Ribosomes
They are the most abundant organelles in the cell. In vacuole Cell Wall Fiber Structure
them the assembly of amino acids is carried out in
the synthesis of proteins. Although animal cells also have this organelle, in
the plant cell there is generally the presence of a
large, central vacuole, which occupies a large part It is composed mainly of
Golgi complex cellulose, formed by linear
of the cell volume. Its main function is to be a
water reserve, in which some amino acids and bonds of glucose.
It is a membrane system responsible for the necessary mineral salts are dissolved.
compaction, modification and distribution of
proteins in the cell.
Chloroplasts
plasma membrane They are the organelles in which the photosynthesis process occurs. They contain
The cells are surrounded by a cellular chlorophyll inside, a green pigment that allows the photosynthesis process to be carried
membrane that is essential for their out by capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy. It has, like the
mitochondria, its own DNA.
viability, since it serves to contain, shape
and protect them. It allows both the Structure of the Chloroplast It is
passage of water, nutrients and other formed by a double membrane:
necessary substances, as well as the exit of an external one that shapes and
waste, and regulates the entry of covers the doroplast, and an internal
substances that may be harmful to the cell. one that folds.
Cytoplasm
It is a substance made up of water, nutrients, sugars and In this membrane, the first part of
proteins, which occupies almost the entire cell volume. In photosynthesis occurs in structures
the cytoplasm are the structures, organelles, and called thylakoids.
substances that the cell needs to carry out its vital
functions.
It then finishes completing itself in the
space between the membrane, called
the stroma. It is also there where the
Mitochondria reserves of nutrients (sugars, starch)
that were synthesized during
They are organelles that function as energy centers of the cell. photosynthesis are stored.
Cellular respiration occurs in them, in which nutrients, such as
glucose, are broken down to obtain energy necessary for cellular
functions. This energy is stored in a molecule called adenosine
triphosphate or ATP. It has its own DNA inside.
Eukaryotic cells:
Endosymbiotic Theory or of Serial Endosymbiosis: plants, some protists
Core
It is a theory described by the American scientist Lynn Margulis, They become
It is a characteristic structure of the eukaryotic cell. It is which explains the appearance of the eukaryotic cell, its nucleus in chloroplasts
surrounded by a membrane, called the nuclear membrane. and organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. The theory
Inside it is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), its main functions are proposes that their emergence was from the integration of
to contain hereditary information for cell replication and prokaryotic organisms inside another prokaryotic organism
coordinate cellular functions. (endosymbiosis).
Ancestral photosynthetic
Aerobic bacteria. bacteria
Nucleolus Lysosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Peroxisomas Guest
It is a small, dense region within the nucleus, They are vesicles produced in In both plant and animal cells there are They are vesicles that
whose main function is the production and the Golgi complex, which two types. On the one hand, the Rough intervene in the
assembly of ribosomal components. degrade proteins and lipids to Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER), with degradation of fatty
It is formed by ribosomal DNA molecules, simpler molecules. In plant attached ribosomes and responsible for acids and toxic
ribosomal proteins, and is surrounded by a cells in particular they are less protein synthesis; on the other, the substances.
layer of condensed chromatin. abundant since they produce Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER),
their own food. without ribosomes attached to its DNA Bacteria become:
Eukaryotic cells:
membrane, responsible for lipid peroxisomes
synthesis. mitochondria animals, fungi, some protists
You might also like
- GeneralBiology1 Module1Document4 pagesGeneralBiology1 Module1Kirsteen KimNo ratings yet
- Samillao Gen Bio Week 2 Q1Document11 pagesSamillao Gen Bio Week 2 Q1Gem Kyla Mae SamillanoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Document4 pagesEukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Dharyl FloresNo ratings yet
- Atlas de Histologc3ada Gartner 3ed Parte 1Document87 pagesAtlas de Histologc3ada Gartner 3ed Parte 1Marcelo EsquisattoNo ratings yet
- Microb Group 4Document1 pageMicrob Group 4Syafiqa UmairahNo ratings yet
- CelsszDocument6 pagesCelsszHITANSH NIJHAWANNo ratings yet
- Completed Concept Map PDFDocument1 pageCompleted Concept Map PDFBombo MartinNo ratings yet
- Cell Membran E: Function Cont. Function Structure Importance World DependenceDocument1 pageCell Membran E: Function Cont. Function Structure Importance World DependenceendlessNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Presentation PawitchayaDocument23 pagesPlant Cell Presentation PawitchayaPawitchayaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument1 pageBiologySaba.u AlmullaNo ratings yet
- Bio Reading Essentials Structures & OrganellesDocument5 pagesBio Reading Essentials Structures & OrganellesValerie FallerNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument11 pagesCell AnalogyMikaella Jayne CatanaoanNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Structure and Function Dhruv Tejusinghani P1Document6 pagesCell Organelle Structure and Function Dhruv Tejusinghani P1GamingWithDhruv100% (2)
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Biology Cells Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageBiology Cells Graphic OrganizerMaci StackhouseNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells NotesDocument7 pagesBio Cells Notesnabita20211No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TransportDocument4 pagesCell Structure and TransportAena Valerie CaalimNo ratings yet
- Las #6 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #6 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationNurul Fatihah Binti MamatNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e FunctionDocument14 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e Functionwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Organelos CélulasDocument1 pageOrganelos CélulasTatiana Alvarez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Review On Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesReview On Animal and Plant CellLadymae GalolaNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry (Midterms)Document3 pagesBiological Chemistry (Midterms)ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Comparing Plant and Animal CellDocument38 pagesComparing Plant and Animal CellRegie G. GalangNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and Function: Module - 1Document35 pagesCell - Structure and Function: Module - 1Manas TripathiNo ratings yet
- 3b-Bspsy-Gen-Zoo-Format-Doc (Long Test Part 1 & 2 and Video Evaluation)Document5 pages3b-Bspsy-Gen-Zoo-Format-Doc (Long Test Part 1 & 2 and Video Evaluation)JohnCaesar P SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture 3: The Cell 1: 1.describe The Structure and Function of The Components of The Endomembrane SystemDocument3 pagesBiology Lecture 3: The Cell 1: 1.describe The Structure and Function of The Components of The Endomembrane Systemphuc thienNo ratings yet
- Nathanael Kean Dimasacat - Worksheet - Cells StructureDocument4 pagesNathanael Kean Dimasacat - Worksheet - Cells StructureNathanael Kean DimasacatNo ratings yet
- 3b-Bspsy-Gen-Zoo-Format-Doc (Long Test Part 1 & 2)Document4 pages3b-Bspsy-Gen-Zoo-Format-Doc (Long Test Part 1 & 2)JohnCaesar P SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument2 pagesCellTamarah RomeroNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument15 pagesBiologyChit su su zawNo ratings yet
- Cellstructure PDFDocument3 pagesCellstructure PDFGohar imranNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures & Functions: Cells Have Many Different Functions and Come in Many Shapes and SizesDocument3 pagesCell Structures & Functions: Cells Have Many Different Functions and Come in Many Shapes and SizesFrank Mecel Arzaga DimalantaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- Cells NoteDocument6 pagesCells NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1-Cell ComponentsDocument3 pagesActivity No. 1-Cell ComponentsKyla QuilantangNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureIrvin Jacob AquinoNo ratings yet
- Zárate CellsDocument9 pagesZárate CellsCAROLINA ELIZABETH ZARATE CHECANo ratings yet
- Big Picture On The Cell PosterDocument1 pageBig Picture On The Cell PosterWellcome Trust100% (1)
- Cell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Document6 pagesCell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Mark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Revision-Map Chapter 5Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 5shinyy566No ratings yet
- Canva ExampleDocument1 pageCanva Exampleapi-565439029No ratings yet
- Plant V Animal Cells Mapping Filled inDocument1 pagePlant V Animal Cells Mapping Filled inndlovuclara04No ratings yet
- Assignment Cell - ANSDocument3 pagesAssignment Cell - ANSAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapPramod Jaiswal81% (21)
- The Human CellDocument3 pagesThe Human CellA HNo ratings yet
- 4 Structures and OrganellesDocument5 pages4 Structures and Organellessalmasadiq2008No ratings yet
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- Bio Review Tasksf23Document16 pagesBio Review Tasksf23Shayan UzzamanNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Organelle Biochemical Process ImportanceDocument5 pagesOrganelle Biochemical Process Importanceaira roperezNo ratings yet
- 001 - Science 2 ImageDocument1 page001 - Science 2 Imagesantiago Estrada VasquezNo ratings yet
- ViewpdfDocument12 pagesViewpdfAnant DwivediNo ratings yet
- The Cell (Smallest Unit) : A Region of DNADocument2 pagesThe Cell (Smallest Unit) : A Region of DNAIZZATY ATIRAH IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in BetweenDocument1 pageAnimal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in Between04Annisa PutrianeNo ratings yet
- The Cell History Structure of Cell Cell Organelles: Unicellular OrganismsDocument7 pagesThe Cell History Structure of Cell Cell Organelles: Unicellular OrganismsvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 8 - Chapter 08Document13 pagesExp SC 8 - Chapter 08megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- M2 - L1. Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument2 pagesM2 - L1. Cell Structures and FunctionsPrincess Paula ArguidasNo ratings yet
- Asa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaDocument1 pageAsa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaMary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- Preamble of The ConstitutionDocument1 pagePreamble of The ConstitutionGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Careers PosterDocument1 pageCareers PosterGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- A Brief Guide To Atmospheric PollutantsDocument1 pageA Brief Guide To Atmospheric PollutantsGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Acids Acid Strength and ConcentrationDocument1 pageA Guide To Acids Acid Strength and ConcentrationGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- HUMAN ANATOMY Single FrameDocument1 pageHUMAN ANATOMY Single FrameGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Biodegradable PlasticsDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Biodegradable PlasticsGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Physics PDFDocument6 pagesPhysics PDFAriel Nolberto Jarita Ccama100% (1)
- A Short Guide To Arrows in ChemistryDocument1 pageA Short Guide To Arrows in ChemistryJefferson RibeiroNo ratings yet
- SymmetryDocument1 pageSymmetryGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- TagDocument2 pagesTagGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Kindle 3Document1 pageKindle 3GREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Contact Us: Xyz Fresh 9989790008Document2 pagesContact Us: Xyz Fresh 9989790008GREEN BOX100% (1)
- Subscription FormDocument1 pageSubscription FormGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Business CardDocument2 pagesBusiness CardGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Sangam DairyDocument2 pagesSangam DairyGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Xyz Trifold Brochure FinalDocument2 pagesXyz Trifold Brochure FinalGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- English Plant NurseryDocument106 pagesEnglish Plant NurseryGREEN BOX100% (1)
- Poultry HousingDocument13 pagesPoultry HousingGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit TestDocument2 pagesCell Unit Testapi-385753111No ratings yet
- Page 1 of 8 Kalinga State University College of Health and Natural Sciences Bachelor of Science in BiologyDocument8 pagesPage 1 of 8 Kalinga State University College of Health and Natural Sciences Bachelor of Science in BiologyLeah MacadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Inheritance Chapter 5 InheritanceDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Inheritance Chapter 5 InheritancesuhanaNo ratings yet
- Biol 110 Test 1 Study GuideDocument2 pagesBiol 110 Test 1 Study Guideapi-281761748No ratings yet
- Jake Facciobene Cells Practice Worksheet 2 1 PDFDocument2 pagesJake Facciobene Cells Practice Worksheet 2 1 PDFJake FacciobeneNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument8 pagesBIOENERGETICSSarah CalventasNo ratings yet
- The Microscope Parts and Use: Name: - PeriodDocument8 pagesThe Microscope Parts and Use: Name: - PeriodHector ZavalaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument33 pagesThe CellZay SalazarNo ratings yet
- Cell Modification, Cell Cycle, MitosisDocument9 pagesCell Modification, Cell Cycle, MitosisIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.No ratings yet
- 01 - Intro To Central Dogma and Structure of DNA-RNA PDFDocument5 pages01 - Intro To Central Dogma and Structure of DNA-RNA PDFRene Cesar San AntonioNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Animal PhysiologyDocument594 pagesEssentials of Animal PhysiologyMihalache Alex100% (3)
- CH-8 Notebook Work-Answer KeyDocument2 pagesCH-8 Notebook Work-Answer KeyEeshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit Five Kingdom Classification: StructureDocument23 pagesUnit Five Kingdom Classification: Structurekaladhar reddyNo ratings yet
- Gr-8 CEll - Structure and Function Answer KeyDocument5 pagesGr-8 CEll - Structure and Function Answer KeyT. Dharshini100% (1)
- Statistics in Human Genetics and Molecular Biology-Chapman and Hall - CRC (2009)Document282 pagesStatistics in Human Genetics and Molecular Biology-Chapman and Hall - CRC (2009)Ziauddin AzimiNo ratings yet
- Pembelahan Sel: Langsung Tidak Langsung Mitosis MeiosisDocument68 pagesPembelahan Sel: Langsung Tidak Langsung Mitosis MeiosisPutti AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Heamatology Assignment-Adesanmi Ademola - 221506462Document7 pagesHeamatology Assignment-Adesanmi Ademola - 221506462El-rohyKalongoNo ratings yet
- HepatoblastomaDocument6 pagesHepatoblastomaNurul IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell 3Document9 pagesAnimal Cell 3api-320844972No ratings yet
- 7.2 WKBK KeyDocument13 pages7.2 WKBK KeyJohn WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Eukaryotic Cell For Zoo 101Document34 pagesParts of A Eukaryotic Cell For Zoo 101Francez Anne GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Sci7 q2 Mod5 CelltheoryDocument35 pagesSci7 q2 Mod5 CelltheoryShenzhen Henry-PachecoNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal MutationDocument3 pagesChromosomal MutationChristian jayr BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Learning Lesson Plan - The CellDocument3 pagesCooperative Learning Lesson Plan - The Cellapi-328213220No ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet PDFAvery WrightNo ratings yet
- Tutorial W4 SCES3373Document5 pagesTutorial W4 SCES3373PRBMSK50622 Mathilda Durie Anak RowneyNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY NuggetsDocument233 pagesMICROBIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY NuggetsFaraz SayedNo ratings yet
- Meiosis WebquestDocument3 pagesMeiosis Webquestapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Cell As Basic Unit of Life: MesokaryoteDocument79 pagesCell As Basic Unit of Life: MesokaryotetabilinNo ratings yet
- BSC 250 Chapter 3 Blank NotesDocument10 pagesBSC 250 Chapter 3 Blank NotessarahreyNo ratings yet