Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Theory: The Building Blocks of Life
Uploaded by
Shmaira Ghulam RejanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Theory: The Building Blocks of Life
Uploaded by
Shmaira Ghulam RejanoCopyright:
Available Formats
Eastern Quezon College, Inc.
R. Marco St., Brgy. Penafrancia Gumaca, Quezon
SY 2021-2022
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
LAS # 6 ATTACHMENT: DO NOT COPY! FOR FURTHER READINGS ONLY!
CELLS AS BUILDING BLOCKS
Everything is made from building blocks, including living things. All living things are made up of
cells. Some of them are made up of only one cell and others are made up of many cells.
Cells are amazing. They are made up of similar building blocks, but do many different things
depending on how they are programmed. Some cells carry oxygen to the parts of the body. Other cells
defend the body against invading bacteria and viruses. There are cells that transmit signals throughout
the body, like the signals from your eyes to your brain while reading. Some cells can even convert the
sun’s energy into food. This process is called photosynthesis. There are many things that cells can do.
Cells also create other cells in a process called cell division.
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living things.
Discovery of the Cell
The cell got its name from an Englishman named Robert Hooke in the year 1665. He first saw and
named his discovery as cell, while he was experimenting with a new instrument which we now call as
“microscope”. From his experiment, he cut a very thin slice of cork. He observed this thin slice under a
microscope. He saw a series of tiny box-like compartments that reminded him of the cells in the
monastery. He saw the empty walls of the cells, which had once contained living protoplasm.
After his discovery, other scientists found cells in wood, leaves, and roots. In 1835 Felix
Dujardin, a French biologist discovered protoplasm. Three years later, a German biologist, Matthias
Jakob Schleiden proposed the hypothesis that all plants are made up of cells. The following year, German
zoologist, Theodor Schwann after the observation of animal tissue, extended his hypothesis by
proposing that all animals are also made up of cells. He also proposed that the life processes of all
organisms took place within cells. In 1858, Rudolf Virchow provided evidence that cells reproduce to
form new cells.
The results of investigations, including the work of Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow led to the
development of the cell theory, which states that:
1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
2. Cells are the basic building units of life.
3. New cells come from existing cells by cell reproduction.
Some theories were based primarily on the hypotheses and investigations done by Robert Hooke,
Felix Dujardin, Matthias Jakob Schleiden, Theodor Schwann and Rudolf Virchow. However, the cell
theory was based on discoveries of many biologists. This served as a basis for biological knowledge about
cells and their properties.
All living things are made up of cells. In some ways, the cells of some organisms are the same,
having similar structures and functions, but in some other ways, they are different.
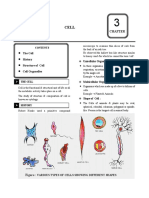
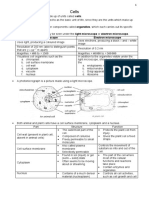
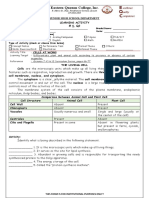
Plant Cell and Animal Cell
The structures of plant and animal cells are related to the functions they perform. The skin cells
are flat and arranged into sheets, which are characteristically adapted for covering or lining a surface.
Pollen grain cells are tiny, light and with spines. They are useful and can easily be blown away by the wind.
They may also be carried by the legs of insects to facilitate pollination.
Most of the plants are autotrophic organisms. They are capable of making their own food for
growth and development through the process of photosynthesis. Plants have eukaryotic cells that have
distinct nucleus and other membrane- bound organelles like fungi and animal cells. They are distinguished
by the presence of cell walls made of cellulose and plastids like chloroplasts. Green plants contain
chlorophyll necessary for photosynthesis and large vacuoles.
THIS FORM IS FOR INSTITUTIONAL PURPOSES ONLY!
Eastern Quezon College, Inc.
R. Marco St., Brgy. Penafrancia Gumaca, Quezon
SY 2021-2022
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
Plant cells have plastids that vary in size, shape, and functions. Chloroplastids have green pigment, while
xanthophylls and carotenoids can be found in other plastids. Those plastids leak pigments and are used
for storage.
Mature plant cells contain large vacuoles bounded by a single semi-permeable membrane called
tonoplast. The vacuoles contain a purple pigment or anthocyanin. It also stores by-products of
metabolism like organic substances that reserve materials.
Like plants, all members of the animal kingdom are multicellular and made up of eukaryotic cells.
Animal cells have no cell wall and no plastids. They do have a special set of organelles called centrioles.
They are active during the reproduction of the cell. Centrioles contain microtubules, which help to
separate and sort-out the chromosomes during cell division.
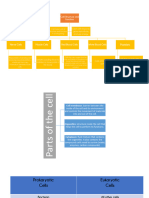
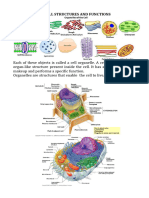
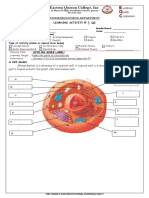
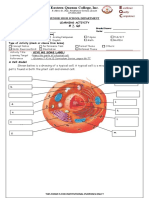
The Parts of a Cell
Main Components of a Cell and Their Functions
Cell Component Description Functions
Cell Membrane A protective coat made mostly of a double Separates and protects a cell
layer of lipids and proteins from its surrounding
environment. A variety molecules
are embedded within the
membrane that acts as channels
pumps, moving different
molecules into and out of the
cell.
Cytoskeleton A scaffold made up of proteins Organizes and maintains the
cell’s shape; anchors organelles
in place; helps during
endocytosis- the uptake of
external materials by a cell; and
moves parts of the cell in
processes of growth and
motility. Controls the cell
structure by directing, bundling,
and aligning filaments.
Cytoplasm It is a large fluid space inside the cell. The cytosol is composed of
Contains a mixture of ions and fluids in dissolved nutrients, help break
solution within the cell, and the organelles down waste products and moves
contained in it which is separated from the material around the cell through
intercellular “soup” by their own membranes a process called cytoplasm
streaming. It is an excellent
conductor of electricity that
creates a perfect environment
for the mechanics of the cell.
The function of the cytoplasm
and the organelles, which reside
in it, are critical to a cell’s
survival.
Membrane-bound Can only be found in eukaryotes A set of little organs that
organelles specializes in carrying out vital
functions.
THIS FORM IS FOR INSTITUTIONAL PURPOSES ONLY!
Eastern Quezon College, Inc.
R. Marco St., Brgy. Penafrancia Gumaca, Quezon
SY 2021-2022
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane
This is the outer layer of a cell that assists in the movement of molecules in and out of
the cell. It protects the cell. The cell membrane is a semi-permeable membrane, which is made
up of phospholipids (fat) molecules and protein. It is found around the cell and serves as a
barrier keeping foreign materials in and out of the cell. The cell membrane has the property to
control the passage of substances through it. It allows some materials to pass through at a
different rate, but prevents other materials to pass through.
Cell Wall- The cell can only be found in plants and gives a distinct
structural shape and protection to the plant. It is made up of cellulose.
Chloroplast- The chloroplast is known as the power generator of the
cell. It can convert solar energy into chemical energy through
photosynthesis. It is also known as chlorophyll-bearing plastids.
Cytoplasm- the cytoplasm is the fluid surrounding the contents of a cell
and forms a vacuole.
Endoplasmic Reticulum- The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is the
transport network for molecules that enter the cell. It plays an
important role in protein synthesis. The Smooth ER serves as the
site for lipid synthesis. The rough ER is abundant in growing cells
and is responsible for transporting the newly synthesized protein to
the Golgi Apparatus.
Golgi Apparatus- the Golgi apparatus is made of plates arranged one
on top of another that controls the flow of molecules in the cell. It
packages proteins before distributing to different organelles.
Lysosome- commonly called the “garbage collector” of the cell. It is
a spherical body bounded by single membrane and rich with digestive
enzymes that speed up biochemical reactions.
Mitochondrion- it is the energy storage of the cell/powerhouse
of the cell. It plays a significant role in cell respiration. It is a
THIS FORM IS FOR INSTITUTIONAL PURPOSES ONLY!
Eastern Quezon College, Inc.
R. Marco St., Brgy. Penafrancia Gumaca, Quezon
self-replicating organelle that takes place inSYvarious
2021-2022numbers, sizes, and shapes in the cytoplasm
of eukaryotic cells. It produces energy in eukaryotic cells through complex metabolic processes.
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
Nucleus- the nucleus is called the “brain” of a cell. It contains the
genetic information that establishes every natural process within an
organism. It houses the chromosomes and it is the place where almost
all DNA replication occurs. The nucleus controls the chemical reaction
within the cytoplasm and stores the information needed for cell
division.
Ribosomes- the ribosomes are called the “protein synthesis
machine”. Protein synthesis is very important in all cells. They
are responsible for processing the genetic information carried
by messenger RNA.
Central Vacuole- the central vacuole is composed of packages of
substances used in the cell or secreted by it.
Plant Cell
THIS FORM IS FOR INSTITUTIONAL PURPOSES ONLY!
You might also like
- LAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsDocument7 pagesLAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsJeanne RanielleNo ratings yet
- PSLE Booklet Life Open-Ended Part1Document25 pagesPSLE Booklet Life Open-Ended Part1Teoh Han JieNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function Semi Detailed LPDocument8 pagesCell Structure and Function Semi Detailed LPCJ Perito75% (4)
- The Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument72 pagesThe Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Multiple-Choice QuestionsRyan100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Function ReviewerDocument4 pagesCell Structure and Function ReviewerLeandre Jasmine ReyesNo ratings yet
- C2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismDocument39 pagesC2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismyourmoNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Illustrated ReportDocument21 pagesCell Biology Illustrated ReportIlze Krauze100% (11)
- Thematic Unit Lesson Plan FinalDocument30 pagesThematic Unit Lesson Plan Finalapi-398862244No ratings yet
- Grade 7 TG SCIENCE 2nd QuarterDocument60 pagesGrade 7 TG SCIENCE 2nd QuarterAilyn Soria Ecot100% (2)
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapPramod Jaiswal81% (21)
- Revision Practice Questions - Cells & TransportDocument11 pagesRevision Practice Questions - Cells & TransportMarina BrazendaleNo ratings yet
- 1st Ch. CellsDocument27 pages1st Ch. CellsAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocument19 pagesCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Cell Structure & Organization - Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Cell Structure & Organization - Lecture Notesapi-372850888% (8)
- Cell Notes Class 9Document18 pagesCell Notes Class 9Anshu DashNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument1 pagePerformance TaskShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- 0893 Lower Secondary Science Stage 7 Scheme of Work - tcm143-595695Document103 pages0893 Lower Secondary Science Stage 7 Scheme of Work - tcm143-595695manoj0% (1)
- Pattern in Natures NotesDocument12 pagesPattern in Natures NoteskakaNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument11 pagesCell AnalogyMikaella Jayne CatanaoanNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Second Trimester ScienceDocument36 pagesStudy Guide Second Trimester ScienceuzielcgcursoNo ratings yet
- Inte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Document11 pagesInte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument15 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesMai YoussifNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (Definitions) - Cell StructureDocument3 pagesGen Bio (Definitions) - Cell StructureMary Vhenn SamonteNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 1: THE STUDY OF LIFEDocument25 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 1: THE STUDY OF LIFEJuanito MerciNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Document4 pagesEukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Dharyl FloresNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Modules 1 3Document36 pagesGeneral Biology Modules 1 3Glen MillarNo ratings yet
- Cell theory discoveries and importanceDocument4 pagesCell theory discoveries and importanceJoven J. AndohoyanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Life ScienceDocument7 pagesEarth and Life Science Life ScienceRegina PalacioNo ratings yet
- Nathanael Kean Dimasacat - Worksheet - Cells StructureDocument4 pagesNathanael Kean Dimasacat - Worksheet - Cells StructureNathanael Kean DimasacatNo ratings yet
- Microscope Discoveries Led to Cell Theory DevelopmentDocument14 pagesMicroscope Discoveries Led to Cell Theory DevelopmentLaiza Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Structures WorksheetCharlene BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingDocument4 pagesA Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingJONAVIE DEMALATANo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesCell Structure and Functions in 40 CharacterscarlNo ratings yet
- CelsszDocument6 pagesCelsszHITANSH NIJHAWANNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- 1.1cell ConceptDocument10 pages1.1cell ConceptMokariya SanjayNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- 2 - Organisation of The OrganismDocument6 pages2 - Organisation of The OrganismAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- Gen Bio 2Document12 pagesGen Bio 2Ma.Dulce ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesPlant and Animal Cell OrganellesGraceNo ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDocument28 pagesAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNo ratings yet
- Plant vs Animal CellDocument2 pagesPlant vs Animal CellJastine Managbanag DautilNo ratings yet
- Cell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaDocument10 pagesCell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Cells NoteDocument6 pagesCells NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsDocument11 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsMorgan LockeNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- NeucleDocument25 pagesNeucleUjala SinghNo ratings yet
- Week 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their Vital FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their Vital FunctionsChristine Suizo SebucaoNo ratings yet
- Living beings at the cellular levelDocument10 pagesLiving beings at the cellular levelMaria Jose RomanNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and Structure in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesCell Theory and Structure in 40 CharactersAshlee TalentoNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Notes Human AnatomyDocument4 pagesNotes Human AnatomyLeslie Ann MesolisNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Notesarnienina.niloNo ratings yet
- Notes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)Document38 pagesNotes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)salinaNo ratings yet
- Biology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesBiology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsEmilio Villafria IVNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Function in 40 Charactersshankaram shankaram100% (1)
- TOPIC 2 - CellDocument9 pagesTOPIC 2 - CellAl Johan Atienza100% (1)
- 3.2 Reinforcement: Key ConceptDocument1 page3.2 Reinforcement: Key ConceptEyad TalaatNo ratings yet
- Pinma Privae High School Biology: Cell StructureDocument15 pagesPinma Privae High School Biology: Cell StructureChit su su zawNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955Document9 pagesSubmitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955mahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- Sample AssignmentDocument4 pagesSample Assignmentmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- Las 3Document1 pageLas 3Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Unpack Standards and Competencies SeminarDocument18 pagesUnpack Standards and Competencies SeminarShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument4 pagesMIDTERMShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM ATTACHMENTSDocument16 pagesMIDTERM ATTACHMENTSShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Asian Studies Exam Offers InsightsDocument2 pagesAsian Studies Exam Offers InsightsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Names Reveal Asia's Rich DiversityDocument6 pagesDescriptive Names Reveal Asia's Rich DiversityShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- 10745-Article Text-41358-1-10-20200314Document13 pages10745-Article Text-41358-1-10-20200314Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 1 AttachmentsDocument4 pagesLas 1 AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument2 pagesPRELIMShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 3Document1 pageLas 3Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #1 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #1 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las 2 AttachmentsDocument6 pagesLas 2 AttachmentsShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Label the Parts of a Typical CellDocument1 pageLabel the Parts of a Typical CellShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Using Instructional Materials for Quality Primary EducationDocument5 pagesUsing Instructional Materials for Quality Primary EducationShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #6Document1 pageLas #6Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Bill of Rights Is Important To An Individual Because Without These, People Cannot Have Their Protection Against Violation and DiscriminationDocument5 pagesBill of Rights Is Important To An Individual Because Without These, People Cannot Have Their Protection Against Violation and DiscriminationShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #8 AttachmentDocument3 pagesLas #8 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #6Document1 pageLas #6Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Art 8 Q1 TransferDocument7 pagesArt 8 Q1 TransferShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Las #7Document1 pageLas #7Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Socio CulturalDocument5 pagesSocio CulturalShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Eastern Quezon College, Inc: (See The Attachment LAS# 1 and Read It)Document4 pagesEastern Quezon College, Inc: (See The Attachment LAS# 1 and Read It)Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Trends and IssuesDocument8 pagesTrends and IssuesShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Existentialism's basic premise explainedDocument1 pageExistentialism's basic premise explainedShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Third Republic: People Seethed With RebellionDocument4 pagesThird Republic: People Seethed With RebellionShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Southeast Asian Fabrics and AttireDocument5 pagesSoutheast Asian Fabrics and AttireShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity # 11Document2 pagesLearning Activity # 11Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterDocument1 pageLearning Activity # 15: A Virtue Is An Excellent Trait of CharacterShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Biology Pupil's Book S4Document307 pagesBiology Pupil's Book S4obaj obajNo ratings yet
- LetsBuildAPlantCell PDFDocument7 pagesLetsBuildAPlantCell PDFmasturinaNo ratings yet
- 2 Review BookletDocument6 pages2 Review BookletBruce ZhouNo ratings yet
- Bio Task 4Document1 pageBio Task 4Estimada, Janzen Clarisse CatliNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Comprehensive ReviewDocument62 pagesCell Biology Comprehensive ReviewZhuolu PanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test 888ecoDocument2 pagesChapter Test 888ecoRandolf CruzNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life - NCERT Based PYQsDocument9 pagesCell - The Unit of Life - NCERT Based PYQsAkhil singhNo ratings yet
- Structure & Functions of the CellDocument3 pagesStructure & Functions of the CellHarshit KumarNo ratings yet
- Food Production and Utilization of PlantsDocument33 pagesFood Production and Utilization of PlantsSamKris Guerrero MalasagaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Exemplar - Cell StructureDocument6 pagesMCQ Exemplar - Cell StructurenitikaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic DNA OrganizationDocument26 pagesProkaryotic DNA OrganizationKerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- Phenolic Metabolism in Plants PDFDocument416 pagesPhenolic Metabolism in Plants PDFasaad lahmarNo ratings yet
- 1-Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument19 pages1-Characteristics of Living OrganismsLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- Final Reviewer-Science (151-180)Document3 pagesFinal Reviewer-Science (151-180)KAREN BUENAVISTANo ratings yet
- Cells WorksheetDocument2 pagesCells WorksheetJake FacciobeneNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Question Paper 1Document12 pagesCell Structure: Question Paper 1rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument44 pagesCell Structure and FunctionPedro SuyuNo ratings yet
- 2.07 Photosynthesis AlternateDocument4 pages2.07 Photosynthesis AlternateJasmine VeraNo ratings yet
- The actual length of the mitochondrion is 1.20 μmDocument90 pagesThe actual length of the mitochondrion is 1.20 μmYashwinni VijayasekarNo ratings yet
- High School Students Examine Onion and Cheek Cells Under MicroscopeDocument4 pagesHigh School Students Examine Onion and Cheek Cells Under MicroscopeMarc AnthonyNo ratings yet
- ChloroplastDocument3 pagesChloroplastdrug123addict25No ratings yet