Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dexamethasone-Drug Nomenclature
Uploaded by
PxPPxH Chan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesDexamethasone is a corticosteroid used to decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system. It works by decreasing the migration of white blood cells and reversing increased capillary permeability. Common side effects include depression, hypertension, increased blood sugar, and poor wound healing. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of adverse effects and interactions with other drugs. Dexamethasone requires careful dosage adjustments and has specific considerations for use in pregnancy, sepsis, cerebral edema, and screening for Cushing's syndrome.
Original Description:
Original Title
DEXAMETHASONE-DRUG NOMENCLATURE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDexamethasone is a corticosteroid used to decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system. It works by decreasing the migration of white blood cells and reversing increased capillary permeability. Common side effects include depression, hypertension, increased blood sugar, and poor wound healing. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of adverse effects and interactions with other drugs. Dexamethasone requires careful dosage adjustments and has specific considerations for use in pregnancy, sepsis, cerebral edema, and screening for Cushing's syndrome.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesDexamethasone-Drug Nomenclature
Uploaded by
PxPPxH ChanDexamethasone is a corticosteroid used to decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system. It works by decreasing the migration of white blood cells and reversing increased capillary permeability. Common side effects include depression, hypertension, increased blood sugar, and poor wound healing. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of adverse effects and interactions with other drugs. Dexamethasone requires careful dosage adjustments and has specific considerations for use in pregnancy, sepsis, cerebral edema, and screening for Cushing's syndrome.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
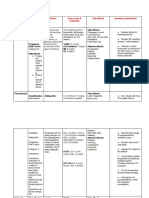
DRUG CLASSIFICATIO MECHANISM OF DRUG-TO- DOSE, ROUTE, & SIDE NURSING CONSIDERATION
NAME N & INDICATION ACTION DRUG FREQUENCY EFFECTS
INTERACTIO &
N ADVERSE
EFFECTS
Generic Classification: Decreases inflammation by Increase: DECREASE LOCAL CNS: Assess:
Name: Corticosteroid suppression of migration of toxicity— INFLAMMATION (ORAL) Depression, Potassium, blood, urine glucose while receiving
Dexamethas Glucocorticoid polymorphonuclear cycloSPORINE Adults. Day 1: 4 to 8 mg I.M. Days 2 headache, long-term therapy; hypo/hyperglycemia, Weight
one Anti-inflammatory leukocytes, fibroblasts, and 3: 3 mg/day P.O. divided every 12 mood daily; notify prescriber of weekly gain >5 lb, B/P,
Immunosuppressant reversal of increased Increase: side hr. changes, pulse; notify prescriber of chest pain
Brand capillary permeability and effects—alcohol, Day 4: 1.5 mg/day P.O. divided every euphoria
Name: Indications: lysosomal stabilization, salicy- 12 hr. Days 5 and 6: 0.75 mg/day P.O. CV: I&O ratio; be alert for decreasing uri-
Dexasone Inflammation, allergies suppresses normal immune lates, as a Hypertension nary output, increasing edema
cerebral edema, response, no amphotericin B, single dose. EENT:
septic shock, mineralocorticoid effects digoxin, Increased Cerebral edema: LOC, and headache, baseline
dexamethasone cycloSPO- DECREASE CEREBRAL EDEMA intraocular and periodically
suppression test for Steroid substances secreted RINE, diuretics, (ORAL) pressure,
Cushing syndrome, by fetal adrenal glands NSAIDs Adults: 2 mg every 6 hr for 48 hr, cataracts Pregnancy/breastfeeding: no well-controlled
adrenocortical cause uterine contractions. followed by collection of 24-hr urine ENDO: HPA studies; use only if benefit outweighs fetal risk;
insufficiency The placenta may have a Increase: specimen to determine 17- suppression, discontinue breastfeeding or product
role by producing CRH dexamethasone hydroxycorticosteroid level. hyperglycemia
(Corticotropin releasing action—salic- , sodium, fluid Teach patient/family
DURING LABOR: hormone). During the last ylates, SEPTIC SHOCK: retention, To notify prescriber if therapeutic response
weeks of pregnancy, cortisol estrogens, (IV) pheochromo- decreases because dosage adjustment may be
improves the Bishop and DHEA-S hormonal Adult: 1.67-5 mg/kg slowly over cytoma needed
score of the cervix and (Dehydroepiandrosterone contracep- several minutes, may be repeated
thus causes softening sulfate), CRH in the fetus tives, within 2-6 hours until condition is GI: Nausea, To take with food or milk
of the cervix and increase, also maternal ketoconazole, stable and usually for up to 72 hours. peptic That bruising may occur easily
reduces the length of estrogens.Th. This results in macrolide Alternatively, initial dose may be ulceration, That if on long-term therapy, a high-protein diet may
time between labor modification of the antiinfec- followed by continuous infusion of 2.5 vomiting be needed
induction and the start contractility of the uterus. tives, NSAIDs mg/kg per 24 hours. INTEG: Acne,
of the active phase of Child: 167-333 mcg/kg daily. poor wound Not to discontinue abruptly because
childbirth. Decrease: healing, adrenal crisis can result
Studies have shown that potassium SCREENING TEST FOR CUSHING'S ecchymosis, About symptoms of adrenal insufficiency: nausea,
Pregnancy category: corticosteroids analogues as levels—thiazide/ SYNDROME (ORAL) petechiae, anorexia, fatigue, dizziness, dyspnea, weakness,
C dexamethasone could loop diuretics, Adult: 2 mg at 11 pm, followed by a hirsutism joint pain, hypertension
improve the Bishop score of amphotericin B blood test for plasma cortisol at 8 am
the cervix and thus causes the following morning. Alternatively, META: Corticosteroid injections are given intramuscularly
softening of the cervix and ACTIVITIES: 500 mcg 6 hourly for 48 hours, then Hypokalemia, at a 90-degree angle with a 22-25 gauge, 1-1.5 inch
reduces the length of time alcohol use: measure plasma cortisol at 8 am on fluid retention, long sterile needle into the upper arm, buttock, or
between labor induction and Increased risk of the 3rd morning (with 24-hour urine hypokalemic thigh. Be sure to document medication, dose, time,
delivery but further studies in GI bleeding collections for determination of 17- alkalosis and date, as well as the site of administration.
that field is still needed & no hydroxycorticosteroid excretion).
studies in prelabour rupture MS: Fractures, Administration of ACS is recommended to speed
of membranes were done. ADRENOCORTICAL osteoporosis, fetal lung maturity in all women who are preterm
INSUFFICIENCY (ORAL) weakness, and have an increased likelihood of giving birth
OTHER: Adults. Highly individualized dosage arthralgia, within 7 days, regardless of other complications of
based on severity of disorder. Usual: myopathy pregnancy. ACS should be initiated even if it is
Preterm babies do not have
0.75 believed that the full course may not be completed
enough surfactant in their
to 9 mg/day in divided doses. prior to delivery. Delivery should not be delayed in
lungs. Surfactant helps the
Children. Highly individualized, based order to complete the ACS course in cases where
lungs expand during
on severity of disorder. 0.02 to 0.3 delivery should be expedited, such as
breathing, and therefore
mg/kg/day in three or four divided chorioamnionitis or severe pre-
babies who lack surfactant
doses. eclampsia/eclampsia. In women with diabetes,
commonly develop RDS.
blood sugars should be closely monitored and
ACS increase the natural
additional insulin may be required. Women on
production of surfactant, and
thus reduce the risk that DURING LABOR/ IMMINENT chronic steroids can receive ACS but may also
newborns will develop PRETERM BIRTH: (IM) need a stress dose of their steroids at the time of
severe RDS if born early. Give dexamethasone (or delivery. There are no absolute contraindications
ACS have also been shown betamethasone) 24mg IM in divided for ACS.
to have a protective effect doses. A regimen of 12mg IM every 12
on cerebral blood vessels, hours for two doses is recommended Tocolysis: Medications to stop uterine contractions
thus reducing the risk of for ease of administration, but other (such as nifedipine or indomethacin) may be useful
intraventricular hemorrhage, regimens are also acceptable. to prolong pregnancy for a short time (up to 48
and on the intestines, thus hours) to allow administration of ACS or transfer to
reducing the chance of a higher level facility. Tocolysis has not been shown
necrotizing enterocolitis. to reduce rates of preterm birth.vii iii Transfer to a
higher level facility: A woman with an increased
likelihood of a preterm birth should be cared for in a
facility where both the mother and baby can receive
appropriate care
Antibiotics: There is strong evidence supporting
antibiotic use for preterm prelabor rupture of
membranes (PPROM) because it delays labor and
reduces neonatal infection rates.ii Antibiotics
should be given to women with PPROM. Give
ampicillin 2gms IV twice daily and erythromycin
250mg orally three times daily for two days,
followed by amoxicillin 500mg orally and
erythromycin 250mg orally three times daily to
complete 7 days of therapy. Multiple studies have
shown no improvement in outcomes from the use of
antibiotics in women with intact membranes and
preterm labor.
You might also like
- 28 Day Hormone Balance Reset PlanDocument112 pages28 Day Hormone Balance Reset PlanKowsalya subbiah100% (2)
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument28 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaWindelyn Gamaro0% (1)
- Adrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical AntagonistsDocument20 pagesAdrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical Antagonistsapi-3859918No ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument10 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument34 pagesSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsLohithNo ratings yet
- Aspirn 4Document2 pagesAspirn 4salwaNo ratings yet
- Propofol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPropofol Drug StudyAngelica shane Navarro100% (2)
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: DR Tarek M Nasrallah Al - AzharDocument97 pagesNonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: DR Tarek M Nasrallah Al - AzharTarek NasrallahNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone PDFDocument4 pagesHydrocortisone PDFsangita bssmetNo ratings yet
- Obs Gyn 2017Document121 pagesObs Gyn 2017visaga50% (2)
- Vancomycin DRUGSTUDYDocument3 pagesVancomycin DRUGSTUDYEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Obstetrical Nursing AntepartumDocument28 pagesObstetrical Nursing AntepartumAyeza DuaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- Case Study On ANC WITH Severe Anemia FINALDocument53 pagesCase Study On ANC WITH Severe Anemia FINALSoumya Rajeswari100% (1)
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Paracetamol, AcetaminophenDocument3 pagesGeneric Name:: Paracetamol, AcetaminophenShanel Aubrey Aglibut100% (1)
- PropofolDocument3 pagesPropofolamelwd100% (1)
- Red Form Labor Insurance Maternity Benefits Application Form - English - LAOBAODocument2 pagesRed Form Labor Insurance Maternity Benefits Application Form - English - LAOBAOBlue DumoneNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameMacarayo AldemaeNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone DrugStudyDocument8 pagesDexamethasone DrugStudySophia IbuyanNo ratings yet
- CM (Drug Study)Document4 pagesCM (Drug Study)Angel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Methylergometrine Maleate Bupivacaine HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesDexamethasone Methylergometrine Maleate Bupivacaine HydrochlorideOmyl-Khayr M. SulogNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: CnsDocument4 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: CnsRoxy TofyNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study ClinidineDocument6 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study ClinidinehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument3 pagesEndocrinemarie curryNo ratings yet
- General: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)Document7 pagesGeneral: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)jenm1228No ratings yet
- MethylprednisoloneDocument4 pagesMethylprednisoloneadryananestesiNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone (Final)Document11 pagesHydrocortisone (Final)Zyla KrisshaNo ratings yet
- PARGAD - CON1A - Module 11 Assignment (Endocrine Drugs and Diabetes Mellitus Drugs)Document9 pagesPARGAD - CON1A - Module 11 Assignment (Endocrine Drugs and Diabetes Mellitus Drugs)Samantha PargadNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University College of Nursing: Psychotropic Drug Study in Psychiatry As A Nursing SpecialtyDocument2 pagesCebu Normal University College of Nursing: Psychotropic Drug Study in Psychiatry As A Nursing SpecialtyJvWoodzNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis and NCP Ob Ward PoldoDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis and NCP Ob Ward PoldosatruetalagaNo ratings yet
- Threatened Abortion DrugsDocument1 pageThreatened Abortion DrugsDivine Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Material, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)Document6 pagesMaterial, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)vincent materialNo ratings yet
- Drug 2Document4 pagesDrug 2Abie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Antihypertension DrugsDocument2 pagesAntihypertension DrugsMarieCrisNo ratings yet
- ADDISONS DSE - Etio Trends&Issues + DSDocument9 pagesADDISONS DSE - Etio Trends&Issues + DSgraceNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDexamethasoneXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyNine SaguiboNo ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbations of Multiple Sclerosis, Cerebral Edema Associated With Primary or Metastatic Brain Tumor, Craniotomy, or Head Injury.Document3 pagesAcute Exacerbations of Multiple Sclerosis, Cerebral Edema Associated With Primary or Metastatic Brain Tumor, Craniotomy, or Head Injury.Micah Alexis CandelarioNo ratings yet
- DonepezilDocument2 pagesDonepezilAmberNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation StrokeDocument17 pagesCase Presentation StrokeGURUPRAKASH RNo ratings yet
- Medicines Affecting The Male Reproductive OrgansDocument11 pagesMedicines Affecting The Male Reproductive OrgansKristine Las GregorioNo ratings yet
- 4.... NSAIDs 4.4... RADocument14 pages4.... NSAIDs 4.4... RANim DCNo ratings yet
- 1060 FTP PDFDocument5 pages1060 FTP PDFsimonchikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Endocrine System 2Document12 pagesChapter 6 - Endocrine System 2AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease FileDocument25 pagesAddison's Disease FileZyla KrisshaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug Classificati ON Mechanism of Action Rationale Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Drug Classificati ON Mechanism of Action Rationale Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Filgastrim (GCSF)Document3 pagesFilgastrim (GCSF)Kyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study UtiDocument3 pagesDrug Study UtiJeleya graceNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- Professor Emma BakerDocument23 pagesProfessor Emma BakerNagla FathiNo ratings yet
- NCM107 Lab Drug Study Manalo BSN 2BDocument4 pagesNCM107 Lab Drug Study Manalo BSN 2BBethrice MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Clinical Case Analysis Name of Patient Age: 52 Gender: M Address Date Admitted: Diagnosis Nursing HistoryDocument12 pagesQuestions:: Clinical Case Analysis Name of Patient Age: 52 Gender: M Address Date Admitted: Diagnosis Nursing Historyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Medical ManagementDocument3 pagesMedical ManagementMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- Course TaskDocument96 pagesCourse TaskJoelynMacalintalNo ratings yet
- FlecainideDocument3 pagesFlecainideAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- FaciitisDocument17 pagesFaciitisdalaginding clophNo ratings yet
- M&N MGMTDocument3 pagesM&N MGMTMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Group-M9-A-Case-Study-1 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesGroup-M9-A-Case-Study-1 - Drug StudyRen Mark CanlasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SengdocxDocument4 pagesDrug Study SengdocxMica OmotsosircNo ratings yet
- Drug Name WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesDrug Name WPS OfficeCAMILLE GAIL HADJIRANINo ratings yet
- FINALS 4 - Care of The Acutely Ill Burn PatientDocument117 pagesFINALS 4 - Care of The Acutely Ill Burn PatientPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- FINALS 2 - Care of The Patient With Problems in Glucose MetabolismDocument81 pagesFINALS 2 - Care of The Patient With Problems in Glucose MetabolismPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- FINALS 1 - Care of The Patient With An Acute Gastrointestinal Bleed or PancreatitisDocument76 pagesFINALS 1 - Care of The Patient With An Acute Gastrointestinal Bleed or PancreatitisPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Young Man With Cardiac Arrest Secondary To Undiagnosed Mediastinal MassDocument4 pagesYoung Man With Cardiac Arrest Secondary To Undiagnosed Mediastinal MassPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - MINDANAODocument8 pagesGroup 5 - MINDANAOPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs - Head NursingDocument1 pageVital Signs - Head NursingPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- 4 Emergency and Mass Casualty NursingDocument7 pages4 Emergency and Mass Casualty NursingPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesDiabetes MellitusPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Review-1 (Q3)Document23 pagesReview-1 (Q3)PxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- CTT Retdem GuideDocument5 pagesCTT Retdem GuidePxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Ob DrugsDocument46 pagesOb DrugsPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Prospective Study EincDocument10 pagesProspective Study EincPxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Music 9 Q2 M2Document16 pagesMusic 9 Q2 M2PxPPxH ChanNo ratings yet
- Manonmaniam Sundaranar University: B.Sc. Psychology - I YearDocument72 pagesManonmaniam Sundaranar University: B.Sc. Psychology - I Yearhimansu reddyNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument6 pagesDevelopmental PsychologySean RicoNo ratings yet
- Immunization Routine Table1Document11 pagesImmunization Routine Table1Fred C. MirandaNo ratings yet
- Module 3-Approaches in Literary Criticism: I. Performance TaskDocument5 pagesModule 3-Approaches in Literary Criticism: I. Performance TaskChum Vergara100% (1)
- Abortn Law and Policy in IndiaDocument9 pagesAbortn Law and Policy in IndiaABHINAV DEWALIYANo ratings yet
- J Ejogrb 2020 11 052Document10 pagesJ Ejogrb 2020 11 052taki takiwNo ratings yet
- CTG Analyzer: A Graphical User Interface For CardiotocographyDocument4 pagesCTG Analyzer: A Graphical User Interface For CardiotocographySebastian PerezNo ratings yet
- Recalls 3Document26 pagesRecalls 3Charisse CaydanNo ratings yet
- DmpaDocument6 pagesDmpanadeem khanNo ratings yet
- OBGyn Endof Rotation OutlineDocument35 pagesOBGyn Endof Rotation OutlinehevinpatelNo ratings yet
- Soal Biologi Uas Kls Xi 08-09Document5 pagesSoal Biologi Uas Kls Xi 08-09dinisyifaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CompilationDocument5 pagesDrug Study CompilationMikes CastroNo ratings yet
- Contraception - #2Document4 pagesContraception - #2Eingel Mer EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- JSS2 Basic Science Lesson Note PDFDocument40 pagesJSS2 Basic Science Lesson Note PDFJuddy ScienceNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Lec Quizzes 1Document5 pagesNCM 109 Lec Quizzes 1Fatima TañedoNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument3 pagesEssential Newborn CareSheene Ainasthazia Diego AngNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document6 pagesScience 5Reuelyn ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Buku Rekomendasi KebidananDocument14 pagesDaftar Buku Rekomendasi KebidananTiara PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Reflection 3 5 JennyDocument2 pagesReflection 3 5 JennyJHON DAVE BAYON-ONNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2016.08.010Document20 pagesAccepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2016.08.010Elizabeth VivancoNo ratings yet
- Neonatal HyperthyroidismDocument30 pagesNeonatal HyperthyroidismVishal SidanaNo ratings yet
- Counseling For Family PlanningDocument90 pagesCounseling For Family PlanningShang DimolNo ratings yet
- Biblical EthicsDocument105 pagesBiblical EthicsDavid John MorandarteNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self (Report)Document53 pagesUnderstanding The Self (Report)Jaymark S. GicaleNo ratings yet
- An Interview Based Project On "Professional Choices of People"Document25 pagesAn Interview Based Project On "Professional Choices of People"Alpha BlogNo ratings yet