Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Icse - Locations and Functions
Uploaded by
tiwarikhushi3800 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views15 pagesOriginal Title
ICSE_LOCATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views15 pagesIcse - Locations and Functions
Uploaded by
tiwarikhushi380Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
REVISION WORKSHEET-STD X(ICSE)
Sr.No. STRUCTURE LOCATION FUNCTION
outermost in
animal cells. Lies
next to cell wall in Regulates the entry of certain solutes and
1 Cell membrane plant cells ions
Surrounding
plasma Allows substances in solution to enter and
membrane in leave the cell without hindrance and gives
2 Cell wall plant cells rigidity and shape to the plant cell
Region
surrounding
centrioles located Initiates and regulates cell division in
3 Centrosome near the nucleus animal cells only
In the cytoplasm
4 Chloroplasts of plant cells Trap solar energy for photosynthesis
In the
Chromatin nucleoplasm in
5 Fibres interphase Carry hereditary information or genes
Clear spaces in
the cytoplasm
with water or
other substances Give turgidity to plant cells by pressing
6 Vacuoles in solution against the cell wall
On the surfaces
of leaves and in
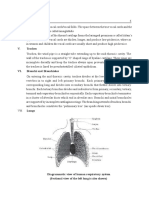
the green stems
of herbaceous Diffusion of gases for photosynthesis and
7 Stomata plants respiration
On the surfaces Diffusion of gases for photosynthesis and
8 Lenticels of woody stems respiration
On the margins of
leaves at the tips
9 Hydathodes of vein endings Guttation or Exudation
Being transparent allows sunlight to reach
Waxy layer on the the mesophyll of leaves. Prevents
10 Cuticle surfaces of leaves evaporation of water from leaf-surfaces
In the grana of
11 Thylakoids chloroplasts Site of light reaction of photosynthesis
Matrix of Site of Biosynthetic phase of
12 Stroma chloroplast photosynthesis
At the aperture
between the Maintains unidirectional flow of
Right atrium and deoxygenated blood from the right atrium
13 Tricuspid Valve the right ventricle and the right ventricle
At the aperture
between the Left Maintains unidirectional flow of
Bicuspid or atrium and theLeft deoxygenated blood from the left atrium
14 Mitral Valve ventricle and the left ventricle
At the opening of
Pulmonary the right ventricle Maintains unidirectional flow of
semilunar into the deoxygenated blood from the right
15 valves pulmonary artery ventricle into the pulmonary artery
At the point of
Aortic origin of aorta
semilunar from the left Prevents back flow of oxygenated blood
16 valves ventricle from the aorta into the left ventricle
Pocket shaped In the lumen of Maintain unidirectional flow of blood
17 valves veins towards the heart
Localise infections and prevent it from
18 Tonsils Sides of the neck spreading to the body as a whole
In the abdomen,
behind the
stomach and Acts as a blood reservoir, produces
above the left lymphocytes, destroys worn-out red blood
19 Spleen kidney cells, in an embryo it produces RBCs
on either side of
the back bone
and protected by
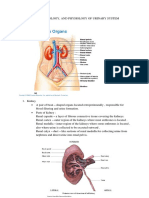
20 Kidneys the last two ribs Primary excretory organs
Arising from the
hilum in the
median surface of
each kidney and
connects behind
with the urinarry
bladder in the
lower part of the Transports urine from the kidney to the
21 Ureter abdomen urinary bladder
Expanded portion
of the ureter in
22 Renal Pelvis each kidney Receives urine from the collecting ducts
Muscular sac in
the pelis just
Urinary above and behind
23 Bladder the pubic bne Stores urine temporarily till it is expelled
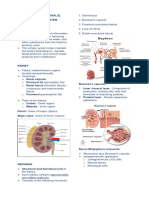
Bowman's
24 capsule In the renal cortex Receives the ultrafiltrate
Lodged in the
Bowman's
25 Glomerulus capsule Performs ultrafiltration
Proximal
Convoluted In the renal Reabsorbs 2/3rds of water and much of
26 Tubule cortex glucose
Reabsorption of remaining chlorides and
Distal some water. Walls secreting K+ and
Convoluted foreign chemicals such as Penicillin and
27 Tubule In the renal cortex other drugs into the forming urine
In the renal
28 Loop of Henle medulla Some absorption of water and sodium ions
Cerebral Outer portion of Enables us to think, reason out, invent,
29 Cortex the cerebrum plan and memorise
Just at the base Helps in maintaining body balance,
of the brain and posture and equilibrium along with
under the theinternal ear. Co-ordinates the working
30 Cerebellum cerebrum of voluntary muscles
Between the two
cerebral
Corpus hemispheres Transfers nerve impulses from one
31 Callosum internally cerebral hemisphere to the other
Controls involuntary activities of internal
Lowest portion of organs like peristalsis of the alimentary
Medulla the brain at the canal, movement of breathing, beating of
32 Oblongata base of the skull the heart etc.
carries nerve impulses from one cerebellar
hemisophere to the other, co-ordinates
Centre of the muscuklar movements on both sides of
brain below the the body, controls breathing along with the
33 Pons varolli cerebellum MO
In the relays pain and pressure impuses from the
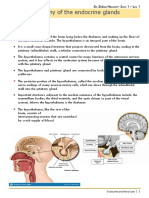
34 Thalamus Diencephalon various parts of the body to the cerebrum
Below the
thalamus in the Controls body temperature, anger, hunger,
35 Hypothalamus Diencephalon thirst and the pituitary
Small tubular part
36 Mid Brain of the brain Reflexes involving eyes and ears
pair of chains of
nerves and
ganglia on either
sides of the back Controls involuntary actions of the internal
37 ANS bone organs
Nerves arise from
the spinal cord
Sympathetic between the neck
Nervous and the waist Prepares the body for violent action
38 System region against abnormal conditions
Anteriorly in the
head and neck
Parasympathet and the other
ic Nervous posterior in sacral Concerned with re-establishing normal
39 System region conditions after the violent act is over
Between the
meninges,
ventricles of the
brain, central Acts like a cushion and protects the brain
canal of the spinal and spinal cord from injuries by absorbing
40 CSF cord mechanical shocks
Extends from the
MO down almost
the whole length
of the back bone
to the end at the
second lumbar Concerned with reflexes below the neck,
vertebra and lies conducts sensory impuses from the skin
withi the neural and muscles to the brain , conducts motor
canal of the responses from the brain to the muscles of
41 Spinal Cord vertebrae the trunk and limbs
Secrete tears that have bactericidal
lysozymes to kill germs, lubricate the eyes,
Lacrimal Upper sideward keep the front surface of the eye clean by
42 Glands portion of the orbit washing away dust particles
At the back of the
eye almost at the
centre on the
horizontal axis of Region of acute, brightest and colour
43 Yellow Spot the eyeball vision
Lateral to the
yellow spot on the
nasal side of the
44 Blind spot retina Point of no vision and origin of optic nerve
front chamber filled with aqueous humour that keeps the
Aqueous between the lens lens moist and protects it from physical
45 chamber and cornea shock, refracts light
Larger cavity Has vitreous humour that helps in
Vitreous behind the eye maintaining the shape of the eye ball and
46 chamber lens in the eye protects the retina and its nerve endings
In the middle ear
cavity wherein the
handle of the
Malleus is
attached to the
innerv surface of
the ear drum, and
the flat part of the
stirrup to the oval
window and the Their lever like movement transmits sound
Incus is found vibrations from the tympanum to the oval
47 Ear Ossicles inbetween the two window
Connecting the
Eustachain middle ear cavity Equalises air pressure on either side of the
48 Tube with the pharynx Tympanum allowing it to vibrate freely
In the median Converts sound vibrations to nerve
49 Organ of Corti cochlear canal impulses, helps in differntiating between
d f of Glucocorticoids,
Secretion i it h
Mineralocorticoids by the adrenal cortex
Adrenal Fitting like caps and adrenaline and noradrenaline byb the
50 Glands above the kidneys medulla
Below the
stomach in the Has Islets of Langerhans that secrete
51 Pancreas duodenal loop Glucagon, Insulin and Somatostatin
Bilobed, Butterfly
like structure
saddled onto the
Trachea, just
below the larynx
in front of the
52 Thyroid neck Secretes Thyroxine and Calcitonin
Small projection
hanging from the
base of the
midbrain below Secretes Gonadotropins, other tropic
53 Pituitary the hypothalamus hormones, Oxytocin, ADH
In thin walled
cutaneous
pouches called
scrotal sacs
54 Testes extraabdominally Spermatogenesis
Packaging tissues
between the coils
of the
Leydig's or Seminiferous Secrete androgens of which the main one
55 Interstitial cells tubules is Testosterone
Fitting like a cap
on the upper pole Stores spems for some days till they
56 Epididymis of the testis mature
Arising from each
testis, travelling
upward through
the inguinal
canal,looping
over the ureters
of their side,
coming together
and joining the
urethra at the
back of the Transports sperms from the testis to the
57 Vas Deferens urinary bladder Urethra
between the
posterior surface
of the Urinary Produces a secretion that serves as a
Seminal Bladder and the medium for transportation of the sperms
58 Vesicles rectum and activates them
Surrounding the
urethraclose to its Pours an alkaline secretion into the semen
origin from the as it passes through the urethra and this
59 Prostate urinary bladder neutralises the acid in the female vagina
Open into the
Bulbo-Urethral urethra just
or Cowper's before it enters Its secretion lubricatyes the tip of the penis
60 Glands the penis during coitus
In front of the
61 Penis scrotum Serves for passing out of semen and urine
In women that are
located in the
pelvis, one on
each side of the
62 Ovaries uterus Oogenesis
One on either
side of the uterus
opening near the
ovary on one side
and into the
uterus on the
63 Oviducts other side Site of Fertilisation
In the pelvic
cavity between
the UB and the Site of implantation of the blastocyst and
64 Uterus rectum growth of the foetus
Allows diffusion of Oxygen, nutrients, from
mother to the foetus; eliminates Carbon-di
oxide, urea and other wastes from foetus
Disc-like structure to the mother, acts as an endocrine gland
attached to the and secretes Oestrogens and
65 Placenta uterine wall Progesterone
Has the amniotic fluid that protects the
Sac around the embryo from physical damage by jerks or
embryo even mechanical shocks, keeps even presssure
before the all around the embryo, allows the foetus,
formation of the some restricted movement, prevents
66 Amnion allantois sticking of the foetus to the amnion
You might also like
- Location and Functions of OrgansDocument9 pagesLocation and Functions of OrgansMuhammad Sibtain RazaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Exact Location and Functions.Document7 pagesBiology - Exact Location and Functions.Soham MultaniNo ratings yet
- Location and Function Ws 10thDocument23 pagesLocation and Function Ws 10thJotham SolomonNo ratings yet
- Z - Bio 208 Location and Function 2018 - 19Document14 pagesZ - Bio 208 Location and Function 2018 - 19arinnNo ratings yet
- Semester Ii Biology NotesDocument16 pagesSemester Ii Biology NotesAAYUSHNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: Renal /urinary SystemDocument62 pagesHuman Anatomy,: Renal /urinary Systemsapana shresthaNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 6 SummaryDocument6 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 6 SummaryDana PorterNo ratings yet
- What Is Homeostasis?: Body Cells Work Best If They Have The Correct EnvironmentDocument45 pagesWhat Is Homeostasis?: Body Cells Work Best If They Have The Correct EnvironmentNatty ChikumbaNo ratings yet
- N Ephron 1111Document9 pagesN Ephron 1111Syed Sakline HossainNo ratings yet
- Practical Notes Class X Uman BiologynewnDocument8 pagesPractical Notes Class X Uman BiologynewnMayankNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument49 pagesNeuro AnatomyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Dr. Kamal KV FINAL BOOST PDFDocument41 pagesDr. Kamal KV FINAL BOOST PDFReeba janetNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System: Paired Kidneys A Ureter For Each Kidney Urinary Bladder UrethraDocument28 pagesThe Urinary System: Paired Kidneys A Ureter For Each Kidney Urinary Bladder UrethraWorknesh AmlakuNo ratings yet
- Functions Locations ReasoningsDocument6 pagesFunctions Locations ReasoningsAppyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15 Cardiovascular SystDocument6 pagesExercise 15 Cardiovascular Systholie madroneroNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 26 Urinary System Doran MLS 1 FDocument15 pagesAnaphy Chapter 26 Urinary System Doran MLS 1 FayenaNo ratings yet
- Prepared by ShakirullahDocument99 pagesPrepared by ShakirullahKhan AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Li 1 Anatomy, Histology, PhysiologyDocument17 pagesLi 1 Anatomy, Histology, PhysiologysandyaadindaNo ratings yet
- The Adrenal GlandsDocument34 pagesThe Adrenal Glandsashgee1No ratings yet
- Anph111 Reviewer (Urinary & Endocrine)Document7 pagesAnph111 Reviewer (Urinary & Endocrine)Maria Clarisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine Glands: HypothalamusDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamusgashbin latifNo ratings yet
- Terminology 1A&PDocument30 pagesTerminology 1A&PNadan KhanNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys IDocument8 pagesThe Kidneys Ior1da2sa3No ratings yet
- DR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Document86 pagesDR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Bilal YimamNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument40 pagesKidneyOlaifa victorNo ratings yet
- Blood Brain BarrierDocument11 pagesBlood Brain Barrierdmutethia68No ratings yet
- Deptals ReviewerDocument8 pagesDeptals ReviewerAnsel Francis RapsingNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Chapter 14 (Autonomic Nervous System) PDFDocument60 pagesLecture Notes For Chapter 14 (Autonomic Nervous System) PDFdwataNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument3 pagesArticleSafi MohammedNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument25 pagesEndocrine SystemLits KhoNo ratings yet
- Paper 9th Biology Annual MutaqaddimmDocument3 pagesPaper 9th Biology Annual MutaqaddimmmunawarNo ratings yet
- AnmaphyDocument18 pagesAnmaphyDE LEON ALLIANA MARIENo ratings yet
- Absorption Process by Which Substances Are Taken Into The Cell or An OrganismDocument40 pagesAbsorption Process by Which Substances Are Taken Into The Cell or An OrganismelanineNo ratings yet
- Seminar Cs 15 NovDocument24 pagesSeminar Cs 15 Novzeenatn1995No ratings yet
- 12 - Endocrine SystemDocument20 pages12 - Endocrine SystemNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument64 pagesNervous System-Anatomy & PhysiologyDeshi SportsNo ratings yet
- 1 - Anatomy of KidneysDocument22 pages1 - Anatomy of KidneysAHMAD YUNUSA GARBANo ratings yet
- L1 - KidneyDocument27 pagesL1 - KidneyKhadeja JayashNo ratings yet
- 2006RememberedQuestions (Full Answered)Document19 pages2006RememberedQuestions (Full Answered)Vladimir ArgirovicNo ratings yet
- Terminology Notebook-Ch. 19-21: Chapter 19 Respiratory System Understanding Words p735Document10 pagesTerminology Notebook-Ch. 19-21: Chapter 19 Respiratory System Understanding Words p735InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Zoology IDocument8 pagesZoology ISalman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument8 pagesCirculatory System Notesthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Protection of Spinal CordDocument17 pagesProtection of Spinal Cordkirann nawabNo ratings yet
- Classx BiologyDocument11 pagesClassx Biologyapi-492628083No ratings yet
- Study Material - 2Document5 pagesStudy Material - 2rohitsonkarrohit15No ratings yet
- Bio 8-10, 11-12thDocument7 pagesBio 8-10, 11-12thniranjanaNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Lesson 1Document26 pagesQ1 - Lesson 1Espher MacabitasNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Biomedical Research 4080 Words 155pDocument155 pagesDictionary of Biomedical Research 4080 Words 155pMSKCNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument38 pagesCirculatory SystemNilesh SahaNo ratings yet
- Homework BioDocument5 pagesHomework BioEllen MadakiweNo ratings yet
- GR 10 - Biology - Structure and Location NotesDocument6 pagesGR 10 - Biology - Structure and Location NotescnarwadkarNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Ginjal Dr. BernDocument193 pagesFisiologi Ginjal Dr. Bernheta aprianaNo ratings yet
- I. II. Brain Stem III. Cerebellum IV. Diencephalon V. Cerebrum VI. Cranial NervesDocument60 pagesI. II. Brain Stem III. Cerebellum IV. Diencephalon V. Cerebrum VI. Cranial Nervesgaurav021No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument44 pagesNervous SystemIsmailNo ratings yet
- V. Trachea: Zoology-IIDocument22 pagesV. Trachea: Zoology-IIVenkatesh JoguNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 (Urinary System)Document6 pagesUNIT 10 (Urinary System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Circ TESTDocument5 pagesCirc TESTCabo VlogNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation and Pradaxa: Jaclyn Davis, RNDocument40 pagesAtrial Fibrillation and Pradaxa: Jaclyn Davis, RNJaclyn Mattes DavisNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Surgery Made Ridiculously Simple: by Art Wallace, M.D., PH.DDocument21 pagesCardiac Surgery Made Ridiculously Simple: by Art Wallace, M.D., PH.DElias TalaniNo ratings yet
- Human Biology Study GuideDocument12 pagesHuman Biology Study GuideDawn RobinNo ratings yet
- Heart CH 12 PDFDocument65 pagesHeart CH 12 PDFGabriel Tafalla100% (1)
- SirkulasiDocument17 pagesSirkulasiJessica VanyaNo ratings yet
- 9700 m20 Ms 22 PDFDocument13 pages9700 m20 Ms 22 PDFTissa YuanNo ratings yet
- Q - A Random 8Document5 pagesQ - A Random 8Yuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Kuliah Pakar EKG - Ferdy Lainsamputty (@unsrit)Document31 pagesKuliah Pakar EKG - Ferdy Lainsamputty (@unsrit)akreditasi pkmkakas22No ratings yet
- Chapter 31: Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic SystemsDocument12 pagesChapter 31: Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic SystemsMelissa WrightNo ratings yet
- 10th STD Science 100 Important Questions Eng Version 2022 by ArunDocument35 pages10th STD Science 100 Important Questions Eng Version 2022 by ArunSriNo ratings yet
- Noonan Syndrome - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment NORDDocument24 pagesNoonan Syndrome - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment NORDSerik AdaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiology An Introduction: 12 Cardiomyopathy With Joseph S. Alpert, M.DDocument36 pagesCardiology An Introduction: 12 Cardiomyopathy With Joseph S. Alpert, M.DpasambalyrradjohndarNo ratings yet
- PTMC Percutaneous Balloon Mitral Valvuloplasty (PBMV) .NicvdDocument42 pagesPTMC Percutaneous Balloon Mitral Valvuloplasty (PBMV) .NicvdNavojit Chowdhury100% (1)
- Cardiology Summary PDFDocument62 pagesCardiology Summary PDFSyamsuriWahyuNo ratings yet
- BME411 - Physiological Fluid MechanicsDocument93 pagesBME411 - Physiological Fluid Mechanicsjoyonize08No ratings yet
- Science 9 ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience 9 ReviewerArgie MabagNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper-04 (Solved)Document14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper-04 (Solved)cbsesamplepaper0% (1)
- CARDIAC TUMORS Approach To ManagementDocument12 pagesCARDIAC TUMORS Approach To ManagementAnkit GulatiNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of A Frog Heart With The Effects of Temperature, Neurotransmitters, and Electrical IsolationDocument17 pagesThe Physiology of A Frog Heart With The Effects of Temperature, Neurotransmitters, and Electrical IsolationAbir Hasan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Sample Transes 2Document11 pagesSample Transes 2Sophia SalamatNo ratings yet
- FBA Unit-2Document37 pagesFBA Unit-2bathula hariniNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply and Nerve Supply of HeartDocument23 pagesBlood Supply and Nerve Supply of HeartNomel Jones100% (1)
- ACHAI DLaboratory Actiivty 11 - The HeartDocument6 pagesACHAI DLaboratory Actiivty 11 - The HeartSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 - Transport in HumansDocument84 pagesChapter 08 - Transport in Humanshussaini polackNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Myocytes CultureDocument6 pagesCardiac Myocytes CultureÉmerson MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Data Interpretation in Anesthesia 2017Document450 pagesData Interpretation in Anesthesia 2017Noni Frista Al Azhari100% (2)
- PKDocument155 pagesPKonline TheldaNo ratings yet
- My Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMy Cheat SheetTenzin KyizomNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy of Heart in VertebratesDocument8 pagesComparative Anatomy of Heart in VertebratesErika MatiasNo ratings yet