0% found this document useful (0 votes)
188 views6 pagesEngineering Stress Analysis Guide
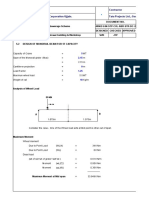
1. The document analyzes and designs angle frame supports for a mesh panel with a maximum unsupported span of 900mm and maximum width of 1500mm.
2. Calculations are shown to check the stresses in the vertical angle section supports based on IS standards, including axial stress, bending stress, shear stress, and combined stresses.
3. The results of the analysis indicate that the designed angle section satisfies all design checks against permissible stresses and deflection criteria, and is therefore safe to use as supports for the expandable mesh panel.
Uploaded by
mangeshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
188 views6 pagesEngineering Stress Analysis Guide
1. The document analyzes and designs angle frame supports for a mesh panel with a maximum unsupported span of 900mm and maximum width of 1500mm.
2. Calculations are shown to check the stresses in the vertical angle section supports based on IS standards, including axial stress, bending stress, shear stress, and combined stresses.
3. The results of the analysis indicate that the designed angle section satisfies all design checks against permissible stresses and deflection criteria, and is therefore safe to use as supports for the expandable mesh panel.
Uploaded by
mangeshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd