Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prelim Act 3
Uploaded by
tristancornejo8Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prelim Act 3
Uploaded by
tristancornejo8Copyright:
Available Formats
Cornejo Tristan G
CE – CAD1
PRLEIM ACTIVITY 3
Instruction: answer the following questions below. Answer must be handwritten.
1. What is free hand lettering?
-Freehand lettering refers to the process of manually creating text or annotations within
a computer-aided design (CAD) software without the use of predefined fonts or automated text
tools. Engineers or drafters use a stylus or mouse to draw letters directly onto the design
interface, mimicking the appearance of handwritten text. This technique allows for greater
flexibility and customization in labeling drawings, diagrams, or plans. Freehand lettering can add
a personal touch to technical drawings and is often used for annotations, notes, or callouts
where precise placement or unique styling is desired. While it offers creative freedom, it may
require more time and skill compared to using standard text tools in CAD software.
2. What are the conventions for engineering lettering?
-Engineering lettering or also known as “Technical lettering”,
It is the process of forming letters, numerals, guidelines, lettering styles, spacing and other
characters that provides major specifications that describe an object in engineering lettering with
highly detailed documentation of information for fellow engineers. These conventions typically
involve the use of uppercase letters in a sans-serif font to enhance readability Technical lettering
was used for writing or carve technical drawings architectural plans, maps, and other
documents
3. What are the common mistakes in engineering lettering?
-Inconsistent letter height is a frequent error in technical lettering that can cause confusion
and misreading of the text. Inappropriate word and letter spacing also affects readability and
professional presentation. Another common problem is using a font or lettering style that is
incorrect or doesn't follow engineering standards. Inaccurate letter alignment on the horizontal
or vertical axes can affect how well the lettering looks overall and how precise it is. Using the
wrong tools, like drafting templates or rulers, can lead to messy or uneven letters. Last but not
least, ignoring the value of honing writing techniques can contribute to these errors and impede
clear communication in engineering drawings.
4. What are the types of Multiview projection? Define each.
Orthographic Projection- Using many 2D perspectives of an object, an orthographic
projection can be used to depict a 3D object. Multiviews are an additional term for orthographic
drawings. Top, front, and right side are the viewpoints that are most frequently employed.
Isometric Projection- A technique for visualizing three-dimensional things that engineers,
technical illustrators, and occasionally architects utilize. The technique aims to display the
object's principal dimensions in an undistorted manner while combining the illusion of depth,
similar to that of a perspective rendering.
Oblique Projection- An oblique drawing gives the impression of being pictorial by drawing the
receding surfaces at an angle and the front view at actual size. The benefit of this type of
projection is that it may display an object's One View, or Front View, without distortion.
Axonometric Projection- The feature that distinguishes axonometric projection from multiview
projection is the inclined position of the object with respect to the planes of projection. When a
surface or edge of the object is not parallel to the plane of projection, it appears foreshortened
Trimetric Projection- An image is created using three axes like in a perspective drawing. This
produces a three-dimensional picture of the thing being drawn by concurrently viewing it from
three separate angles. In trimetric drawings, the three axes are usually positioned at angles of
30, 60, and 90 degrees to one another.
Dimetric Projection- Another kind of perspective drawing that creates an image with two axes
is called dimetric drawing. When anything is drawn diametrically, it is simultaneously viewed
from two angles, giving the impression that the object is two dimensions deep. In dimetric
drawing, the two axes are usually positioned 45 degrees and 135 degrees apart.
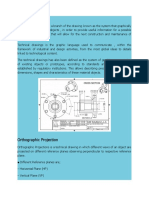
5. What is orthographic projection and provide at least one sample.
Orthographic projection The technique of orthographic projection is a method of representing
three-dimensional objects by three two dimensional drawings, in each of which the object is
viewed along parallel lines that are perpendicular to the plane of the plane of the drawing. For
example an orthographic projection of a house typically consists of a plan view, a front view and
a side view
You might also like
- Digital Assignment-1: Product Development and ManagementDocument9 pagesDigital Assignment-1: Product Development and ManagementSanjit RameshNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing Guide - 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesTechnical Drawing Guide - 40 CharactersJenny TingsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Engineering Drawing and Its Instruments: © Copy Right: Rai University 3.155 / 3A.155 / 3B.155 / 4A.151 / 7.151 3Document3 pagesLesson 2 Engineering Drawing and Its Instruments: © Copy Right: Rai University 3.155 / 3A.155 / 3B.155 / 4A.151 / 7.151 3Аисыафирул КасимNo ratings yet
- Aphical ModellingDocument16 pagesAphical ModellingDhanush Karthik RajanNo ratings yet
- 1 Instruments MKSDocument3 pages1 Instruments MKSPrasanna Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing or Drafting: Methods SketchingDocument10 pagesTechnical Drawing or Drafting: Methods SketchingMark BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- Unit 08Document21 pagesUnit 08elliottashley22No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Technical DrawingDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Technical Drawingdavid78% (9)
- Cad Cam Full Detail PracticalDocument45 pagesCad Cam Full Detail PracticalSamarNo ratings yet
- Internship On 2D Design and Management: Handout MaterialDocument52 pagesInternship On 2D Design and Management: Handout MaterialPrasad Govind KumbharNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing - WikipediaDocument45 pagesTechnical Drawing - WikipediaAngelee PaskieNo ratings yet
- The Role of Engineering Drawing Production ReviewDocument2 pagesThe Role of Engineering Drawing Production ReviewSafira ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 CadDocument23 pagesLesson 1 CadBlank UndefeatedNo ratings yet
- Lukisan Kejuruteraan ReportDocument18 pagesLukisan Kejuruteraan Reportaq laparNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided DesignDocument26 pagesComputer Aided DesignEngr Fazal AkbarNo ratings yet
- Drawings & SpecificationsDocument15 pagesDrawings & SpecificationsNathan RusereNo ratings yet
- DrawDocument36 pagesDrawHassan XoghayeNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 Basics of Machine DrawingDocument9 pagesPractical 2 Basics of Machine Drawingy2k405 kaosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Technical DraftingDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Technical Draftingjhun.atienzaNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument65 pagesEngineering DrawingEngr Fazal AkbarNo ratings yet
- Learn Basic Drawing and Drafting SkillsDocument36 pagesLearn Basic Drawing and Drafting SkillsJc SantosNo ratings yet
- Abs Trac Final 2Document39 pagesAbs Trac Final 2DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENo ratings yet
- Not To Be Confused With Technical DrawDocument3 pagesNot To Be Confused With Technical DrawBryan PanilaNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing, Drafting or Drawing, Is The Act andDocument11 pagesTechnical Drawing, Drafting or Drawing, Is The Act andAjhay BonghanoyNo ratings yet
- Notes - Enh 215 - Technical Design and DrawingsDocument27 pagesNotes - Enh 215 - Technical Design and DrawingsKEVIN OMONDINo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument27 pagesEngineering Drawingjacob100% (1)
- IGCSE Systems and Control PresentationDocument330 pagesIGCSE Systems and Control PresentationBrad BridgesNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument26 pagesEngineering DrawingChristian Makande100% (1)
- Engineering DrawingDocument99 pagesEngineering DrawingBinu ChandranNo ratings yet
- Technical DraftingDocument21 pagesTechnical DraftingJun SalmorinNo ratings yet
- Technical DrawingDocument10 pagesTechnical DrawingDanica Nicole BuhatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1zulhafizzanNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument97 pagesEngineering DrawingMurari VattipalliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing: Credit HoursDocument40 pagesEngineering Drawing: Credit Hoursinam ullahNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Course BookDocument48 pagesEngineering Drawing Course Bookgirishkaundinya100% (15)
- Drafting For Architectural DesignDocument47 pagesDrafting For Architectural DesignDezyne EcoleNo ratings yet
- Orthographic ProjectionpresentationDocument23 pagesOrthographic ProjectionpresentationJan JayNo ratings yet
- Architectural GraphicsDocument67 pagesArchitectural GraphicsAgathaAurea100% (1)
- Application of Engineering Drawing in Chem. Engg.Document3 pagesApplication of Engineering Drawing in Chem. Engg.ArslanQureshi0% (1)
- Engineering DrawingDocument49 pagesEngineering DrawingSãröj Shâh100% (2)
- Engineering Drawing and CADDocument53 pagesEngineering Drawing and CADpajarillo0100% (1)
- Computer Aided Engineering Graphics As Per The New Syllabus B Tech I Year of U P Technical UniversityDocument227 pagesComputer Aided Engineering Graphics As Per The New Syllabus B Tech I Year of U P Technical UniversitykpkrisNo ratings yet
- Basic Working Drawing: Why Are Working Drawings Used?Document21 pagesBasic Working Drawing: Why Are Working Drawings Used?Brett AmbilNo ratings yet
- Notes on Mechanical Drawing - Prepared for the Use of Students in Mechanical, Electrical and Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandNotes on Mechanical Drawing - Prepared for the Use of Students in Mechanical, Electrical and Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Drawing and Electrical Circuit DesigningDocument17 pagesDrawing and Electrical Circuit Designingkudzidza3No ratings yet
- Modul English For Engineering II UnlockedDocument11 pagesModul English For Engineering II UnlockedRikko PutraNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Drawing - Projection Drawing, Isometric and Oblique Drawing, Working DrawingsFrom EverandMechanical Drawing - Projection Drawing, Isometric and Oblique Drawing, Working DrawingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Part OneDocument78 pagesLecture 1 Part Onewubied100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing: North South UniversityDocument14 pagesEngineering Drawing: North South UniversityMD. Zobayer Ahmed 1610766642No ratings yet
- Technical Drawing GuideDocument8 pagesTechnical Drawing GuideMori JinNo ratings yet
- National Textile UniversityDocument20 pagesNational Textile UniversitysarmadranaNo ratings yet
- 4 Basics - of - Technical - DrawingDocument50 pages4 Basics - of - Technical - DrawingVio100% (1)
- Engineering Design and CADDocument35 pagesEngineering Design and CADrika_efriNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Eng-Drawing - IntroductionDocument34 pagesModul 1 Eng-Drawing - IntroductionnanangasNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument25 pagesEngineering DrawingElena Edna100% (1)
- Technical drawing guideDocument10 pagesTechnical drawing guideShiela Mae Falsis SalesNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Course: An IntroductionDocument13 pagesEngineering Drawing Course: An Introductionvipsdgr8No ratings yet
- Progressive Steps in Architectural Drawing - A Step-by-Step Method for Student Draughtsmen Together with Details of Construction and DesignFrom EverandProgressive Steps in Architectural Drawing - A Step-by-Step Method for Student Draughtsmen Together with Details of Construction and DesignRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Virtual Presence PresentationDocument11 pagesVirtual Presence Presentationmini369No ratings yet
- Isometric ProjectionsDocument62 pagesIsometric ProjectionsRoni EnjelaniNo ratings yet
- (GPU Gems 1) Randima Fernando - GPU Gems - Programming Techniques, Tips and Tricks For Real-Time Graphics. 1-Addison-Wesley Professional (2004)Document783 pages(GPU Gems 1) Randima Fernando - GPU Gems - Programming Techniques, Tips and Tricks For Real-Time Graphics. 1-Addison-Wesley Professional (2004)Vishnu RamachandranNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks Education Detailed Drawing ExercisesDocument51 pagesSolidWorks Education Detailed Drawing ExercisesLeonardo AlexNo ratings yet
- EDU Detailed Drawings Exercises 2017 PDFDocument51 pagesEDU Detailed Drawings Exercises 2017 PDFTheZsooltiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Axonometric ProjectionDocument38 pagesChapter 14 - Axonometric ProjectionPurece EugenNo ratings yet
- Lect1 VK AdvDocument70 pagesLect1 VK AdvRACHIT16No ratings yet
- Texturing in MayaDocument13 pagesTexturing in MayaGeorgie LeslieNo ratings yet
- Fire Hydrant Ref. Elevation 10.00M: Existing CHB FenceDocument1 pageFire Hydrant Ref. Elevation 10.00M: Existing CHB FenceUmali De Castro NhelNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Psychology GCSE - Topic A - Monocular Depth CuesDocument3 pagesYear 10 Psychology GCSE - Topic A - Monocular Depth CuesjosephsparksNo ratings yet
- Unlit Simple Water ShaderDocument3 pagesUnlit Simple Water ShaderEdwin ErdiyanaNo ratings yet
- Research ReporDocument12 pagesResearch ReporBin Aqlan AqlanyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 EditedDocument32 pagesUnit 7 EditedtadyNo ratings yet
- GLEW GLFW Library SetupDocument37 pagesGLEW GLFW Library SetuprobinNo ratings yet
- Stereoscopy: Submitted By-Saumya Tripathi 2K7/ME/304Document22 pagesStereoscopy: Submitted By-Saumya Tripathi 2K7/ME/304Saumya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Problem It AsDocument379 pagesProblem It Asfernando paucarNo ratings yet
- EDU Detailed Drawings Exercises 2017Document51 pagesEDU Detailed Drawings Exercises 2017PAULA ANDREA ROJAS SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Xel Noggit's Log 09-16-09Document382 pagesXel Noggit's Log 09-16-09theX3LNo ratings yet
- ASME Y14.4M-1989 Pictoral DrawingDocument16 pagesASME Y14.4M-1989 Pictoral DrawingloebNo ratings yet
- 10ravens 3D 013 Kitchen Decorations 01Document16 pages10ravens 3D 013 Kitchen Decorations 01Agus RahayuNo ratings yet
- TEXTURE MAPPING TECHNIQUES EXPLAINEDDocument32 pagesTEXTURE MAPPING TECHNIQUES EXPLAINEDاقوالِ زریں -Golden WordsNo ratings yet
- Crack TCS NQT 2022 in One GoDocument3 pagesCrack TCS NQT 2022 in One GoshivanshNo ratings yet
- Unknown FileDocument26 pagesUnknown Filebadruz zamaniNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks Education Detailed Drawing ExercisesDocument51 pagesSolidWorks Education Detailed Drawing ExercisestotoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Orthographic ProjectionsDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Orthographic ProjectionsLinh DoNo ratings yet
- Normal MapsDocument16 pagesNormal Mapsbomimod100% (5)
- Pictorial Sketching TechniquesDocument14 pagesPictorial Sketching TechniquesMohammed GhisheerNo ratings yet
- Axonometric Projection Is A Type of Parallel ProjectionDocument10 pagesAxonometric Projection Is A Type of Parallel ProjectionJeston Ugalde100% (1)
- BITS Pilani: Computer Aided Analysis and Design (ME G611) Seminar Presentation 2Document33 pagesBITS Pilani: Computer Aided Analysis and Design (ME G611) Seminar Presentation 2Vipul AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling Essentials: Introduction To 3D Modeling TechniquesDocument49 pages3D Modeling Essentials: Introduction To 3D Modeling TechniquesEfe Ariaroo100% (1)