Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Energy Engineering
Uploaded by
nityanandOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Energy Engineering
Uploaded by
nityanandCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy Engineering – 17ME71 2020-21
Module No. 1: Thermal Energy Conversion System
Syllabus:
Thermal Energy conversion system: Review of energy scenario in India, General philosophy
and need of energy, Different Types of fuels used for steam generation, Equipment for
burning coal in lump form, strokers, different types, Oil burners, Advantages and
disadvantages of using pulverized fuel, Equipment for preparation and burning of pulverized
coal, unit system and bin system. Pulverized fuel furnaces, cyclone furnace
Coal and ash handling, Generation of steam using forced circulation, high and supercritical
pressures. Chimneys: Natural, forced, induced and balanced draft, Calculations and numerical
involving height of chimney to produce a given draft. Cooling towers and Ponds. Accessories
for the Steam generators such as Superheaters, De-superheater, control of superheaters,
Economizers, Air preheaters and re-heaters.
1. Energy scenario in India
India is both a major energy producer and consumer. India currently ranks as the world’s
eleventh greatest energy producer, accounting for about 2.4% of the world’s total annual
energy production, and as the world’s sixth greatest energy consumer, accounting for 3.3% of
the world’s total annual energy consumption. Thus, India is a net energy importer, mostly due
to the large imbalance between oil production and consumption.
Table 1.1: Sector wise energy consumption
Sector Energy consumption
Industry 49%
Transport 22%
Residential 10%
Agriculture 5%
Others 14%
Table 1.2: Electrical energy generation
Resource Energy generation
Thermal (Coal, Gas, Diesel) 64%
Nuclear 3%
Hydro 25%
Renewable sources 8%
7th Semester ME Page 1 of 2
Energy Engineering – 17ME71 2020-21
Available energy resources:
A. Conventional
(i) Fossil fuel
(ii) Hydro resources
(iii) Nuclear resources
B. Non-conventional
(i) Wind energy
(ii) Solar energy
(iii) Biomass energy
(iv) Geothermal resources
(v) Ocean tidal energy
(vi) Ocean wave and OTEC resources
Need of energy:
The energy need of a nation can be broadly divided into the following sectors:
1. Domestic sector (houses, offices and commercial buildings)
2. Transportation sector
3. Agriculture sector
4. Industry sector
Consumption of energy in a country indicates increased activities in these sectors. This
implies better comforts at home due to use of various appliances, better transport facilities,
more agricultural and industrial production. Therefore, per capita energy consumption of a
country is an index of the standard of living or prosperity of the people of the country.
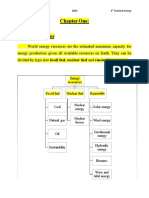
2. Types of fuel used
a. Solid (Coal)
b. Liquid (Oil)
c. Gas (Natural gas)
d. Nuclear fuel
A. Based on Occurrence: B. Based on state
Primary fuel Secondary fuel Solid Liquid Gas
(Natuarl) (Artificial)
Wood Gasoline
Peat Diesel
Lignite Kerosene
Natural gas Coke gas
Petroleum Blast furnace gas
7th Semester ME Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Topc 2 HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE - StudentDocument36 pagesTopc 2 HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE - StudentMuhammad AzarulNo ratings yet
- Cessna 152 Electrical System ExplainedDocument4 pagesCessna 152 Electrical System ExplainedJoséMendesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 1Document78 pagesUnit 1 Part 1nanthanaNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources: Dr. Banamali DalaiDocument209 pagesRenewable Energy Sources: Dr. Banamali DalaiK RaghuNo ratings yet
- ENERGY SOURCES GUIDEDocument36 pagesENERGY SOURCES GUIDErajat bagsNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Energy Sources: Energy Source Can Be Divided Into 3-TypesDocument17 pagesUNIT-1 Energy Sources: Energy Source Can Be Divided Into 3-TypesSuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- Non-Conventional Energy SourcesDocument69 pagesNon-Conventional Energy SourcesCse 2k17No ratings yet
- RES Merged Slides 1-6 - CompressedDocument454 pagesRES Merged Slides 1-6 - Compressedyadomiy377No ratings yet
- TME 223 - Module 6 - 2020 - 2021Document48 pagesTME 223 - Module 6 - 2020 - 2021Skill ShareNo ratings yet
- G.-Shanmugam-200-Years-of-Fossil-Fuels-and-Climate-Change-1900-2100Document21 pagesG.-Shanmugam-200-Years-of-Fossil-Fuels-and-Climate-Change-1900-2100Rut Accilio HerreraNo ratings yet
- Status of Geothermal Energy Amongst The World's Energy SourcesDocument10 pagesStatus of Geothermal Energy Amongst The World's Energy SourcesGloria Luciana Muñoz VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Energy Scenario OverviewDocument37 pagesEnergy Scenario OverviewSreejith P. MenonNo ratings yet
- Biotech 3Document72 pagesBiotech 3Omid Karimi SadaghianiNo ratings yet
- SMEA3013Document75 pagesSMEA3013HarshNo ratings yet
- NCEPG AssignmentDocument6 pagesNCEPG AssignmentkamalNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 1.1 Energy Scenario Part-I: Objective Type Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesChapter: 1.1 Energy Scenario Part-I: Objective Type Questions and AnswersAnonymous VDn6xxNo ratings yet
- ResDocument29 pagesResBarathkumar0% (1)
- Non-Conventional Energy Sources ExplainedDocument47 pagesNon-Conventional Energy Sources ExplainedPuneeth hr2100% (1)
- Chapter 2 explores energy types and sourcesDocument45 pagesChapter 2 explores energy types and sourcesjohn kayhnNo ratings yet
- ENERGY The EnterpriseDocument16 pagesENERGY The Enterpriseapoorva apoorvaNo ratings yet
- Geography of The UK. Lesson 7Document8 pagesGeography of The UK. Lesson 7Roxana MireaNo ratings yet
- NSE_S1 IS_Ch 5 Energy Sources_Article ReadingDocument6 pagesNSE_S1 IS_Ch 5 Energy Sources_Article ReadingasayilaltaNo ratings yet
- PIKE Renewable Energy 2014-2015Document76 pagesPIKE Renewable Energy 2014-2015AdistiNo ratings yet
- Ncer NotesDocument77 pagesNcer NotesAkashNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation and ManagementDocument83 pagesEnergy Conservation and Managementbmdbmdbmd100% (1)
- ME 3239 Combustion for Energy Conversion Lecture 1Document30 pagesME 3239 Combustion for Energy Conversion Lecture 1John LingNo ratings yet
- 1st Class-6th Jan 2023Document51 pages1st Class-6th Jan 2023Manish meenaNo ratings yet
- Master's Program Energy Efficiency Course OverviewDocument51 pagesMaster's Program Energy Efficiency Course OverviewRabi SarmaNo ratings yet
- Oil Crops For Energy: G Koc Ar, Ege University Solar Energy Institute, Izmir, TurkeyDocument10 pagesOil Crops For Energy: G Koc Ar, Ege University Solar Energy Institute, Izmir, TurkeyDiegoVasqzNo ratings yet
- SDG & Renewable EnergyDocument16 pagesSDG & Renewable EnergyDionisius 23No ratings yet
- Unit1Class1 20200713154914Document20 pagesUnit1Class1 20200713154914Paarth PrakashNo ratings yet
- Energy Supply Investigation 2022Document4 pagesEnergy Supply Investigation 2022Amaya CembellinNo ratings yet
- 07042020124050lecture Notes of Renewable Energy and Green TechnologyDocument108 pages07042020124050lecture Notes of Renewable Energy and Green TechnologyMinhaj GhouriNo ratings yet
- Recommended Books:: Introduction To Types of Renewable Energy, Fuel Cell and Heat Pump SystemsDocument37 pagesRecommended Books:: Introduction To Types of Renewable Energy, Fuel Cell and Heat Pump SystemsTahaMustahsanNo ratings yet
- Biogas LecturesDocument99 pagesBiogas LecturesNishantShahNo ratings yet
- Optimizing The Exploitation of Natural Energy Resources in Nigeria For Accelerated Socio-Economic Development: Strategies and Opportunities For InvestmentDocument57 pagesOptimizing The Exploitation of Natural Energy Resources in Nigeria For Accelerated Socio-Economic Development: Strategies and Opportunities For InvestmentState House Nigeria100% (1)
- Piroliza Art IasiDocument10 pagesPiroliza Art IasiCristina TynaNo ratings yet
- Fuel ConsumptionDocument11 pagesFuel ConsumptionMerick Diamante Jr.No ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1Sipra SamuiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 IntroductionDocument37 pagesUnit-1 Introduction2k21cse093No ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument35 pagesNuclear ChemistryKarpaga MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 World Energy ScenarioDocument43 pagesUnit 5 World Energy ScenarioRitvikNo ratings yet
- BioenergyDocument16 pagesBioenergyVivek 2K21B241No ratings yet
- تأشيرات الشرحيات المطلوبة1Document6 pagesتأشيرات الشرحيات المطلوبة1احمد كريم خلفNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Developmentin MalawiDocument21 pagesSolar Energy Developmentin MalawiJohn TauloNo ratings yet
- Agro Waste To Refuse-Derived Fuel Converting Machine PaperDocument4 pagesAgro Waste To Refuse-Derived Fuel Converting Machine PaperCronsentNo ratings yet
- CHN-112 ENERGY ENGINEERING: RICHARD SMALLEY, NOBEL PRIZE WINNER 1996Document69 pagesCHN-112 ENERGY ENGINEERING: RICHARD SMALLEY, NOBEL PRIZE WINNER 1996HIRALAL GARGNo ratings yet
- Thesis 123456Document50 pagesThesis 1234563306 PRANAY KUMAR REDDY . PNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology and EnergyDocument2 pagesScience, Technology and EnergySuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes of New and Renewable Energy TechnologyDocument109 pagesLecture Notes of New and Renewable Energy TechnologyPower SystemNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Energy ScenarioDocument37 pages1.1 Energy ScenarioShalu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eenrgy Audit and Management Books-GuideDocument750 pagesEenrgy Audit and Management Books-GuideAnonymous LHGQqOB100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Reader - Energy in BuildingsDocument35 pagesChapter 5 - Reader - Energy in Buildingsdidem mutNo ratings yet
- Environmental Geography and Sustainable DevelopmentDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Geography and Sustainable DevelopmentAriefz WillNo ratings yet
- FRF MergedDocument201 pagesFRF MergedSrinivas KumarNo ratings yet
- New A Review of Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument9 pagesNew A Review of Renewable Energy ResourcesrahulNo ratings yet
- Biochar Production, Activation and Adsorptive Applications: A ReviewDocument23 pagesBiochar Production, Activation and Adsorptive Applications: A ReviewmarianasouborNo ratings yet
- Article On Renewable EnergyDocument14 pagesArticle On Renewable EnergyPoonam YadavNo ratings yet
- Sun, Wind and Desert: MENA, the upcoming Clean Energy World ChampionFrom EverandSun, Wind and Desert: MENA, the upcoming Clean Energy World ChampionNo ratings yet
- Our Energy Future: Resources, Alternatives and the EnvironmentFrom EverandOur Energy Future: Resources, Alternatives and the EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Katalog Mitsubishi SRLD-K100Document12 pagesKatalog Mitsubishi SRLD-K100singgihNo ratings yet
- CT SizingDocument34 pagesCT Sizingivishnurk100% (1)
- Canadian Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Mechanic Practice Manual (Diagrams, Questions & Answers)Document73 pagesCanadian Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Mechanic Practice Manual (Diagrams, Questions & Answers)Victor Kavhendekete, MTechMgt, BTech100% (2)
- English 11test Unit 9 10 11Document2 pagesEnglish 11test Unit 9 10 11Suri V TranNo ratings yet
- Comsol Acdc RF V43aDocument102 pagesComsol Acdc RF V43aHaris Apriyanto0% (1)
- Start Reducing Factory Operating Costs and Carbon Emissions in Just One Month - .Document6 pagesStart Reducing Factory Operating Costs and Carbon Emissions in Just One Month - .ranNo ratings yet
- Vco WDocument8 pagesVco Wapi-3725139No ratings yet
- Lesson 16: Surface Area and VolumeDocument27 pagesLesson 16: Surface Area and VolumemisterreidNo ratings yet
- Kepler's laws of planetary motionDocument3 pagesKepler's laws of planetary motionOmema AmirNo ratings yet
- Sotra Anchor and ChainDocument164 pagesSotra Anchor and ChainX-Titan Wan de Pirates100% (2)
- Presentation Capacitor Start Motor (Group 4)Document14 pagesPresentation Capacitor Start Motor (Group 4)Surajit ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Baja HollowDocument14 pagesPerhitungan Baja Hollowm. RizaldiNo ratings yet
- SI Units Hukum Gas Ideal Turbin Efis Power Pressure Tcompress Flow Mdot Vnormal Mol RDocument3 pagesSI Units Hukum Gas Ideal Turbin Efis Power Pressure Tcompress Flow Mdot Vnormal Mol RAhmad ZaenudinNo ratings yet
- Final Report Transmission Line TowerDocument41 pagesFinal Report Transmission Line TowersarankumarNo ratings yet
- DEE-23106 Fundamentals of Electrical and Power Engineering: Exercise #1Document12 pagesDEE-23106 Fundamentals of Electrical and Power Engineering: Exercise #1shoptodipNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics-Challenge-VDocument3 pagesThermodynamics-Challenge-VteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- Gas Power CycleDocument49 pagesGas Power CycleNafisa AnikaNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Forces TestDocument17 pagesYear 9 Forces Testaysha kamar halabiNo ratings yet
- Solidworks Report of Light PoleDocument12 pagesSolidworks Report of Light PoleThahir ShahNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material QuestionsDocument82 pagesEngineering Material QuestionsRakesh Inani67% (3)
- Renewable Energy SourceDocument9 pagesRenewable Energy SourceyeabmotherNo ratings yet
- CVD Diamond BookletDocument28 pagesCVD Diamond BookletАндрей ВольхинNo ratings yet
- Physics Xi Wave, Sound & Motion Chapter # 8Document6 pagesPhysics Xi Wave, Sound & Motion Chapter # 8Afshan ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. IntroductionDocument18 pagesChapter 1. IntroductionMerlin MendozaNo ratings yet
- 8.6 MV Feeder Earth-Fault ProtectionDocument20 pages8.6 MV Feeder Earth-Fault Protectionbiviana81No ratings yet
- PHYSICS FOR HEALTH SCIENCE ActivitiesDocument10 pagesPHYSICS FOR HEALTH SCIENCE ActivitiesMyrel Joy Fabiaña LucdayNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper - 9 Term-1Document11 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - 9 Term-1JatinNo ratings yet
- Air To Water Catalog Standard 20220419Document34 pagesAir To Water Catalog Standard 20220419coin pvhNo ratings yet