Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quarter 2 Biotech
Uploaded by
baloranberyljean0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesQuarter 2 Biotech
Uploaded by
baloranberyljeanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
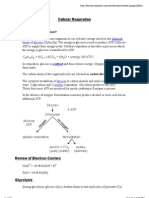
The overall equation for aerobic cellular
QUARTER 2 BIOTECH
respiration is:
TERMINOLOGY
ADP- Adenosine diphosphate
ATP- Adenosine triphosphate
NAD- Nicotinaamide Adenine dinuclectide When you eat a potato, your body gradually
NADH- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide breaks it down through a process called cellular
plus Hydrogen respiration, converting it into energy. This energy,
FAD- Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate),
FADH- Flavin Adenine dinucleotide fuels various activities like thinking, exercising, or
plus Hydrogen even lounging on the couch. Cellular respiration
PGAL- Phosphoglyceraldehyde involves three main steps: Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle,
OAA- Oxaloacetic Acid and Oxidative Phosphorylation.
COA- Coenzyme A
1Glycolysis: Think of it like investing energy to get
more energy. The cell invests 2 ATP molecules to
start glycolysis, but later gains 4 ATP molecules,
Cellular respiration
resulting in a net profit of 2 ATP molecules.
-takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of Glycolysis also produces NADH, which is crucial for
each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the the next steps.
cytoplasm, while the TCA cycle occurs inside the
matrix of the
mitochondria. Meanwhile, oxidative phosphorylation
occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane, with
protons diffusing across into the membrane and later 2. Krebs Cycle: This happens in the mitochondria,
pumped back into the matrix. the powerhouse of the cell. Pyruvate, formed in
glycolysis, enters the Krebs cycle. This cycle
-Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically produces NADH and FADH2, which carry
(using oxygen), or anaerobically (without "energized electrons" used to generate ATP. One
cycle yields 3 NADH and 1 FADH2.
oxygen).
During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts
3Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative
with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by
Phosphorylation: NADH and FADH2 donate their
the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created electrons to the electron transport chain, creating
as byproducts. an electrochemical gradient. ATP synthase then
uses this gradient's energy to convert ADP to ATP.
Oxygen is crucial here; without it, ATP synthesis pyruvate oxidation yields one acetyl-CoA, one NADH,
stops. and one CO2 per pyruvate, while the TCA cycle
produces one GTP, three NADH, one FADH2, and two
CO2. NADH and FADH2 contribute to the electron
transport chain, enabling oxidative phosphorylation to
The overall energy yield is around 32 ATP
produce an additional 28-30 ATP and 28-30 water
molecules from one glucose molecule, but this is
molecules per glucose. Consequently, the overall
an estimate. Cellular respiration also produces cellular respiration process yields approximately 30-32
intermediates used in creating molecules like ATP per glucose molecule.
proteins and nucleic acids. The by-products are
CO2, water, and some heat, which the body
usually discards.
In summary, when you eat a potato, your body's
cellular respiration converts it into ATP, providing
the energy needed for your daily activities.
ABSTRACT NOTES
-The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage,
but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and
NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide derived from vitamin B3, is
a universal electron acceptor that is crucial in the
process of cellular respiration. Another important
universal electron acceptor is FAD, a flavin nucleotide
from vitamin B2. These acceptors are often used in
catabolic processes and are reduced into NADH and
FADH2, respectively.
-Glycolysis requires an input of glucose, two ATP, two
ADP, and two NAD+. Reactants for pyruvate oxidation
are pyruvate, NAD+, and coenzyme A (CoA). One TCA
cycle requires acetyl-CoA, one ADP, three NAD+, and
one FAD. Finally, oxidative phosphorylation and the
electron transport chain use the reactants ADP, NADH,
FADH2, and O2.
-Cellular respiration culminates in the production of ATP
and water as final end products. In the absence of
oxygen, glycolysis occurs, generating two pyruvate
molecules, four ATPs (net two ATP), two NADH, and two
water molecules per glucose. With oxygen present,
You might also like
- STPM BIOLOGY RespirationDocument14 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Respirationwkwhui75% (4)
- Physiology of StarvationDocument59 pagesPhysiology of StarvationMitesh Sinha100% (3)
- SCHOOL COPY Gen Bio 1 - Q2 Module 4Document20 pagesSCHOOL COPY Gen Bio 1 - Q2 Module 4PLS help me get 1k subsNo ratings yet
- Histo Lec Finals Long Quiz 1 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesHisto Lec Finals Long Quiz 1 Answer KeyJules Reyes100% (1)
- Quarter 2 BiotechDocument2 pagesQuarter 2 BiotechbaloranberyljeanNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationKuroNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument29 pagesRespiration in PlantsJahanzeb SafdarNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter - Biology ReviewerDocument1 page2nd Quarter - Biology ReviewerGrass SellerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesLecture Notes On Cellular RespirationBhillee Agas ValdezNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument11 pagesRespirationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration PDFAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in PlantsjanakiramannadesanNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument27 pagesCell RespirationJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis & Kreb's CycleDocument33 pagesGlycolysis & Kreb's CycleMapple Hernandez BelenNo ratings yet
- Respiration 5.2.1Document11 pagesRespiration 5.2.1bexNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Ms. K. Smith Bhs-Biology 6 FormDocument47 pagesRespiration: Ms. K. Smith Bhs-Biology 6 FormJanae CampbellNo ratings yet
- EMGBS Bio G11 U5 NoteDocument80 pagesEMGBS Bio G11 U5 NoteDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEJee MascardoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Energy: Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument12 pagesCellular Energy: Photosynthesis & RespirationGobiNo ratings yet
- 14 Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument4 pages14 Respiration in Plants-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Ch-14 Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes BiologyDocument5 pagesCh-14 Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes BiologyMANDAL VIKRAMNo ratings yet
- ADPATPand Cellular RespirationDocument43 pagesADPATPand Cellular RespirationJessa CabusaoNo ratings yet
- ADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationDocument30 pagesADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationJillian Lao100% (2)
- Summary Notes (2022-2024 Syllabus)Document6 pagesSummary Notes (2022-2024 Syllabus)darshanpandaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument6 pagesRespiration in Plants-NotesAnirudh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Cell RepDocument21 pagesCell Repvictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- Reporting in Science Group 7Document14 pagesReporting in Science Group 7Ashley Santander IbañezNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument28 pagesCellular RespirationPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bio 1130 Outline Week 9Document13 pagesBio 1130 Outline Week 9Tonet LapeNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 1. GlycolysisDocument5 pagesCellular Respiration 1. GlycolysisMoreen LamsenNo ratings yet
- Biochem GlycolysisDocument7 pagesBiochem Glycolysisnabilahuda92No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & Respiration: By: James Grant & Aimee IrvinDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis & Respiration: By: James Grant & Aimee IrvindunklinjNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - ColumnedDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration - ColumnedAndre Miguel LlanesNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants - Shobhit NirwanDocument14 pagesRespiration in Plants - Shobhit Nirwananitalimbachiya86No ratings yet
- Respiration and PhotorespirationDocument29 pagesRespiration and PhotorespirationThảo UyênNo ratings yet
- PS and CRDocument34 pagesPS and CRErika MatiasNo ratings yet
- 2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoDocument6 pages2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoLucas BuSheaNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm: GlycolysisDocument4 pagesCytoplasm: Glycolysisapi-296833859No ratings yet
- An Overview of Glycolysis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Glycolysis and Cellular Respirationabdulrehman999No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 Module 4.4 Respiration RevisionDocument5 pagesBiology Unit 4 Module 4.4 Respiration RevisionRebekah Louise Penrice-RandalNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Uses Energy in Glucose To Make: Krebs CycleDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration Uses Energy in Glucose To Make: Krebs CycleVince Josue LopezNo ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration (A)Document19 pagesEnergy and Respiration (A)mptneuro2024No ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-BioDocument17 pagesMitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-Biocassidy conchaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 14 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationCJ100% (1)
- Biology 1113 Notes Unit 4Document17 pagesBiology 1113 Notes Unit 4Shane YacyshynNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration HandoutsDocument5 pagesCellular Respiration HandoutsivyNo ratings yet
- MR Jabbie GlycosisDocument48 pagesMR Jabbie Glycosisvandytommy308No ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Botany Ch10 RespirationDocument4 pagesHsslive XI Botany Ch10 RespirationAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Hingher PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in Hingher PlantsTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationJefferyNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 RespirationDocument11 pagesTopic 5 RespirationPriya Kumar100% (1)
- HW8 - Metabolism 1Document2 pagesHW8 - Metabolism 1Christopher GalivoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds GlucoseDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds Glucosemegamega11No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesDocument5 pagesCellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesStealthstr1keNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Unit 2 Study GuideDocument2 pagesAP Bio Unit 2 Study GuideRana MehaiNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesCellular RespirationAirene JabagatNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Unit 5: Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyDocument138 pagesUnit 5: Unit 5: Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyMovie FlexNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration FoldableDocument11 pagesCellular Respiration FoldableVivy LiuNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide and Convert These Into Sugar and Oxygen.) : Chapter 8: Fuels For LifeDocument4 pagesCarbon Dioxide and Convert These Into Sugar and Oxygen.) : Chapter 8: Fuels For LifeSailor MehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HematologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction To HematologyClaire Nicole100% (1)
- DRB 13-14 - Metabolic Pathways Dan EngeeneringDocument43 pagesDRB 13-14 - Metabolic Pathways Dan EngeeneringItsAndrioNo ratings yet
- Oksidasi PiruvatDocument14 pagesOksidasi Piruvatadelia salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism QuestionsDocument5 pagesMetabolism QuestionsErjus Hoxhaj100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 HematopoiesisDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 2 HematopoiesisAMELIA DALE MARQUEZNo ratings yet
- Energy System NotesDocument3 pagesEnergy System Notesapi-267326015100% (1)
- (Transes) Human Histology - 13 Lymphoid SystemDocument17 pages(Transes) Human Histology - 13 Lymphoid SystemReina CastronuevoNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic TrainingDocument18 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic TrainingIzzat RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Immune Response and InflammationDocument16 pagesIntroduction To The Immune Response and InflammationAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- Dietary Bioactive Compounds As Modulators of Mitochondrial FunctionDocument18 pagesDietary Bioactive Compounds As Modulators of Mitochondrial FunctionMarioNo ratings yet
- Reticuloendothelial System (RES)Document17 pagesReticuloendothelial System (RES)Elidadi KatoNo ratings yet
- Blood 2Document13 pagesBlood 2abbaslafeNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Shukur Wasman Smail PHD Student in ImmunologyDocument12 pagesHematology: Shukur Wasman Smail PHD Student in ImmunologyShukr Wesman BlbasNo ratings yet
- Hormones in Metabolism (DR - Ani Retno)Document45 pagesHormones in Metabolism (DR - Ani Retno)AciNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: TEST II. Modified True or False. Indicate Whether The Statement Is True or False. If False, Change TheDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 1: TEST II. Modified True or False. Indicate Whether The Statement Is True or False. If False, Change TheMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONo ratings yet
- Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolism: Chapter ObjectivesDocument11 pagesLipid and Amino Acid Metabolism: Chapter ObjectivesLarry411100% (1)
- Energy System Development TheoryDocument31 pagesEnergy System Development Theorydna sncNo ratings yet
- Jacob Tsypkin - Balancing Energy Systems Needs For CrossFit AthletesDocument8 pagesJacob Tsypkin - Balancing Energy Systems Needs For CrossFit AthletesBalázs RapiNo ratings yet
- Krebs Cycle EtcDocument28 pagesKrebs Cycle EtcRex IanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Matching - The Organ Systems: DirectionsDocument2 pagesAdvanced Matching - The Organ Systems: DirectionsDanixa MonzónNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Stored EnergyDocument57 pagesHow Cells Release Stored EnergykylevNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesLymphatic Systempriya garciaNo ratings yet
- Quiz GlycolysisDocument1 pageQuiz GlycolysisCCSASHSJayzeelyn Vanessa CornejoNo ratings yet
- Botany - RespirationDocument4 pagesBotany - RespirationbaalajiNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Pathway ChemistryDocument15 pagesBasic Principles of Pathway ChemistrySanket AherNo ratings yet
- Blood Quiz 2Document5 pagesBlood Quiz 2BASHAR ALAROOMINo ratings yet
- Mcr-Prs Lec Chapter14 (Word Format)Document4 pagesMcr-Prs Lec Chapter14 (Word Format)Ali UyNo ratings yet