Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DLP He Food Preservation Tools
Uploaded by
Daisyjoyce TorresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DLP He Food Preservation Tools
Uploaded by
Daisyjoyce TorresCopyright:
Available Formats
School CALOOCAN CENTRAL ELEM.
Grade Level Grade 6
SCHOOL
Teacher DAISY JOYCE S. TORRES Learning Area TLE (H.E)
Grades 1 Teaching Date: MARCH 21, 2024 Quarter Third Quarter
to 12
DAILY Grade & Section
LESSON
PLAN
I. OBJECTIVES
Demonstrates an understanding of and skills into basics of food preservation
A. Content Standards
Preserves food using appropriate tools and materials and applying the basics of food
B. Performance Standards preservation
C. Learning Competencies/ TLE6HE-Og-11
Objectives 3.2 Uses the tools/utensils and equipment and their substitutes in food preservation /
Write the LC code for each processing.
-
II. CONTENT Food Preservation
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide pages
2. Learner’s Materials pages Life Skills Through TLE
3. Textbook pages Makabuluhang Gawaing Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan (pages not available)
4. Additional Materials from
Learning Resource (LR)
portal
B. Other Learning Resources Bantigue, R.M. and Pangilinan, J.P. (2014) Growing up with Home Economics and
Livelihood Education. FNB Educational, Inc. QC.
Preservation of Fruits and Vegetables (1977). Bureau of Plant Industry
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson
or presenting the new Recap of previous lesson
lesson Different types of preserving foods.
B. Establishing a purpose for This lesson is on the tools/instruments/utensils and equipment that we use for food
the lesson preservation
C. Presenting Ask the learners on the importance of familiarizing the learners with the
examples/instances of the tools/utensils and equipment in food preservation
new lesson
D. Discussing new concepts Ask the difference between tools/instruments and equipment.
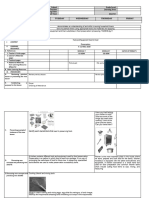
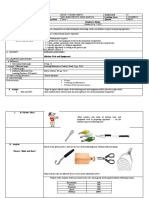
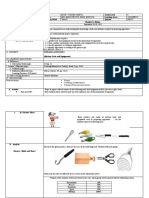
and practicing new skills Ask the learners examples of these tools/instruments:
#1
Response may include knives, fork, spoon, whisk, spatulas, graters, wooden mallets,
containers, plastic bins with airtight lids, ceramic dishes with plastic lids and foil
containers, jars, bag, food brushes, measuring cups, colander, strainer, timer, weighing
scale, measuring spoons, handheld can opener, cooking thermometer, etc.
Ask the learners examples of equipment used in food preservation: juicer, mixer,
electric can opener, blender, refrigerator, stove, oven.
What then is the difference between tools and equipment?
One major difference is the use of electricity.
E. Discussing new concepts Discuss the different tools and equipment.
and practicing new skills The teacher will show photos or drawings of examples of tools/instruments and
#2 equipment.
F. Developing mastery (leads Where do we use the following tools?
to Formative Assessment 1. Fork
3) 2. Spoon
3. Hand towel
4. Weighing scale
5. Grater
6. Measuring spoons
7. Glass measuring cup
8. Chopping board
9. Tray
Hand towel
G. Finding practical Ask the learners the importance of using tools and equipment in food preservation.
applications of concepts Familiarize yourselves with the tools/instruments used in the preservation of food.
and skills in daily living
H. Making generalizations Tools and equipment contribute to the success of food preservation.
and abstractions about the
lesson
I. Evaluating learning LET’S DO TOGETHER
Fill in the blanks with the correct answers with the words from the box.
Strainer Kitchen Funnel Weighing Oven Tray
knife Scale
1. ________ used to determine the weight of an ingredient.
2. A tool used to transfer fine or liquid ingredient to a container with small
opening.
3. Where can you place the foods to be dried if the sun is not present?
4. ________ used to cut, chop, slice and peel meat, fish, fruits and vegetable.
5. ________ used to separate solid food to liquid.
J. Additional activities for Draw at least 10 tools used in food preservation and label them.
application or remediation
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who earned ___Lesson is carried. Move on to the next objective.
80% in the evaluation ___Lesson is not carried.
___% of the pupils got 80% mastery.
No. of learners who require addition
B. al activities for remediation
(score below 80%)
C. Did the remedial lessons ___Yes ___No
work? No. of learners who ____ of learners who caught up the lesson
have caught up with the VI- R. DUTERTE VI- F. MARCOS JR. VI- B. AQUINO III VI- D. MACAPAGAL
lesson
D. No. of learners who continue ___ of learners who require additional activities for remediation
to require remediation
VI- R. DUTERTE VI- F. MARCOS JR. VI- B. AQUINO III VI- D. MACAPAGAL
E. Which of my teaching Strategies used that work well:
strategies worked well? Why 1. ___Metacognitive Development: Examples: Self assessments, note taking and studying
did these work? techniques, and vocabulary assignments.
2. ___Bridging: Examples: Think-pair-share, quick-writes, and anticipatory charts.
3.
4. ___Schema-Building: Examples: Compare and contrast, jigsaw learning, peer teaching, and
projects.
5.
6. ___Contextualization:
7. Examples: Demonstrations, media, manipulatives, repetition, and local opportunities.
8.
9. ___Text Representation:
10. Examples: Student created drawings, videos, and games.
11. ___Modeling: Examples: Speaking slowly and clearly, modeling the language you want students
to use, and providing samples of student work.
Other Techniques and Strategies used:
___ Explicit Teaching
___ Group collaboration
___Gamification/Learning throuh play
___ Answering preliminary
activities/exercises
___ Carousel
___ Diads
___ Differentiated Instruction
___ Role Playing/Drama
___ Discovery Method
___ Lecture Method
Why?
___ Complete IMs
___ Availability of Materials
___ Pupils’ eagerness to learn
___ Group member’s
collaboration/cooperation
in doing their tasks
___ Audio Visual Presentation
of the lesson
You might also like
- John Dee - Sigillum Dei Aemeth or Seal of The Truth of God EnglishDocument2 pagesJohn Dee - Sigillum Dei Aemeth or Seal of The Truth of God Englishsatyr70286% (7)
- LP in Cookery. Starch and CerealsDocument5 pagesLP in Cookery. Starch and CerealsJohanna Manzo100% (6)
- Detailed LE - Lesson 1 Caregiving 7Document9 pagesDetailed LE - Lesson 1 Caregiving 7Elaine Delas Alas100% (6)
- DLP 6 Tle - He Q2 Aug. 26-30 Week 3Document16 pagesDLP 6 Tle - He Q2 Aug. 26-30 Week 3Seo Yeo JinNo ratings yet
- KitcheN Utensils Lesson Plan 7Document2 pagesKitcheN Utensils Lesson Plan 7Nheia Mheia Ramsenitsirc88% (8)
- French Legal SystemDocument3 pagesFrench Legal SystemGauravChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Christian Education of Zendeling-Based at The Kalimantan Evangelical Church (GKE)Document16 pagesChristian Education of Zendeling-Based at The Kalimantan Evangelical Church (GKE)Editor IjrssNo ratings yet
- Molina Vs de La Riva 6 Phil 12 INOKDocument2 pagesMolina Vs de La Riva 6 Phil 12 INOKErick Jay InokNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Artifact 1 - Personal Cultural Project Edu 280Document10 pagesPortfolio Artifact 1 - Personal Cultural Project Edu 280api-313833593No ratings yet
- DLL - Food Preservation TLE HE 6 by Gloria MacayDocument3 pagesDLL - Food Preservation TLE HE 6 by Gloria Macayfrank niel fajilanNo ratings yet
- COT-TLE - LESSON-PLAN - 3rd QuarterDocument9 pagesCOT-TLE - LESSON-PLAN - 3rd QuarterChristine Joy PerionNo ratings yet
- Tle 6 Mam Melba (Victoria)Document2 pagesTle 6 Mam Melba (Victoria)Precious IdiosoloNo ratings yet
- Exploring Useful and Harmful Materials in Science (Grade 5)Document5 pagesExploring Useful and Harmful Materials in Science (Grade 5)timothy castilloNo ratings yet
- HE6 W7a PDFDocument4 pagesHE6 W7a PDFK TIRINo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 7Document3 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 7Diomedes ColarNo ratings yet
- Epp6dlpq3 03132024Document2 pagesEpp6dlpq3 03132024kevinbert.balagbaganNo ratings yet
- Les3 2Document3 pagesLes3 2Joie MyrrhNo ratings yet
- 4A Lesson Exemplars Using The Idea Instructional ProcessDocument3 pages4A Lesson Exemplars Using The Idea Instructional Processrose arianne nadayao100% (4)
- LE Cookery Week 2Document7 pagesLE Cookery Week 2Imus City-Michael ZunigaNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Plan TLE 6Document6 pagesSample Lesson Plan TLE 6Emely LibradillaNo ratings yet
- Storing AppetizerDocument2 pagesStoring AppetizerROSALYNN MATANo ratings yet
- DLL Tle-He-6 Q3 W7Document10 pagesDLL Tle-He-6 Q3 W7Ela KimNo ratings yet
- THIRD IDEA-EXEMPLAR-G9 Week 1Document5 pagesTHIRD IDEA-EXEMPLAR-G9 Week 1Reginald CalderonNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: I. ObjectivesJustine Cedrick Tolentino DacaraNo ratings yet
- DLL 1 CookeryDocument3 pagesDLL 1 CookeryRodolfo Cubangbang100% (2)
- Cleaning SanitizingDocument5 pagesCleaning SanitizingNoel Adan Castillo67% (3)
- DLL FbsDocument5 pagesDLL FbsslayNo ratings yet
- VIEDOR-Q1-DLL-November 1-5, 2021Document5 pagesVIEDOR-Q1-DLL-November 1-5, 2021Kathlene Faith ViedorNo ratings yet
- Classification of ToolsDocument3 pagesClassification of ToolsJinky AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- Cookery Aug 30-Sept 2Document7 pagesCookery Aug 30-Sept 2JessalynJorolanMaghanoyNo ratings yet
- DLL For Objective 16Document2 pagesDLL For Objective 16Jacquilyn Dela Cruz100% (1)
- DLL - Day 1 Food Processing G7-SharonDocument2 pagesDLL - Day 1 Food Processing G7-SharonPerez AshyraNo ratings yet
- Lsson Plan EPP 6Document10 pagesLsson Plan EPP 6Gabshanlie TarrazonaNo ratings yet
- Lsson Plan EPP 6Document10 pagesLsson Plan EPP 6Gabshanlie TarrazonaNo ratings yet
- Cookery DLL (Week 7)Document3 pagesCookery DLL (Week 7)Maria Crestita Doria Montoyo100% (1)
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledLyrna Martinez LlanderNo ratings yet
- Equipment 2Document2 pagesEquipment 2Michael ChavezNo ratings yet
- D01 DLL ACP LO1 Select UseFarmTools UseFarmToolsEquipmentDocument2 pagesD01 DLL ACP LO1 Select UseFarmTools UseFarmToolsEquipmentJuanito AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- Tle-Bpp 8-Q1-M2Document17 pagesTle-Bpp 8-Q1-M2IvanJosh Pangan13No ratings yet
- Rosario Cookery1Document5 pagesRosario Cookery1Bernadeth Irma Sawal Caballa100% (1)
- LO2. Maintain Appropriate Kitchen Tools, Equipment, and ParaphernaliaDocument4 pagesLO2. Maintain Appropriate Kitchen Tools, Equipment, and ParaphernaliaMichael Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Sept 19 Day 5Document2 pagesSept 19 Day 5Rochelle VilelaNo ratings yet
- Cookery DLL (Week 6)Document3 pagesCookery DLL (Week 6)Maria Crestita Doria MontoyoNo ratings yet
- Grades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LOG School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument3 pagesGrades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LOG School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterMae Love Nabarro100% (1)
- August 12, 2019Document4 pagesAugust 12, 2019Maria Kathleen Evangelio JognoNo ratings yet
- Les3 1Document4 pagesLes3 1Joie MyrrhNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Grade 9Document6 pagesThird Quarter Grade 9Mae Love Nabarro100% (1)
- Science 5 DLL CotDocument7 pagesScience 5 DLL CotDwight Spencer Ardimer100% (1)
- DLP 6 Tle He Q2 Aug 26 30 Week 3Document17 pagesDLP 6 Tle He Q2 Aug 26 30 Week 3Mhermina MoroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan 1LADARAN JUSTINRALPH100% (1)
- 3rd COT DLLDocument2 pages3rd COT DLLConnie Reyes San Gabriel80% (5)
- DLL - Tle 6 - Q3 - W8Document4 pagesDLL - Tle 6 - Q3 - W8Melanie DucalangNo ratings yet
- Grade 7-Q1 Module 2TechVoc TVEDocument20 pagesGrade 7-Q1 Module 2TechVoc TVEChristian RilloNo ratings yet
- DLL - Day 2 Food Processing G7-SharonDocument2 pagesDLL - Day 2 Food Processing G7-SharonPerez AshyraNo ratings yet
- 1.feb 13 17 Week 1 Day 1Document2 pages1.feb 13 17 Week 1 Day 1Joan Elizabeth Conde RamosNo ratings yet
- G8 Cookery 1Document5 pagesG8 Cookery 1Joemari VistavillaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatMary Joy C. AdornaNo ratings yet
- DLL SCIENCE WEEK 10-Fadfwedfwdqgehgda42346532536555seDocument12 pagesDLL SCIENCE WEEK 10-Fadfwedfwdqgehgda42346532536555seDee ZaidNo ratings yet
- DLL Q1 W1 D3 CaregivingDocument2 pagesDLL Q1 W1 D3 CaregivingThea PinesNo ratings yet
- Tle-Cookery 7-Q1-M2Document15 pagesTle-Cookery 7-Q1-M2carla ventura100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log G8 TLEDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log G8 TLEMervin PaciaNo ratings yet
- DLL Bread 7 q3 wk7Document4 pagesDLL Bread 7 q3 wk7joy m. peraltaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Tle 4THDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Tle 4THMary Joy DizonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar - TLE-Q4-W2Document7 pagesLesson Exemplar - TLE-Q4-W2bombaneaileen100% (1)
- Elementary Science Experiments: Analyzing Data to Make PredictionsFrom EverandElementary Science Experiments: Analyzing Data to Make PredictionsNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Health Education Grade 6 March 22 2024 - PasigDocument5 pagesCatch Up Health Education Grade 6 March 22 2024 - PasigDaisyjoyce TorresNo ratings yet
- Application For StatisticianDocument1 pageApplication For StatisticianDaisyjoyce TorresNo ratings yet
- DM No. 148 S. 2024 2024 Division School Press Conference and Contests and Other Journalism Related ActivitiesDocument50 pagesDM No. 148 S. 2024 2024 Division School Press Conference and Contests and Other Journalism Related ActivitiesDaisyjoyce TorresNo ratings yet
- Batas Pambansa Bilang 232-Education Act of 1982Document16 pagesBatas Pambansa Bilang 232-Education Act of 1982Erika Kristina MortolaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Paper 12 D. TorresDocument3 pagesDiscussion Paper 12 D. TorresDaisyjoyce TorresNo ratings yet
- Discussion Paper 13 D. TorresDocument3 pagesDiscussion Paper 13 D. TorresDaisyjoyce TorresNo ratings yet
- Discussion Paper 15 D. TorresDocument1 pageDiscussion Paper 15 D. TorresDaisyjoyce TorresNo ratings yet
- Discussion Paper 14 D. TorresDocument2 pagesDiscussion Paper 14 D. TorresDaisyjoyce TorresNo ratings yet
- Discussion Paper 16 D. TorresDocument2 pagesDiscussion Paper 16 D. TorresDaisyjoyce TorresNo ratings yet
- Developing Mental Health-Care Quality Indicators: Toward A Common FrameworkDocument6 pagesDeveloping Mental Health-Care Quality Indicators: Toward A Common FrameworkCarl FisherNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesReno TadashiNo ratings yet
- The Novel TodayDocument3 pagesThe Novel Todaylennon tanNo ratings yet
- Eaap Critical Approaches SamplesDocument2 pagesEaap Critical Approaches SamplesAcsana LucmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: Sanil VargheseDocument55 pagesNursing Informatics: Sanil VarghesePalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- InvestMemo TemplateDocument6 pagesInvestMemo TemplatealiranagNo ratings yet
- Spelling Menu Days and MonthsDocument1 pageSpelling Menu Days and MonthsLisl WindhamNo ratings yet
- Yield of Concrete - tcm45-341215 PDFDocument3 pagesYield of Concrete - tcm45-341215 PDFBijaya RaulaNo ratings yet
- La FolianotesDocument4 pagesLa Folianoteslamond4100% (1)
- 17PME328E: Process Planning and Cost EstimationDocument48 pages17PME328E: Process Planning and Cost EstimationDeepak MisraNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Listening Practice OUT AND ABOUT 1Document1 pageUnit 6 Listening Practice OUT AND ABOUT 1Marta Sampedro GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Mathematics For ManagementDocument3 pagesWorksheet For Mathematics For Managementabel shimeles100% (1)
- Analysis of The SPM QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnalysis of The SPM QuestionsHaslina ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Text Mapping: Reading For General InterestDocument17 pagesText Mapping: Reading For General InterestIndah Rizki RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint PhysicsDocument12 pagesCheckpoint PhysicsRishika Bafna100% (1)
- Tutorial Getting Started With Code Aster PDFDocument12 pagesTutorial Getting Started With Code Aster PDFEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Second LawBHAGWAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- 7 Strategies To Assess Learning NeedsDocument11 pages7 Strategies To Assess Learning Needshammouam100% (1)
- English Reading Kit Level 1: Pupil's Assessment ManualDocument15 pagesEnglish Reading Kit Level 1: Pupil's Assessment ManualGretylle Quicoy100% (1)
- Anxiety DisordersDocument10 pagesAnxiety DisordersAhmed AntarNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam (Regulatory Framework and Legal Issues in Business Law) 2021 - Prof. Gerald SuarezDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam (Regulatory Framework and Legal Issues in Business Law) 2021 - Prof. Gerald SuarezAlexandrea Bella Guillermo67% (3)
- IC HDL Lab ManualDocument82 pagesIC HDL Lab ManualRakshitha AngelNo ratings yet
- Task 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureDocument2 pagesTask 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureJaepiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1session 2 Performance MGMTDocument38 pagesUnit 1session 2 Performance MGMTMayank TrivediNo ratings yet
- Working With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaDocument26 pagesWorking With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaAngela BeatriceNo ratings yet