Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Solid State Workbook
Uploaded by
ledrapotriCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Solid State Workbook
Uploaded by
ledrapotriCopyright:
Available Formats
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ CBSE Pattern Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-0 Exact Duration :_________
Very Short Answer Type (1 Mark)
1. Why are solids rigid?
2. Refractive index of a solid is observed to have the same value along all directions, comment on the nature
of the solid. Would it show cleavage property?
3. Why do solids have a definite volume?
4. A compound forms hexagonal close-packed structure. What is the total number of voids in 0.5 mol of it?
How many of these are tetrahedral voids?
5. A compound is formed by two elements M and N, atoms of N forms ccp lattice and atoms of M occupy
1/3rd of tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound ?
6. An element with molar mass 2.7 10 2 kg per mole forms a cubic unit cell with edge length 405 pm. If its
density is 2.7 103 kg m 3 , what is the nature of the cubic unit cell ?
Short Answer Type-I (2 Marks)
7. What type of defect can arise when a solid is heated? Which physical property is affected by it and in
what way ?
8. Explain how vacancies are introduced in an ionic solid when a cation of higher valency is added as an
impurity in it.
9. Ionic solids, which have anionic vacancies due to metal excess defect, develop colour. Explain with the
help of a suitable example.
10. What type of substances would make better magnets, ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic. Justify your
answer.
11. What makes glass different from a solid such as quartz? Under what conditions could quartz be
converted into glass?
12. Classify each of the following solids as ionic, metallic, molecular, network (covalent) or amorphous :
(i) Tetraphosphorus decaoxide (P4O10 ) (ii) Ammonium phosphate, (NH4 )3 PO4
(iii) SiC (iv) I2 (v) P4
(vi) Plastics (vii) Graphite (viii) Brass
(ix) Rb (x) LiBr (xi) Si
13. (a) ‘Stability of a crystal is reflected in the magnitude of its melting point’. Comment.
(b) The melting points of some compounds are given below : Water = 273 K, Ethyl alcohol = 155.7 K,
Diethyl ether = 156.8 K, Methane = 90.5 K. What can you say about the intermolecular forces
between these molecules ?
CBSE Pattern 1 Level - 0 | The Solid State
Short Answer Type-II (3 Marks)
14. A cubic solid is made up of two elements X and Y. Atoms Y are present at the corners of the cube and
atoms X at the body centre. What is the formula of the compound ? What are the coordination numbers
of X and Y ?
15. Niobium crystallizes in a body centred cubic structure. If its density is 8.55 g cm-3, calculate atomic
radius of niobium, given that its atomic mass is 93 u.
16. Analysis shows that nickel oxide has the formula Ni0.98O. What fractions of the nickel exist as Ni2+and
Ni 3+ions?
17. Copper crystallizes into a fcc lattice with edge length 3.61 × 10–8 cm, show that the calculated density is
in agreement with its measured value of 8.92g cm–3.
18. Non -stoichiometric cuprous oxide, Cu2O can be prepared in the laboratory. In this oxide, copper to
oxygen ratio is slightly less than 2: 1. Can you account for the fact that this substance is a p-type
semiconductor?
19. Ferric oxide crystallizes in a hexagonal close packed array of oxide ions with two out of every three
octahedral holes occupied by ferric ions. Derive the formula of the ferric oxide.
Long Answer Type (5 Marks)
20. Classify each of the following as being either a p-type or n-type semiconductor:
(i) Ge doped with In (ii) Si doped with B.
21. Gold (atomic radius = 0.144 nm) crystallises in a face centred unit cell. What is the length of the side of
the cell ?
22. In terms of band theory, what is the difference
(i) between a conductor and an insulator. (ii) between a conductor and a semiconductor ?
23. Aluminium crystallises in a cubic close packed structure. Its metallic radius is 125 pm.
(i) What is the length of the side of the unit cell?
(ii) How many unit cells are there in 1.00 cm3 of aluminium ?
24. If NaCI is doped with 10–3mol % SrCI2, what is the concentration of cation vacencies ?
25. Sudanshu made a model of the unit cell of diamond. It resembled the unit cell of ZnS. If the unit cell of
ZnS has 4 units of ZnS per unit cell. It has the same packing efficiency as ZnS. But diamond is the
hardest known substance.
(a) What is the number of atoms of carbon per unit cell of diamond?
(b) Why diamond is the hardest non substance?
(c) What is the value that Sudanshu can derive from these facts?
CBSE Pattern 2 Level - 0 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-1 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-1 Exact Duration :_________
1. Which one of the following is a covalent crystal?
(A) Rock salt (B) Ice (C) Quartz (D) Dry ice
2. Graphite is a:
(A) molecular solid (B) covalent solid (C) ionic solid (D) metallic solid
3. Glass is a:
(A) micro-crystalline solid (B) super cooled liquid
(C) gel (D) polymeric mixture
4. Iodine is a:
(A) electrovalent solid (B) atomic solid
(C) molecular solid (D) covalent solid
5. The ability of a given substance to assume two or more crystalline structure is called:
(A) amorphism (B) isomorphism
(C) polymorphism (D) isomerism
6. Which of the following statements about amorphous solids is incorrect?
(A) They melt over a range of temperature (B) They are anisotropic
(C) There is no orderly arrangement of particles (D) They are rigid and incompressible
7. The number of hexagonal faces that are present in a truncated octahedron is:
(A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 8
8. The number of atoms contained in a fcc unit cell of a monoatomic substance is :
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 4 (D) 6
9. The unit cell with dimensions 90 , a b c is :
(A) cubic (B) triclinic (C) hexagonal (D) tetragonal
10. For which crystal system a = b = c and 90 :
(A) tetragonal (B) hexagonal (C) rhombohedral (D) monoclinic
11. Number of atoms in the unit cell of Na (bcc type crystal) and Mg (fcc type crystal) are respectively:
(A) 4, 4 (B) 4, 2 (C) 2, 4 (D) 1, 1
12. Which has no element of symmetry?
(A) Hexagonal (B) Orthorhombic (C) Cubic (D) Triclinic
13. A fcc unit cell of aluminium contains the equivalent of how many Al atoms?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
14. The axial angles in triclinic crystal system are :
(A) 90 (B) 90 , 90
(C) 90 (D) 90
15. Possible number of different type of crystal lattice present in all types of crystals is:
(A) 23 (B) 7 (C) 230 (D) 14
DTS - 1 3 Level - 1 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-2 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-1 Exact Duration :_________
16. Ice crystallises in a hexagonal lattice having volume of the unit cell as 132 10 24 cm 3 . If density is
0.92 g cm 3 at a given temperature, then number of H2O molecules per unit cell is
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
17. Edge length of M X (fcc structure ) is 7.2 Å. Assuming M X contact along the cell edge, radius of
X ion is (r 1.6Å) .
M
(A) 2.0 Å (B) 5.6 Å (C) 2.8 Å (D) 3.8 Å
18. The arrangement ABC ABC ABC ………….. packing of identical spheres is referred as:
(A) Octahedral close packing (B) hexagonal close packing
(C) tetrahedral close packing (D) cubic close packing
19. The coordination number of Al in the crystalline state of AlCl3 is :
(A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 8
20. Which is not the correct statement for ionic solids in which positive and negative ions are held by strong
electrostatic attractive forces?
(A) The radius ratio r / r increases as coordination number increases
(B) As the difference in size of ions decreases, coordination number increases
(C) When coordination number is eight, the r / r ratio lies between 0.225 to 0.414
(D) In ionic solid of the type AX (ZnS, Wurtztite), the coordination number of Zn2+ and
S2 respectively are 4 and 4
21. The lattice points of a crystal of hydrogen iodide are occupied by :
(A) HI molecules (B) H atoms and I atoms
(C) H+ cations and I anions (D) H2 molecules and I2 molecules
22. Which set of characteristics of ZnS crystal is correct?
(A) Coordination number (4 : 4) : ccp ; Zn2+ ion in the alternate tetrahedral voids
(B) Coordination number (6 : 6); hcp ; Zn2+ ion in all tetrahedral voids
(C) Coordination number (6 : 4) ; hcp ; Zn2+ ion in all octahedral voids
(D) Coordination number (4 : 4) ; ccp ; Zn2+ ion in all tetrahedral voids
23. A compound of ‘A’ and ‘B’ crystallises in a cubic lattice in which ‘A’ atoms occupy the lattice points at the
corners of the cube. The ‘B’ atoms occupy the centre of each face of the cube. The probable empirical
formula of the compound is :
(A) AB2 (B) A3B (C) AB (D) AB3
24. Arrangement of sulphide ions in zinc blende is :
(A) simple cubic (B) hcp (C) bcc (D) fcc
25. Each rubidium halide crystallising in the NaCl-type lattice has a unit cell length 0.30 Å greater than that
for corresponding potassium salt (r 1.33Å ) of the same halogen. Hence, ionic radius of Rb is
(K )
(A) 1.18 Å (B) 1.48 Å (C) 1.63 Å (D) 1.03 Å
DTS - 2 4 Level - 1 | The Solid State
26. A compound is formed by elements A and B. This crystallises in the cubic structure where the A atoms
are at the corners of the cube and B atoms are at the body centres. The simplest formula of the
compound is :
(A) AB (B) A6B (C) A8B4 (D) AB6
27. A solid compound contains X, Y and Z atoms in a cubic lattice with X atom occupying the corners. Y
atoms in the body centred positions and Z atoms at the centres of faces of the unit cell. What is the
empirical formula of the compound?
(A) XY2Z3 (B) XYZ3 (C) X2Y2Z3 (D) X8YZ6
o
28. Sodium metal crystallises in body centered cubic lattice with cell edge, 4.29 A . What is the radius of
sodium atom?
o o o o
(A) 2.86 A (B) 6.81 A (C) 1.68 A (D) 1.86 A
29. Number of unit cells in 4g of X (atomic mass = 40) which crystallises in bcc pattern is ( N A = Avogadro
No.)
0.1 N A
(A) 0.1 N A (B) 2 0.1 N A (C) (D) 2 NA
2
30. The 8 : 8 type of packing is present in :
(A) MgF2 (B) CsCl (C) KCl (D) NaCl
DTS - 2 5 Level - 1 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-3 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-1 Exact Duration :_________
31. The crystalline structure of NaCl is :
(A) hexagonal close packing (B) face centred cubic
(C) square planar (D) body centred cubic
32. What is the coordination number of body centred cubic unit cell?
(A) 8 (B) 6 (C) 4 (D) 12
33. In NaCl type structure the coordination number of Na+ and Cl are :
(A) 6, 6 (B) 6, 8 (C) 8, 8 (D) 8, 6
34. Which of the following statement is not correct?
(A) The units of surface tension are dynes cm 1
(B) The units of viscosity coefficient of a liquid is ‘poise’
(C) CsCl crystallizes in body centred cubic type of lattice
(D) The coordination number of S2 in ZnS is 6
35. In which of the following crystals all the tetrahedral voids are not occupied?
(A) NaCl (B) ZnS (C) CaF2 (D) Na2O
36. In an antifluorite structure, cations occupy :
(A) octahedral voids (B) centre of cube
(C) tetrahedral voids (D) corners of cube
37. What is the number of tetrahedral voids per atom in a crystal?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 6 (D) 8
38. A solid is made of two elements X and Z. the atoms Z are in ccp arrangement while the atom X occupy all
the tetrahedral sites. What is the formula of the compound?
(A) XZ (B) XZ2 (C) X2Z (D) X2Z3
39. Fraction of the total volume occupied by atoms in a simple cube is:
3 2
(A) (B) (C) (D)
6 8 6 3
40. An alloy of copper, silver and gold is found to have copper constituting the ccp lattice. If silver atoms
occupy the edge centres and gold is present at body centre, the alloy has a formula :
(A) CuAgAu (B) Cu4 Ag2Au
(C) Cu4 Ag3Au (D) Cu4 Ag4Au
41. Copper crystallizes in fcc lattice with a unit cell edge of 361 pm. The radius of copper atom is :
(A) 181 pm (B) 108 pm
(C) 128 pm (D) 157 pm
42. Which of following unit cell does not exist in cubic system?
(A) primitive (B) body centered (C) face centered (D) end centered
43. Bravais lattices are of
(A) 8 types (B) 9 types (C) 12 types (D) 14 types
DTS - 3 6 Level - 1 | The Solid State
44. What is the percentage packing efficiency of the unit cells as shown?
(A) 72% (B) 68%
(C) 90% (D) 84%
45. Which of the following represents incorrect representation of defect in crystals?
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
DTS - 3 7 Level - 1 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-4 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-1 Exact Duration :_________
46. Lithium borohydride crystallizes in an orthormobic system with 4 molecules per unit cell. The unit cell
dimensions are a 6.8Å, b 4.4Å and c 7.2Å . If the molar mass is 21.76, then the density of crystals
is:
(A) 0.6708 g cm 3 (B) 1.6708 g cm 3
(C) 2.6708 g cm 3 (D) None of these
47. KCl crystallises in the same type of lattice as does NaCl. Given that r /r 0.55 and
Na Cl
r /r 0.74 . Calculate the ratio of the side of the unit cell for KCl to that of NaCl.
K Cl
(A) 1.123 (B) 0.0891
(C) 1.414 (D) 0.414
48. How many number of atoms are there in a cube based unit cell having one atom on each corner and two
atoms on each body diagonal of cube :
(A) 8 (B) 6 (C) 4 (D) 9
49. A metal crystallises in a bcc lattice. Its unit cell edge length is about 300 pm and its molar mass about
50 g mol 1 . What would be the density of the metal ( in g cm 3 ) ?
(A) 3.1 (B) 6.2 (C) 9.3 (D) 12.4
50. The cubic unit cell of Al (molar mass 27 g mol 1 ) has an edge length of 405 pm. Its density is
2.7g cm 3 . The cubic unit cell is :
(A) face centred (B) body centred
(C) primitive (D) edge centre
r
51. The radius ratio of an ionic solid ( A B ) is 0.69. What is the coordination number of B ?
r
(A) 6 (B) 8 (C) 2 (D) 10
52. A metal has bcc structure and the edge length of its unit cell is 3.04 Å . The volume of the unit cell in
cm3 will be :
(A) 1.6 10 21 cm 3 (B) 2.81 10 23 cm 3
(C) 6.02 10 23 cm 3 (D) 6.6 10 24 cm 3
53. In orthorhombic, the value of a, b and c are respectively 4.2 Å, 8.6 Å and 8.3 Å . Given the molecular
mass of the solid is 155 g mol 1 and its density is 3.3 g/cc, the number of formula units per unit cell is :
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 6
54. Identify the incorrect statement regarding a crystal showing Schottky defect?
(A) Entropy of the crystal increases
(B) The density of the overall crystal decreases
(C) The cation are missing at some lattice points and occupy intertitial sites
(D) Electrical neutrality of the crystal is maintained
DTS - 4 8 Level - 1 | The Solid State
55. Three elements P, Q and R crystallize in a cubic solid lattice. The P atoms occupy the corners, Q atoms
the cube centres and R atoms the edges. The formula of the compound is:
(A) PQR (B) PQR 2 (C) PQR 3 (D) PQ3R
56. In a solid lattice, the cation has left a lattice site and is located at an interstitial position, the lattice
defect is :
(A) Frenkel defect (B) Schottky defect
(C) F-centre defect (D) Valency defect
57. Schottky defects occurs mainly in electrovalent compound where
(A) positive ions and negative ions are of dissimilar size
(B) positive ions and negative ions are of similar size
(C) positive ions are small and negative ions are big
(D) positive ions are big and negative ions are small
58. Which of the following statements is correct?
(A) Silicon doped with boron is an n-type semiconductor
(B) Silicon doped with arsenic is a p-type semiconductor
(C) Metals are good conductors of electricity
(D) Electrical conductivity of semiconductors decreases with increasing temperature
59. In a face centred cubic arrangement of A and B atoms whose A atoms are at the corner of the unit cell
and B atoms at the face centres. One of the A atom is missing from one corner in unit cell. The simplest
formula of the compound is:
(A) A 7B3 (B) AB3 (C) A 7B24 (D) A 2B3
60. Which one of the following defects in the crystals lowers its density?
(A) Frenkel defect (B) Schottky defect
(C) F-centres (D) Interstitial defect
DTS - 4 9 Level - 1 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-5 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-1 Exact Duration :_________
61. Schottky defect is generally observed in :
(A) NaCl (B) KCl
(C) CsCl (D) All of these
62. The flame colours of metal ions are due to :
(A) Frenkel defect (B) Schottky defect
(C) Metal deficiency defect (D) Metal excess defect
63. Doping of silicon (Si) with boron (B) leads to :
(A) n-type semiconductor (B) p-type semiconductor
(C) metal (D) insulator
64. Density of a crystal remains unchanged as a result of :
(A) Ionic defect (B) Schottky defect
(C) Frenkel defect (D) Crystal defect
65. Which of the following statement is true?
(A) Some complex metal oxides behave as superconductor
(B) Zinc oxide can act as superconductor
(C) An impurity of tetravalent germanium in trivalent gallium creates electron deficiency
(D) A Frenkel defect is formed when an ion is displaced from its lattice site to an interstitial site
66. If we mix a pentavalent impurity in a crystal lattice of germanium, what type of semiconductor formation
will occur?
(A) p-type (B) n-type
(C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None the two
67. Which of the following has the highest value of energy gap?
(A) Aluminium (B) Silver
(C) Germanium (D) Diamond
68. The elements commonly used for making transistors are :
(A) C and Si (B) Ga and In
(C) P and As (D) Si and Ge
69. How many nearest and next nearest neighbours respectively does sodium have in f.c.c. lattice:
(A) 8, 8 (B) 12, 6
(C) 6, 8 (D) 8, 2
70. The cation/anion radius ratio for a triangular arrangement of
anions in which the cation is in contact with the anions (but does
not push them apart) as shown in the figure is
(A) 0.866 (B) 0.414
(C) 0.155 (D) 0.500
DTS - 5 10 Level - 1 | The Solid State
71. If a metal has a bcc crystal structure, the coordination number is 8 because:
(A) each atom touches four atoms in the layer above it, four in the layer below it and none in its own
layer.
(B) each atom touches four atoms in the layer above it, four in the layer below it and one in its own
layer.
(C) two atoms touch four atoms in the layer above them, four in the layer below them, and none in
their own layer.
(D) each atom touches eight atoms in the layer above it, eight in the layer below it and none in its
own layer.
72. In a ccp structure, the:
(A) first and third layers are repeated (B) first and fourth layers are repeated
(C) second and fourth layers are repeated (D) first, third and sixth layers are repeated
73. The numbers of tetrahedral and octahedral holes in a ccp array of 100 atoms are respectively
(A) 200 and 100 (B) 100 and 200
(C) 200 and 200 (D) 100 and 100
74. The size of Cl ion is 1.8Å . The size of a cation for which a change in coordination just becomes
possible from 6 to 8 in an ideal ionic crystal would be:
(A) 0.7452Å (B) 1.3176Å (C) 0.405Å (D) 1.8Å
75. Lithium forms body centred cubic structure. The length of the side of its unit cell is 351 pm. Atomic
radius of the lithium will be :
(A) 75 pm (B) 300 pm (C) 240 pm (D) 152 pm
DTS - 5 11 Level - 1 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-6 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-2 Exact Duration :_________
76. What fraction of the surface of a crystal of Cd at T 298K consists of vacancies?
sub H Cd 112.01 kJ mol 1 . Energy needed to form a vacancy is approximately 50% of sub H .
(A) 6.02 × 10–23 (B) 6.02 × 1022
(C) 1.5 × 10–10 (D) 1.50 × 1010
77. Germanium has been doped with impurity as shown in I, II, III and IV and based as it statements
(A) to (D).
are given
A. n-type semiconductor is formed in I and III
B. p-type semiconductor is formed in II and IV
C. P-type semiconductor is formed in II and IV
D. p-type semiconductor is formed in I and III
Select the correct statement(s).
(A) A, B (B) C, D (C) A, D (D) A, B, C
78. Statement I : A ferromagnetic substance becomes a permanent magnet, when it is placed in a magnetic
field.
Statement II : All the domains get oriented in the direction of magnetic field.
(A) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of
Statement I
(B) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of
Statement I
(C) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(D) Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
DTS - 6 12 Level - 2 | The Solid State
79. Experimentally it was found that a metal oxide has formula M0.98O . Metal M, present as M2 and M3
in the oxide. Fraction of the metal which exists as M 3 would be :
(A) 95.92% (B) 4.08% (C) 6.05% (D) 93.95%
For question no. 80 - 81
(A) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of
Statement I
(B) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of
Statement I
(C) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(D) Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
80. Statement I : In the case of anti-ferromagnetic substances, magnetic moment is zero.
Statement II : Domains get oriented in the direction of applied magnetic field.
81. Statement I : Electrical conductivity of semiconductors increases with rise in temperature.
Statement II : There is a small energy gap between conduction band and valence band.
82. Calcium crystallizes in a face-centred cubic unit cell with a = 0.556 nm. Calculate the density if it
contained 0.1 % Vacancy defects.
(A) 1.90 g/cm3 (B) 1.54 g/cm3 (C) 3.4 g/cm3 (D) 5.4 g/cm3
83. How many ‘nearest’ and ‘next nearest’ neighbours respectively does potassium have in s.c.
lattice:
(A) 8, 8 (B) 6, 12 (C) 6, 8 (D) 8, 2
84. An fcc lattice has lattice parameter a = 400 pm. Calculate the molar volume of the lattice including all the
empty space:
(A) 92.3 mL (B) 50 mL (C) 42 mL (D) 38.5 mL
85. The ionic radii for Na and Br ions is 1.012Ao and 1.973 Ao respectively. What the coordination no. of
r
Na is predicted on the basis of the radii ratio ?
r
(A) 6 (B) 8 (C) 4 (D) 2
DTS - 6 13 Level - 2 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-7 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-2 Exact Duration :_________
86. The coordination number of a metal crystallizing in a hexagonal close-packed structure is:
(A) 12 (B) 4 (C) 8 (D) 6
87. Radius ratio for NaCl is 0.525, for KBr is 0.60 and for KCl is 0.65. Find radius ratio for NaBr.
(A) 0.485 (B) 0.585
(C) 0.378 (D) 0.454
88. Select the correct statement(s).
(A) Due to the pairing of electrons, magnetic moment is cancelled
(B) Paramagnetic substances are weakly attracted by magnetic field
(C) Ferromagnetic substances cannot be magnetised permanently
(D) The domains in anti-ferromagnetic substances are oppositely oriented with respect to each other
89. In a crystal lattice of a compound, each corner of a cube is joined by sodium, each edge of a cube has
oxygen and centre of a cube is joined by tungsten (W), then give its formula :
(A) Na2WO4 (B) NaWO3
(C) Na3WO3 (D) Na2WO3
90. Statement 1 : In any ionic solid (MX) with Schottky defects, the number of positive and negative ions
are same.
Statement 2 : Equal numbers of cation and anion vacancies are present
(A) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True and Statement-2 is a correct explanation for
Statement-1
(B) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True and Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for
Statement-1
(C) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
(D) Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True
Passage for question no. 91-92
Titanium (II) oxide has a rock salt structures. X-ray diffraction data shows that the length of one edge of the cubic
unit cell for TiO with 1 : 1 ratio of Ti to O is 418 pm and the density is 4.92 g cm–3. (Atomic mass of Ti = 48)
91. What is the type of defect?
(A) Frenkel (B) Schottky
(C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None of these
92. % of vacancies (defects) in the structure is:
(A) 15.5% (B) 84.5%
(C) 62.0% (D) 38.0%
93. A crystal is made up of particles X, Y and Z. X forms FCC packing, Y occupies all octahedral voids of X
and Z occupies all tetrahedral voids of X. If all the particles along one body diagonal are removed, then
the formula of the crystal would be:
(A) XYZ2 (B) X2YZ2
(C) X8H4Z5 (D) X5Y4Z8
DTS - 7 14 Level - 2 | The Solid State
94. Frenkel defect is caused due to :
(A) An ion missing from the normal lattice site creating a vacancy
(B) An extra positive ion occupying an interstitial position in the lattice
(C) An extra negative ion occupying an interstitial position in the lattice
(D) The shift of a positive ion from its normal lattice site to an interstitial site
95. What is the maximum number of layers of atoms in close packed planes that will lie within two imaginary
2
parallel planes having a distance between them of 13 R (where R is the radius of atom) in the copper
3
crystal (FCC)? (Consider the atoms to be within the parallel planes if their centres are on or within the
two parallel planes)
(A) 5 (B) 6
(C) 7 (D) 8
DTS - 7 15 Level - 2 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-8 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-2 Exact Duration :_________
96. Analysis show that nickel oxide consists of nickel ion with 96% ions having d8 configuration and 4%
having d7 configuration. Which amongst the following best represents the formula of the oxide.
(A) Ni1.02O1.00 (B) Ni0.96O1.00
(C) Ni0.98O0.98 (D) Ni0.98O1.00
3
*97. In the fluorite structure if the radius ratio is 1 , how many ions does each cation touch?
2
(A) 4 anions (B) 12 cations (C) 8 anions (D) No cations
*98. Following three planes (P1, P2, P3) in an FCC unit cell are shown. Consider the following statements and
choose the correct option that follow :
(A) P1 contains no three dimensional voids
(B) P2 contains only octahedral voids
(C) P3 contains both octahedral and tetrahedral voids
(D) All are true
99. In a cubic unit cell, A atoms are present on alternate corners, B atoms are present on alternate faces and
C atoms are present on alternate edges and body centre of the cube. The simplest formula of compound
is :
(A) ABC4 (B) A2BC4 (C) AB2C4 (D) ABC2
*100. For the spinel structure (MgAl2O4), the correct statement is(are) :
(A) 50% octahedral voids are occupied by ions
(B) Al3+ is equally distributed in tetrahedral and octahedral voids
(C) Oxide ions occupy CCP lattice
(D) 12.5% tetrahedral voids are occupied by ions
Paragraph for Question No. 101 – 103
In a unit cell atoms (A) are present at all corners lattice, (B) are present at alternate faces and all edge centres,
Atoms (C) are present at face centres left from (B) and 1 at each body diagonal at distance of 1/4th of body
diagonal from corner.
101. Formula of the given solid is:
(A) A3B8C7 (B) AB4C6 (C) A6B4C8 (D) A2B9C11
102. A tetrad axis is passed from the given unit cell and all the atoms touching the axis are removed. Find the
possible formula of the compound left:
(A) AB3C6 and AB4C5 (B) A3B6C7 and A3B6C5
(C) A4B5C8 and A4B5C7 (D) AB2C and ABC2
DTS - 8 16 Level - 2 | The Solid State
103. Total fraction of voids occupied are:
(A) 0.58 (B) 0.25
(C) 0.48 (D) 0.86
104. If the lattice parameter of Si = 5.43 Å and the mass of Si atom is 28.08 1.66 10 27 kg , the density of
silicon in kg m 3 is ; (Given : Silicon has Diamond cubic structure)
(A) 2330 (B) 1115
(C) 3445 (D) 1673
105. The lattice parameter of GaAs (radius of Ga = 1.22 Å, As = 1.25 Å) is:
(A) 5.635 Å (B) 2.852 Å
(C) 5.774 Å (D) 4.94 Å
DTS - 8 17 Level - 2 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-9 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-2 Exact Duration :_________
106. In cubic ZnS, if the radii of Zn and S atoms are 0.74 Å and 1.70 Å, the lattice parameter of cubic ZnS is:
(A) 11.87 Å (B) 5.635 Å (C) 5.14 Å (D) 2.97 Å
107. An elemental crystal has a density of 8570 kg m 3 . The packing efficiency is 0.68. If the closest distance
between neighbouring atoms is 2.86 Å, the mass of one atom is (1 amu = 1.66 10 27 kg )
(A) 186 amu (B) 93 amu (C) 46.5 amu (D) 43 amu
108. A metal (M° = 100 gm/mole) having density 10 gm/cm3 forms a cubic lattice. If the radius of an atom is
1.4 Å find packing fraction. [N A 6 1023 per mole] .
(A) 0.74 (B) 0.69 (C) 0.54 (D) 0.90
109. Every atom or ion that forms an FCC unit cell is surrounded by:
(A) six octahedral holes and eight tetrahedral holes
(B) eight octahedral holes and six tetrahedral holes
(C) six octahedral holes and six tetrahedral holes
(D) eight octahedral holes and four tetrahedral holes
110. Consider the structure of CsCl (8 : 8 co-ordination). How many Cs+ ions occupy the second-nearest
neighbour locations of a Cs+ ion?
(A) 8 (B) 24 (C) 6 (D) 16
3 3
111. A metal of density 7.5 10 kg m has an FCC crystal structure with lattice parameter a = 400 pm.
Calculate the number of unit cells present in 0.015 kg of the metal.
(A) 6.250 10 22 (B) 3.125 1023
(C) 3.125 1022 (D) 1.563 1022
112. The ratio of the volume of a tetragonal lattice unit cell to that of a hexagonal lattice unit cell is:
(both having same respective lengths)
3 2 2 a2
(A) abc (B) (C) c (D) 1
2 3 3 3 b
113. A FCC lattice has a lattice parameter a = 400 pm. Calculate the molar volume of the lattice including all
the empty space.
(A) 10.8 mL (B) 96 mL
(C) 8.6 mL (D) 9.6 mL
114. A tetrahedral void in FCC is formed by atoms at:
(A) 3 corners +1 face centre (B) 3 face centres +1 corner
(C) 2 face centres +2 corner (D) 2 face centres +1 corner +1 body centre
115. What is the density of Na2O having anti-fluorite type crystal structure, if edge length of cube is 100 pm
and what is the effect on density by 0.05% Frenkel defect?
(A) 823.5 g/cm3, density decreases (B) 414.16 g/cm3, density decreases
(C) 823.5 g/cm3, density remains same (D) 414.16 g/cm3, density remains same
DTS - 9 18 Level - 2 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-10 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Level-2 Exact Duration :_________
*116. If the radius of Cs+ = 1.69 Å and Br 1.96 Å, then which of the following is correct statement?
(A) Edge length of unit cell is 4.2 Å (B) Coordination number for Cs+ is 8
(C) CsBr has BCC type structure (D) Br ions touch each other along the edge
*117. The given is the arrangement of atoms in a crystallographic plane:
Which plane correctly represents the adjacent drawn structure?
(A) Face plane in FCC (B) Body diagonal plane in FCC
(C) Face plane in BCC (D) Body diagonal plane in BCC
118. In an FCC unit cell, atoms are numbered as shown below. The atoms not
touching each other are:
(Atoms numbered 3 is face centre of front face)
(A) 3 and 4 (B) 1 and 3
(C) 1 and 2 (D) 2 and 4
119. The number of nearest neighbours and next nearest neighbours of a Na+ ion in a crystal of NaCl are
respectively:
(A) 6 Na , 12 Cl (B) 6 Cl , 12 Na
(C) 12 Cl , 6 Na (D) 6 Cl , 6 Na
120. In the closest packing of atoms,
(A) The size of tetrahedral void is greater than that of octahedral void
(B) The size of tetrahedral void is smaller than that of octahedral void
(C) The size of tetrahedral void is equal to that of octahedral void
(D) The size of tetrahedral void may be greater or smaller or equal to that of octahedral void
depending upon the size of atoms
121. To get a n-type semiconductor, the impurity to be added to silicon should have which of the following
number of valence electrons :
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 5
122. Which of the following solids is not an electrical conductors
I. Mg(s) II. TiO(s) III. I2(s) IV. H2O(s)
The correct choice is :
(A) I only (B) II only
(C) III and IV (D) II, III and IV
123. Which of the following represents correct order of conductivity in solids?
(A) metals insulators K semiconductors
(B) metals insulators semiconductors
(C) metals semiconductors insulators zero
(D) metals semiconductors insulators zero
DTS - 10 19 Level - 2 | The Solid State
*124. The value of magnetic moment is zero in the case of antiferromagnetic substances because the domains:
(A) get oriented in the direction of the applied magnetic field
(B) get oriented opposite to the direction of the applied magnetic field
(C) are oppositely oriented with respect to each other without the application of magnetic field
(D) cancel out each other’s magnetic moment
*125. Amorphous solid can also be called:
(A) Pseudo solids (B) True solids
(C) Super cooled liquid (D) Super cooled solids
DTS - 10 20 Level-2 | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet – 11 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ Numerical Value Type for Exact Duration :_________
JEE Main
126. A compound AB has a rock salt type of structure (with A : B 1 : 1 ). The formula weight of AB is
1
1
6.023Y g mol and the closest A B distances is Y 3 nm. Calculate the density of the lattice
3
in Kg m .
o
127. The edge length of unit cell of a metal having molecular weight 75g / mol is 5 A which crystallizes in
cubic lattice. If the density is 2 g / cc then find the radius of metal atom N A
6 1023 . Give the
answer in pm.
128. The density of solid argon is 1.65 g / ml at 233C. If the argon atom is assumed to be
sphere of radius 1.54 10 8 cm, what percentage of solid argon is apparently empty space? (atomic mass
number of Argon is 40)
129. Potassium fluoride KF has NaCl structure. Its density is 2.48 g cm 3 and its molar
mass is 58 g mol 1. Compute the distance in picometer between K and F ions in KF. (Given that
1/3
155.318 5.375 ) , Atomic mass K = 39, F = 19)
130. An element has unit cell made up of planes as shown below:
Co-ordination number of a lattice point in the above solid is __________ .
131. How many next nearest neighbours of Cs are present in CsCl structure?
o
132. Metallic gold crystallises in FCC lattice. The edge length of the cubic unit cell is 4.07 A . What is the
closest distance between two gold atoms?
133. The packing efficiency of a simple cubic crystal with an interstitial atom exactly fitting at the body center
is approximately __________ .
134. Aluminium metal crystallises in a face centred cubic lattice. If crystal radius of aluminium is 144 pm, the
edge length of a cube is ____________. pm
135. Diamond exists in FCC unit cell with 50% tetrahedral sites also occupied. The effective number of carbon
atoms in a unit cell of diamond is
136. Radius of cation and anion ( A 2 and B2 ) is 100 and 241.42 pm respectively. What is the edge length of
the cubic unit cell formed when A 2 and B2 are packed together?
DTS - 11 21 Numerical Value Type | The Solid State
137. What will be the new coordination number of chloride ion if all sodium ions are removed from the NaCl
crystal?
138. A metallic element crystallises into a lattice containing a sequence of layers of ABABAB….. Any packing
of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What percentage by volume of this lattice is empty space?
139. If the unit cell length of sodium chloride crystal is 600 pm, then its density will be ___________ g/cc.
140. For a solid with the following structure, the coordination number of the point B is ____________ .
DTS - 11 22 Numerical Value Type | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-1 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ JEE Main (Archive) Exact Duration :_________
1. CsBr has bcc structure with edge length 4.3 pm. The shortest interionic distance in between Cs and
Br is : (1993)
(A) 3.72 Å (B) 1.86 Å
(C) 7.44 Å (D) 4.3 Å
2. The coordination number of a metal crystallising in a hexagonal close pack is (1999)
(A) 12 (B) 4 (C) 8 (D) 6
3. In a solid AB having the NaCl structure, A atoms occupy the corners of the unit cell. If all the face center
atoms are removed along one of the axis then formula of the resulting compound is (2001)
(A) A 3B4 (B) AB2
(C) AB (D) A 4 B3
4. Na and Mg crystallize in bcc and fcc type crystals respectively, then the number of atoms of Na and Mg
present in the unit cell of their respective crystals is : (2002)
(A) 4 and 2 (B) 9 and 14
(C) 14 and 9 (D) 2 and 4
5. Graphite is a soft lubricant extremely difficult to melt. The reason for this anomalous behaviour is that
graphite: (2003)
(A) is a non-crystalline substance
(B) is an allotropic form of diamond
(C) has molecules of variable molecular masses like polymers
(D) has carbon atoms arranged in large plates of ring of strongly bound carbon atoms with weak
interplate bonds
6. How many unit cells are present in cube shaped ideal crystal of NaCl of mass 1.00 g ? [Atomic masses
Na = 23, Cl = 35.5] (2003)
21 21
(A) 2.57 10 (B) 5.14 10
(C) 1.28 10 21 (D) 1.71 10 21
7. What type of crystal defects is indicated in the diagram given below ? (2004)
Na Cl Na Cl Na Cl
Cl Cl Na Cl
Cl Na Cl Na Na
(A) Frenkel and Schottky defects (B) Schottky defect
(C) Interstitial defect (D) Frenkel defect
8. In orthorhombic, the value of a, b and c are respectively 4.2 Å, 8.6 Å and 8.3 Å . Given the molecular
mass of the solute is 155 gm mol 1 and that of density is 3.3 gm/cc, the number of formula units per
unit cell is : (2005)
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 6
DTS-1 23 JEE Main (Archive) | The Solid State
9. A substance A X BY crystallises in a face centred cubic (fcc) lattice in which atoms ‘A’ occupy each corner
of the cube and atoms ‘B’ occupy the centres of each face of the cube. Identify the correct composition of
the substance A X BY : (2005)
(A) AB3 (B) A 4 B3
(C) A 3B (D) composition cannot be specified
10. Total volume of atoms present in a face-centre cubic unit cell of a metal is : (r is atomic radius)
(2006)
20 24 12 16
(A) r 3 (B) r 3 (C) r 3 (D) r 3
3 3 3 3
11. Potassium crystallizes in a bcc lattice, hence the coordination number of potassium in potassium metal
is : (2007)
(A) 0 (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 8
12. In a compound atoms of element Y form ccp lattice and those of element X occupy 2/3rd of tetrahedral
voids. The formula of the compound will be : (2008)
(A) X4Y3 (B) X2Y3 (C) X2Y (D) X3Y4
13. Copper crystallises in fcc with a cell length of 361 pm. What is the radius of copper atom ? (2009)
(A) 127 pm (B) 157 pm (C) 181 pm (D) 108 pm
14. Percentage of free space in cubic close packed structure and in body centred packed structure are
respectively? (2010)
(A) 30% and 26% (B) 26% and 32%
(C) 32% and 48% (D) 48% and 26%
15. The edge length of a face centred cubic cell of an ionic substance is 508 pm. If the radius of the cation is
110 pm, the radius of the anion is : (2010)
(A) 288 pm (B) 398 pm (C) 618 pm (D) 144 pm
DTS-1 24 JEE Main (Archive) | The Solid State
wDate Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-2 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ JEE Main (Archive) Exact Duration :_________
16. In a face centred cubic lattice, atom A occupies the corner positions and atom B occupies the face centre
positions. If one atom of B is missing from one of the face centred points, the formula of the
compound is: (2011)
(A) AB2 (B) A 2B3 (C) A 2B5 (D) A 2B
17. Lithium forms body centred cubic structure. The length of the side of its unit cell is 351 pm. Atomic
radius of the lithium will be : (2012)
(A) 75 pm (B) 300 pm (C) 240 pm (D) 152 pm
18. Experimentally it was found that a metal oxide has formula M0.98O . Metal M , present as M2 and M3
in the oxide. Fraction of the metal which exists as M3 would be : (2013)
(A) 7.01% (B) 4.08% (C) 6.05% (D) 5.08%
19. Which of the following exists as covalent crystals in the solid state? (2013)
(A) Iodine (B) Silicon (C) Sulphur (D) Phosphorus
20. A metal crystallizes in a face centred cubic structure. If the edge length of its unit cell is ‘a’, the closest
approach between two atoms in metallic crystal will be: (2013)
a
(A) (B) 2a (C) 2 2a (D) 2a
2
21. An ionic compound has a unit cell consisting of A ions at the corners of a cube and B ions on the centres
of the faces of the cube. The empirical formula for this compound would be (2013)
(A) AB (B) A2B (C) AB3 (D) A3B
22. CsCl crystallizes in body centred cubic lattice. If ‘a’ its edge length, then which of the following expression
is correct? (2014)
3a
(A) r r 3a (B) r r
Cs Cl Cs Cl 2
3
(C) r r a (D) r r 3a
Cs Cl 2 Cs Cl
23. Sodium metal crystallizes in a body centred cubic lattice with a unit cell edge of 4.29Å . The radius of a
sodium atom is approximately. (2015)
(A) 1.86 Å (B) 3.22Å (C) 5.72 Å (D) 0.93Å
24. Which of the following compounds is metallic and ferromagnetic? (2016)
(A) TiO2 (B) CrO2 (C) VO2 (D) MnO2
25. A metal crystallises in face centred cubic structure. If the edge length of its unit cell is `a’, the closest
approach between two atoms in metallic crystal will be: (2017)
a
(A) 2a (B) (C) 2a (D) 2 2a
2
26. Which type of `defect’ has the presence of cations in the interstitial sites? (2018)
(A) Frenkel defect (B) Metal deficiency defect
(C) Schottky defect (D) Vacancy defect
DTS-2 25 JEE Main (Archive) | The Solid State
27. The one that is extensively used as a piezoelectric material is : (2019)
(A) tridymite (B) amorphous silica
(C) quartz (D) mica
28. At 100°C, copper (Cu) has FCC unit cell structure with cell edge length of x Å. What is the approximate
density of Cu (in g cm 3 ) at this temperature ? [Atomic Mass of Cu = 63.55 u] (2019)
105 422 205 211
(A) (B) (C) (D)
x3 x3 x3 x3
29. A compound of formula A 2B3 has the hcp lattice. Which atom forms the hcp lattice and what fraction of
tetrahedral voids is occupied by the other atoms : (2019)
2
(A) hcp lattice-B, Tetrachedral voids-A
3
2
(B) hcp lattice-A, Tetrachedral voids-B
3
1
(C) hcp lattice-A, Tetrachedral voids-B
3
1
(D) hcp lattice-B, lim Tetrachedral voids-A
3 h 0
30. A solid having density of 9 103 kg m 3 forms face centred cubic crystals of edge length 200 2 pm. What
is the molar mass of the solid? [Avogadro constant 6 1023 mol 1, 3 ] (2019)
(A) 0.0305 kg mol 1 (B) 0.0216 kg mol 1
(C) 0.4320 kg mol 1 (D) 0.0432 kg mol 1
31. Which primitive cell has unequal edge lengths (a b c) and all axial angles different from 90°? (2019)
(A) Triclinic (B) Tetragonal
(C) Monoclinic (D) Hexagonal
32. The radius of the largest sphere which fits properly at the centre of the edge of a body centred cubic unit
cell is : (Edge length is represented by ‘a’) (2019)
(A) 0.047 a (B) 0.027 a (C) 0.134 a (D) 0.067 a
33. Element ‘B’ forms ccp structure and ‘A’ occupies half of the octahedral voids, while oxygen atoms occupy
all the tetrahedral voids. The structure of bimetallic oxide is : (2019)
(A) A 4 B2O (B) A 2BO4 (C) AB2O4 (D) A 2B2O
34. An element has a face-centred cubic (fcc) structure with a cell edge of a. The distance between the
centres of two nearest tetrahedral voids in the lattice is: (2019)
a 3
(A) 2a (B) (C) a (D) a
2 2
35. The ratio of number of atoms present in a simple cubic, body centered cubic and face centered cubic
structure are, respectively: (2019)
(A) 4:2:1 (B) 8:1:6
(C) 4:2:3 (D) 1:2:4
DTS-2 26 JEE Main (Archive) | The Solid State
36. Consider the bcc unit cells of the solids 1 and 2 with the
position of atoms as shown below. The radius of atom B is
twice that of atom A. The unit cell edge length is 50% more
in solid 2 than in 1. What is the approximate packing
efficiency in solid 2? (2019)
(A) 65% (B) 45%
(C) 90% (D) 75%
37. The statement that is INCORRECT about the interstitial compounds is: (2019)
(A) they are very hard (B) they have metallic conductivity
(C) they are chemically reactive (D) they have high melting points
38. Which of the following compounds is likely to show both Frenkel and Schottky defects in its crystalline
form? (2020)
(A) CsCl (B) AgBr (C) ZnS (D) KBr
39. `X’ melts at low temperature and is a bad conductor of electricity in both liquid and solid state. X is:
(A) Carbon tetrachloride (B) Silicon carbide (2020)
(C) Zinc sulphide (D) Mercury
DTS-2 27 JEE Main (Archive) | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-1 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ JEE Advanced (Archive) Exact Duration :_________
1. Sodium metal crystallizes in a bcc cubic lattice with the cell edge, a = 4.29Å. What is the radius of
sodium atom? (1994)
2. CsBr has bcc structure with edge length of 43 pm. The shortest interionic distance between cation and
anion is : (1995)
(A) 3.72 pm (B) 1.86 pm (C) 7.44 pm (D) 4.3 pm
3. A metallic element crystallizes into a lattice containing a sequence of layer of ABABAB…. Any packing of
layers leaves out voids in the lattice. What percentage of this lattice is empty space? (1996)
4. Chromium metal crystallizes with a body centred cubic lattice. The length of the unit edge is found to be
287 pm. Calculate the atomic radius. What would be the density of chromium in g/cm3.? (1997)
5. A metal crystallizes into two cubic phases, face centred cubic (fcc) and body centred cubic (bcc), whose
unit cell lengths are 3.5 and 3.0Å, respectively, Calculate the radius of densities of fcc and bcc. (1999)
6. The coordination number of a metal crystallizing in a hexagonal close-packed structure is: (1999)
(A) 12 (B) 4 (C) 8 (D) 6
7. The figures given below show the location of atoms in three crystallographic planes in a fcc lattice. Draw
the unit cell for the corresponding structures and identify these planes in your diagram. (2000)
(a) (b) (c)
8. In a solid AB having the NaCl structure, A atoms occupy the corners of the cubic unit cell. If all the face
centred atoms along one of the axes are removed, then the resultant stoichiometry of the solid is:
(A) AB2 (B) A2B (2001)
(C) A4B3 (D) A3B4
9. A substance A x B y crystallizes in a face-centred cubic lattice in which atoms A occupy the centres of
each face of the cube and B occupy each corner of the cube. Identify the correct composition of the
substane (2002)
(A) AB3 (B) A 4 B3
(C) A 3B (D) Cannot be specified
10. You are given Marbles of diameter 10 mm. They are to be placed such that their centres are lying in a
square bound by four lines each of length 40mm. What will be the arrangement of marbles in a plane so
that maximum number of marbles can be placed inside area? Sketch the diagram and derive expression
for the number of molecules per unit area. (2003)
11. The crystal AB (rock salt structure) has molecular weight 6.023 y u, where y is an arbitrary number in u.
If the minimum distance between cation and anion is y1/3 nm and the observed density is 20kg/ m 3 ,
find the (i) density in kg/ m 3 and (ii) type of defect. (2004)
DTS-1 28 JEE Advanced (Archive) | The Solid State
12. Which of the following fcc structure contain cations in alternate tetrahedral voids? (2005)
(A) NaCl (B) ZnS (C) Na2O (D) CaF2
13. The edge length of unit cell of a metal having molecular weight 75g/mol is 5Å which crystallizes in cubic
lattice. If the density is 2 g/cc then find the radius of metal atom. (N A 6 10 23 ) . Give the answer in
pm. (2005)
14. An element crystallizes in fcc lattice having edge length 400 pm. Calculate the maximum diameter of
atom which can be placed in interstitial site without distorting the structure. (2005)
15. Match the crystal system/unit cells mentioned in Column I with their characteristic features mentioned
in Column II. (2007)
Column I Column II
(A) simple cubic and face-centred cubie (p) have these cell parameters a = b = c and
(B) cubic and rhombohedral (q) are two crystal systems
(C) cubic and tetragonal (r) have only two crystallographic angles of 90°
(D) hexagonal and monoclinic (s) belong to same crystal system
DTS-1 29 JEE Advanced (Archive) | The Solid State
Date Planned : __ / __ / __ Daily Tutorial Sheet-2 Expected Duration : 90 Min
Actual Date of Attempt : __ / __ / __ JEE Advanced (Archive) Exact Duration :_________
Paragraph for Question no. 16 - 18 (2008)
In hexagonal systems of crystals, a frequently encountered arrangement of atoms is
described as a hexagonal prism. Here, the top and bottom of the cell are regular
hexagons and three atoms are sandwiched in between them. A space-filling model
of this structure, called hexagonal close-packed (HCP), is constituted of a sphere on
a flat surface surrounded in the same plane by six identical spheres as closely as
possible. Three spheres are then placed over the first layer so that they touch each
other and represent the second layer. Each one of these three spheres touches
three spheres of the bottom layer. Finally, the second layer is covered with a third
layer that is identical to the bottom layer in relative position. Assume radius of
every sphere to be ‘r’.
16. The number of atoms in this HCP unit cell is :
(A) 4 (B) 6 (C) 12 (D) 17
17. The volume of this HCP unit cell is
64
(A) 24 2 r 3 (B) 16 2 r 3 (C) 12 2 r 3 (D) r3
3 3
18. The empty space in this HCP unit cell is :
(A) 74% (B) 47.6% (C) 32% (D) 26%
*19. The correct statement(s) regarding defects in solids is(are) : (2009)
(A) Frenkel defect is usually favored by a very small difference in the sizes of cation and anion
(B) Frenkel defect is a dislocation defect
(C) Trapping of an electron in the lattice leads to the formation of F-centre
(D) Schottky defects have no effect on the physical properties of solids
20. The packing efficiency of the two-dimensional square unit cell shown below is : (2010)
(A) 39.27% (B) 68.02%
(C) 74.05% (D) 78.54%
21. A compound Mp X q has cubic packing (ccp) arrangement of X. Its unit
cell structure is shown below. The empirical formula of the compound is :
(A) MX (B) MX2 (2012)
(C) M2X (D) M5X14
22. The arrangement of X ions around A ion in solid AX is given in
the figure (not drawn to scale). If the radius of X is 250 pm, the
radius of A is : (2013)
(A) 104 pm (B) 125 pm
(C) 183 pm (D) 57 pm
DTS-2 30 JEE Advanced (Archive) | The Solid State
23. If the unit cell of a mineral has cubic close packed (ccp) array of oxygen atoms with m fraction of
octahedral holes occupied by aluminium ions and n fraction of tetrahedral holes occupied by magnesium
ions, m and n, respectively, are : (2015)
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(A) , (B) 1, (C) , (D) ,
2 8 4 2 2 4 8
*24. Which of the following statements is(are) correct? (2015)
(A) The coordination number of each type of ion in CsCl crystal is 8
(B) A metal that crystallizes in bcc structure has a coordination number 12
(C) A unit cell of an ionic crystal shares some of its ions with other unit cells
(D) The length of the unit cell in NaCl is 552 pm
(r 95pm ; r 181pm)
Na Cl
*25. The CORRECT statement(s) for cubic close packed (ccp) three dimensional structure is(are) : (2016)
(A) The number of the nearest neighbours of an atom present in the topmost layer is 12
(B) The efficiency of atom packing is 74%
(C) The number of octahedral and tetrahedral voids per atom are 1 and 2, respectively.
(D) The unit cell edge length is 2 2 times the radius of the atom
26. A crystalline solid of a pure substance has a face – centred cubic structure with a cell edge of 400 pm. If
the density of the substance in the crystal is 8 g cm–3, then the number of atoms present in 256 g of the
crystal is N 1024 . The value of N is ____________. (2017)
27. Consider an ionic solid MX with NaCl structure. Construct a new structure (Z) whose unit cell is
constructed from the unit cell of MX following the sequential instructions given below. Neglect the charge
balance. (2018)
(i) Remove all the anions (X) except the central one
(ii) Replace all the face centered cations (M) by anions (X)
(iii) Remove all the corner cations (M)
(iv) Replace the central anion (X) with cation (M)
number of anions
The value of in Z is ___________.
number of cations
DTS-2 31 JEE Advanced (Archive) | The Solid State
You might also like
- Yrk Mohan 2ND Puc Chemistry 2023 Model QuestionsDocument5 pagesYrk Mohan 2ND Puc Chemistry 2023 Model QuestionsNaga Raj S100% (1)
- Solid State: Subjective Question For Board ExaminationDocument14 pagesSolid State: Subjective Question For Board ExaminationzohaibsalamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Year T-5Document3 pagesChemistry 1st Year T-5Amir HabibNo ratings yet
- Solid States Question PaperDocument1 pageSolid States Question PaperSomu Yashawant ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- DPP 8Document3 pagesDPP 8Rajdeep GangulyNo ratings yet
- Xii ChemistryDocument119 pagesXii ChemistryAftab AliNo ratings yet
- Cet Paper-1Document6 pagesCet Paper-1smalhaar111No ratings yet
- Objectives - I Solid State 1Document4 pagesObjectives - I Solid State 1Sridip BasuNo ratings yet
- Solid State 1Document6 pagesSolid State 1bibhas_samantaNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Solid State Gujcet PyqDocument19 pagesCh-1 Solid State Gujcet PyqWhoaretoNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument128 pagesChemistryharshit jakharNo ratings yet
- Solid State MCQ & CsaDocument10 pagesSolid State MCQ & Csashivansh upadhyay100% (1)
- 12 Chem Solid1to7Document7 pages12 Chem Solid1to7Johnson PackiyarajNo ratings yet
- 12 Chem SolidDocument28 pages12 Chem SolidJohnson PackiyarajNo ratings yet
- 12 Chem SolidmcqDocument4 pages12 Chem SolidmcqJohnson PackiyarajNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument4 pagesMCQarpitapanda157No ratings yet
- Solid State 60 MCQsDocument62 pagesSolid State 60 MCQsDark MysteryNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument9 pagesSolid StateSomu Yashawant ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Solid State Revision SheetDocument6 pagesSolid State Revision SheetRumaysa -No ratings yet
- Chemistry Uttam Chapter Paper SolutionsDocument175 pagesChemistry Uttam Chapter Paper Solutionsswanandbarapatre12No ratings yet
- Crystal StructureDocument16 pagesCrystal StructureᎽᎪsh ᏒᎪj sᎥᏁᎶhNo ratings yet
- Solid State, PDFDocument4 pagesSolid State, PDFRaj DasNo ratings yet
- THE Solid State: Chapter - 1Document7 pagesTHE Solid State: Chapter - 1Mohamed YaseenNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry MCQS Question BankDocument5 pagesPhysical Chemistry MCQS Question BankMUHAMMAD JUNAID0% (2)
- JR IitDocument3 pagesJR IitGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Solid State: Objective Type Questions Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesSolid State: Objective Type Questions Multiple Choice QuestionsSnehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- 12 MCQDocument3 pages12 MCQAmsha HegdeNo ratings yet
- Chem Prev QuesDocument43 pagesChem Prev QuesMelwin JosephNo ratings yet
- Solid State 12th Chemistry Practice PaperDocument3 pagesSolid State 12th Chemistry Practice PaperNived DohaleNo ratings yet
- Solid State DPPDocument10 pagesSolid State DPPHarsha vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- S.S. Tutorials 2020-21: Question Number 24 To 26 Carry Three Marks EachDocument2 pagesS.S. Tutorials 2020-21: Question Number 24 To 26 Carry Three Marks EachSonuSharmaNo ratings yet
- Test Solid State and SolutionDocument1 pageTest Solid State and Solutionrajneesh kumarNo ratings yet
- DPP 01 Solid StateDocument14 pagesDPP 01 Solid Stateanupamgupta112No ratings yet
- 10+2 Assignment-1 - Solid State - ChemistryDocument6 pages10+2 Assignment-1 - Solid State - ChemistryAnishwar SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Solid State Previous Qns. and AnswersDocument7 pagesThe Solid State Previous Qns. and AnswersSooraj SubhashNo ratings yet
- Solid State Chem 12th 2ndDocument30 pagesSolid State Chem 12th 2ndSagarEricGaourNo ratings yet
- The Solid State: Unit-1Document7 pagesThe Solid State: Unit-1Rams ChanderNo ratings yet
- The Solid State Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersDocument19 pagesThe Solid State Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersRohit Chavariya100% (1)
- Model Practice test-II ChemistryDocument9 pagesModel Practice test-II ChemistryNØ RÙĪZNo ratings yet
- Day-4 Solid StateDocument4 pagesDay-4 Solid StatepriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Solid State 1Document20 pagesSolid State 1Kamal Jit DhimanNo ratings yet
- DPP 01 Solid StateDocument14 pagesDPP 01 Solid StateRajubhaiyaa RajubhaiyaaNo ratings yet
- 295 4 Solid State Practice ProblemsDocument11 pages295 4 Solid State Practice ProblemsArijit SinghNo ratings yet
- The Solid StateDocument31 pagesThe Solid StateAnuj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chem 13072015Document4 pagesChem 13072015udaysrinivasNo ratings yet
- Solid State-1Document12 pagesSolid State-1Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDocument9 pagesThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- BITSAT Chemistry SET 1Document8 pagesBITSAT Chemistry SET 1Sara MannNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Chem QBDocument129 pagesTerm 1 Chem QBRahul MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank RKLDocument31 pagesChemistry Question Bank RKLSahil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solid State Mcqs Chemistry For Mht-CetDocument4 pagesSolid State Mcqs Chemistry For Mht-Cetsahil100% (1)
- 04 1 Solid State 15 4 2023 PDF Margdarshan 2 0 Solid ST JindalJi247Document5 pages04 1 Solid State 15 4 2023 PDF Margdarshan 2 0 Solid ST JindalJi24735 Pranay KumarNo ratings yet
- Document From Vipin SinghDocument5 pagesDocument From Vipin SinghShashwatNo ratings yet
- C Module 5ADocument86 pagesC Module 5ASundareshwar SNo ratings yet
- DPP-1 (Solid State)Document2 pagesDPP-1 (Solid State)VINAY SHARMANo ratings yet
- EditedDocument70 pagesEditedVimal PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chem Test-1 Solid StateDocument4 pagesChem Test-1 Solid StateTNo ratings yet
- So PDocument2 pagesSo PledrapotriNo ratings yet
- Text and TableDocument2 pagesText and TableledrapotriNo ratings yet
- ExcavateDocument1 pageExcavateledrapotriNo ratings yet
- DIY PresentationDocument4 pagesDIY PresentationledrapotriNo ratings yet
- Distribution, Density and Growth: Chapter-2Document9 pagesDistribution, Density and Growth: Chapter-2Pranjal KumarNo ratings yet
- The Solid State Workbook SolutionsDocument23 pagesThe Solid State Workbook SolutionsledrapotriNo ratings yet
- Diy ProjectDocument15 pagesDiy ProjectledrapotriNo ratings yet
- SLG Phy 2 Module 8.0 Lesson 8.4.1 Resistors and Resistor Combinations Part 1Document7 pagesSLG Phy 2 Module 8.0 Lesson 8.4.1 Resistors and Resistor Combinations Part 1FishBowl GangNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test B PhysicsDocument6 pagesChapter Test B PhysicsRashed AlawaishehNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy: DR - Rosy MallikDocument8 pagesSpectroscopy: DR - Rosy MallikTangudu Tejeswar RaoNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Fluid PropertiesDocument9 pagesReservoir Fluid PropertiesAnonymous LLLK3pqNo ratings yet
- Repair of Corroded and Buckled Short Steel Columns Using Concrete-Filled GFRP JacketsDocument9 pagesRepair of Corroded and Buckled Short Steel Columns Using Concrete-Filled GFRP JacketsclarkgaguiNo ratings yet
- M.SC PhysicsDocument73 pagesM.SC Physicsnitu kumariNo ratings yet
- ENGN.2060 Assignment 02 SolutionDocument4 pagesENGN.2060 Assignment 02 SolutionCloie ChavezNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Bioavailability Enhancement of BCS Class II Drugs: A ReviewDocument11 pagesTechniques For Bioavailability Enhancement of BCS Class II Drugs: A ReviewAfridhausmanNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument10 pagesPhysics FormulasFaith Laurence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Physics Report Band Gap of SemiconductorDocument5 pagesPhysics Report Band Gap of SemiconductorTumzangwanaNo ratings yet
- Aijstpme (2012) 5 (4) 7-20Document14 pagesAijstpme (2012) 5 (4) 7-20maziar60No ratings yet
- B 14873473Document74 pagesB 14873473GiovanniCuocoNo ratings yet
- ETABS ColumndesignDocument1 pageETABS ColumndesignPujan NeupaneNo ratings yet
- 고분자재료공학(5) 강의자료Document40 pages고분자재료공학(5) 강의자료RajaAkmalNo ratings yet
- T-Roff Girder DesignDocument41 pagesT-Roff Girder Designlinda100% (1)
- TDS CPE V3.010-EnDocument3 pagesTDS CPE V3.010-EnspicefooNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 3 - ELL203 - 14th August - 2023Document2 pagesTutorial - 3 - ELL203 - 14th August - 2023Ujjawal MeenaNo ratings yet
- Microstructural, Mechanical and Strain Hardening Behaviour of NiTi Alloy Subjected To Constrained Groove Pressing and Ageing TreatmentDocument14 pagesMicrostructural, Mechanical and Strain Hardening Behaviour of NiTi Alloy Subjected To Constrained Groove Pressing and Ageing TreatmentMoin ANo ratings yet
- PRC Lab ManualDocument3 pagesPRC Lab ManualMazharYasinNo ratings yet
- Fracture Toughness and FatigueDocument93 pagesFracture Toughness and FatigueVanvan BitonNo ratings yet
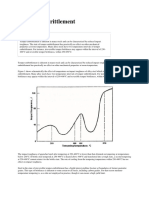
- Temper EmbrittlementDocument13 pagesTemper EmbrittlementAnonymous 5odj1Ic100% (1)
- Over Head ResevoirDocument8 pagesOver Head ResevoirPoulomi BiswasNo ratings yet
- STUDIES ON TRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIES ON GRAPHENE AND S GLASS REINFORCED Al-6061 METAL MATRIX COMPOSITESDocument19 pagesSTUDIES ON TRIBOLOGICAL PROPERTIES ON GRAPHENE AND S GLASS REINFORCED Al-6061 METAL MATRIX COMPOSITESVerma RajamanickamNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Shear Stresses in Circular ShaftsDocument5 pagesDistribution of Shear Stresses in Circular ShaftsSnehasish IsharNo ratings yet
- Participating Institute: AriesDocument2 pagesParticipating Institute: AriesGauravPatelNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor FundamentalDocument5 pagesSemiconductor FundamentalluqmanNo ratings yet
- PWHT RequimentDocument1 pagePWHT Requimentyoutube플래티넘No ratings yet
- CGJ1987241126142 Rowe and ArmitageDocument17 pagesCGJ1987241126142 Rowe and ArmitageSandeep Kumar DangdaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Transport ProcessesDocument2 pagesSolved Problems in Transport ProcessesKristine Ann Villanueva60% (5)
- Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Around The WorldDocument15 pagesNanoscience and Nanotechnology Around The WorldWaseem JavedNo ratings yet