Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4th Quarter INPUT 1 3 SCI10
Uploaded by
Starskie Monacar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
4th-Quarter-INPUT-1-3-SCI10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 page4th Quarter INPUT 1 3 SCI10
Uploaded by
Starskie MonacarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
LLANO HIGH SCHOOL
SCIENCE 10
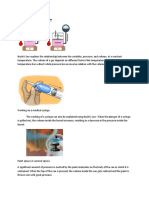
INPUT 1: KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY
INPUT 2: BOYLE’S LAW
Boyle's Law is a fundamental principle in physics that describes how the pressure of a gas changes when its
volume is altered, provided the temperature and the amount of gas remain constant. In simple terms, Boyle's Law states
that if you squeeze a gas into a smaller space, its pressure will increase; conversely, if you allow the gas to expand into a
larger space, its pressure will decrease. This relationship between pressure and volume is inversely proportional, meaning
that as one increases, the other decreases, and vice versa. So, when you decrease the volume, the pressure goes up, and
when you increase the volume, the pressure goes down.
FORMULA:
INPUT 3: CHARLES’S LAW
Charles's Law is another essential principle in physics, specifically dealing with gases. It explains how the volume of
a gas changes with its temperature, keeping the pressure and amount of gas constant. In simple terms, Charles's Law
states that when you heat up a gas, its volume expands, and when you cool it down, its volume contracts. This relationship
between volume and temperature is directly proportional, meaning that as temperature increases, volume increases, and as
temperature decreases, volume decreases. So, if you heat up a balloon, it expands because the air inside it warms up and
takes up more space; if you cool it down, the balloon shrinks because the air inside it cools down and takes up less space.
FORMULA:
You might also like
- Gas LawsDocument4 pagesGas LawsDar W. InNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document6 pagesScience 10Andy ValdezNo ratings yet
- 1avogadro's Law States That, "Equal Volumes of All Gases, at The Same Temperature andDocument3 pages1avogadro's Law States That, "Equal Volumes of All Gases, at The Same Temperature andTrisha Mae DacalloNo ratings yet
- Gas Law Pressure Gas: Boyle's Law (Sometimes Referred To As The Boyle-Mariotte Law, or Mariotte's LawDocument2 pagesGas Law Pressure Gas: Boyle's Law (Sometimes Referred To As The Boyle-Mariotte Law, or Mariotte's LawPRichelleAlfaroNo ratings yet
- Document About Literature and HistoryDocument2 pagesDocument About Literature and HistoryMarieta GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 3-4 Gas Laws Int - Reader - Study - Guide PDFDocument6 pages3-4 Gas Laws Int - Reader - Study - Guide PDFel graceNo ratings yet
- Use The Law To Explain The Following ObservationsDocument6 pagesUse The Law To Explain The Following ObservationsCedric Adrian AblogNo ratings yet
- GASES SendingDocument2 pagesGASES Sendingyoow.youthNo ratings yet
- Real-World Examples: Data AnalysisDocument6 pagesReal-World Examples: Data AnalysisiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Emerald Green and Gold Elegant Applicant Cover LetterDocument4 pagesEmerald Green and Gold Elegant Applicant Cover LetterSam Yvhanne Quinzon TanNo ratings yet
- Practical ApplicationsDocument3 pagesPractical ApplicationsELvin Jay CasiñoNo ratings yet
- TUGOT Boyle's Law and Charles-Gay Lussacs LawDocument15 pagesTUGOT Boyle's Law and Charles-Gay Lussacs LawTito V. Bautista Jr.No ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law, Boyles Law and Charles LawDocument4 pagesIdeal Gas Law, Boyles Law and Charles LawKen QuionNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics Systems: Ing. José de Jesús Mendoza OsorioDocument9 pagesPneumatics Systems: Ing. José de Jesús Mendoza Osoriojox1106No ratings yet
- Mass Earth's Atmosphere: DensityDocument23 pagesMass Earth's Atmosphere: DensityRahul MoottolikandyNo ratings yet
- 1.11 Combined Gas Law (SPA10) Edited Ver.Document17 pages1.11 Combined Gas Law (SPA10) Edited Ver.Jimin ParkNo ratings yet
- Boyle's LawDocument19 pagesBoyle's Lawcabilesrobilyn479No ratings yet
- Gas Law: Boyle'S Law, Charles Law, Gay-Lussac'S Law. Combined Gas Law, and Ideal Gas LawDocument91 pagesGas Law: Boyle'S Law, Charles Law, Gay-Lussac'S Law. Combined Gas Law, and Ideal Gas LawLee MedalloNo ratings yet
- Miguel, John Ryan, D.G Lab Act 7Document3 pagesMiguel, John Ryan, D.G Lab Act 7Simon DeleonNo ratings yet
- Q4 - Science 10 - Week 2Document8 pagesQ4 - Science 10 - Week 2Rayza CatrizNo ratings yet
- What Is A Practical Application of BoyleDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Practical Application of BoyleArmstrong BosantogNo ratings yet
- 3-4 Gas Laws Int - Reader - Study - Guide PDFDocument6 pages3-4 Gas Laws Int - Reader - Study - Guide PDFVara BikkinaNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument2 pagesGas Lawfranklin.yin2020No ratings yet
- Compilation OF Different Gas LawsDocument7 pagesCompilation OF Different Gas LawsJean Angelove SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDF MeteoDocument24 pagesChapter 2 PDF MeteosecretzNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Solids LiquidsDocument2 pagesGas Laws: Solids LiquidsRaymond CabanillaNo ratings yet
- The Gas Laws: Porschia Marie D. Rosalem, LPTDocument48 pagesThe Gas Laws: Porschia Marie D. Rosalem, LPTGio Rico Naquila EscoñaNo ratings yet
- Nature-Of-Gases-Compilation - Montallana and MorenoDocument4 pagesNature-Of-Gases-Compilation - Montallana and MorenoRhave MorenoNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas LawDocument5 pagesCombined Gas LawjalibicharityNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law, Also Referred To As TheDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law, Also Referred To As TheMaria Lana Grace DiazNo ratings yet
- Ep103 Foundation in Chemistry Ii Laboratory Report: Experiment 1 Boyle'S LawDocument7 pagesEp103 Foundation in Chemistry Ii Laboratory Report: Experiment 1 Boyle'S LawKuneswaran RengasamyNo ratings yet
- Gas Law Pressure Gas: Boyle's Law (Sometimes Referred To As The Boyle-Mariotte Law, or Mariotte's LawDocument4 pagesGas Law Pressure Gas: Boyle's Law (Sometimes Referred To As The Boyle-Mariotte Law, or Mariotte's LawDini Daw MangacopNo ratings yet
- Activity # 1: Research The FollowingDocument3 pagesActivity # 1: Research The FollowingHettyNo ratings yet
- TITLE: Boyle's LawDocument3 pagesTITLE: Boyle's LawNabilah MustafaNo ratings yet
- GAS LAWS: Boyle's Law, Charles's Law and Gay-Lussac's Law: Waste-Face-Masks-Ppe-CovidDocument9 pagesGAS LAWS: Boyle's Law, Charles's Law and Gay-Lussac's Law: Waste-Face-Masks-Ppe-CovidMichiiee BatallaNo ratings yet
- Application of BoyleDocument10 pagesApplication of BoyleRuthcel BautistaNo ratings yet
- LawDocument6 pagesLawJaymart BobilesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9 NotesDocument4 pagesChemistry 9 NotesMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Name:Mompati Letsweltse: Physics Laboratory ReportDocument5 pagesName:Mompati Letsweltse: Physics Laboratory ReportMompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- The Behavior of GasesDocument33 pagesThe Behavior of GasesDante MantosNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument8 pagesGas LawsSamantha De LeonNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas Law Lab Report HJM ResearchDocument5 pagesCombined Gas Law Lab Report HJM ResearchHelen100% (4)
- Gases: Animation 3.1: Boyle's Law Source & Credit: WikipediaDocument55 pagesGases: Animation 3.1: Boyle's Law Source & Credit: WikipediaMian MuneebNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument6 pagesUntitled DocumentChukwuemeka OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Q 4 Week 1Document39 pagesQ 4 Week 1Rishalyn Pagola RamirezNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Week 5 6Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Week 5 6Emmanuel ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Matter Can Be Roughly Divided Into Three Main Categories Namely GasesDocument5 pagesMatter Can Be Roughly Divided Into Three Main Categories Namely GasesRe MarNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Lesson 1Document36 pagesMODULE 1 Lesson 1Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory (The Gas Laws) - Chemistry Unit IDocument6 pagesKinetic Theory (The Gas Laws) - Chemistry Unit Imcleodtravis14No ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument2 pagesGas LawsJJAMPPONG PS100% (1)
- Q 4 Week 1Document39 pagesQ 4 Week 1Rishalyn Pagola RamirezNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentcristinemaelumanao18No ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument15 pagesIdeal GasesBookieNo ratings yet
- Definition of Boyle's Law: What Is An Ideal Gas?Document4 pagesDefinition of Boyle's Law: What Is An Ideal Gas?حسين كاظم ياسينNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Science IV: 1.) Boyle's LawDocument6 pagesAssignment: Science IV: 1.) Boyle's LawIrish WahidNo ratings yet
- Boyle S LawDocument22 pagesBoyle S LawNanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law, P V PDocument2 pagesBoyle's Law, P V PMohanNo ratings yet
- Alkali: Latin PH Standard State Acetic Acid Vinegar Sulfuric Acid Car Batteries Redox Oxidation StateDocument4 pagesAlkali: Latin PH Standard State Acetic Acid Vinegar Sulfuric Acid Car Batteries Redox Oxidation StateFatima Erika Ayessa IngkohNo ratings yet
- GasDocument12 pagesGasEgbebessemenow oben ashuNo ratings yet
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- The Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (553)
- The Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameFrom EverandThe Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (88)
- Professor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellFrom EverandProfessor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (147)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Sun in a Bottle: The Strange History of Fusion and the Science of Wishful ThinkingFrom EverandSun in a Bottle: The Strange History of Fusion and the Science of Wishful ThinkingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (38)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- The Quantum Revelation: A Radical Synthesis of Science and SpiritualityFrom EverandThe Quantum Revelation: A Radical Synthesis of Science and SpiritualityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (35)