Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Map
Mind Map
Uploaded by
Andrea RojasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mind Map
Mind Map
Uploaded by
Andrea RojasCopyright:
Available Formats
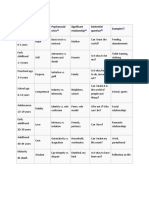
PRENATAL
1er trimester Early
Germinal. childhood (0-5
C. adaptive: incomplete eye pursuit.
C. language: Guttural sounds, Embryonic years)
attends to sounds.
C. personal-social: Looks at the faces
fetal
of the observer.
Childhood (6-11
years)
2do trimester
Adolescence
C. motor: Firm head, symmetrical posture,
open hands. LIFE CYCLE (12-18 years)
C. adaptive: Correct eye pursuit.
C. language: murmurs, laughs, social
vocalization. STAGES OF Youth (19-26
C. personal-social: plays with hands and
clothes, opens mouth to receive food.. DEVELOPMENT years old)
3er trimester Adulthood
4to trimester (27-59 years)
C. motor: sits leaning forward leaning on
his hands. C. Motor: Remains seated, crawls, stands up.
C. adaptive: passes objects from one hand C. adaptive: combines objects, imitates a line
to another.
C. language: vocalizes avidly.
with a pencil. Old age (60-
C. language: says a word, attends to his
C. personal-social: plays with his feet, with
toys.
name, names pictures.
C. personal-social: simple games, undresses
plus)
with fingers, spoon-like.
What is it?
Risks and hazards Physical changes
Adolescence is a phase of life that
During adolescence, young people face risks such marks the transition between childhood During adolescence, young people experience
as drug and alcohol use, as well as social and adulthood. During this period, notable physical changes, such as rapid
pressure to engage in risky behaviors such as young people experience significant growth in height and weight, development of
driving under the influence or having
changes in their bodies, emotions and sexual organs and appearance of body hair.
unprotected sex. These risks can have serious They may also face skin and hair challenges,
impacts on their long-term physical and emotional social relationships.
such as acne and increased scalp oiliness.
health.
Moral development Cognitive changes
During adolescence, young people begin to GENERAL Adolescents acquire more advanced abstract
thinking, critical thinking and problem solving skills.
ADOLESC
develop their own morality, influenced by They may reflect on moral and ideological issues,
their upbringing, personal experiences and but may also show tendencies toward egocentric
social norms. When faced with ethically thinking and difficulties in understanding the
complex situations, they reflect on their
values and beliefs to determine how to act
correctly and fairly.
ENCE viewpoints of others.
Interpersonal relationships
Emotional changes
During adolescence, interpersonal relationships
Social development During adolescence, young people experience
become very important. Young people are significant emotional changes, such as confusion and
During adolescence, young people experience
learning to form bonds with their peers as well insecurity, due to sudden and intense emotions.
remarkable growth in their ability to interact These changes are normal and part of growing up.
as with adults. These relationships can be
socially. As they become more independent and They experience a range of emotions, from happiness
complicated and challenging to manage.
establish their identities, they develop crucial social to anxiety, which can influence their behavior and
Adolescents experience a wide range of emotions skills such as empathy, conflict resolution, and
when interacting with others, from joy to interpersonal relationships.
effective communication. These skills are
sadness and frustration. fundamental to establishing healthy and satisfying
relationships throughout life.
You might also like
- Human Growth and Development TheoriesDocument8 pagesHuman Growth and Development TheoriesThuganamix86% (29)
- Dev Psych ReviewerDocument9 pagesDev Psych ReviewerMARIA ELIZA LOMUNTADNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 - The WorkerDocument37 pagesACTIVITY 1 - The WorkerGHi YHan86% (29)
- Transparency and Open CommunicationDocument10 pagesTransparency and Open Communicationdanial haziqNo ratings yet
- Theories of Development (Management)Document4 pagesTheories of Development (Management)Lynlyn Oprenario PajamutanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Development Autosaved 1Document23 pagesChapter 1. Development Autosaved 1Judyangaangan03No ratings yet
- Activity 4Document5 pagesActivity 4Stephanie Angel OmpadNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa MajorsDocument10 pagesReviewer Sa MajorsdayanlobrinNo ratings yet
- PerDev Worksheet 2Document3 pagesPerDev Worksheet 2Princess Edelyn Mae PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Human Growth and Development TheoriesDocument10 pagesHuman Growth and Development TheoriesIzyanSyafiqah100% (1)
- Tcallp - Balbuena Eugene - MidtermsDocument7 pagesTcallp - Balbuena Eugene - MidtermsEugene BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- INFOGRAPHDocument3 pagesINFOGRAPHJADE PATEGANo ratings yet
- Developmental PyschDocument11 pagesDevelopmental PyschkilluhmaylucianoNo ratings yet
- Clarisse E-PEC 101 Module 2Document3 pagesClarisse E-PEC 101 Module 2Kyji EstradaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Task ExampleDocument7 pagesDevelopmental Task ExampleJade Louise FkshmNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Issues in Adolescents 2Document16 pagesMental Health Issues in Adolescents 2pgsingh9810No ratings yet
- Growth and Dev'tDocument6 pagesGrowth and Dev'tPheobe Grace PapoloniasNo ratings yet
- U6 Wa Educ 5410Document5 pagesU6 Wa Educ 5410TomNo ratings yet
- The Term Growth and Development Both Refers To Dynamic ProcessDocument13 pagesThe Term Growth and Development Both Refers To Dynamic ProcessMarc LiNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent ReviewerDocument8 pagesChild and Adolescent ReviewerMarjorie RagilesNo ratings yet
- WEEK 5 - SocialisationDocument62 pagesWEEK 5 - SocialisationArfa Mirza Bin Mat Nasir C21A1690No ratings yet
- Child Adolescent DevelopmentDocument21 pagesChild Adolescent DevelopmentClaide Vencent Arendain-Cantila DesiertoNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Case StudyDocument8 pagesSchizophrenia Case StudyJohn Carlo Toledo0% (1)
- Go To Page Word 2022 2 1Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022 2 1api-621033980No ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology Prelim ReviewerDocument85 pagesDevelopmental Psychology Prelim ReviewerShay GenillaNo ratings yet
- Uts AssignmentDocument6 pagesUts AssignmentSusa, Maria ErissaNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescence Handout For Chapter 2Document4 pagesChild and Adolescence Handout For Chapter 2Shielorie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Conception and Prenatal DevelopmentDocument28 pagesConception and Prenatal DevelopmentBernardita Timbreza HernandezNo ratings yet
- 6-Kuliah Erik EriksonDocument6 pages6-Kuliah Erik EriksonRita EngelliaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 1 - Task5Document10 pagesProf Ed 1 - Task5kristine buñaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestone ChartDocument101 pagesDevelopmental Milestone ChartEdi Hendri MNo ratings yet
- The Stages of Development and Developmental TasksDocument6 pagesThe Stages of Development and Developmental TasksdevilladaphneleighdNo ratings yet
- Human Development Approaches and TheoriesDocument161 pagesHuman Development Approaches and TheoriesMichelle Villareal CuevasNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development TheoriesDocument8 pagesGrowth and Development TheoriesNiwerg SecoNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrincipleDocument7 pagesChild and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrincipleLeah Mae Bulosan100% (1)
- Developmental Milestones in Infancy and Childhood PDFDocument8 pagesDevelopmental Milestones in Infancy and Childhood PDFJecyl Mae MenorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Psychosocial Development During The First Three YearsDocument5 pagesChapter 6 - Psychosocial Development During The First Three YearsSantos, Shaina MaeNo ratings yet
- PD Lesson 3Document8 pagesPD Lesson 3Jose Emmanuel CalagNo ratings yet
- Child DevelopmentDocument13 pagesChild DevelopmentZulfiya ZNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 ERIKSON MyReviewerDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 9 ERIKSON MyReviewerFrances LouiseNo ratings yet
- ED11-Group 4 - Stages On Human DevelopmentDocument14 pagesED11-Group 4 - Stages On Human DevelopmentMarth Joseph EnopiaNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Myers Review Chart of Erikson's Stages Chapter 4Document1 pageAP Psych Myers Review Chart of Erikson's Stages Chapter 4Tiffany Gallina100% (1)
- 6.health Promoation of School AgeDocument42 pages6.health Promoation of School AgeHamza EmadNo ratings yet
- The Body, The Play and The DramaDocument4 pagesThe Body, The Play and The DramaEzequiel Martins100% (1)
- Personal Development ReviewerDocument5 pagesPersonal Development ReviewerTrixie Ann AldayNo ratings yet
- Approximate Age Virtues Psychosocial Crisis Significant Relationship Existential ExamplesDocument4 pagesApproximate Age Virtues Psychosocial Crisis Significant Relationship Existential ExamplesKim SanchezNo ratings yet
- Profed04 - Chapter 3Document8 pagesProfed04 - Chapter 3RobNo ratings yet
- Stages of Personality DevelopmentDocument1 pageStages of Personality Developmentjoshua sedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-6 - The Physical SelfDocument2 pagesLesson-6 - The Physical SelfbernbilazonNo ratings yet
- The Psychological View of SelfDocument6 pagesThe Psychological View of SelfMark VrazaNo ratings yet
- 1 Module 1 - Concept and Nature of Self: Who Am I?Document9 pages1 Module 1 - Concept and Nature of Self: Who Am I?John MichaelNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Theory Written ReportDocument6 pagesInterpersonal Theory Written ReportFayeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Personal Development 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesReviewer in Personal Development 2nd QuarterDave Homer Huerto MoralesNo ratings yet
- Seeing What Is: The Education Challenges for Teachers and Their StudentsFrom EverandSeeing What Is: The Education Challenges for Teachers and Their StudentsNo ratings yet
- Name: Tamonea Wright GRADE: 10C2 DATE: SEPTEMBER 30, 2021 Subject: Social Studies Teacher: Ms. Pierre Topic: Development Stages of An IndividualDocument2 pagesName: Tamonea Wright GRADE: 10C2 DATE: SEPTEMBER 30, 2021 Subject: Social Studies Teacher: Ms. Pierre Topic: Development Stages of An IndividualZena ForbesNo ratings yet
- To Middle and Late Adolescents: Lesson 1Document31 pagesTo Middle and Late Adolescents: Lesson 1Janice PalleraNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Individual TASK - Table of Psychosocial Theories and TherapyDocument6 pagesWeek 2 Individual TASK - Table of Psychosocial Theories and TherapyAndrew Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- MODULE 10-B - EARLY CHILDHOOD ADocument14 pagesMODULE 10-B - EARLY CHILDHOOD AKaren GimenaNo ratings yet
- SUMMARYDocument28 pagesSUMMARYEvalyn RubeneciaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Growth and Development Ppt. NEWDocument11 pagesStages of Growth and Development Ppt. NEWArt AlbayNo ratings yet
- The Science of Child Development - Chapter 1Document39 pagesThe Science of Child Development - Chapter 1Ehab El OrabyNo ratings yet
- PSYCHLEARNINGMIDTERMDocument2 pagesPSYCHLEARNINGMIDTERMKatrina Marie Ronato SalduaNo ratings yet
- CBCS 1.1 Management and Organisational Behaviour 2020Document3 pagesCBCS 1.1 Management and Organisational Behaviour 2020Kavithri ponnappaNo ratings yet
- Asking Question Discussing His/her Views or Listening Constructive Criticism Citing Ideas From PreviousDocument1 pageAsking Question Discussing His/her Views or Listening Constructive Criticism Citing Ideas From PreviousIana CruzNo ratings yet
- An Appeal To Authority and Credibility. Ethos Is A Means of ConvincingDocument12 pagesAn Appeal To Authority and Credibility. Ethos Is A Means of Convincingjhon valdiviezoNo ratings yet
- Burton, Kelli - A Study of Motivation - How To Get Your Employees Moving - Faculty Cheryl HughesDocument33 pagesBurton, Kelli - A Study of Motivation - How To Get Your Employees Moving - Faculty Cheryl HughesShahnewaze ShohagNo ratings yet
- Immersion NarrativeDocument13 pagesImmersion NarrativeRen-ren MirafloresNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Second Language Acquisition GardenerDocument16 pagesMotivation and Second Language Acquisition GardenerMagdalenaNo ratings yet
- UtilitarianismDocument22 pagesUtilitarianismJoe Carl B. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Sacred Sexuality Reclaiming The Divine Feminine PDFDocument156 pagesSacred Sexuality Reclaiming The Divine Feminine PDFHelidoorNo ratings yet
- Wk1 04 Difference Automatic Inspirational WritingDocument4 pagesWk1 04 Difference Automatic Inspirational WritingAngieNo ratings yet
- By: Prof. JULIA T. CARDONA, PH.DDocument13 pagesBy: Prof. JULIA T. CARDONA, PH.DArnold QuilaquigaNo ratings yet
- Factors Associated With Higher Levels of Depressive Symptoms Among International University Students in The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesFactors Associated With Higher Levels of Depressive Symptoms Among International University Students in The PhilippinesmarielNo ratings yet
- Safety Plan: An Instruction ManualDocument3 pagesSafety Plan: An Instruction ManualJNo ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument2 pagesAction ResearchGeli BaringNo ratings yet
- Teaching Speaking SkillDocument9 pagesTeaching Speaking SkillRohana FernandoNo ratings yet
- Od-4 Classifying Od InterventionsDocument77 pagesOd-4 Classifying Od Interventionskimsr71% (7)
- Certified Guiding Lion ProgramDocument52 pagesCertified Guiding Lion ProgramartmalemitNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus In: The National Teachers College ManilaDocument8 pagesCourse Syllabus In: The National Teachers College ManilaPhil harold NeraNo ratings yet
- ESSAY FINAL PROJECT CALL Group FDocument7 pagesESSAY FINAL PROJECT CALL Group FSherlyta ChristyNo ratings yet
- 2021-Semester 1-Jamal GALLOUJDocument1 page2021-Semester 1-Jamal GALLOUJjamal galloujNo ratings yet
- Environment For LearningDocument6 pagesEnvironment For LearningUrooj ImranNo ratings yet
- What Is Personality?: "Wired Up" Seems To Be at Work, Determining How They React To Situations, AndDocument2 pagesWhat Is Personality?: "Wired Up" Seems To Be at Work, Determining How They React To Situations, Andnguyenduymang12No ratings yet
- What Is The RulesDocument2 pagesWhat Is The RulesDancan OnyangoNo ratings yet
- DLL Q2 W2 Health M2 Eating DisordersDocument5 pagesDLL Q2 W2 Health M2 Eating DisordersRuby RoseNo ratings yet
- Caregiving For Grades 7 To 10Document26 pagesCaregiving For Grades 7 To 10Yeshua YeshaNo ratings yet
- Buchanan (1984) - Moreno Social Atom PDFDocument10 pagesBuchanan (1984) - Moreno Social Atom PDFJorge Pedro TresymedioNo ratings yet
- Lester Levenson - Psychology TodayDocument65 pagesLester Levenson - Psychology TodayAnonymous hUNlch0No ratings yet
- Stress Coping Skills-eBookDocument41 pagesStress Coping Skills-eBookkumarmahiNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter-1 Meda CultureDocument10 pages09 - Chapter-1 Meda CultureSyed ZahidNo ratings yet