Professional Documents
Culture Documents
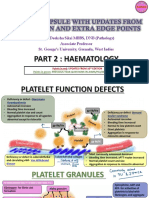
Tumor Microenvironment and The Immune System
Tumor Microenvironment and The Immune System
Uploaded by
nurul hidayahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tumor Microenvironment and The Immune System
Tumor Microenvironment and The Immune System
Uploaded by
nurul hidayahCopyright:
Available Formats
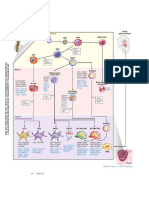
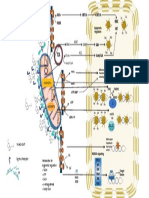
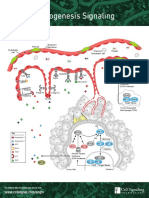
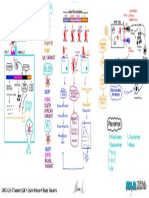
Cross-talk between tumor microenvironment and the immune system
by Dr. Jacintha O’Sullivan and Dr. Joanne Lysaght, Trinity College Dublin and Abcam
Abbreviations
ADAM’s: A disintegrin and NO: Nitric Oxide
PD-1
metalloproteinases NOS-2: Nitric Oxide Synthase
Blood vessel VEGF MDSC Ang-1: Angiopoietin-1 PD-1: Programmed Death-1
MMP9
ARG-1: Arginase-1 PDGF: Platelet Derived Growth
Treg TIM3 Bcl2: B cell lymphoma 2 Factor
NO IL-10 bFGF: basic Fibroblast Growth RANTES: Regulated upon activation
TGF-β TGF-β CD4+ CTLA-4 CAFs:
factor
Cancer Associated
normal T cell expressed and
secreted
CTLA-4
EGFL7 IL-10 Th1
Fibroblasts RCAS-1: Receptor binding cancer
CSF-1: Colony Stimulating Factor-1 antigen expressed on SiSo
TGF-β IFN-γ TIM3 PD-1 CTL: Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte cells
ARG-1 CTLA4: Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte
Antigen 4
SCF: Stem Cell Factor
SDF-1: Stromal Cell-Derived
NOS-2 IL-10 IFN-γ
CTLA-4
DAMPS: Damage Associated Factor-1
TGF-β
Molecular Patterns SIRP-α: Signal-regulatory Protein
VCAM TGF-β ECM: Extracellular Matrix alpha
IL-10 EGF: Epidermal Growth Factor SPI-6: Serine Protease Inhibitor-6
Egfl7: Epidermal Growth Factor TAMs: Tumor Associated
like domain 7 Macrophages
VEGF IL-10 CSF-1
ICAM: Intracellular Adhesion TGF-β: Transforming Growth Factor
Cytolytic Molecule beta
Bcl2 IL-6 IDO: Indoleamine 2,3 Th1: T Helper 1
granules IFN-γ dioxygenase TIM3: T cell Immunoglobulin and
Pericytes CD4 +
IL-17 CD8+ IFN-γ: Interferon Gamma Mucin domain-containing
DAMPS IL: Interleukin molecule-3
ICAM Dendritic IDO Th17 RCAS-1 NK CTL MCP: Monocyte Chemoattractant
Protein
TIMPs: Tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases
SPI-6 MICA NKG2
cells
MDSC: Myeloid Derived Suppressor Treg: Regulatory T cells
Cells uPA: Urokinase-type Plasminogen
MICA: Major histocompatibility Activator
complex class I-related chain VCAM: Vascular Cell Adhesion
TAMs FasL A Molecule
MMPs: Matrix Metalloproteinases VEGF: Vascular Endothelial Growth
TGF-β NK: Natural Killer Factor
MMP12 CD47 soluble FasL Exosomes
PDGF
NKG2: Natural Killer Group 2
VEGF
bFGF PD-L1
SIRPα
The tumor microenvironment affects angiogenesis by interfering with signaling pathways required
for vascular construction. The absence of normal vasculature causes a physical constraint on the
microenvironment. Tumors recruit endothelial cells, fibroblasts inflammatory cells and pericytes,
and these with components of the ECM contribute to the microenvironment composition. Stromal cells
P-selectin EGF
generate both tumor enhancing and suppressing signals. CAF’s and myofibroblasts are stromal cells that
are abnormal, but not malignant, and promote angiogenesis and proliferation. These fibroblasts secrete
growth factors and cytokines that produce oncogenic signals. Activated fibroblasts promote angiogenesis via
expression of SDF-1. Tumor cells also express CXCR4, the receptor for SDF-1 and stromal SDF-1 can stimulate
CSF-1 tumor growth through a paracrine manner. TGF-β causes activation of fibroblasts while PDGF recruits fibroblasts and
MMP 3, 7, 9, 16 induces proliferation. VEGF does not directly recruit fibroblasts, but indirectly supports microenvironmental changes
TGF-β via the regulation of the vascular network. Proteins secreted by the tumor modify the microenvironment by inducing
growth factors and proteases that degrade the ECM, and affect cell motility and adhesion. Stromal cells secrete ECM
proteins, cytokines, growth factors, proteases and protease inhibitors. TIMP’s are endogenous inhibitors of MMP’s and
E-selectin function to balance the protease activity of MMP’s to shift the balance from a pro-angiogenic to an inhibitory
environment.
An anti-tumor immune response begins as a result of local tissue damage due to the
expanding tumor and the release of “danger signals” from dead or dying tumor cells.
A mature dendritic cell will present acquired tumor antigens to T cells in sentinel
lymph nodes. A pro-inflammatory cell mediated immune response with NK
MMP’s 1, 2, 3, 9, 11 cells, Th1 CD4+ T cells and CD8+ CTLs secreting IFN-Y and releasing
cytolytic granules is required for effective killing of tumor cells.
Cathepsin’s B, L, S, K
Fibroblasts
However, many obstacles stand in the way of immune
ADAM’s 10, 17 mediated tumor cell killing, including regulatory T
cells, MDSC, tumor derived exosomes, inhibitory
TIMPs molecules including MICA, CD47, RCAS-1, PD-L1,
SPI-6 and immunosuppressive cytokines such
as IL-10 and TGF-β.
SDF-1 Proteoglycan
MMP2, 9 www.abcam.com
TGF-β Arginase
VEGF
SDF-1 CXCR4 Laminin
CXCR4
RANTES
Fibronectin
Galectins 1,2,3 and 9 SCF
Arginase
Laminin
Key MMP-3 VEGF
Ang-1 CXCR4
Secretes Proteoglycan
uPA bFGF Neutrophils (N2)
Inhibits secretion
IL-8 MMP9
or expression
MCP-1 Proteases Fibronectin
Induces function Mast cells
Inhibits function Extracellular matrix Collagen
Copyright © 2023 Abcam. All rights reserved
You might also like
- USMLE Step 1 Uworld NotesDocument26 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Uworld NotesSweta DabhiNo ratings yet
- Parasites and Allergy, 2006 PDFDocument215 pagesParasites and Allergy, 2006 PDFtrubus100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Test Bank CH 6-9Document33 pagesPathophysiology Test Bank CH 6-9Joyy86% (7)
- Food Allergens - Biochemistry and Molecular NutritionDocument217 pagesFood Allergens - Biochemistry and Molecular NutritionHien PhamNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease MechanismsDocument6 pagesAutoimmune Disease MechanismsHaliunaa BattulgaNo ratings yet
- Catatan KulitDocument11 pagesCatatan KulitwidiaNo ratings yet
- Wallchart StemCell CancerResearch 2013 Lowres PDFDocument1 pageWallchart StemCell CancerResearch 2013 Lowres PDFMazrul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Monocytes in The Tumor MicroenvironmentDocument1 pageMonocytes in The Tumor MicroenvironmentamyNo ratings yet
- ENDOKRINDocument56 pagesENDOKRINvenaNo ratings yet
- Overview - Regulation of ApoptosisDocument1 pageOverview - Regulation of ApoptosisAym mantezNo ratings yet
- Akt PKBDocument1 pageAkt PKBCarl DonaireNo ratings yet
- APO2Document1 pageAPO2Saheed AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- mTOR Signaling PathwayDocument1 pagemTOR Signaling PathwayRichard WooliteNo ratings yet
- Figures 1Document1 pageFigures 1Lex UNo ratings yet
- 8.external Disease and Cornea AAO 2022-2023-33-36 MECANISMOS DE DEFENSADocument4 pages8.external Disease and Cornea AAO 2022-2023-33-36 MECANISMOS DE DEFENSAEduardo Andrés HerreraNo ratings yet
- PI3K Signalling in Immune Cells 07Document1 pagePI3K Signalling in Immune Cells 07Sonia Barbosa CornelioNo ratings yet
- METTL16 Antagonizes MRE11-mediated DNA End Resection and Confers Synthetic Lethality To PARP Inhibition in Pancreatic Ductal AdenocarcinomaDocument31 pagesMETTL16 Antagonizes MRE11-mediated DNA End Resection and Confers Synthetic Lethality To PARP Inhibition in Pancreatic Ductal AdenocarcinomaJackson AlbertNo ratings yet
- B&T Cell Clonality PDFDocument22 pagesB&T Cell Clonality PDFKarla Novoa PérezNo ratings yet
- T Cell Receptor Signaling: F-A CtinDocument2 pagesT Cell Receptor Signaling: F-A CtinOlgaNo ratings yet
- Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Marker Guide (Mouse) : LeukocytesDocument2 pagesTumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Marker Guide (Mouse) : LeukocytesFika Ayu SafitriNo ratings yet
- 1st FloorDocument1 page1st FloorMay SooNo ratings yet
- Pathways Toward Deterioration in COVID-19Document83 pagesPathways Toward Deterioration in COVID-19Mercedes BouterNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrial Control of ApoptosisDocument1 pageMitochondrial Control of ApoptosisAym mantezNo ratings yet
- Inhibition of Apoptosis: TNF-α Survival Factors: Growth Factors, Cytokines, etcDocument2 pagesInhibition of Apoptosis: TNF-α Survival Factors: Growth Factors, Cytokines, etcCESAR JUNIOR ARO TICONANo ratings yet
- Test Test Test: House Wife Kurd 1989Document1 pageTest Test Test: House Wife Kurd 1989Zepta BNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Cancer SyndromesDocument10 pagesHereditary Cancer SyndromesANA GABRIELA PEREZ VIDALNo ratings yet
- 17-CNR-12 Angiogenesis PW Handout-PassDocument2 pages17-CNR-12 Angiogenesis PW Handout-PassBladimir CentenoNo ratings yet
- Review: Predicted Immune ResponsesDocument2 pagesReview: Predicted Immune ResponsesAntonio de Jesús Garcia A.No ratings yet
- COVID 19 7 SARS CoV 2 Variants UK + South African + Brazil VariantsDocument1 pageCOVID 19 7 SARS CoV 2 Variants UK + South African + Brazil VariantsKhalid HabibNo ratings yet
- Decrypting DC Development: News & ViewsDocument3 pagesDecrypting DC Development: News & ViewsAfiq IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- CRISPR PosterDocument1 pageCRISPR PosterOmar Garduño VidalNo ratings yet
- PIIS1538783622162951Document11 pagesPIIS1538783622162951Devil HostNo ratings yet
- T Cell ReceptorDocument1 pageT Cell Receptorrovia achmad .No ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument6 pagesHepatitis BCarmen MargoNo ratings yet
- EUROFLOW ANTIBODY PANELS Cytognos BrochureDocument1 pageEUROFLOW ANTIBODY PANELS Cytognos Brochure82lauNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: The Common Mutation Sites in The Retinoblastoma Protein (PRB) - PRB Is Protein Made UpDocument8 pagesFigure 1: The Common Mutation Sites in The Retinoblastoma Protein (PRB) - PRB Is Protein Made UpSanthiya KunasegaranNo ratings yet
- Catatan ITP Dan AADocument17 pagesCatatan ITP Dan AAngurahardhi88No ratings yet
- In Target PDCD1 905 548/357 548/337Document2 pagesIn Target PDCD1 905 548/357 548/337Jane WongNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Human Immune Cell Characterization by Flow CytometryDocument5 pagesA Guide To Human Immune Cell Characterization by Flow CytometryLeo TolstoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BMS-clinical Immunology-BbDocument46 pagesIntroduction To BMS-clinical Immunology-BbBiology BảoNo ratings yet
- The Grey Zone: What To Do For The "Intermediate Risk" Patient?Document96 pagesThe Grey Zone: What To Do For The "Intermediate Risk" Patient?Shweta GajreNo ratings yet
- Akt PKBDocument1 pageAkt PKBmilenerato2240No ratings yet
- Media 823904 SMXXDocument26 pagesMedia 823904 SMXXДемьян МатченкоNo ratings yet
- Idan's Thesis - FinalDocument32 pagesIdan's Thesis - Finalnachum1989No ratings yet
- Pharma 1aDocument4 pagesPharma 1aaaaalliah2No ratings yet
- Poster Chromatin and Translational Control PathwayDocument1 pagePoster Chromatin and Translational Control PathwayDIEGO ISAAC LARA SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- SARS-CoV-2 Variants - UK + South African + Brazil Variants - Key AtfDocument1 pageSARS-CoV-2 Variants - UK + South African + Brazil Variants - Key AtfJuan Manuel Tapia AlzateNo ratings yet
- WA10004-Directed Differentiation Pluripotent Stem CellsDocument1 pageWA10004-Directed Differentiation Pluripotent Stem CellsJorge Mario “Jorge” Gamboa CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Https - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 16 Fly DBL 00063 Eng WNT B Catenin Diff PW Handout SMDocument2 pagesHttps - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 16 Fly DBL 00063 Eng WNT B Catenin Diff PW Handout SMtamaraNo ratings yet
- Leukemia ?Document1 pageLeukemia ?7ussain7aliNo ratings yet
- Anemias 2Document8 pagesAnemias 2Ivy QueenNo ratings yet
- 2018 03 13 GIM SPR Teaching Immunotherapy ManagementDocument25 pages2018 03 13 GIM SPR Teaching Immunotherapy ManagementTam Le Ngoc KhanhNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Sum SheetDocument10 pagesCystic Fibrosis Sum Sheetnzq7m6ph4dNo ratings yet
- Kleppe2011 GlucagonDocument13 pagesKleppe2011 GlucagonLydie Praxede EkoboNo ratings yet
- Colloidal Gold-Labeled Immunoassay Analyzer Specifications: About EdanDocument2 pagesColloidal Gold-Labeled Immunoassay Analyzer Specifications: About Edanmesssaoudi faresNo ratings yet
- Luminal Phase: Ang-1 Ang-2 Ang-2 Ang-2 Ang-2Document2 pagesLuminal Phase: Ang-1 Ang-2 Ang-2 Ang-2 Ang-2Elena ContiNo ratings yet
- Personelize MedicineDocument12 pagesPersonelize Medicinephindo mawardinataNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland Tumors Gene alteration+IHCDocument4 pagesSalivary Gland Tumors Gene alteration+IHCMohamed ArafaNo ratings yet
- Robbins Capsule Part 2 Lyst9907Document18 pagesRobbins Capsule Part 2 Lyst9907Jose SirittNo ratings yet
- Apoptosis Cancer Signaling PathwaysDocument1 pageApoptosis Cancer Signaling PathwayssyafikaNo ratings yet
- Dr. SirajDocument14 pagesDr. Sirajsavan patelNo ratings yet
- Afc Trong HMDocument7 pagesAfc Trong HMvan anh nguyen huynhNo ratings yet
- PIC Real Time Clock DS1307: Analogue Keys Multiplexed 7seg Display IcspDocument1 pagePIC Real Time Clock DS1307: Analogue Keys Multiplexed 7seg Display Icspveeramaniks408100% (1)
- Vaccines HistoryDocument7 pagesVaccines HistoryCesarNo ratings yet
- New Insights in CIDP-GBSDocument14 pagesNew Insights in CIDP-GBSRenju KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- The Tape-Stripping Technique As A Method For Drug Quantification in SkinDocument27 pagesThe Tape-Stripping Technique As A Method For Drug Quantification in SkinfelinsiamelvanNo ratings yet
- Final Hand Book of Covid 19 AFMCDocument174 pagesFinal Hand Book of Covid 19 AFMCPadmapriya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- HIV - Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome - UnlockedDocument9 pagesHIV - Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome - UnlockedThalia FortuneNo ratings yet
- Finn 2017 TAA Yesterday Today FutureDocument8 pagesFinn 2017 TAA Yesterday Today FutureLinh TranNo ratings yet
- The Interaction Between Autophagy, Helicobacter Pylori, and Gut Microbiota in Gastric CarcinogenesisDocument20 pagesThe Interaction Between Autophagy, Helicobacter Pylori, and Gut Microbiota in Gastric CarcinogenesisWaldo IzyNo ratings yet
- HIV - Human Immunodeficiency Virus.: The Greatest Medical Science Challenge of The Last 40 Years!Document37 pagesHIV - Human Immunodeficiency Virus.: The Greatest Medical Science Challenge of The Last 40 Years!blueblemishNo ratings yet
- 7 Chapter 7 T-Cell Maturation, Activation, and DifferentiationDocument34 pages7 Chapter 7 T-Cell Maturation, Activation, and DifferentiationMekuriya BeregaNo ratings yet
- CD4 Easy Count Kit - Dry - Automate: IVD IVDDocument2 pagesCD4 Easy Count Kit - Dry - Automate: IVD IVDDinesh SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Hipersensibilidad Tipo IV - Cátedra Inmunológica - Escuela de Medicina ''José María Vargas'', Junio 2018Document67 pagesHipersensibilidad Tipo IV - Cátedra Inmunológica - Escuela de Medicina ''José María Vargas'', Junio 2018Enzon BritoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Disease Mechanisms: An Introduction To Cellular MicrobiologyDocument685 pagesBacterial Disease Mechanisms: An Introduction To Cellular MicrobiologyVero VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Question Text Question Type PointsDocument25 pagesQuestion Text Question Type PointsMagda Tvildiani100% (1)
- IgG4 Related DiseaseDocument13 pagesIgG4 Related DiseaseLaura Paola Urquizo100% (1)
- (Download PDF) Inflammation From Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms To The Clinic 4 Volume Set Jean Marc Cavaillon Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Inflammation From Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms To The Clinic 4 Volume Set Jean Marc Cavaillon Online Ebook All Chapter PDFdennis.berganza270100% (7)
- MSC MB Notes - Immunology & CancerDocument23 pagesMSC MB Notes - Immunology & Cancercaroline.fragniere6464No ratings yet
- I PREVENT COVID FLU RSV Clinical GuideDocument15 pagesI PREVENT COVID FLU RSV Clinical GuideServaas OostrikNo ratings yet
- A Clinicopathological Classification of Granulomatous DisordersDocument9 pagesA Clinicopathological Classification of Granulomatous DisordersEma ȚurcașNo ratings yet
- Histology BloodDocument6 pagesHistology BloodNeneng Cutin GanzonNo ratings yet
- Transplantation ImmunologyDocument23 pagesTransplantation ImmunologyCatherine RajanNo ratings yet
- Immunity To Microbes: Prof. Dr. Dr. Djoni Djunaedi, SPPD, KptiDocument24 pagesImmunity To Microbes: Prof. Dr. Dr. Djoni Djunaedi, SPPD, KptiArdea SafiraNo ratings yet
- 24 Lecture PresentationDocument85 pages24 Lecture PresentationWide PutinNo ratings yet
- ResourceDocument320 pagesResourceYudha Arya IrawanNo ratings yet
- JC 18Document8 pagesJC 18emiliaclyde39No ratings yet
- Refresher Course On HIV/AIDS (Bob Meyers)Document90 pagesRefresher Course On HIV/AIDS (Bob Meyers)National Press FoundationNo ratings yet